Primer in use for in vitro diagnosing GJB2 mutation of deaf gene of autosomal recessive inheritance in non-syndrome
An autosomal recessive and syndromic technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of high cost, complicated operation, expensive equipment, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the chance of birth, simple operation steps and improving work efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 Identification of non-syndromic autosomal recessive deafness gene GJB2 gene mutation by ApaI digestion method
[0043] 1. Test samples
[0044] A total of 998 children with non-syndromic deafness were collected from deaf schools across China. The coding region of the GJB2 gene was amplified by PCR, and the known 233-235 sites were preliminarily analyzed by enzyme digestion. At the same time, 204 normal hearing children were taken as the control group. Forward and reverse sequencing was performed on children with 233-235delC heterozygous mutations detected by enzyme digestion, and 40-50 cases were selected from various places for mutation detection in the entire coding region of the GJB2 gene. At the same time, 100 cases of normal hearing children were selected for control detection.
[0045] 2. Primer Design
[0046] Use the GenetoolLite program to assist in the design of improved primers. According to the published mitochondrial gene Cambridge sequence (Cam...
Embodiment 2
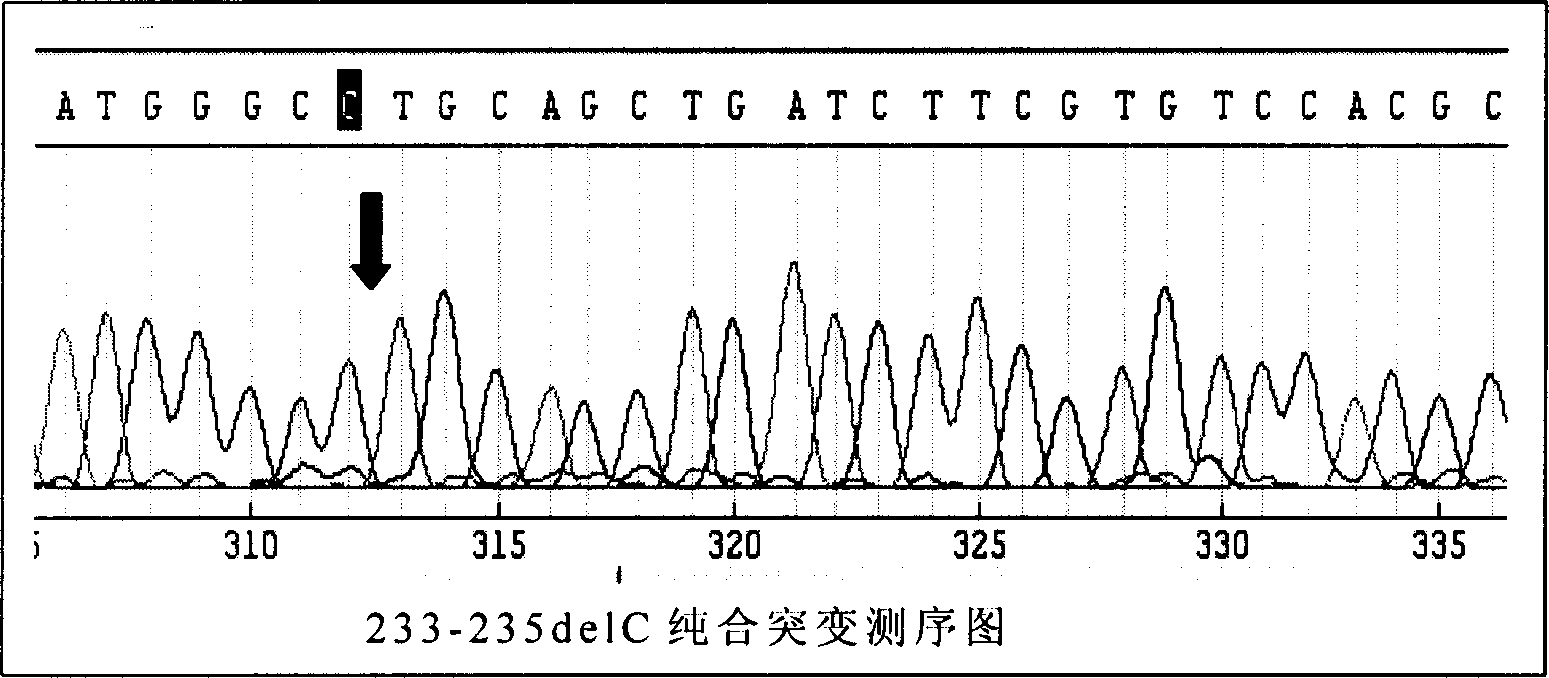
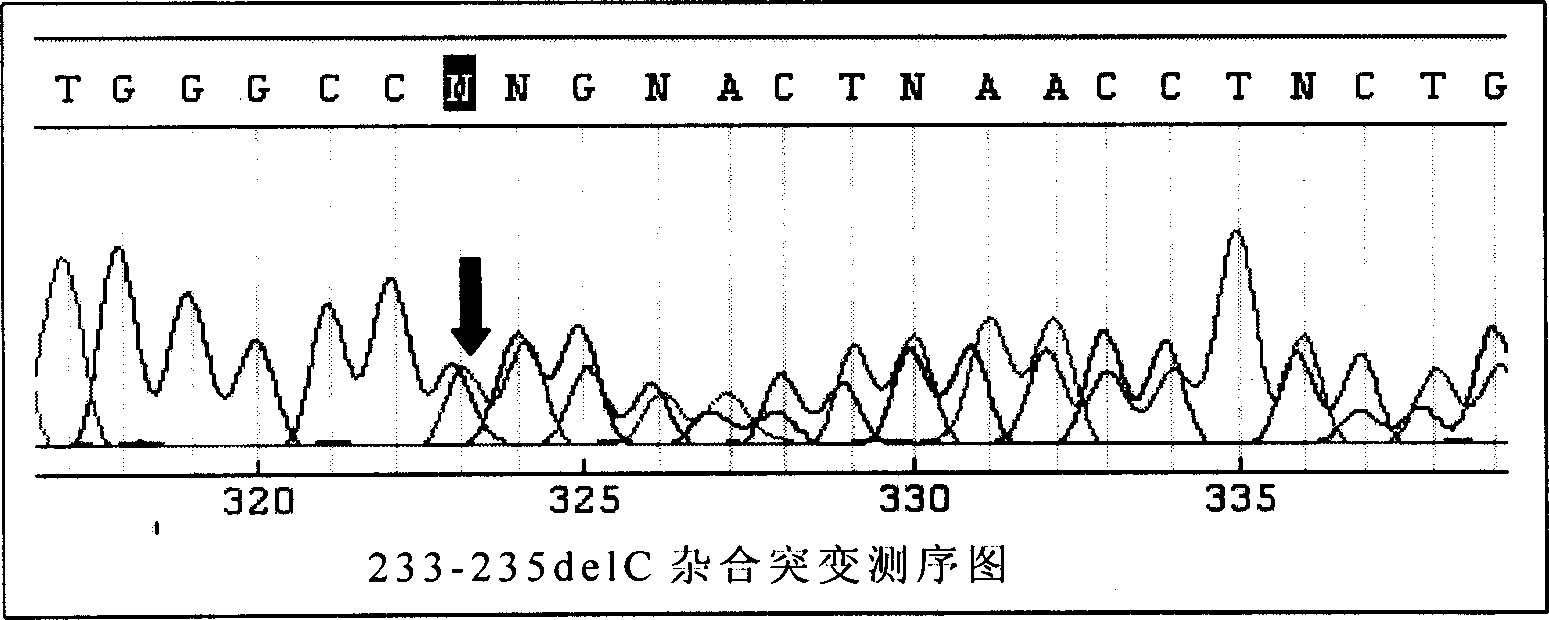
[0070] Example 2. The reliability of the direct sequencing method to test the ApaI enzyme digestion method
[0071] Steps 1-4 are the same as Steps 1-4 in Example 1, except that the root blood DNA is extracted from the sample. The following is the procedure for direct sequencing, in which the aforementioned kits are used.
[0072] 5. PCR product purification 1
[0073] The PCR amplification product of the tested sample was purified in the first step according to the following conditions:
[0074] Add 0.5 times the volume of sodium acetate (PH=5.2), 2.5 times the volume of 100% alcohol, leave it at room temperature for 20 minutes, centrifuge at 5700 rpm for 20 minutes, and remove the supernatant;
[0075] Add 200ul of 75% alcohol, centrifuge at 5700 rpm for 15 minutes, remove the supernatant, and dry at 95°C for 1 minute;
[0076] Add 20ul double distilled water to dissolve; after the DNA content is determined by gel electrophoresis, it is diluted to 5ng / ul.
[0077] 6. Seq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com