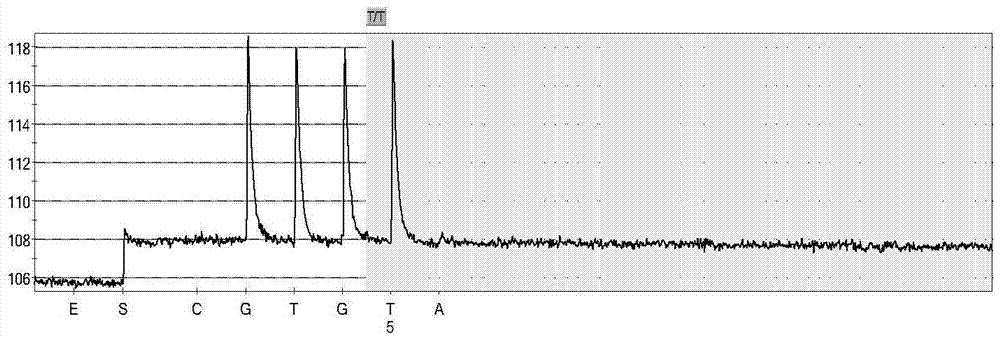
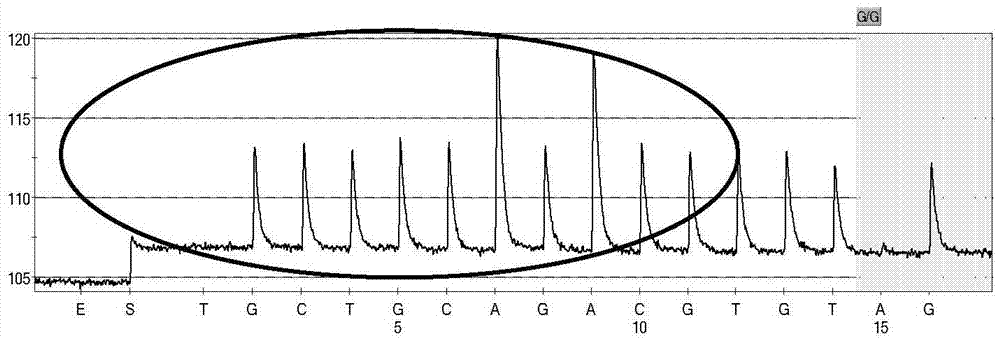
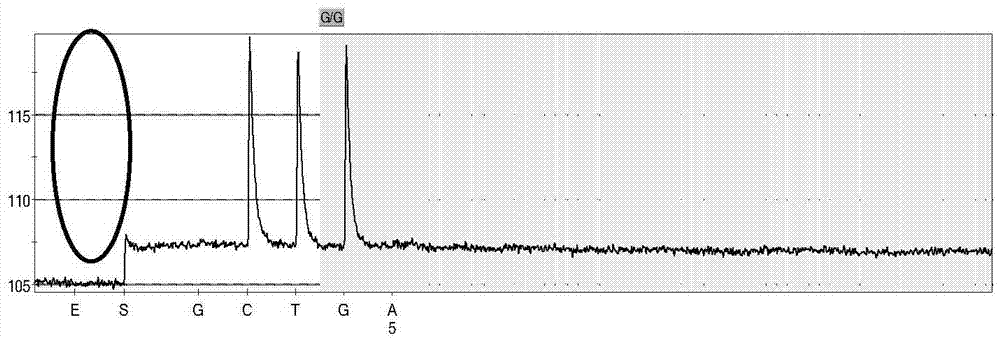
Non-syndromic deafness gene polymorphism detecting kit and application thereof
A technology for deafness genes and syndromes, which is applied in the determination/testing of microorganisms, DNA/RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of long detection time, acceptance, and expensive detection costs, and achieve simple operation, low cost, The effect of small sample size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Example 1: Reagents.
[0054] (1) DNA extraction reagents:
[0055] Purchased from QIAGEN Company.
[0056] (2) PCR reaction solution:
[0057] Amplification primers SEQIDNO: 1-10, synthesized by Shanghai Handsome Biotechnology Co., Ltd.;
[0058] PCRBuffer: purchased from Fermentas, USA;
[0059] MgCl 2 : purchased from the U.S. Fermentas company;
[0060] dNTPs: purchased from Fermentas, USA;
[0061] TaqDNA polymerase: purchased from Fermentas, USA.
[0062] (3) Reagent for single-strand purification:
[0063] 75% (v / v) ethanol solution: purchased from Hangzhou Changzheng Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.;
[0064] 0.2mol / LNaOH: purchased from Shanghai Shisi Hewei Chemical Co., Ltd.;
[0065] 10mM Tris-Acetate (pH7.6): Tris-base was purchased from Sigma, USA, and anhydrous acetic acid was purchased from Hangzhou Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.;
[0066] Binding buffer: 10mM Tris-HCl (Tris-base was purchased from Sigma, USA; hydrochloric acid was purchased from Hangzhou...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Embodiment 2: detection method.
[0075] Instruments: Bio-RadS1000PCR instrument, BeckmanMicrofuge22R desktop microrefrigerated centrifuge, Beijing Liuyi agarose gel electrophoresis instrument, Shanghai Peiqing gel imaging system, QIAGENPyroMarkQ96ID sequencer.
[0076] (1) Extract the DNA in the whole blood sample, the steps are as follows:
[0077] a. The preparation and inspection of reagent materials before the experiment are as follows: check the shelf life of the kit and ensure that ethanol has been added to WashBuffer 1 and 2, and tick the corresponding mark on the bottle; isopropanol (if not available, absolute ethanol can be used instead) and 75% ethanol; 1.5mL Eppendorf tubes and various pipette tips within the expiry date of autoclaving.
[0078] b. Take out the EDTA anticoagulant tube containing whole blood from the refrigerator at 4°C, and mix it upside down several times;
[0079] c. Pipette 900uL of cell lysate into a sterilized 1.5mL Eppendorf tube;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com