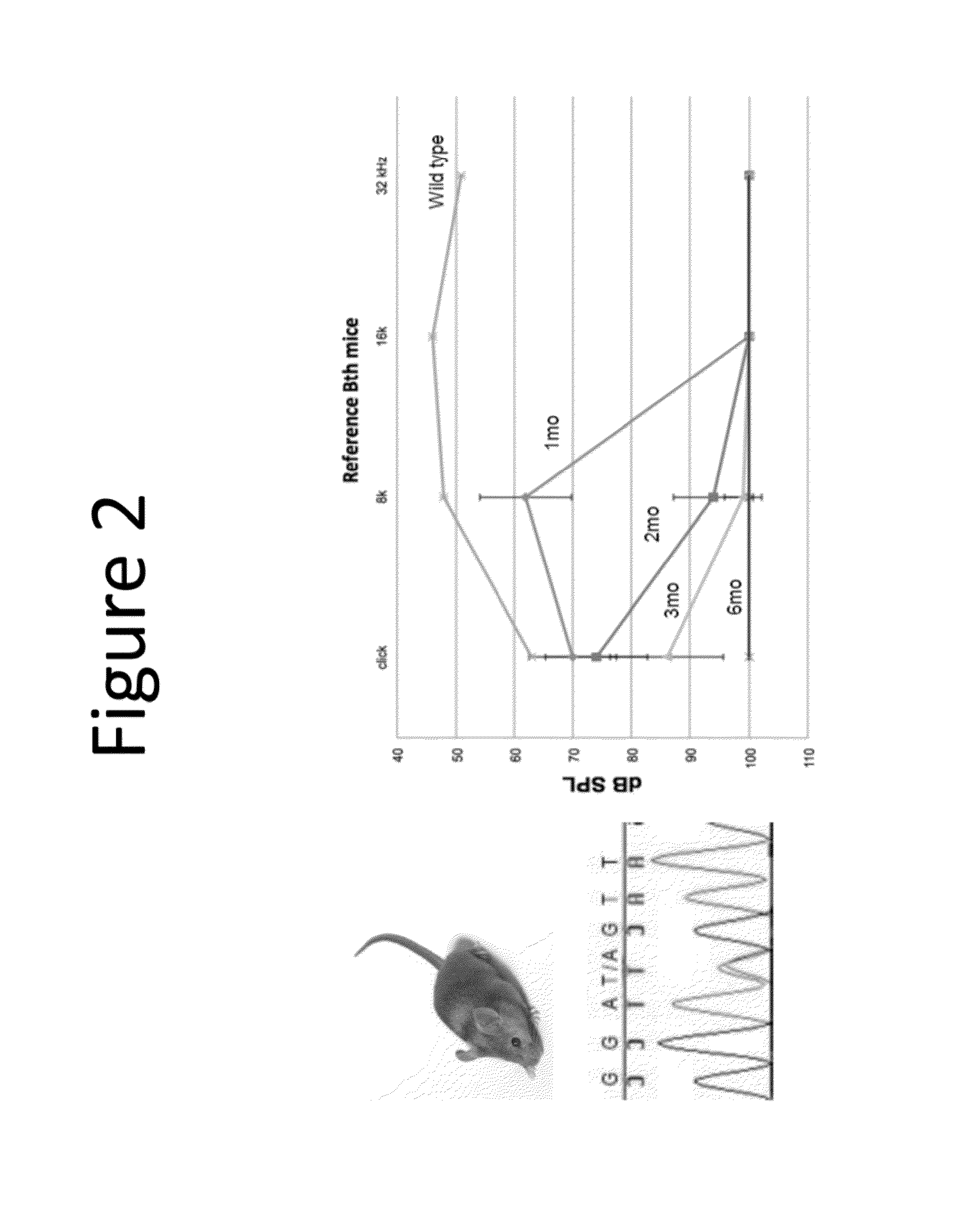
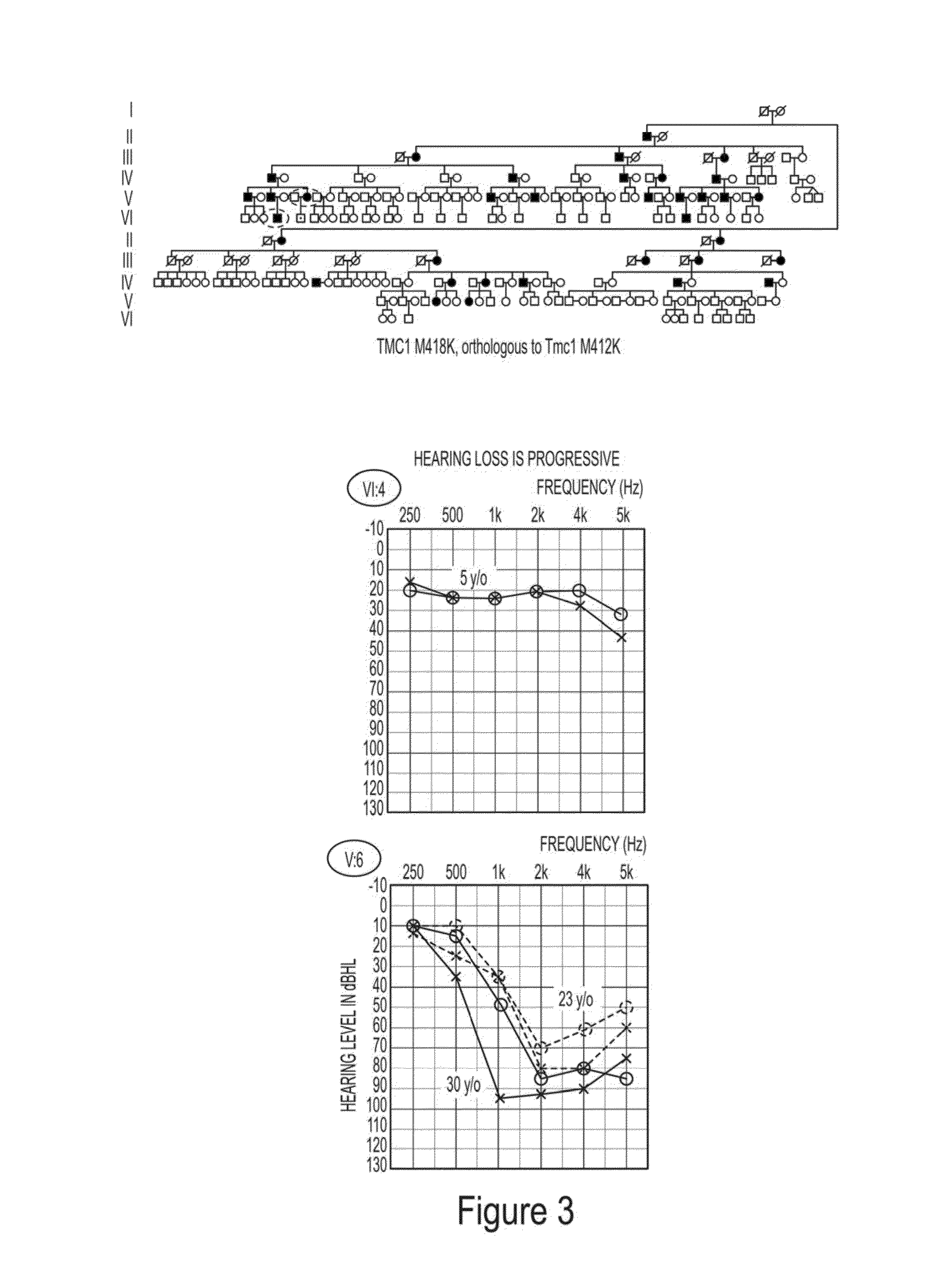
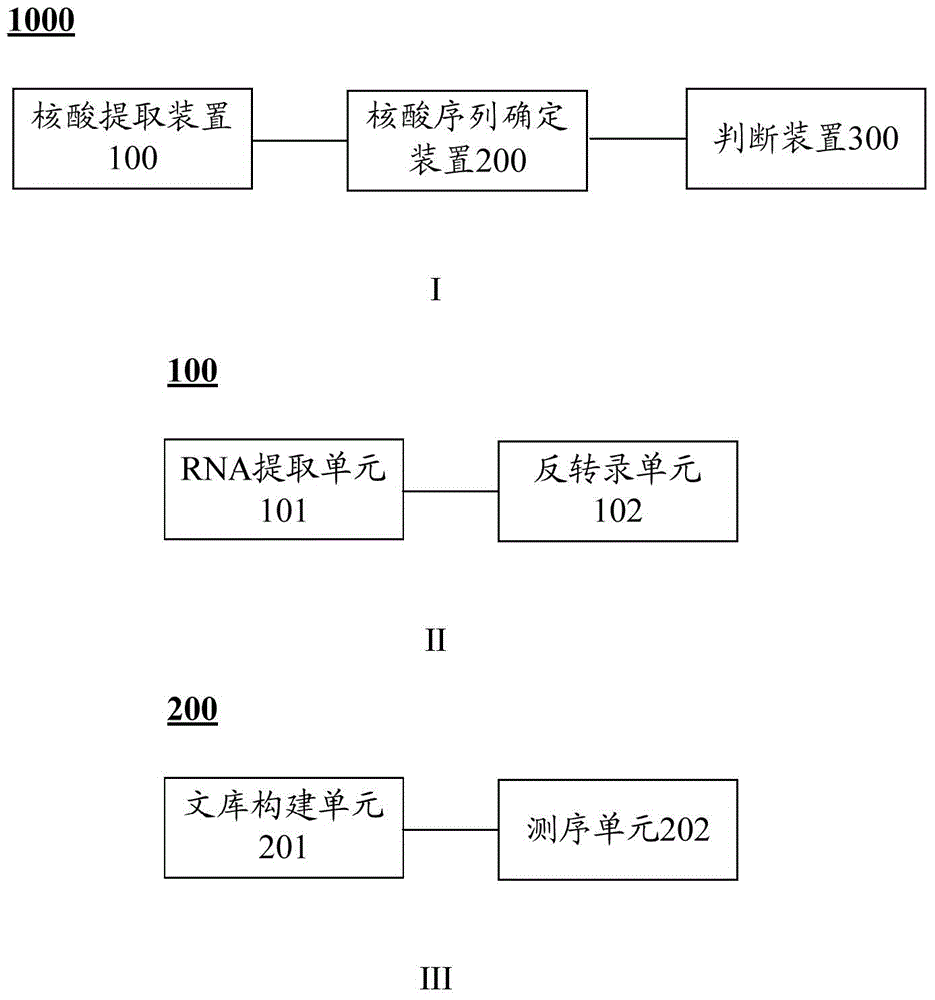
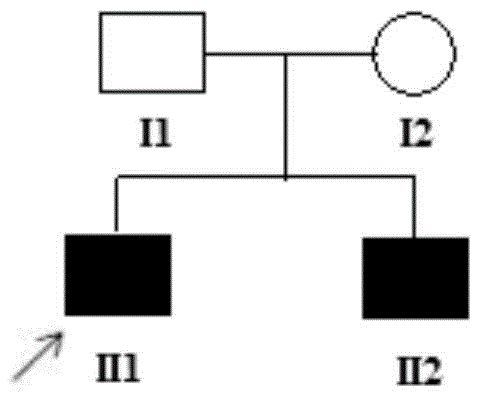
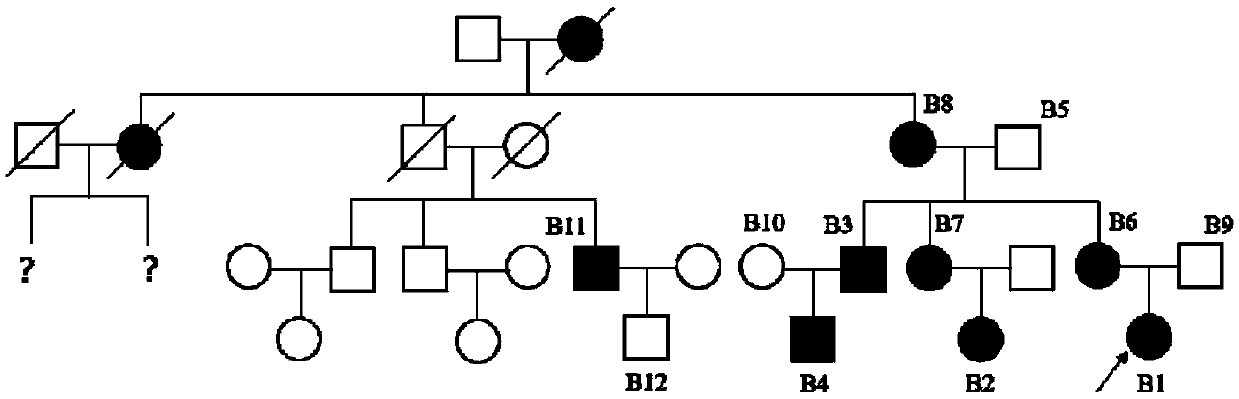
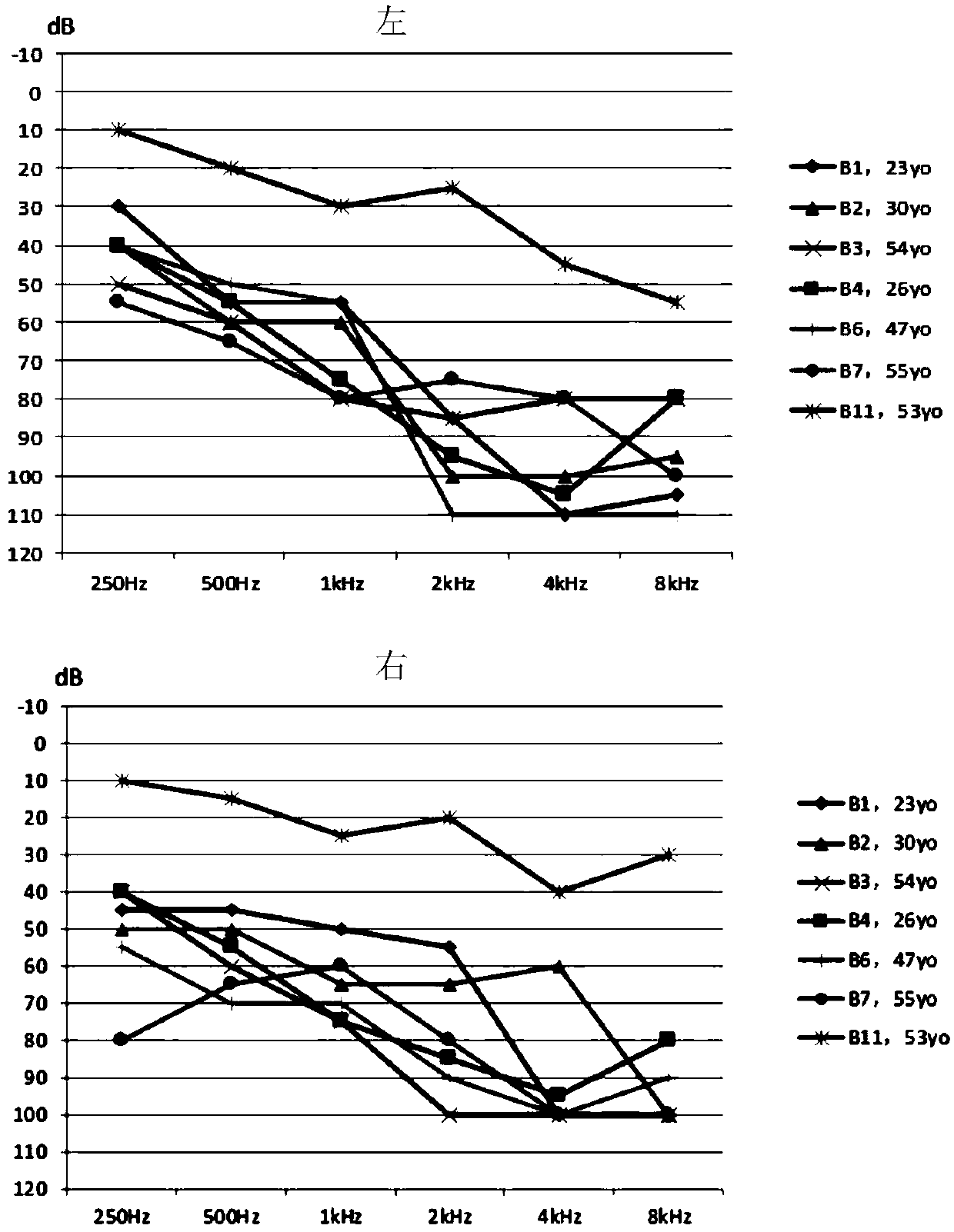
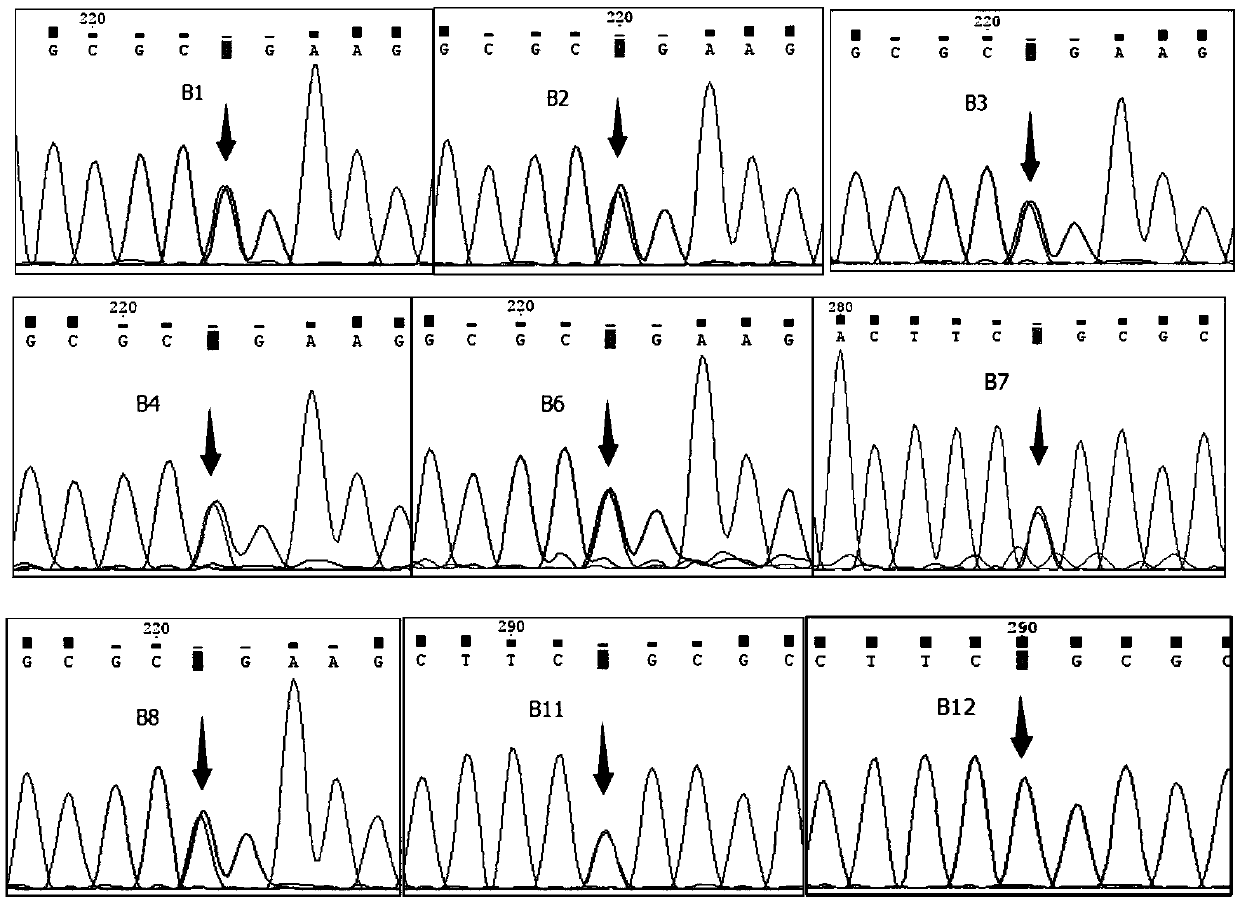
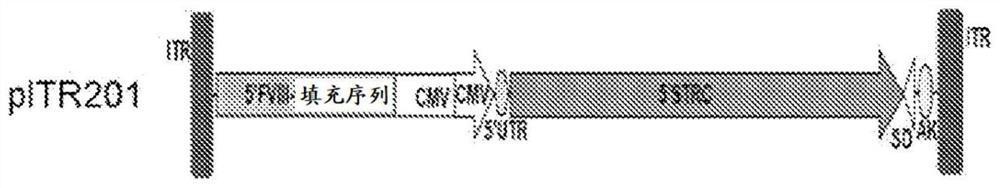
Patents
Literature
39 results about "Non syndromic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition. Non-syndromic craniosynostosis is a non-inherited, isolated finding without related anomalies such as disorders of the limbs, ears or cardiovascular system. It typically involves the early closure of a single growth seam, or suture, in your child’s skull. The specific diagnosis and appearance of a patient with non-syndromic...
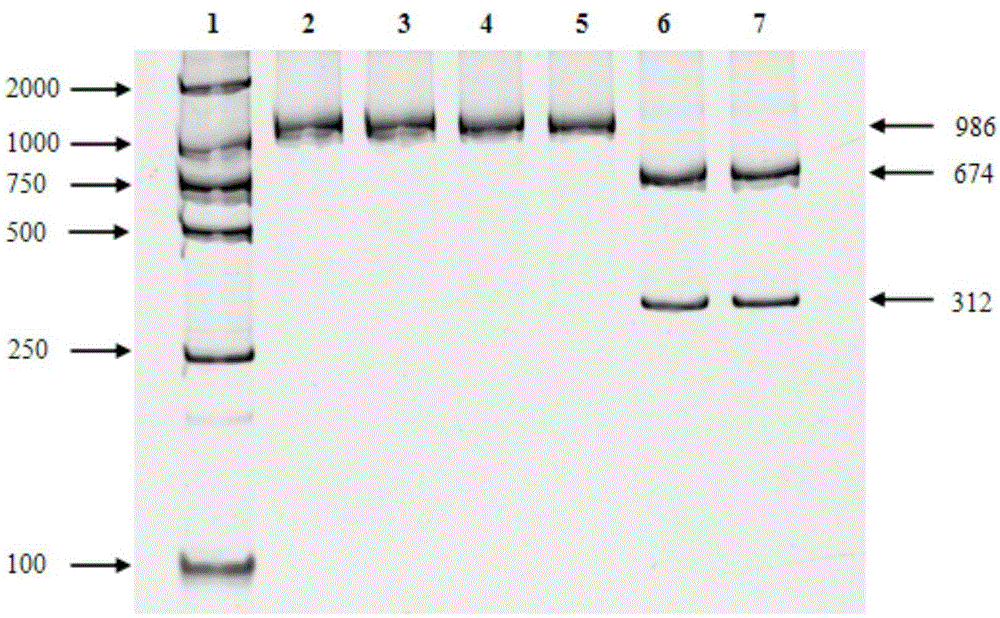
Gene detection kit for hereditary hearing loss
ActiveCN103352080AWide range of usesImprove detection success rateMicrobiological testing/measurementHybrid typeVirulent characteristics
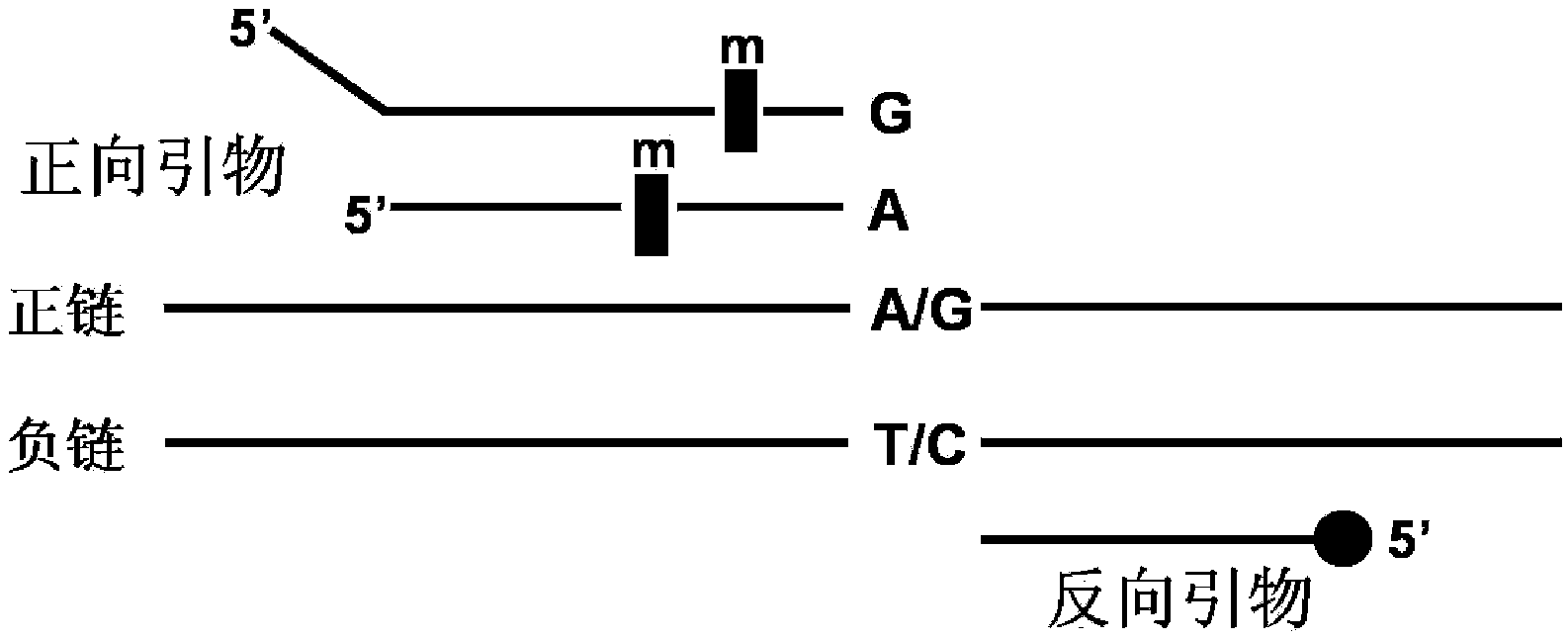
The invention discloses a fluorescence detection kit capable of detecting 17 non-syndromic hereditary hearing loss susceptibility genes. The kit adopts 17 pairs of specific primers to conduct genetic typing on the hearing loss susceptibility genes, and 17 hotspot mutations in four most common Chinese hearing loss related genes can be detected at the same time in a single tube within 3 hours. The kit comprises primer combinations of 17 polymorphic sites of hereditary hearing loss on a GJB2 (CX26) gene, an SLC26A4 (PDS) gene, a GJB3 gene and a 12SrRNA (MTRNR1) gene, can be used for accurately judging the wild type, the pure mutant type or the hybrid type of the 17 sites, and achieves diagnosis and screening of the hearing loss genes. The kit provided by the invention can be applied to rapidly and efficiently detecting the hearing loss genes and is a rapid, convenient, economical and efficient screening kit for hearing loss virulence genes.
Owner:AGCU SCIENTECH +1
Methods and kits for diagnosing and treating mental retardation
InactiveUS20070015194A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementINFANTILE BILATERAL STRIATAL NECROSISNucleic acid sequencing
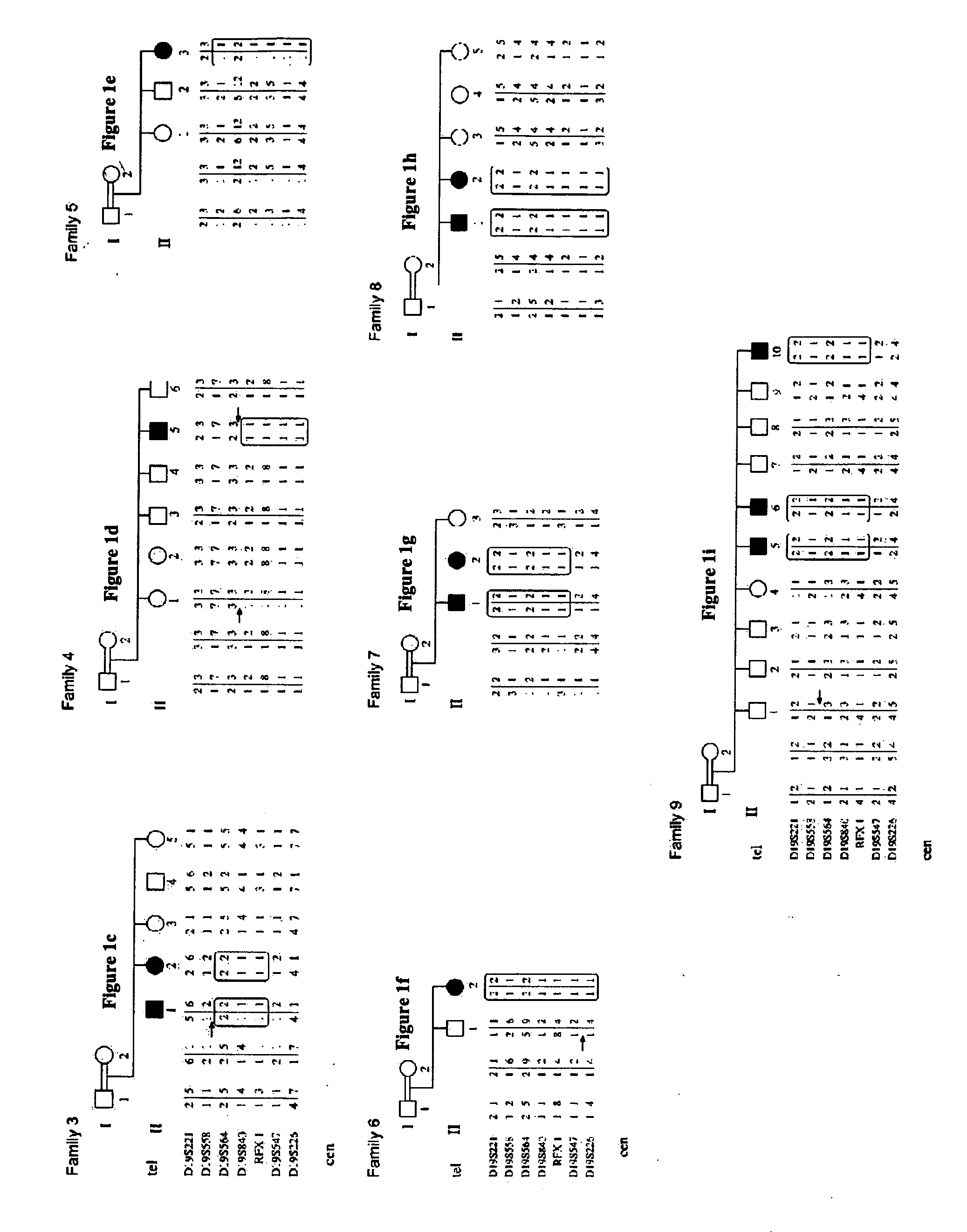
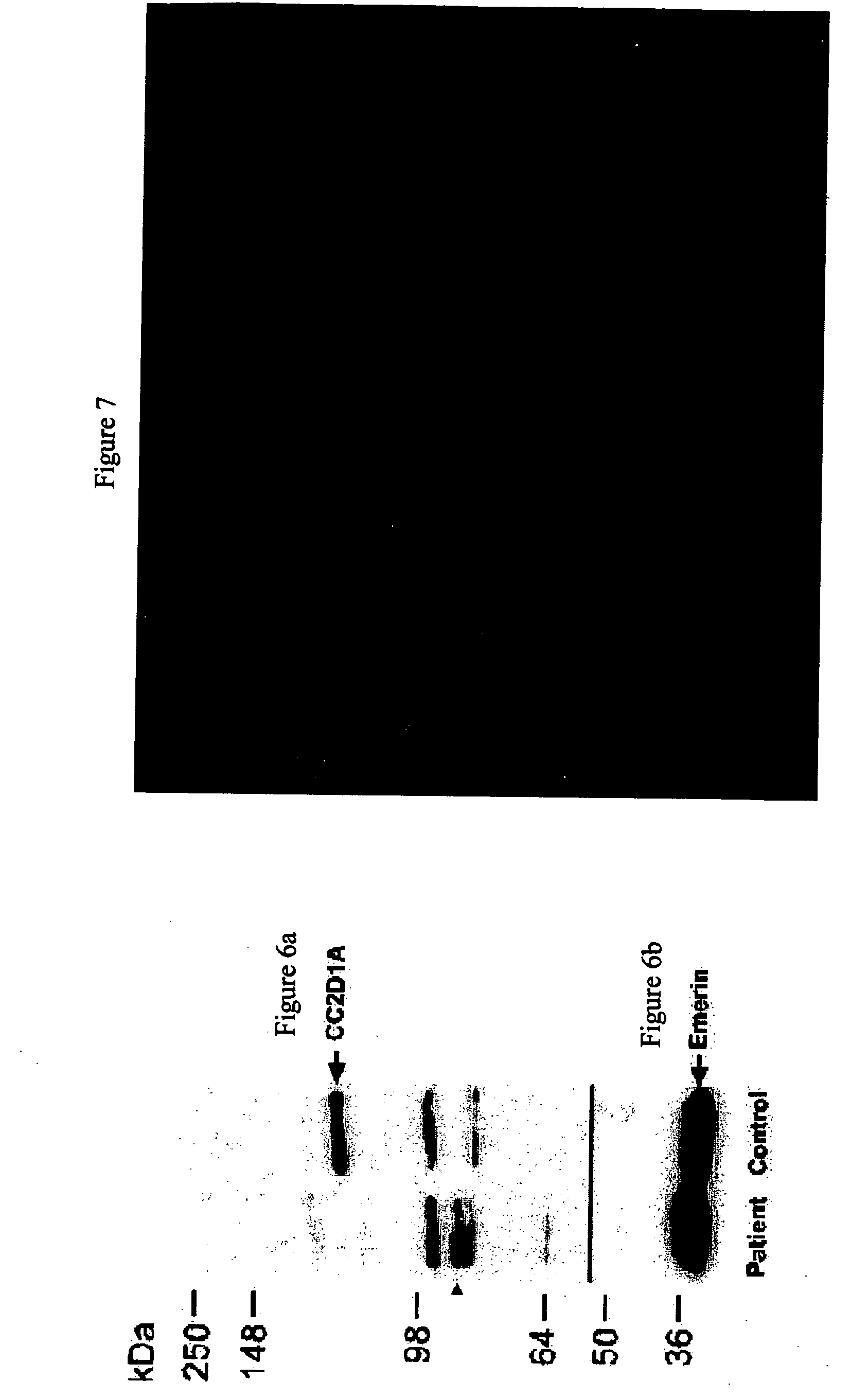
The present invention provides methods, kits, isolated nucleic acid sequences, antibodies and addressable oligonucleotides microarrays which can be for analyzing sequence alterations and detecting the expression level of CC2D1A or nup62 in cells of an individual and thus diagnose nonsyndromic mental retardation (NSMR) and / or infantile bilateral striatal necrosis (IBSN) in the individual. In addition, the present invention provides methods and pharmaceutical compositions which can be used to treat pathologies associated with mental retardation such as NSMR or IBS.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Primer in use for in vitro diagnosing GJB2 mutation of deaf gene of autosomal recessive inheritance in non-syndrome
InactiveCN1873027AAbundant sources of supplyLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerAutosomal recessive inheritance
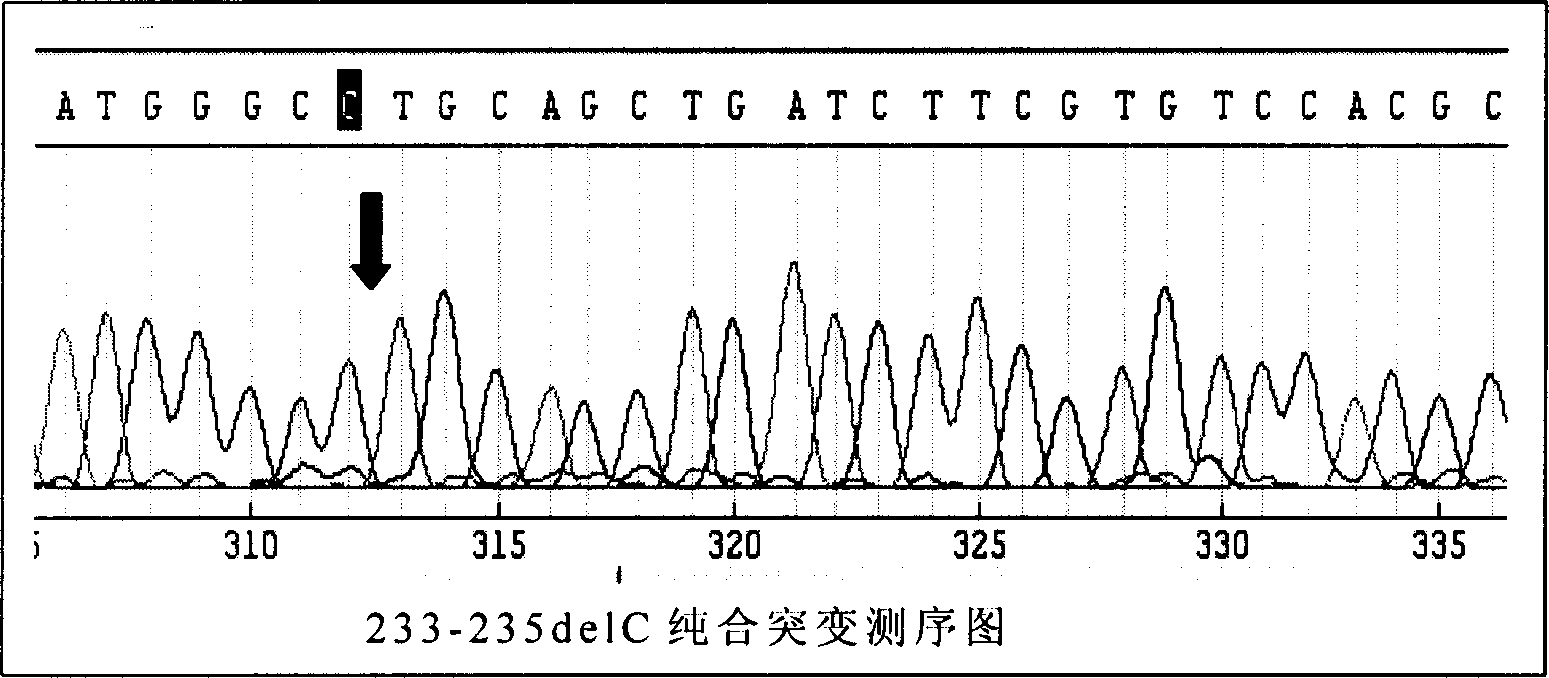
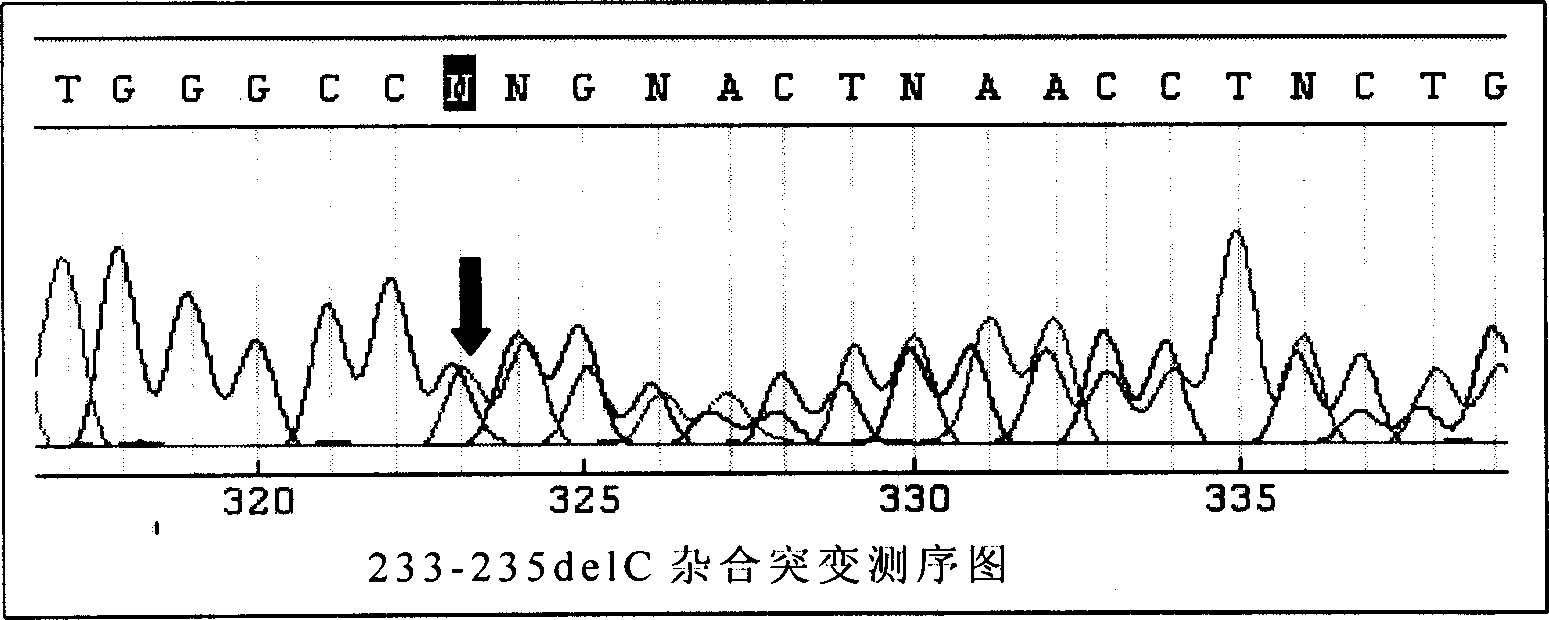
This invention provides primers for in vitro diagnosis of mutation of autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss gene GJB2. The primers can be used for completely amplifying the coding region and upstream or downstream important splicing sequences of GJB2 gene. This invention also provides a test kit for containing the primers and ApaI restriction endonuclease and their application for in vitro detection of 233-235delC mutation of the complete GJB2 coding region. The test kit can also be used for detecting the mutation sites of the GJB2 coding region through sequencing by the forward primer, and detecting deletion or insertion heterozygous mutation through sequencing by the reverse primer. The test kit is suitable for large-scale screening of autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss gene GJB2 mutation and genetic counseling.
Owner:山东三月三基因技术有限公司
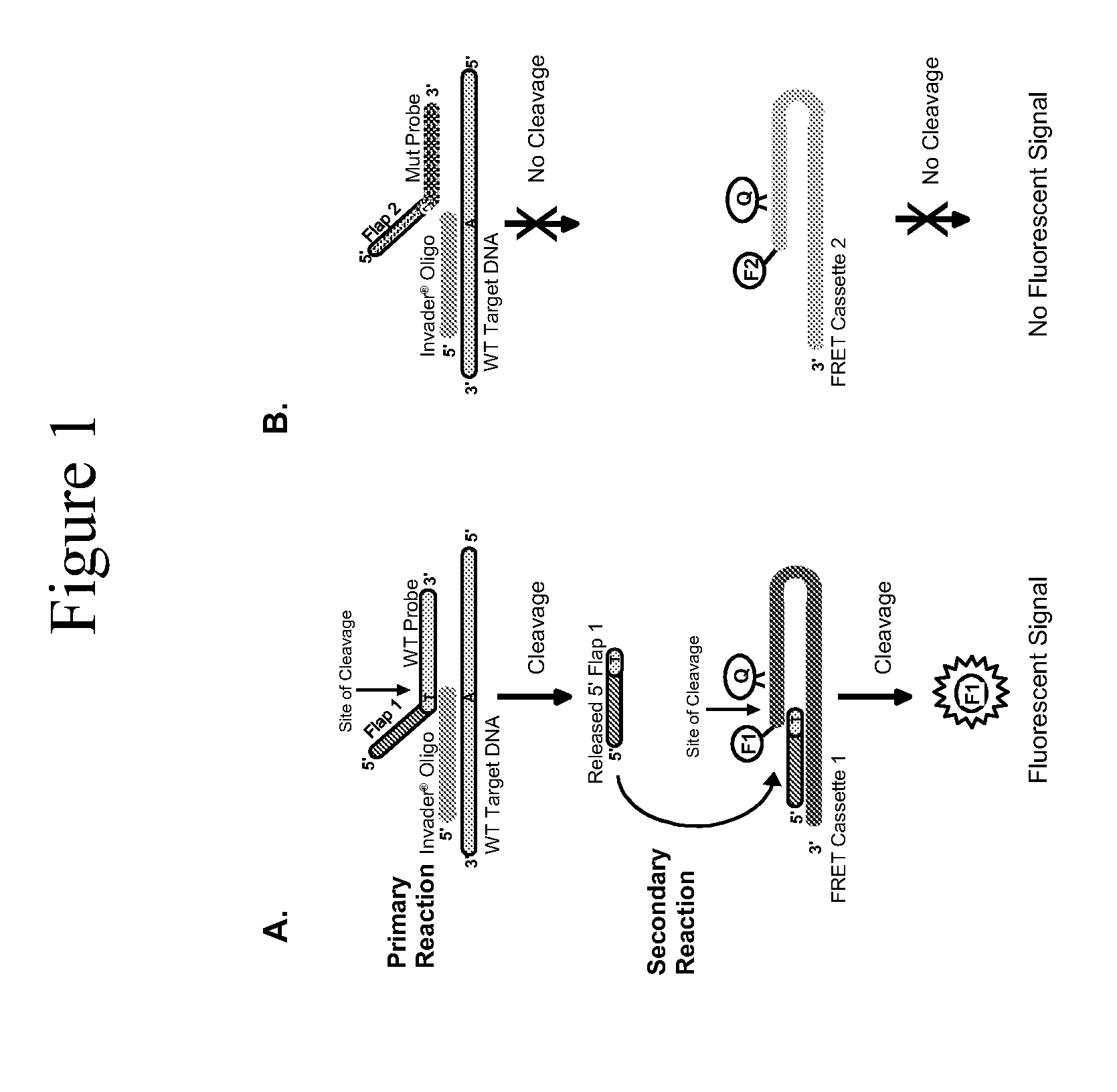
Connexin allele detection assays
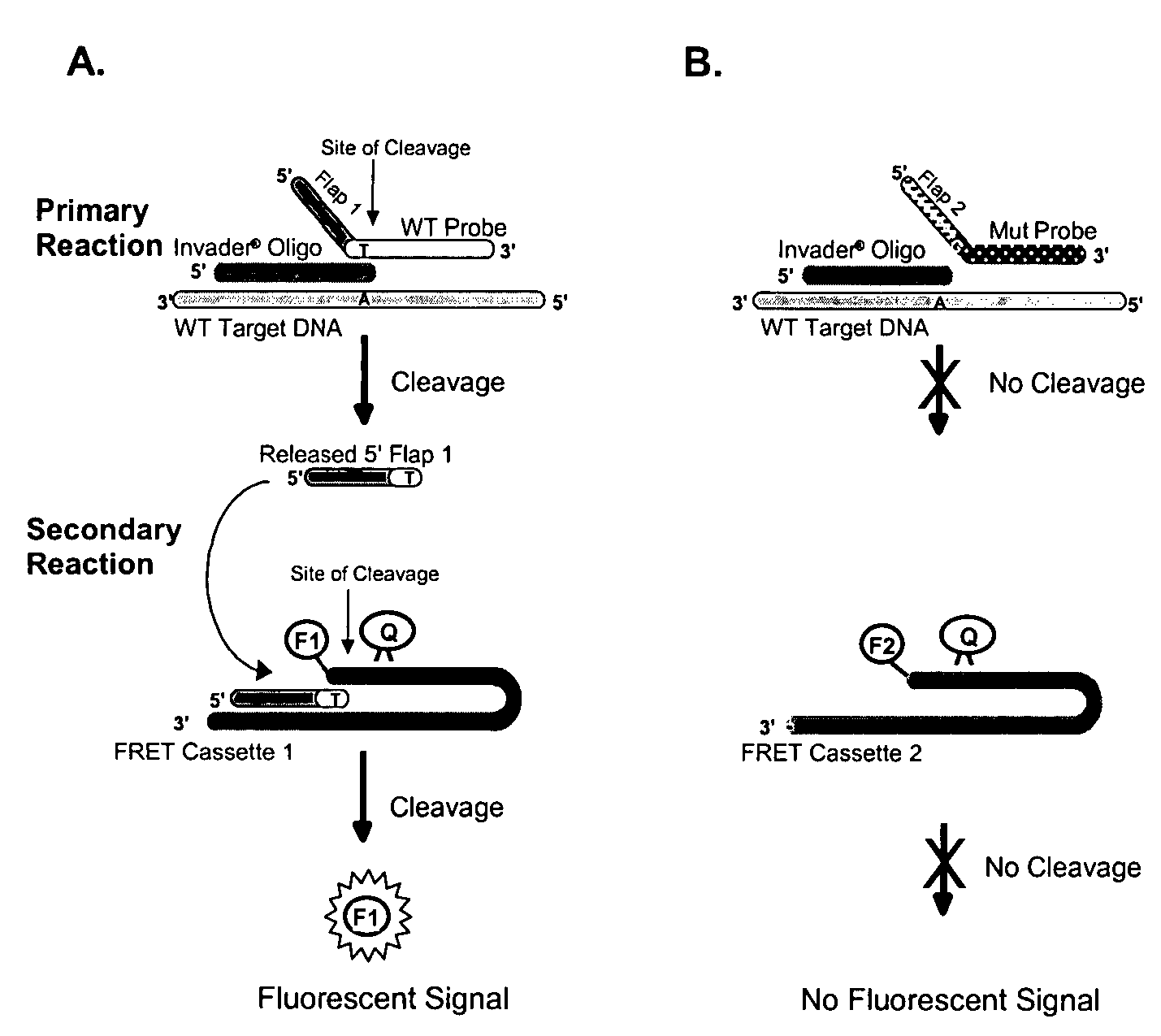
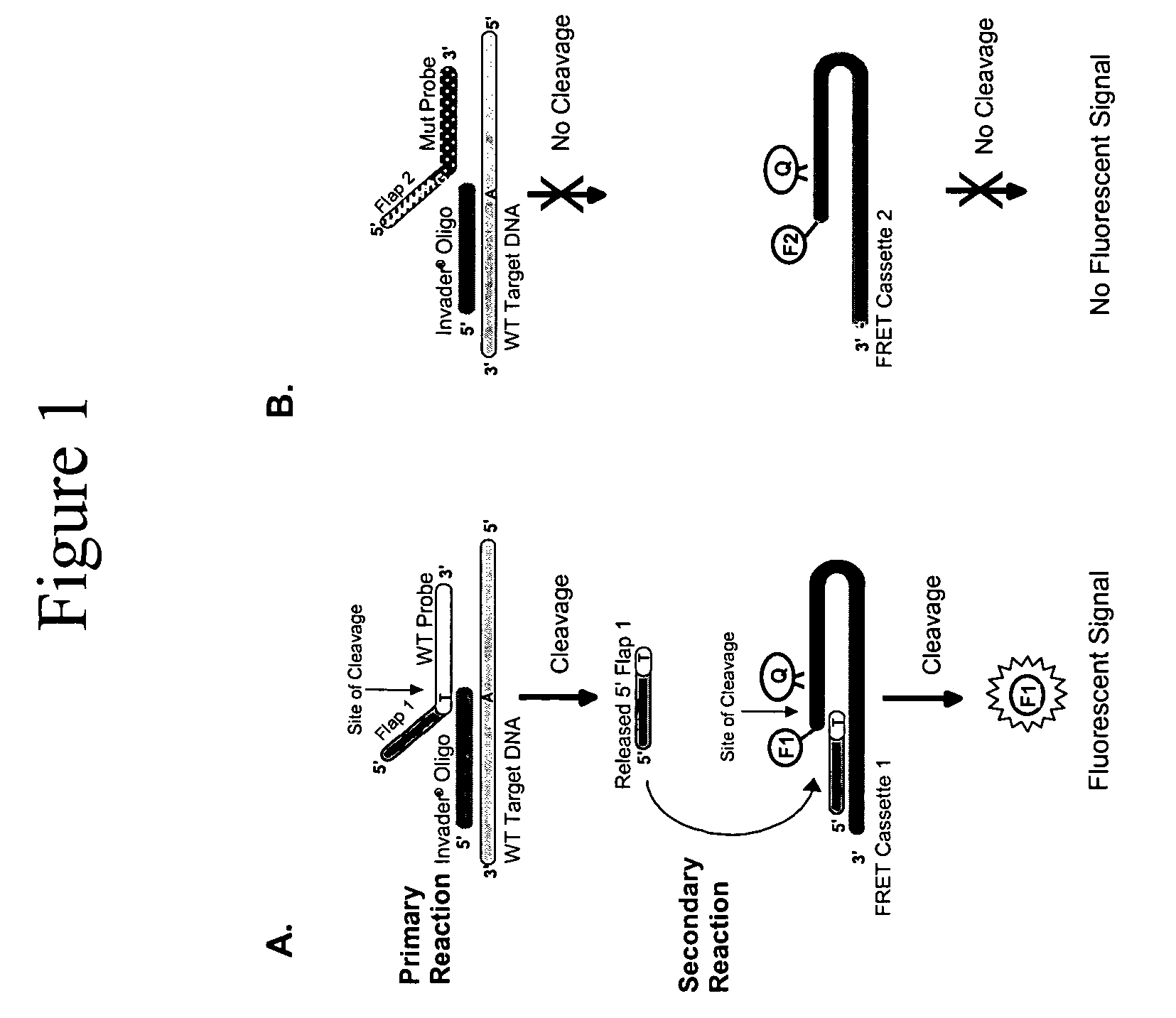
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the detection and characterization of mutations associated with non-syndromic hearing impairment. More particularly, the present invention provides compositions, methods and kits for using invasive cleavage structure assays (e.g. the INVADER assay) to screen nucleic acid samples, e.g., from patients, for the presence of any one of a collection of mutations in the Connexin 26, or gap junction beta 2, gene associated with non-syndromic hearing loss.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Syngap1 dysfunctions and uses thereof in diagnostic and therapeutic applications for mental retardation
InactiveUS20110229891A1Useful in detectionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionFunctional disturbanceGenomic DNA
The invention identifies Syngap1 dysfunctions as causative of mental retardation. Described are methods of detecting mental retardation and methods of detecting non-syndromic mental retardation (NSMR) in a human subject. Particular methods comprise sequencing a human subject's genomic DNA for comparison with a control sequence from an unaffected individual. Also described are probes, kits, antibodies and isolated mutated Syngap1 proteins.
Owner:CENT HOSPITALER UNIV SAINTE JUSTINE +1
Application of NOTCH3 and JAG2 gene SNP ((Single Nucleotide Polymorphism)) loci
InactiveCN103589785AIncreased sensitivityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementIncomplete bilateral cleft lipNormal people
The invention belongs to the field of bio-medical technology, and specifically relates to an application of NOTCH3 and JAG2 gene SNP loci, as well as a kit and a detection method thereof. The application of NOTCH3 and JAG2 gene SNP loci in preparation of a detection kit for diagnosing analogous cleft lip and palate susceptibility is disclosed. The invention discovers that SNP locus rs12082 on NOTCH3 gene and two SNP loci (rs741859, rs2238286) on JAG2 gene are correlated with non-syndromic cleft lip and palate for the first time. Therefore, on that basis, a method and a kit for detecting non-syndromic cleft lip and palate susceptible risk through SNP are provided, moreover, clinic experimental study verifies that the detection method is feasible, and the detection kit provided by the invention has better sensitivity, stability and specificity. The detection kit provided by the invention can be used for cleft lip and palate susceptibility screening for normal people, and can effectively play a role in risk early warning and early diagnosis.
Owner:谢小冬
Methods to prevent and treat autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing loss
ActiveUS20160090597A1Organic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAutosomal dominant traitMedicine
The present invention provides in certain embodiments a method of treating autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing loss (ADNSHL) in a patient in need thereof comprising: (a) identifying a mutation in an ADNSHL-causing gene, (b) preparing a ADNSHL therapeutic miRNA, and (c) administering to the patient a pharmaceutical composition comprising the ADNSHL therapeutic miRNA and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
PTPRQ gene mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN105838720AImprove early diagnosis rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPTPRQ geneMutant
The invention discloses a PTPRQ gene mutant and an application thereof, and specifically relates to an isolated PTPRQ-mutant-coding nucleic acid, an isolated polypeptide, and a method, system, and kit for screening a biological sample susceptible to non-syndromic autosomal-recessive hearing loss. Compared with SEQ ID NO:1, the isolated PTPRQ-mutant-coding nucleic acid has c.3125A>G mutation or c.5981A>G mutation. Whether a new mutant exists in the biological sample is detected, and the fact that if the biological sample is susceptible to non-syndromic autosomal-recessive hearing loss can be effectively detected.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
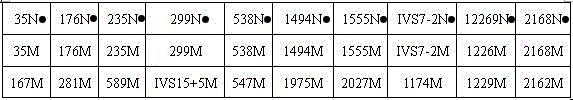
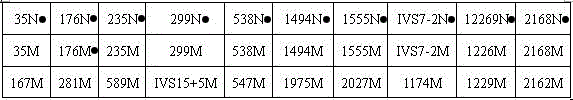
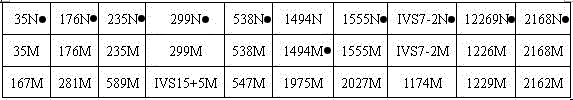
Non-syndromic deafness gene polymorphism detecting kit and application thereof
InactiveCN105441540AAccurate analysisFacilitate the establishment of standardized operating proceduresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTotal DeafnessSlc26a4 gene
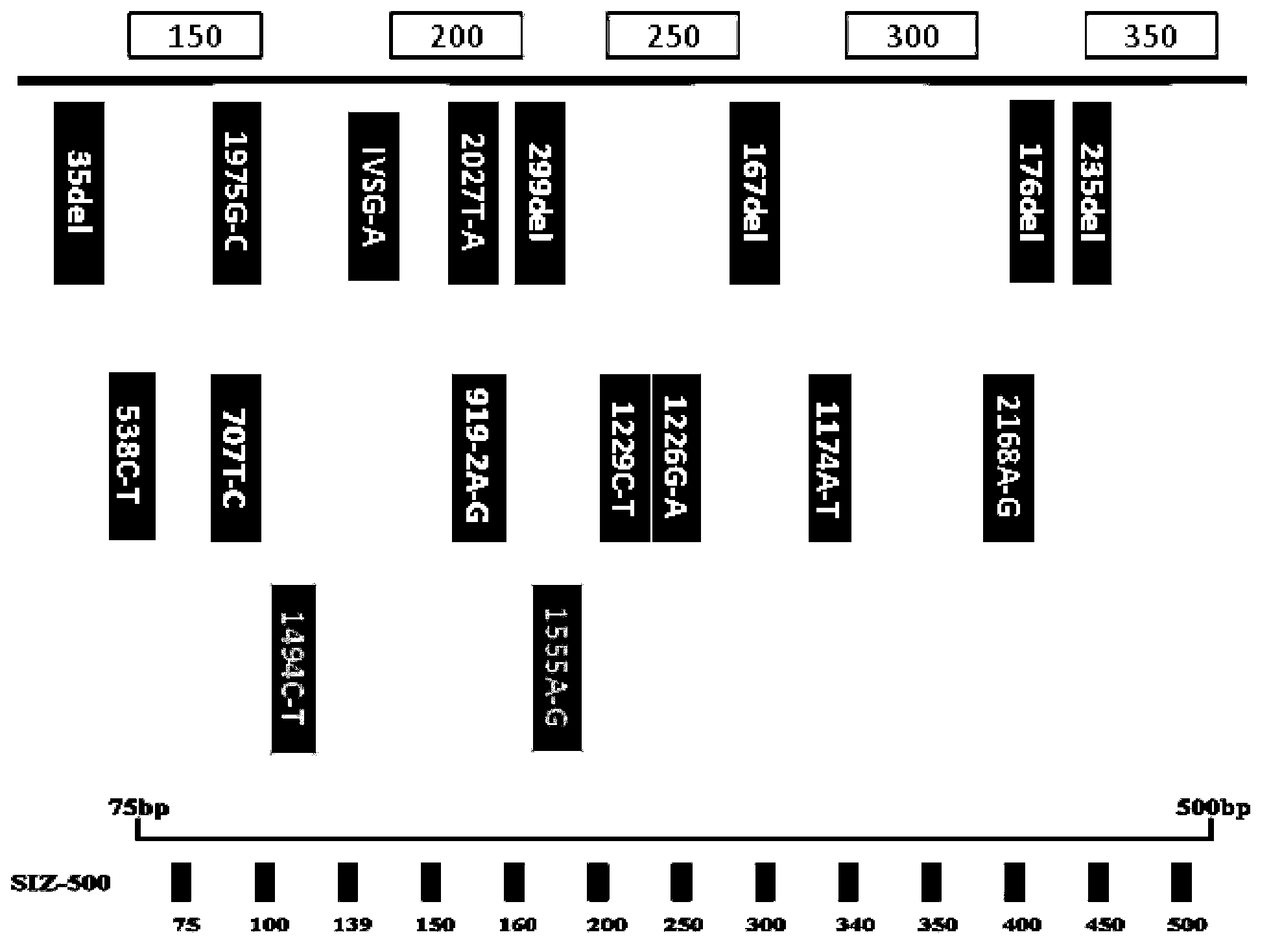
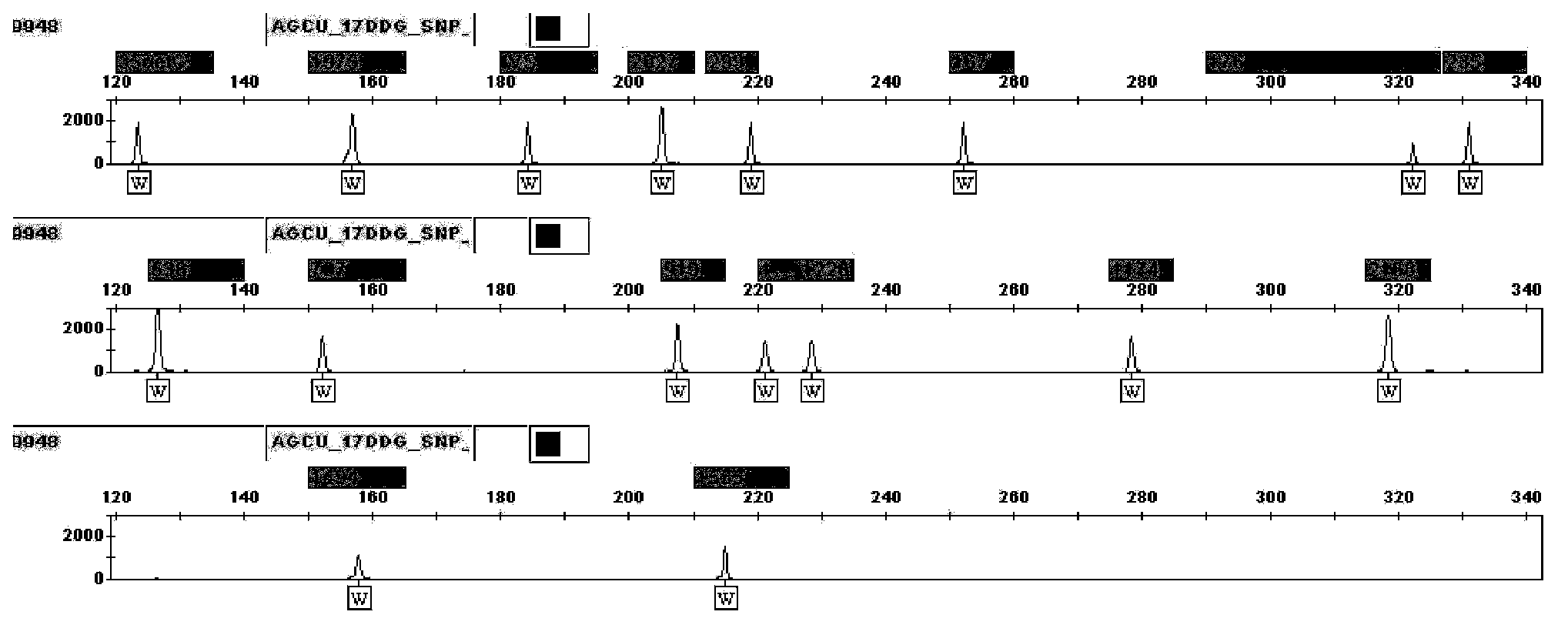
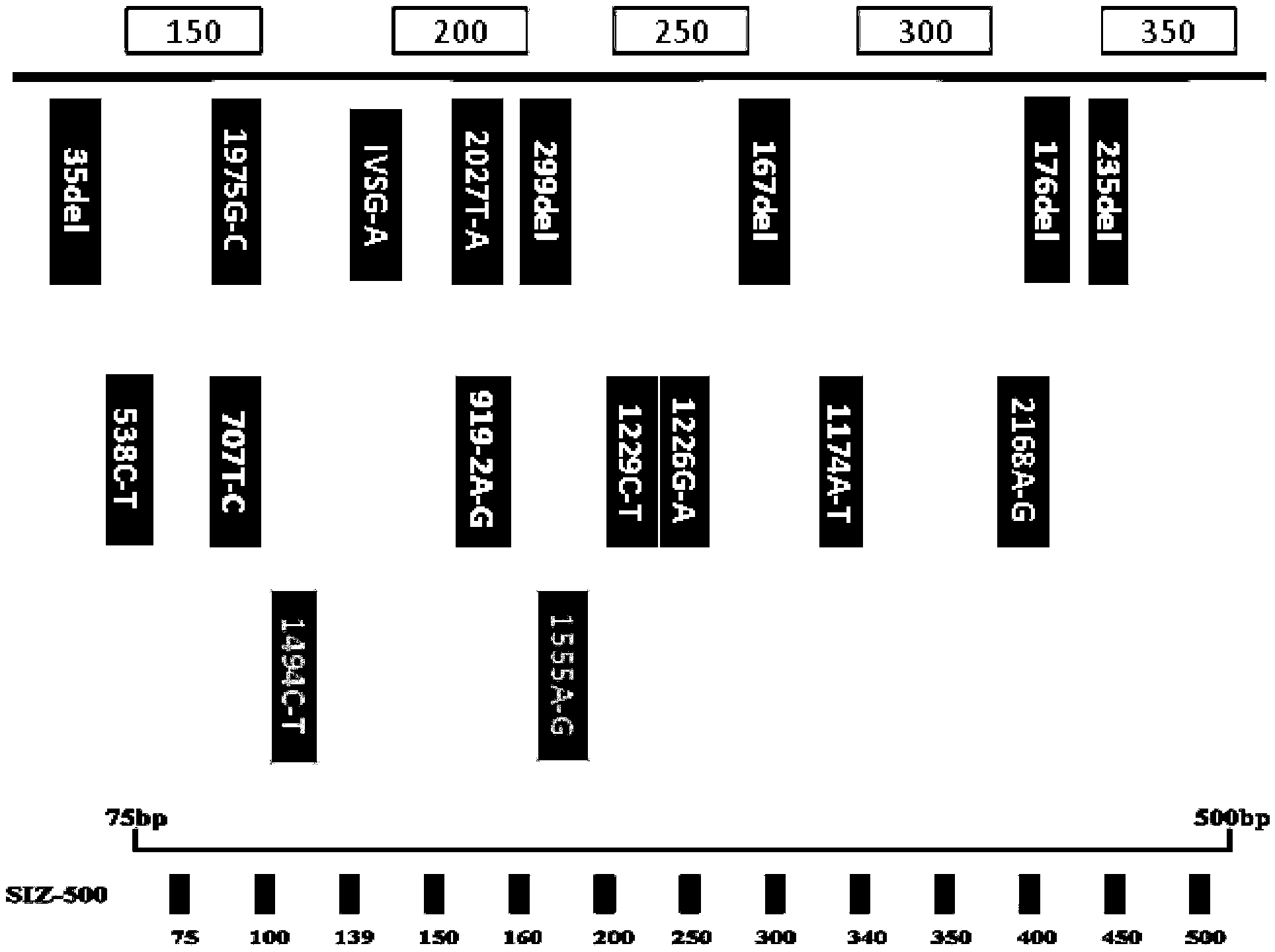
The invention discloses non-syndromic deafness gene polymorphism detecting primers. The primers mainly include five pairs of specific primers and nine sequencing primers for amplification of deafness genes, GJB2 genes, GJB3 genes, SLC26A4 genes and 12SrRNA genes are included, and ten single nucleotide polymorphisms are involved, namely GJB2 (35DELG, 176-191DEL16, 235DELC, 299-300 DEL AT), GJB3 (538C>T, 547G>A), SLC26A4(2168A>G, IVS7A>G) and mitochondria 12SrRNA (1494C>T, 1555A>G). The invention further discloses a kit comprising the primers. Sensitivity is high, results are visual, judgment is more accurate and quicker, and accurate and quick high-pass non-syndromic deafness gene polymorphism detection can be achieved.
Owner:CHANGSHA DIAN MEDICAL SCI INSPECTION CO LTD
SNP marker related to auxiliary diagnosis of non-syndromic congenital heart disease and application thereof
ActiveCN104195228AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHeart diseaseGenetic engineering
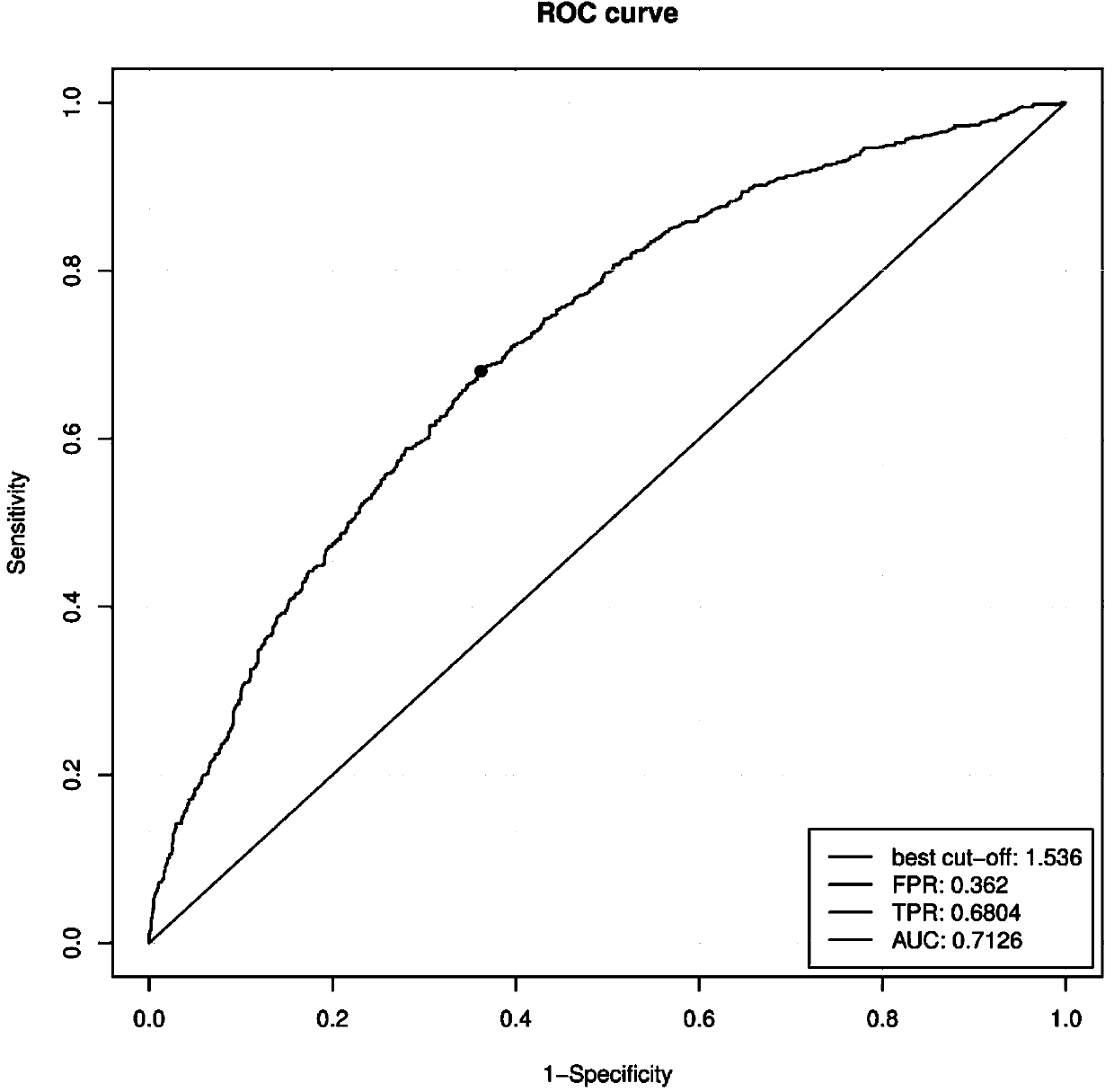
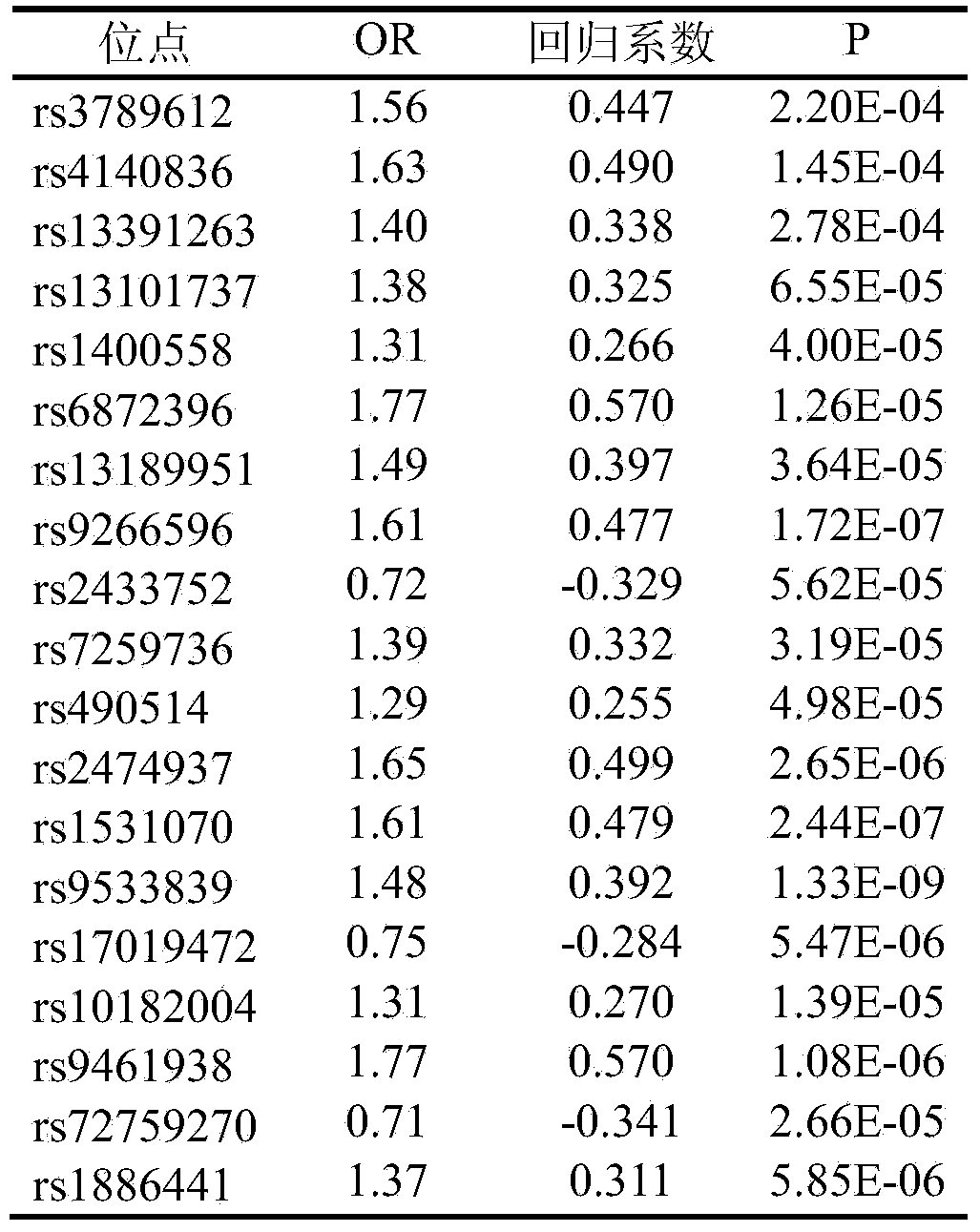
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering and reproductive medicine and discloses an SNP marker related to auxiliary diagnosis of non-syndromic congenital heart disease and an application thereof. The SNP marker is composed of rs3789612, rs4140836, rs13391263, rs13101737, rs1400558, rs6872396, rs13189951, rs9266596, rs7863990, rs2433752, rs7259736, rs490514, rs2474937, rs1531070, rs9533839, rs17019472, rs10182004, rs9461938, rs72759270 and rs1886441. The marker can be used for preparing an auxiliary diagnosis kit of the non-syndromic congenital heart disease.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Gene detection kit for hereditary hearing loss
ActiveCN103352080BWide range of usesImprove detection success rateMicrobiological testing/measurementHybrid typeVirulent characteristics
Owner:AGCU SCIENTECH +1
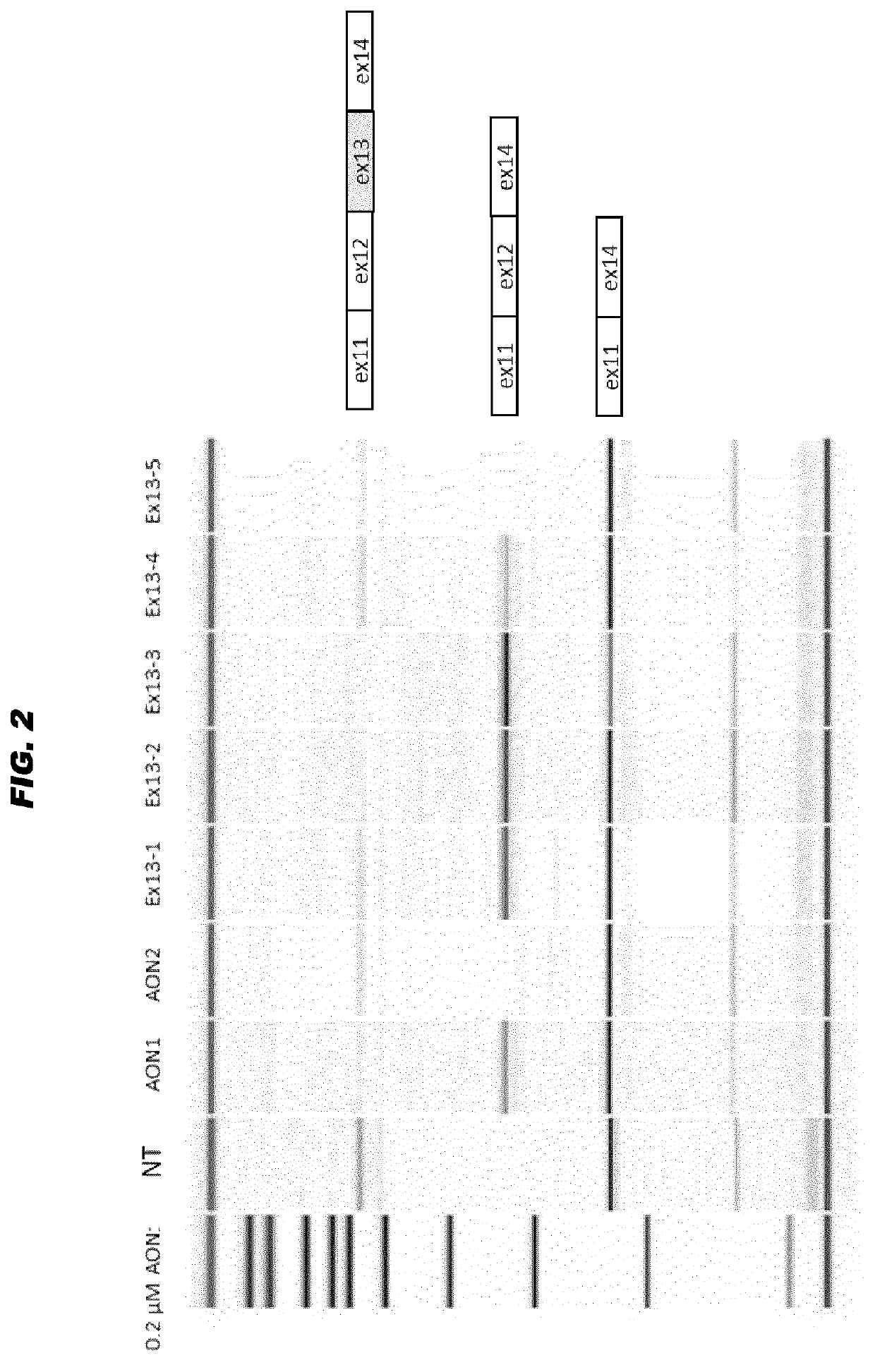
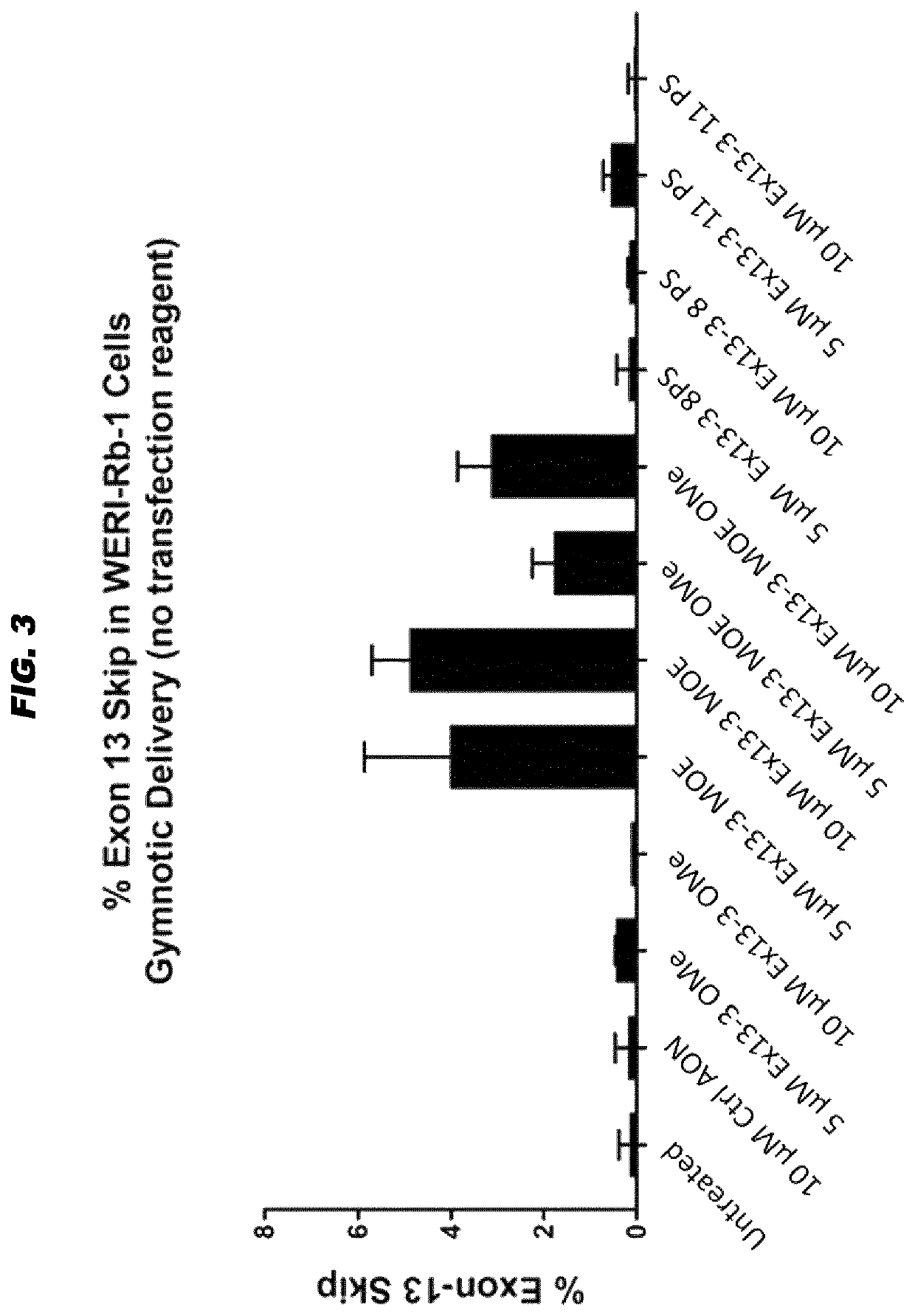
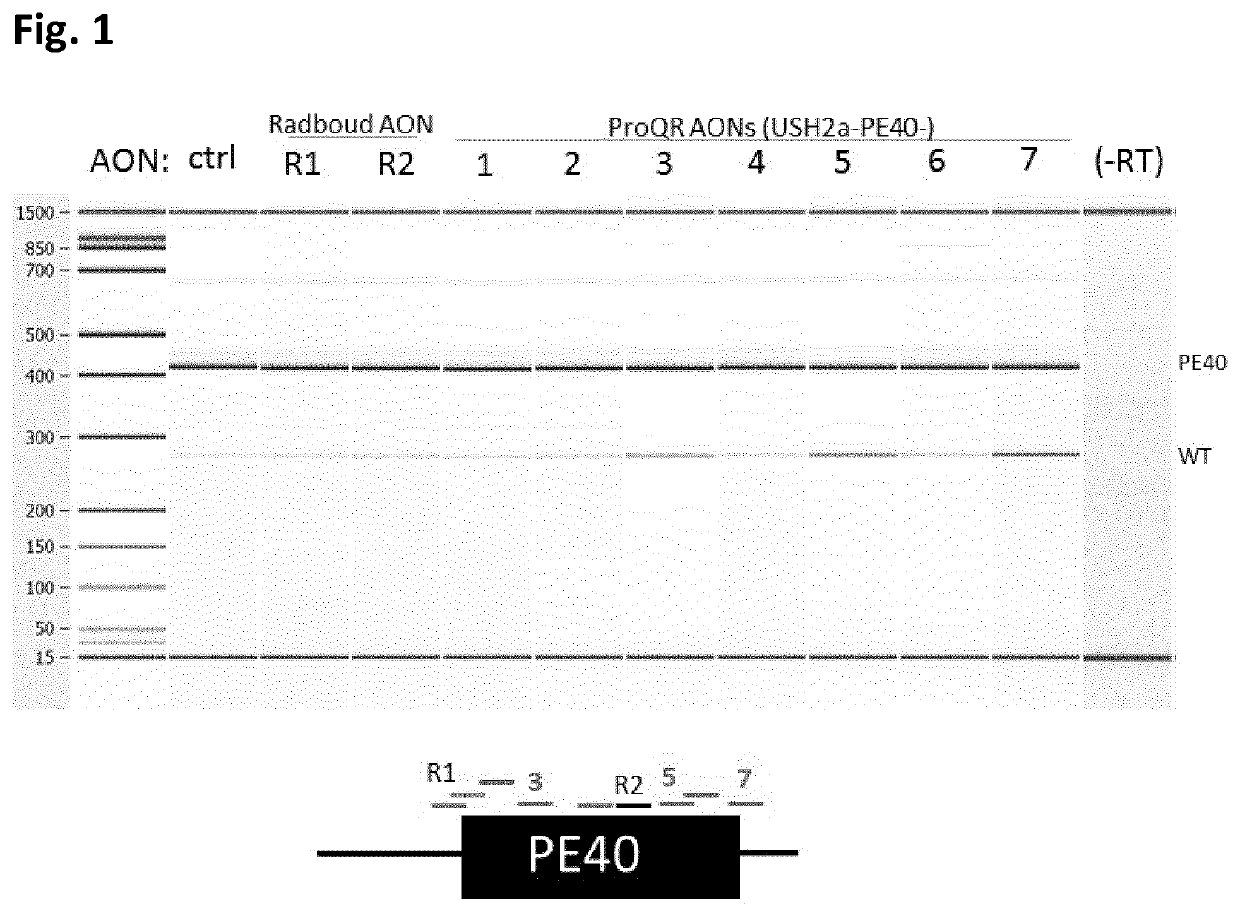
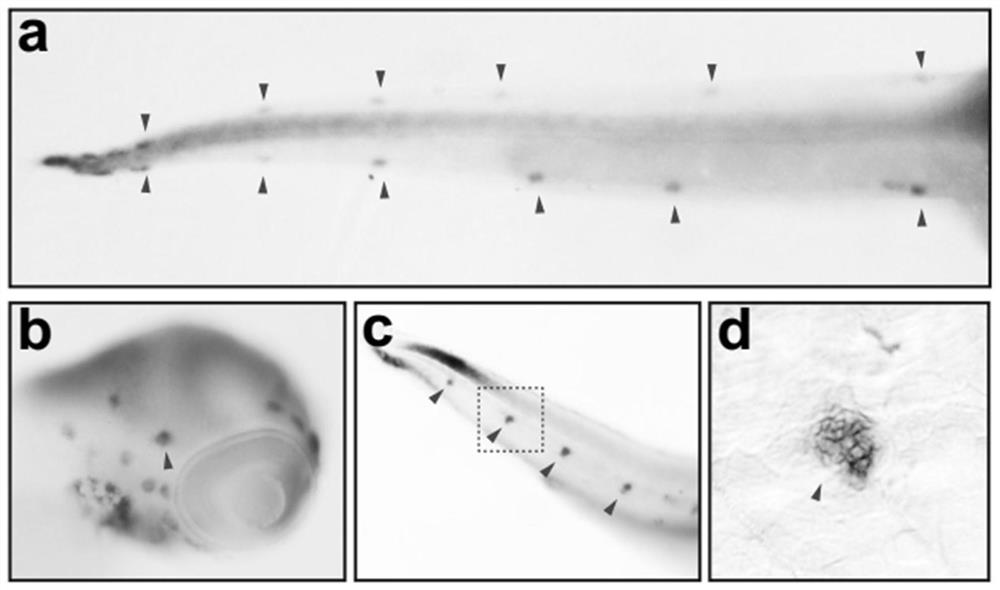
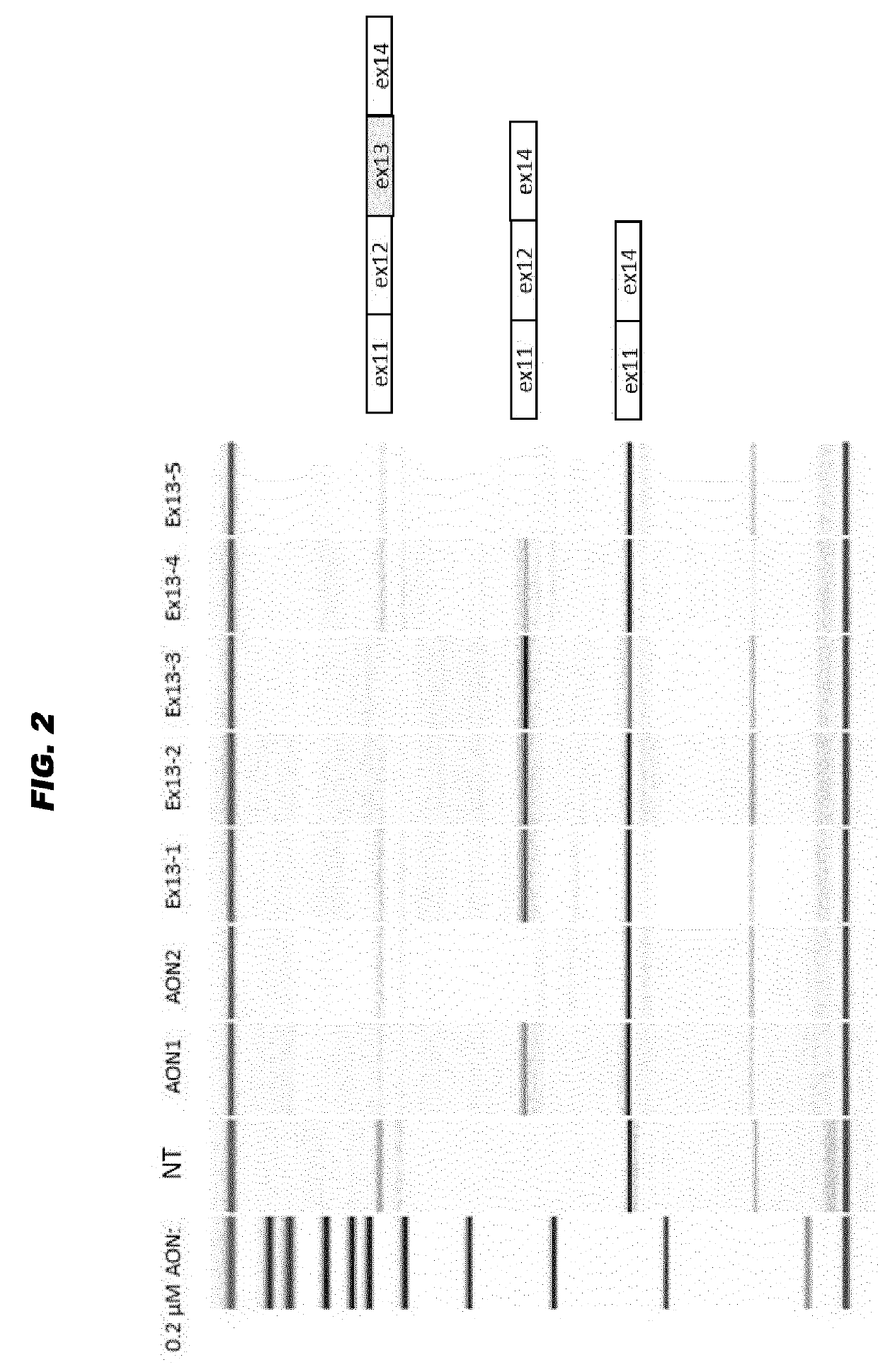
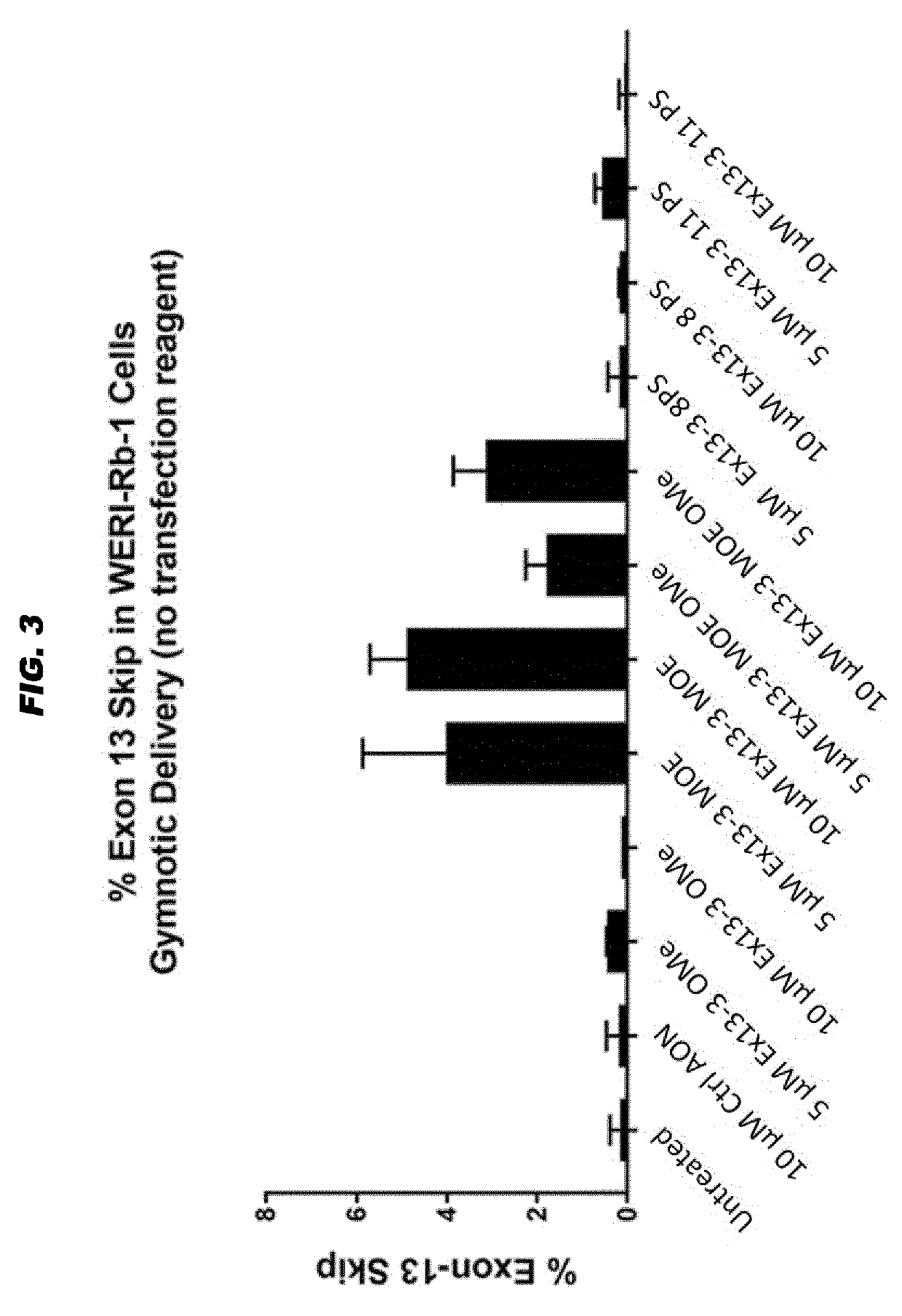
Antisense oligonucleotides for the treatment of eye disease
The invention relates to the fields of medicine and immunology. In particular, it relates to novel antisense oligonucleotides (AONs) that may be used in the treatment, prevention and / or delay of Usher syndrome type II and / or USH2A-associated non syndromic retina degeneration.
Owner:PROQR THERAPEUTICS II BV
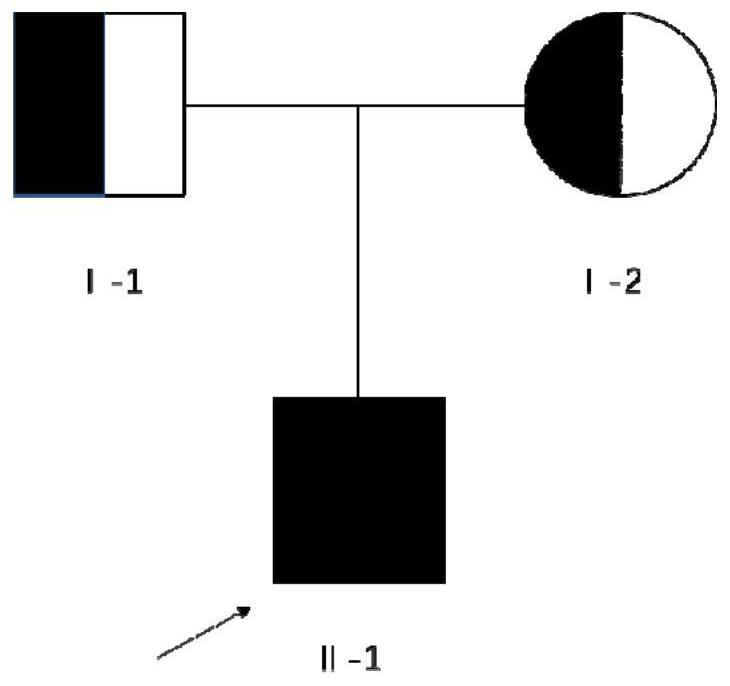
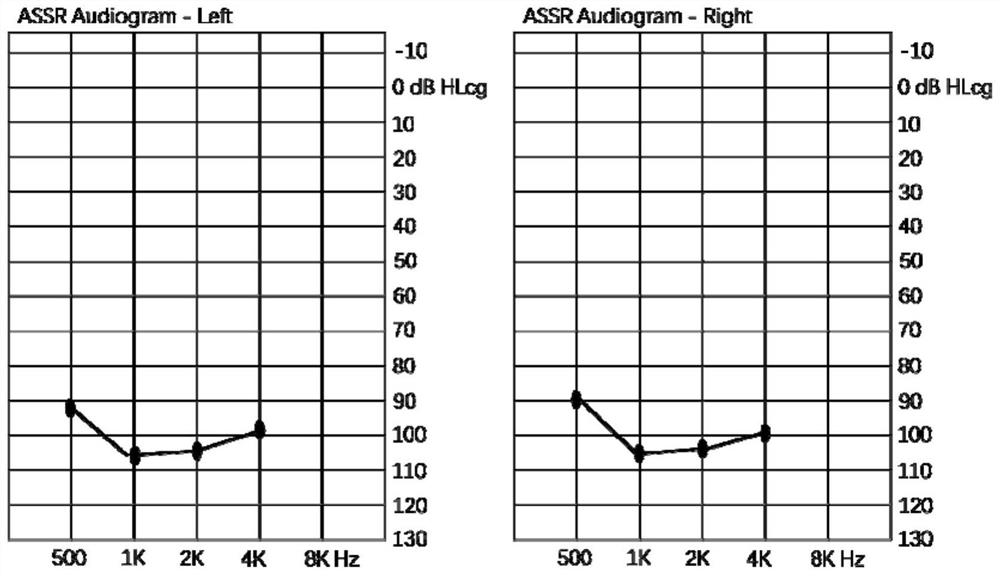
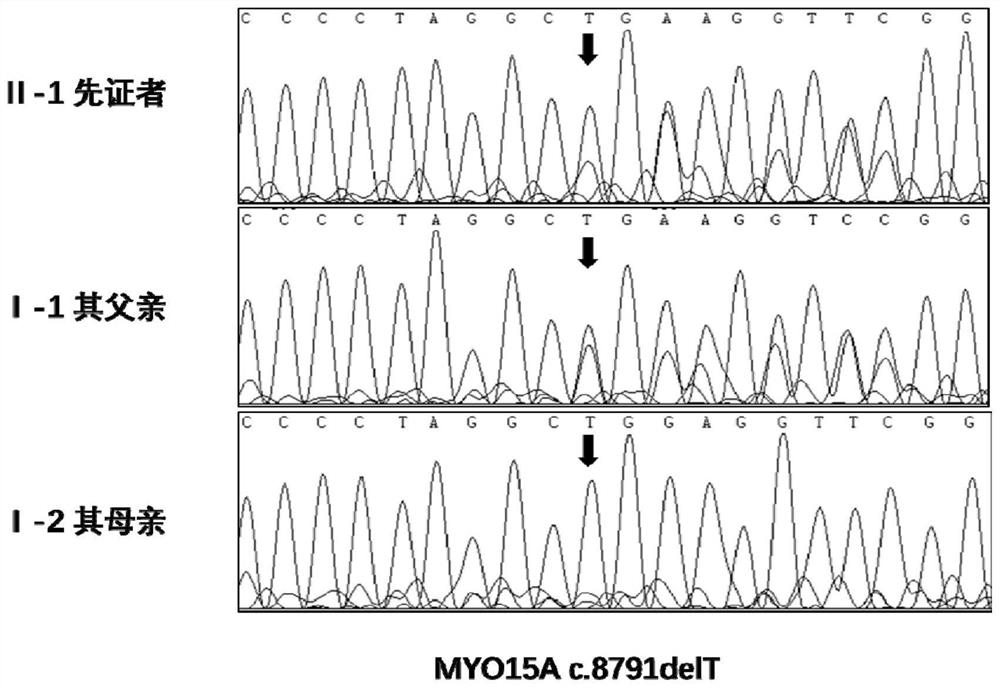
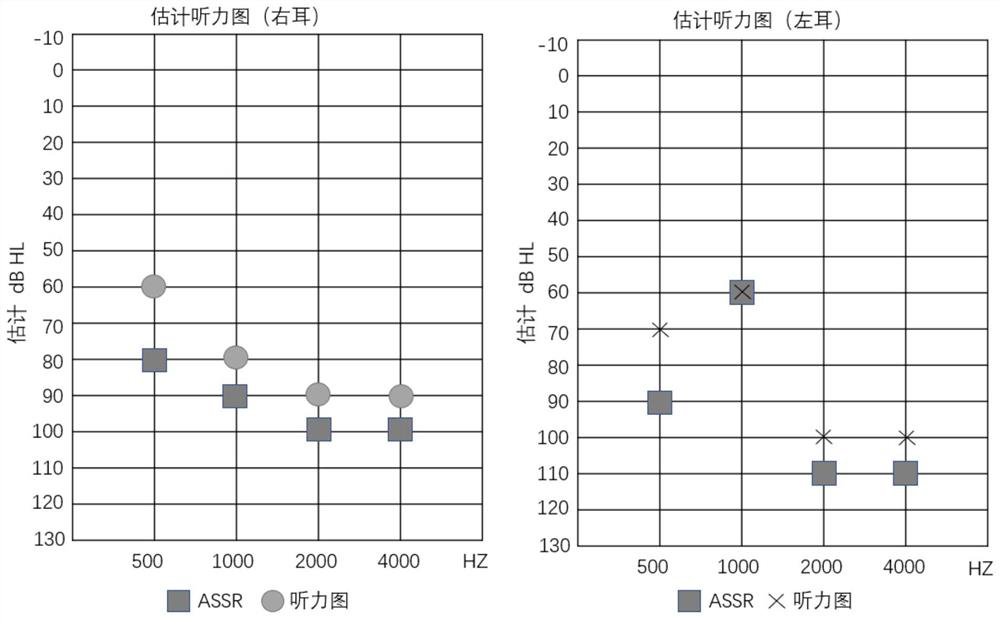
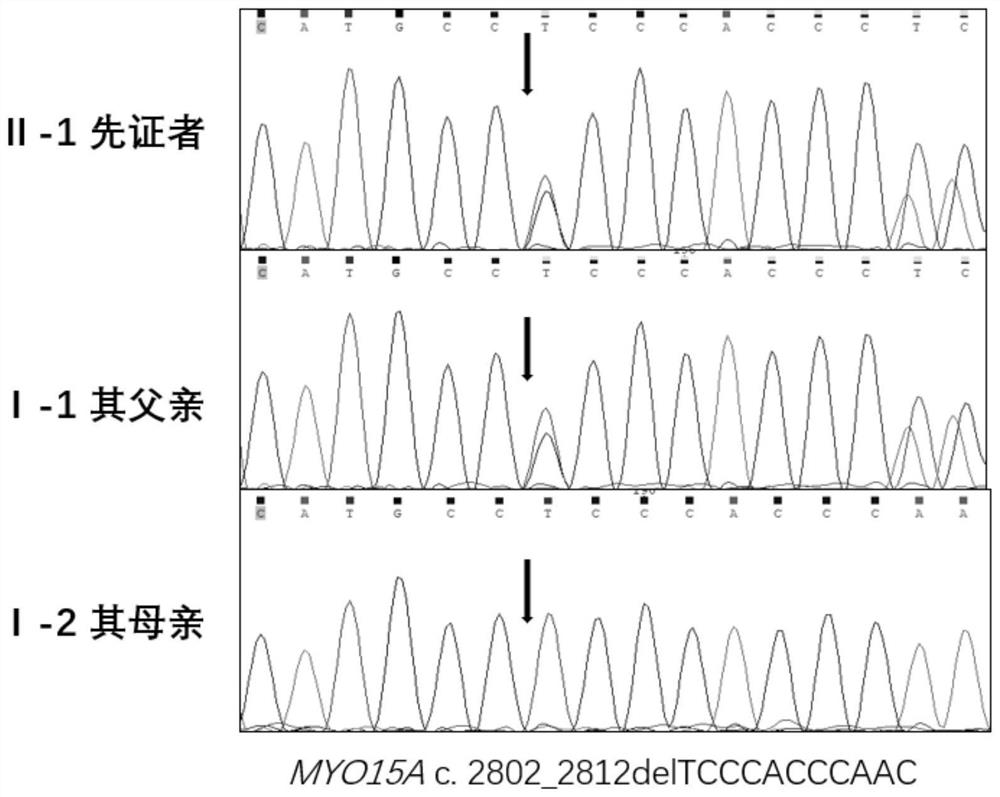
MYO15A gene mutant and application thereof
PendingCN112522275AImprove early diagnosis rateSenses disorderGenetic material ingredientsHL - Hearing lossDisease
The invention provides a non-syndromic hearing loss related gene mutant and application thereof, and particularly provides an MYO15A gene mutant and application thereof. Compared with a wild type MYO15A gene, the gene mutant has the c.10419-10423 del CAGCT mutation and / or the c.8791 del T mutation. The gene mutant is detectable, and by detecting whether the gene mutant is present in a biological sample or not, whether a biological sample suffers from non-syndromic hearing loss or not can be effectively detected. Detection and research of the hereditary hearing loss disease are expanded and perfected through discovery of the gene mutant, and a new detection site and a new detection method and way are provided for diagnosis or treatment of the disease.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD +1
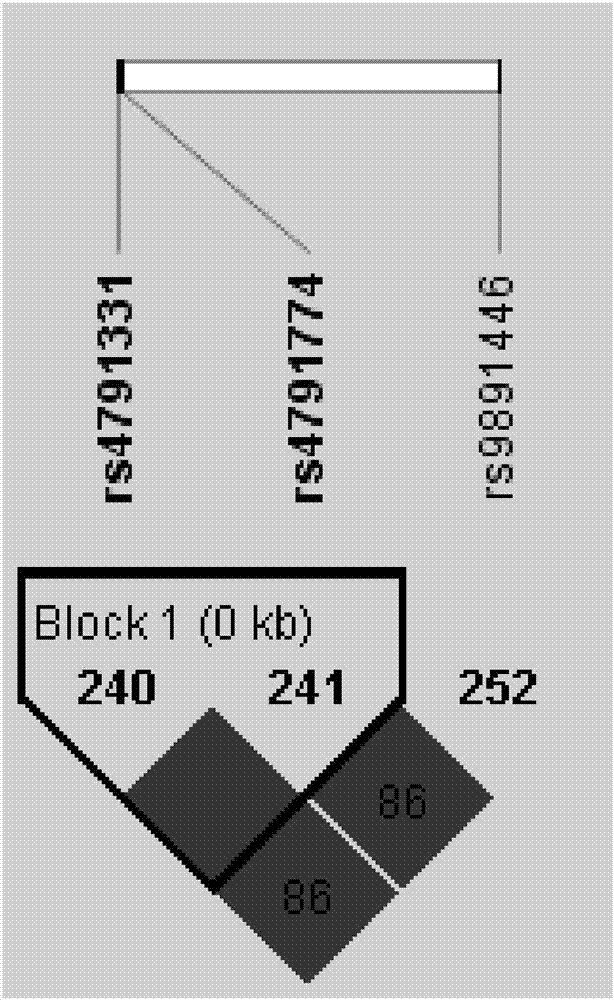
Susceptible SNP site of NTN1 gene and application thereof
InactiveCN106987635AAids in assessing genetic riskMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationIncomplete bilateral cleft lipRisk allele
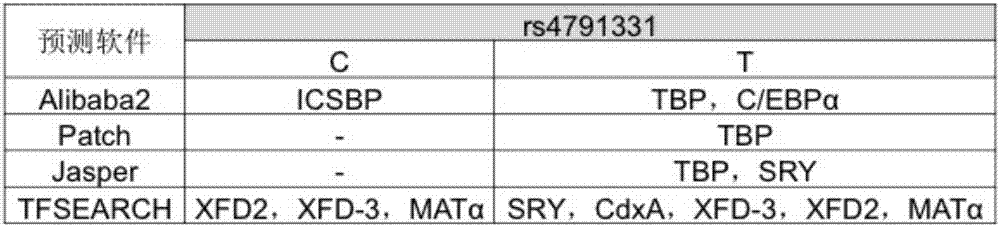
The patent is a susceptible SNP site of an NTN1 gene and an application thereof and discloses a genotype of an SNP marker rs4791331 related to assisted diagnosis of non-syndromic cleft lip and palate. Two alleles exist: T and C, wherein the allele T is a risk allele and an application of the allele T in a diagnostic kit for non-syndromic cleft lip and palate is developed. The invention is conductive to comprehensively evaluating the effect of heritable variation in genesis and development and lapse of NSCO of Chinese Han populations and has important meaning in guiding NSOC high risk groups to prevent and screen.
Owner:AFFILIATED STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL OF NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Connexin allele detection assays
InactiveUS20110111397A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAlleleGap Junction Proteins
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the detection and characterization of mutations associated with non-syndromic hearing impairment. More particularly, the present invention provides compositions, methods and kits for using invasive cleavage structure assays (e.g. the INVADER assay) to screen nucleic acid samples, e.g., from patients, for the presence of any one of a collection of mutations in the Connexin 26, or gap junction beta 2, gene associated with non-syndromic hearing loss.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Methods to prevent and treat autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing loss
ActiveUS9758781B2Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicineAutosomal dominant trait
The present invention provides in certain embodiments a method of treating autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing loss (ADNSHL) in a patient in need thereof comprising: (a) identifying a mutation in an ADNSHL-causing gene, (b) preparing a ADNSHL therapeutic miRNA, and (c) administering to the patient a pharmaceutical composition comprising the ADNSHL therapeutic miRNA and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Oligonucleotides to treat eye disease
The invention relates to the fields of medicine and immunology. In particular, it relates to novel antisense oligonucleotides that may be used in the treatment, prevention and / or delay of Usher Syndrome type II and / or USH2A-associated non syndromic retina degeneration, especially by skipping a pseudo exon (PE40) between exon 40 and 41 in the human USH2A gene.
Owner:PROQR THERAPEUTICS II BV
Non-syndromic cleft lip and palate genetic risk prediction model
PendingCN112397200AImprove forecastImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical automated diagnosisIncomplete bilateral cleft lipGenetic risk
The invention discloses a non-syndromic cleft lip and palate genetic risk prediction model, the formula of which is as follows: in the formula, k is the number of SNP sites; Gi represents the number of genetic risk alleles of the ith SNP site, namely 0, 1 and 2; [beta]i represents the weight of the i-th SNP site; SNP is rs139860270, rs1883873, rs139530062, rs144415105, rs55816698, rs139860270, rs6989548 and rs12952376. According to the genetic risk scoring model, the weak effects of the eight SNPs are superposed, so the prediction of the genetic risk of the non-syndromic cleft lip and palate is greatly improved. The invention provides a genetic risk scoring model for the first time to evaluate the risk leaving ability of non-syndromic cleft lip and palate. The model is high in accuracy, and a more comprehensive, accurate and individualized scientific basis can be provided for risk assessment and prevention and control of cleft lip and palate in China.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
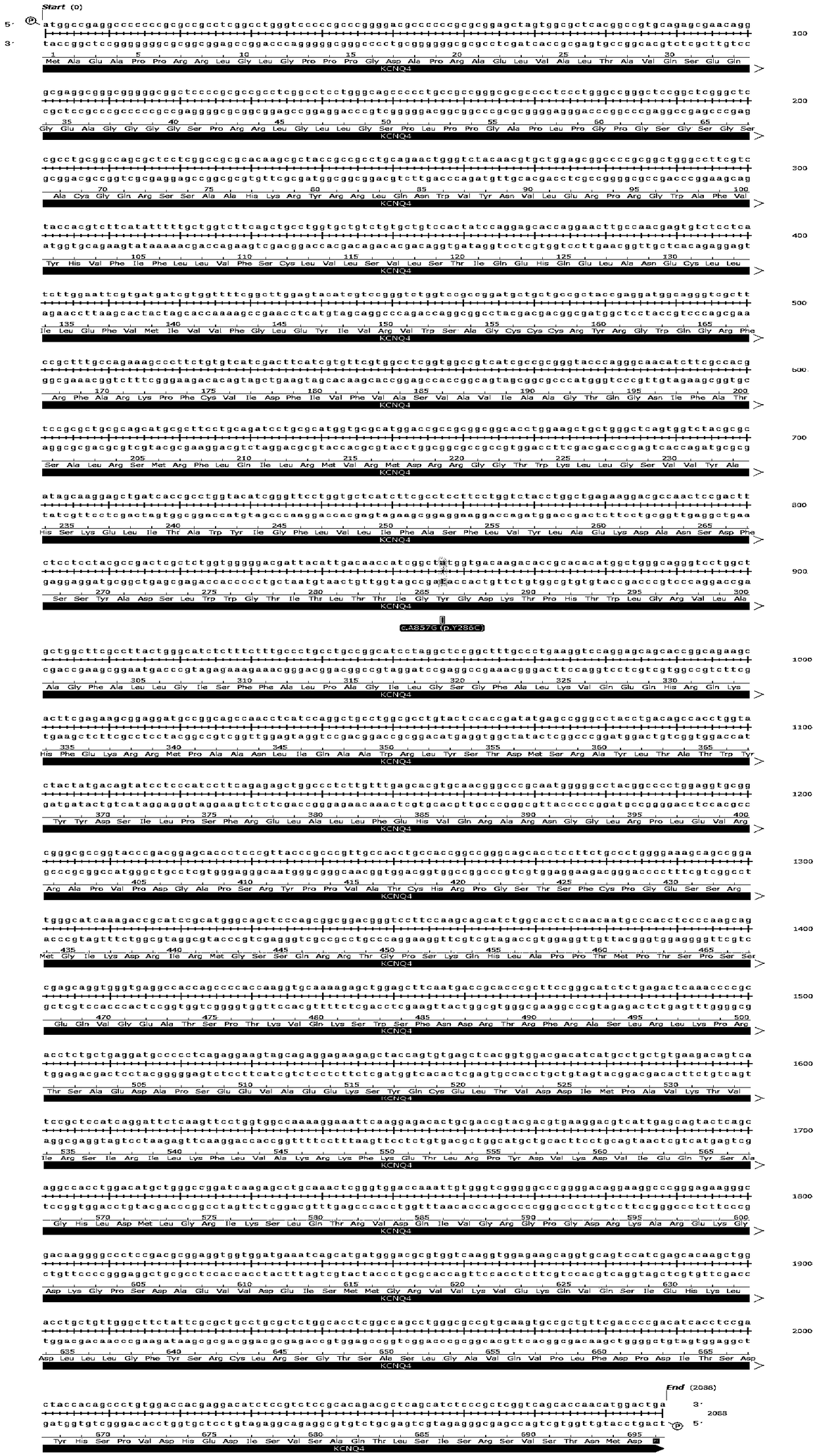
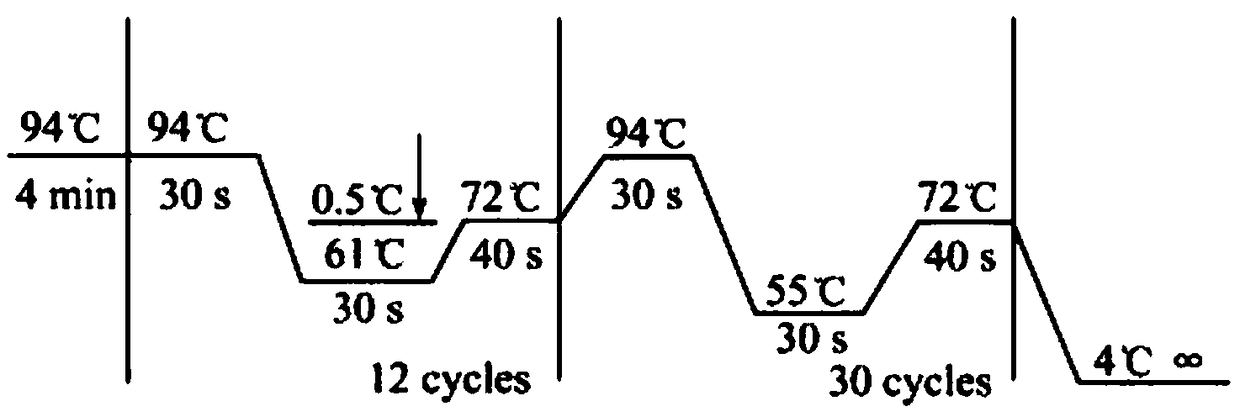
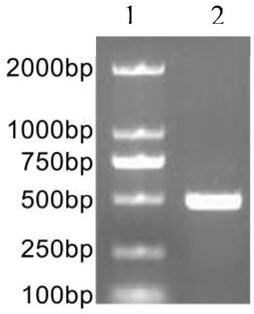
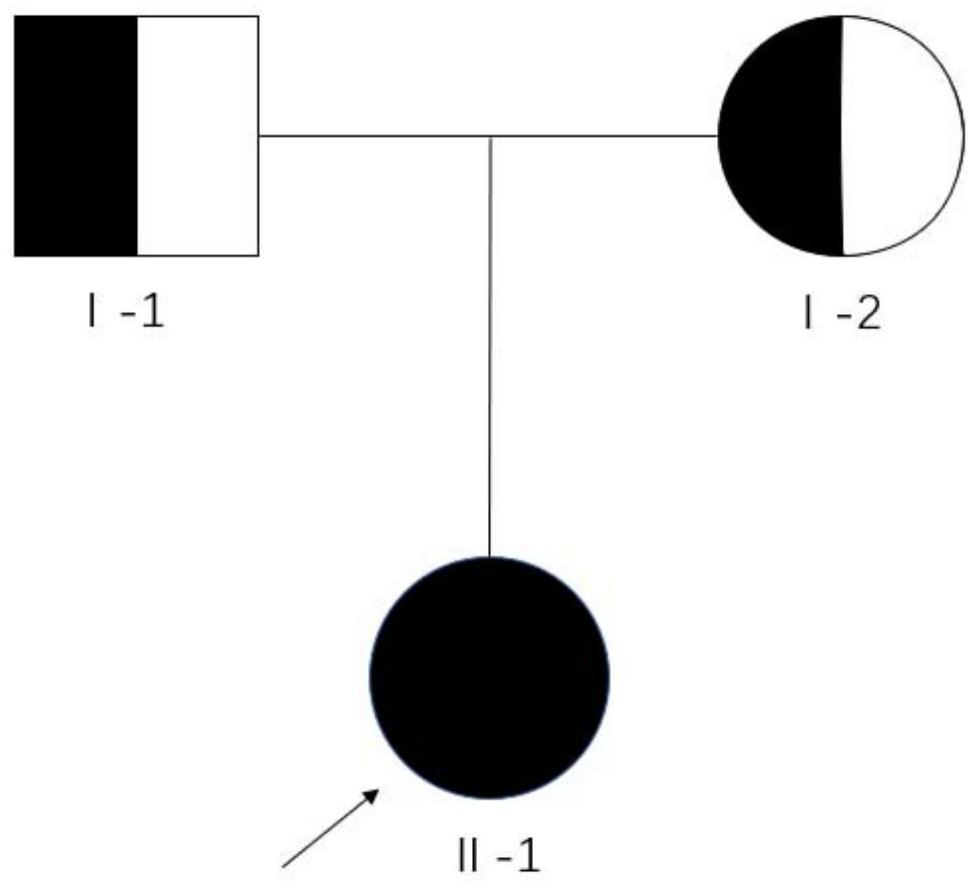
Non-syndromic autosomal dominant hereditary deafness pathogenic gene KCNQ4 mutation detection kit
InactiveCN109355375ATo determine the cause of non-syndromic autosomal dominant deafnessReduce birth rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMutation detectionKCNQ4
The invention discloses a non-syndromic autosomal dominant hereditary deafness pathogenic gene KCNQ4 mutation detection kit. The kit comprises a reagent for extracting DNA from a sample to be detected, a PCR reaction reagent for amplifying the sample DNA, and a reagent for sequencing a PCR amplification product; the PCR reaction reagent for amplifying the sample DNA comprises a PCR primer, and theinvented kit is used for detecting whether the c. A857G mutation exists in a patient KCNQ4 gene so as to diagnose the cause of non-syndromic autosomal dominant hereditary deafness. The kit is beneficial to clinically carrying out the KCNQ4 mutation screening work of the non-syndromic autosomal dominant hereditary deafness patients, and provides basis for the diagnosis of the non-syndromic autosomal dominant hereditary deafness patients.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
MYO15A gene mutant and application thereof
The invention provides an MYO15A gene mutant and an application thereof. The invention provides a gene mutation, and compared with a wild type MYO15A gene, the gene mutation provided by the invention has a c.2802_2812delTCCCACCCAAC mutation and / or a c.5681T>C mutation. The gene mutation is detectable, and whether a biological sample suffers from non-syndromic deafness or not can be effectively detected by detecting whether the gene mutation exists in the biological sample or not. By detecting the gene mutation, the detection and research of the hereditary hearing loss disease are expanded and improved, and a new detection site and a new detection method and approach are provided for the diagnosis or treatment of the disease.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD +1
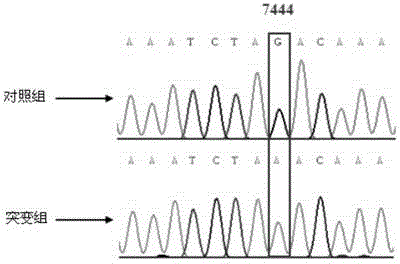
Non-syndromic hearing loss related mitochondria tRNA <Ser(UCN)> 7444G>A mutation detection method and application thereof
InactiveCN105624281APrecious genetic resourcesEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerSaliva sample
The invention a mitochondria tRNA <Ser(UCN)> gene 7444A mutation detection method. The method comprises the following steps: applying the phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol method to extract the DNA in a blood specimen, hairs with hair follicles, mouth mucosa doctor-bars or a saliva sample, and designing a forward primer Ser(UCN)F and a reverse primer Ser(UCN)R in front of and behind 7444; expanding a specific strip including 7444; then adopting XbaI for digestion of the specific strip, and performing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on a product obtained after digestion to identify whether 7444G>A mutation occurs or not. The method realizes result acquisition within several hours, ensures that one enzyme can only recognize a specific deoxynucleotide sequence, is accurate in result, facilitates building a perfect screening technology for non-syndromic hearing loss related mitochondria tRNA <Ser(UCN)> 7444G>A mutation, and can be popularized in clinical detection.
Owner:WENZHOU MAITUO BIOLOGICAL TECH
Non-syndromic deafness gene detection membrane strip and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer
PendingCN105695582AImprove accuracyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGenotypeGene carrier
The invention relates to a hybridized membrane strip capable of being used for medically diagnosing genetic non-syndromic deafness of people, in particular to a non-syndromic deafness gene detection membrane strip and a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer used for amplifying gene segments of a to-be-detected sample. The gene detection membrane strip comprises a substrate as well as normal contrast probes and specific mutation detection probes which are fixed on the substrate and totally comprises 20 mutation detection probes for detecting 20 gene mutation sites and 10 normal contrast probes. The gene detection membrane strip can detect 20 gene mutation sites in 20 mutation types, is used for detection, can directly diagnose the gene types of a to-be-detected person and has the advantages of being high in accuracy, high in specificity, capable of detecting a recessive gene carrier and the like.
Owner:东莞市儿科研究所 +1
Gene mutant and application thereof
The invention discloses nucleic acid related to non-syndromic hereditary hearing loss, a gene mutant and an application thereof. Compared with a wild type COL4A2 gene, the nucleic acid related to thenon-syndromic hereditary hearing loss has c.4951C>T mutation. The nucleic acid is a new related pathogenic nucleic acid of non-syndromic hereditary hearing loss, and by detecting whether the nucleic acid exists in a biological sample or not, whether the biological sample suffers from the non-syndromic hereditary hearing loss or not can be effectively detected. The discovery of the nucleic acid orpathogenic mutation site further expands and perfects the detection and research of the hereditary hearing loss disease, and provides a new detection site, a new detection method and a new detection way for the diagnosis or treatment of the disease.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
Methods of treating non-syndromic sensorineural hearing loss
Provided herein are compositions that include at least two different nucleic acid vectors, where each of the at least two different vectors includes a coding sequence that encodes a different portion of a stereocilin protein, and the use of these compositions to treat non-syndromic sensorineural hearing loss in a subject.
Owner:アコーオスインコーポレイテッド
Mutation within the connexin 26 gene responsible for prelingual non-syndromic deafness and method of detection
A purified polynucleotide having a chain of nucleotides corresponding to a mutated sequence, which in a wild form encodes a polypeptide implicated in hereditary sensory defect, wherein said mutated purified polynucleotide presents a mutation responsible for prelingual non-syndromic deafness selected from the group consisting of a specific deletion of at least one nucleotide.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
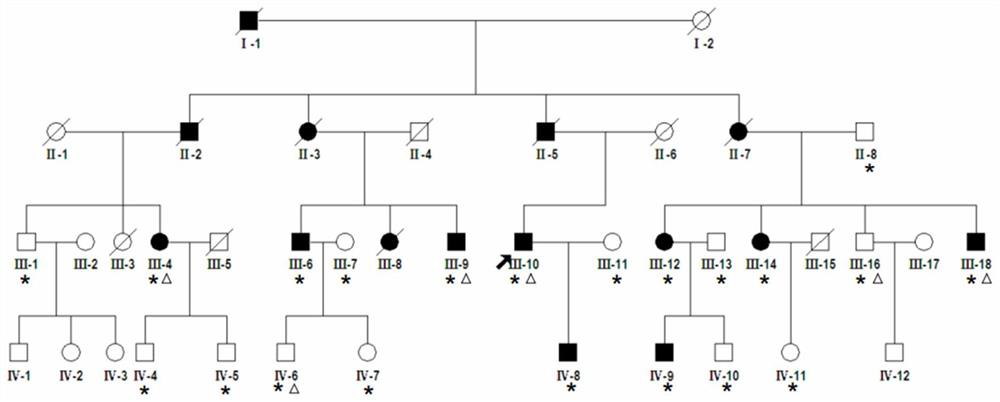
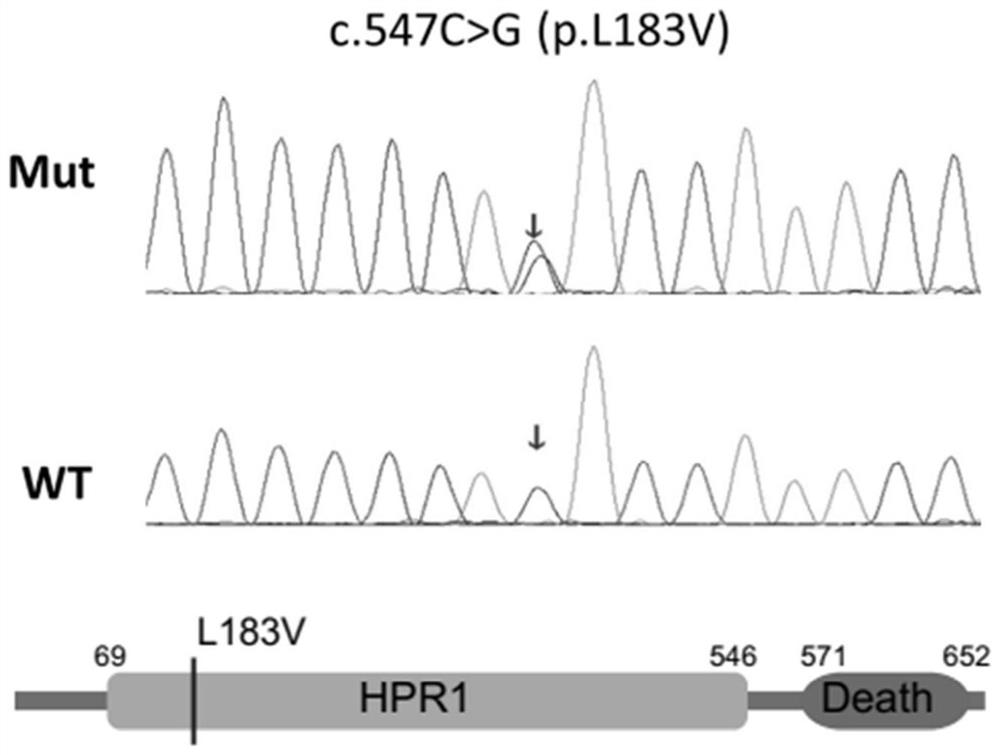
hpr1 gene mutant and its application in the preparation of deafness diagnostic reagents
ActiveCN109852685BGood clinical application valueMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPost translationalNucleotide
The invention discloses a gene mutant of HPR1 and its relationship with autosomal dominant non-syndromic deafness. The mutation site related to deafness is the 547th nucleotide C mutation in the coding region of HPR1 gene to G, It leads to the mutation of amino acid 183 from L to V after translation (c.547C>G, p.L183V). The invention discloses the application of HPR1 gene mutant in the preparation of deafness diagnostic reagents and a diagnostic kit for deafness detection. In the present invention, through exome sequencing analysis and animal experiment verification on deafness family members, it is found that HPR1 has a significant correlation with the occurrence of deafness, and is an important inducement for the occurrence of hereditary deafness, and can be used for early diagnosis of clinical deafness patients. And provide a theoretical basis for early intervention and treatment of deafness.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Antisense oligonucleotides for the treatment of eye disease
ActiveUS20190256847A1Significant positive effectLow amountOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderMedicineImmunologic function
The invention relates to the fields of medicine and immunology. In particular, it relates to novel antisense oligonucleotides (AONs) that may be used in the treatment, prevention and / or delay of Usher syndrome type II and / or USH2A-associated non syndromic retina degeneration.
Owner:PROQR THERAPEUTICS II BV
Mutant N4BP2 gene related to non-syndromic cleft lip and palate and application thereof
PendingCN112458104AHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementIncomplete bilateral cleft lipPrenatal diagnosis
The invention discloses a mutant N4BP2 gene related to non-syndromic cleft lip and palate and application thereof. Compared with an un-mutant N4BP2 Gene with the gene bank accession number of NM_018177.6, the mutant N4BP2 contains respectively contains a non-frameshift deletion mutation site 4: 40133481-40133489delAAGATATTT at a 13 exon, and a missense mutation site 4: 40123905T which is greater than G and a missense mutation site 4: 40122958C which is greater than T at a 9 exon,. The mutant N4BP2 gene can be used for preparing a diagnostic kit for detecting non-syndromic cleft lip andpalate diseases. The discovery of the mutation sites can be used for performing prenatal and postnatal care guidance on family offspring, and can be used as a screening site for carrier screening andprenatal diagnosis screening of the non-syndromic cleft lip and palate diseases for the prenatal and postnatal care guidance of groups.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
A low-frequency SNV marker associated with sporadic non-syndromic CHD and its application
ActiveCN104263724BIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHeart diseaseGenetic engineering
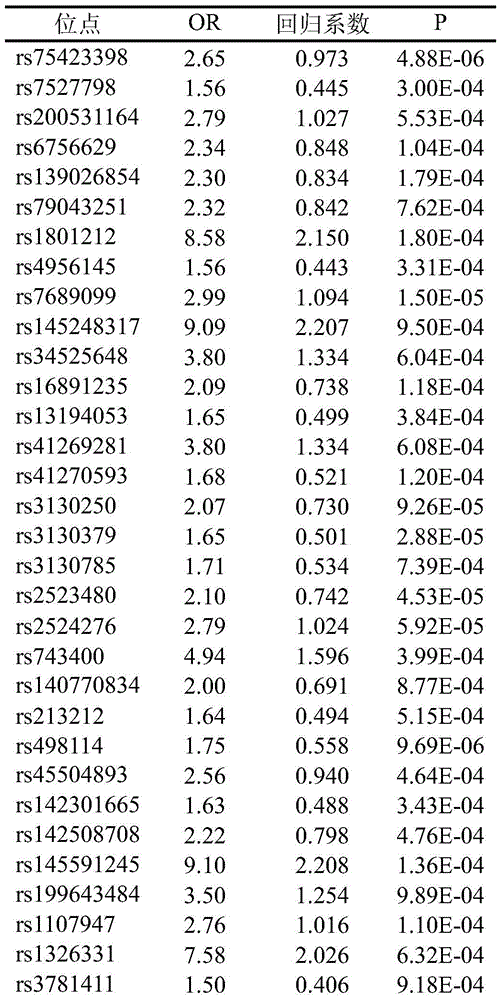
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering and reproductive medicine and discloses a low frequency SNV marker associated with sporadic non-syndromic CHD (congenital heart disease) auxiliary diagnosis and an application of the low frequency SNV marker. The marker is a combination of 41 low frequency SNVs such as rs75423398, rs7527798, rs200531164, rs6756629, rs139026854, rs79043251, rs1801212, rs4956145, rs7689099, rs145248317, rs34525648, rs16891235, rs13194053, rs41269281, rs41270593, rs3130250 and rs3130379. The marker can be used for preparing a sporadic non-syndromic CHD auxiliary diagnosis kit.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Mutation within the connexin 26 gene responsible for prelingual non-syndromic deafness and method of detection
InactiveUS7258975B2Length be determineSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementWild typePolynucleotide
A purified polynucleotide having a chain of nucleotides corresponding to a mutated sequence, which in wildtype form encodes a polypeptide implicated in hereditary sensory defect, wherein said mutated purified polynucleotide presents a mutation responsible for prelingual non-syndromic deafness selected from the group consisting of a specific deletion of at least one nucleotide.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com