hpr1 gene mutant and its application in the preparation of deafness diagnostic reagents
A technology of diagnostic reagents and detection reagents, which is applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., and can solve the problems of delayed disease, aggravated disease, difficult detection and diagnosis of hearing loss, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Example 1. Verification of the correlation between HPR1 and deafness diseases
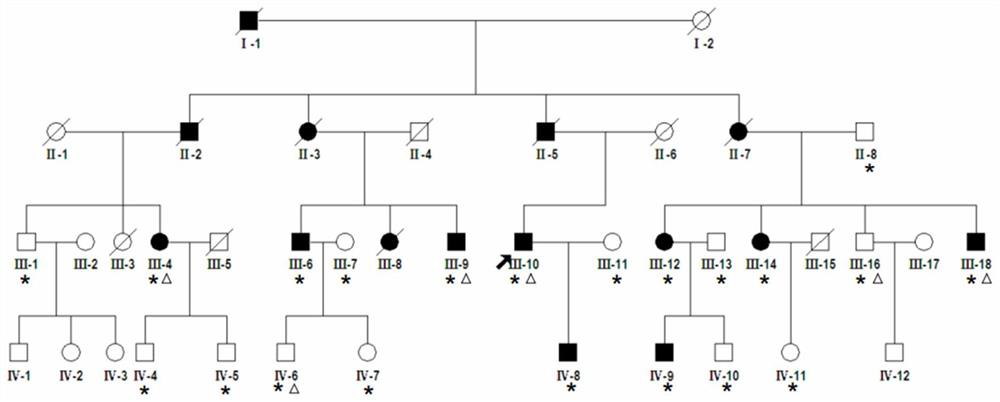
[0051] The first step, sample preparation: clinically discover a family of acquired deafness (such as figure 1 Among them, 15 patients with acquired deafness have been diagnosed, and the peripheral blood samples of the deaf patients in the family (experimental group, 9 people) and non-deaf individuals (18 people) were extracted respectively, and the total RNA of each sample was extracted by TRIzol method, and the Store at -80°C until use.
[0052] The second step, sample exome sequencing and pathogenic mutation gene analysis: use whole exome sequencing technology to sequence and analyze each RNA sample. The specific contents include: using the Illumina TruSeq Exome Enrichment Kit to capture the sequences of exons and surrounding introns of 20,794 expressed genes contained in each sample, and to determine the sequences of microRNA and other non-coding genes. The measurement instrument is HiS...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 Preparation of the kit of the present invention
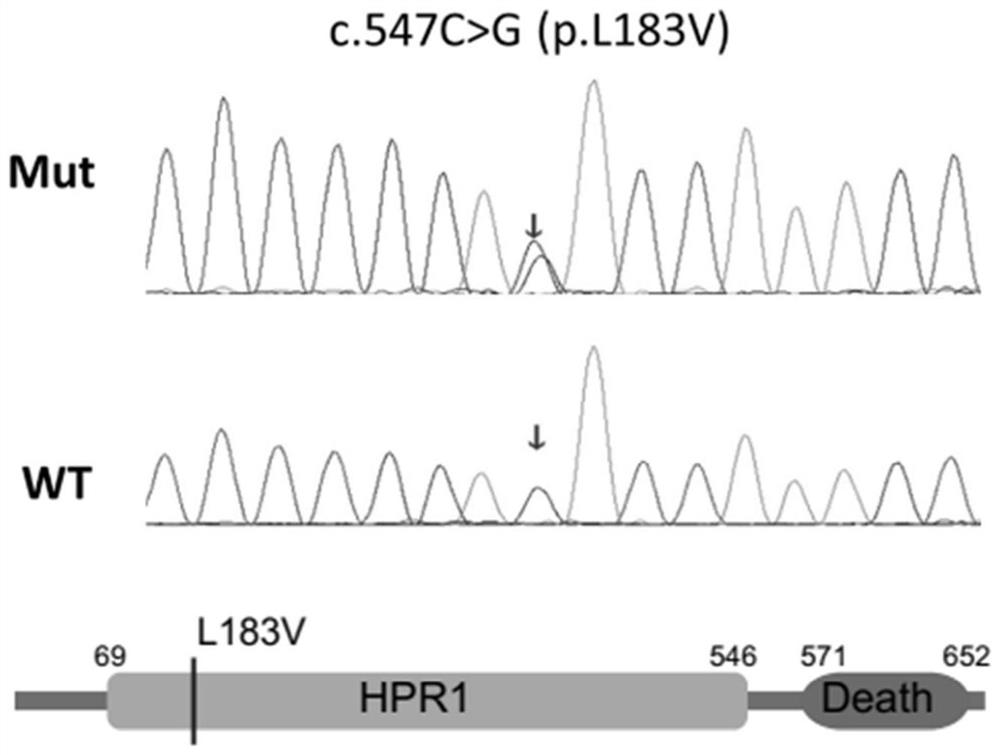
[0056] The sequence of the HPR1 mutant is shown in SEQ ID: NO: 2. Its specific PCR upstream and downstream primers were designed by Primer 5, and the primers were synthesized by Invitrogen. The purity was PAGE grade. The synthesized primers were dissolved in RNase free H2O. The concentration is 10 μM.
[0057] Prepare a kit that includes the following components:
[0058] (a) Extraction system:
[0059] 1) Trizol reagent, 2 tubes, 2000μL / tube;
[0060] 2) Chloroform, 1 tube, 500 μL / tube;
[0061] 3) Absolute ethanol, 1 tube, 8000μL / tube;
[0062] 4) RNase free ddH 2 O, 2 tubes, 2000μL / tube;
[0063] 5) Isopropanol, 8000μL / tube;
[0064] (b) Reverse transcription system:
[0065] 1) Total RNA reverse transcription primer Oligo dT, 1 tube, concentration: 50 μM, 50 μL / tube;
[0066] 2) Reverse transcriptase (200U / μL) 50μL;
[0067] 3) 50μL of dNTP Mixture (10mM each);
[0068] 4) 50μL of reverse transcr...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Example 3 Sequence detection of HPR1 gene in peripheral blood cells of deaf patients
[0077] After adding TRIzol to the peripheral blood cells, it was left at room temperature for 10 min to fully lyse the sample. Add 200 μl of chloroform to each 1 ml of TRIzol, shake vigorously and mix, and leave at room temperature for 3-5 minutes to allow natural phase separation. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 15 min at 4°C. The sample will separate into three layers: the yellow organic phase, the middle layer, and the colorless aqueous phase. The RNA is mainly in the aqueous phase. Transfer the aqueous phase to a new tube. An equal volume of ice-cold isopropanol was added to the supernatant and left at room temperature for 15 min. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm at 4°C for 10 min, discard the supernatant, and precipitate the RNA at the bottom of the tube. Add 1 ml of 75% ethanol to the RNA pellet, and gently shake the centrifuge tube to suspend the pellet. Add 1 ml of 75% ethanol per 1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com