Falling-prevention ultra thin stone composite board
a composite board and stone technology, applied in the direction of covering/lining, construction, building components, etc., can solve the problems of bottlenecking the application of ultra thin, stone veneer would be easily falling off the light base board,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
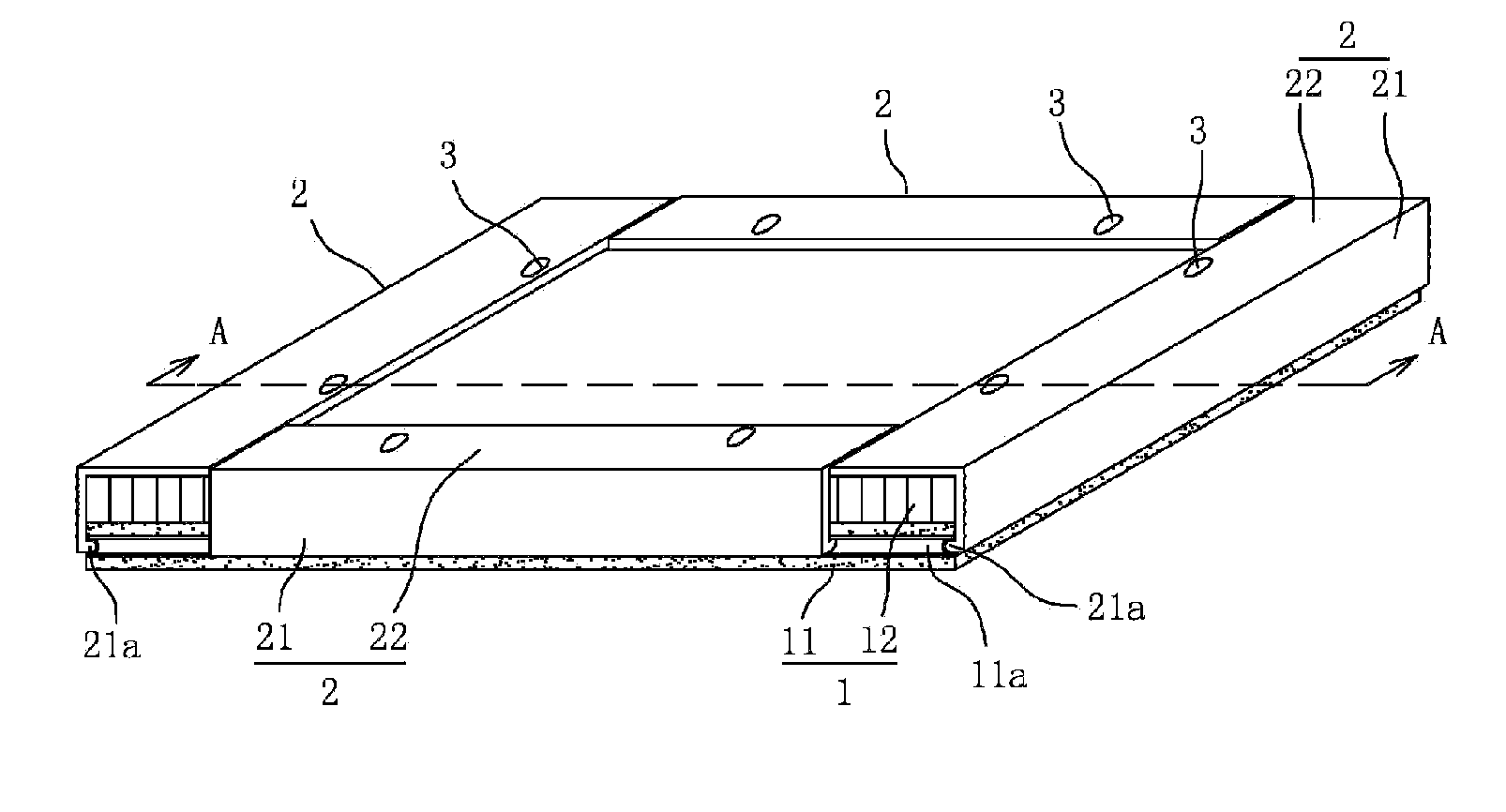
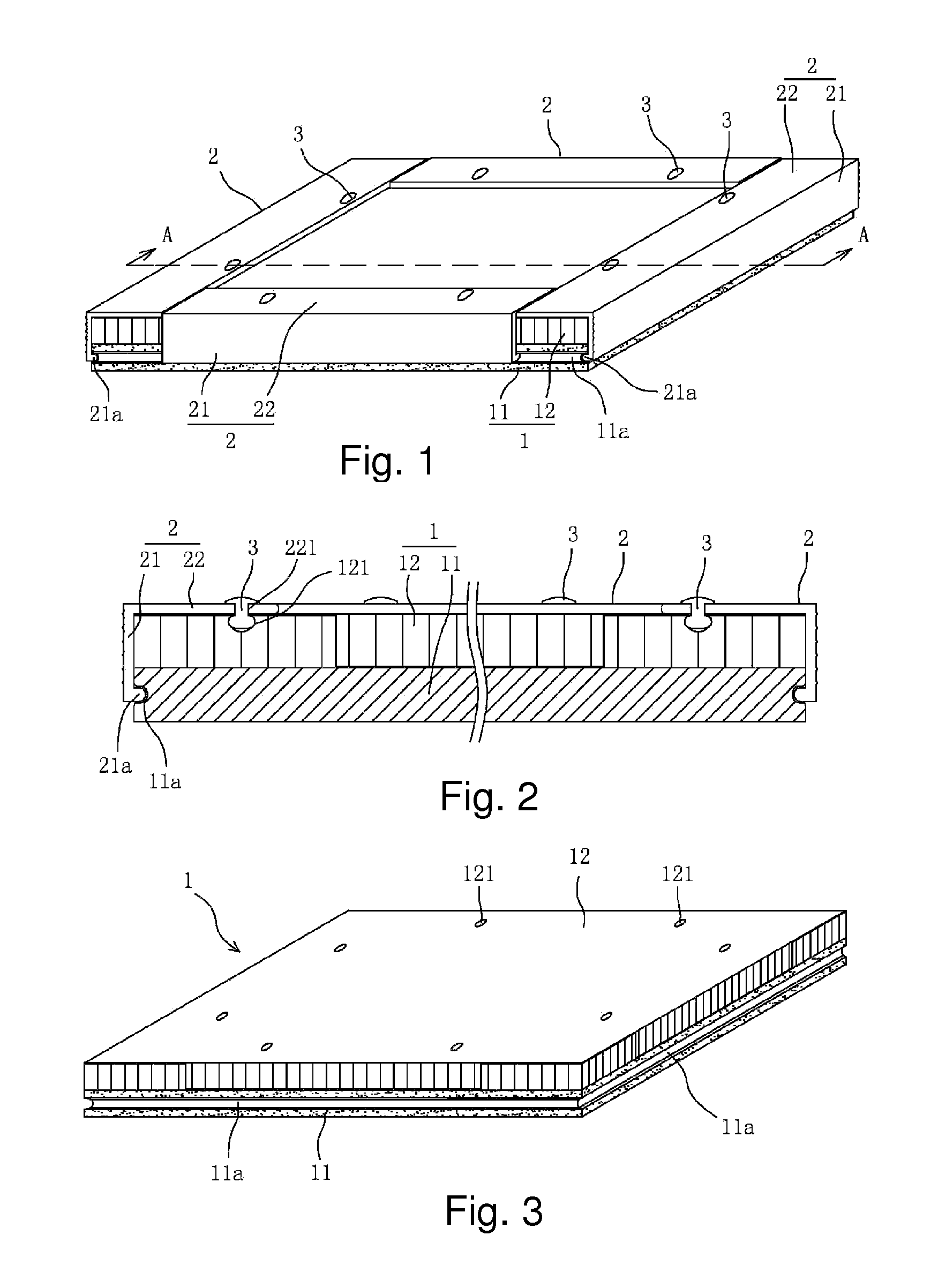
[0023]Refer to FIG. 1, a falling-prevention ultra thin stone composite board is provided with a composite board body 1 and four connecting batten 2, the composite board body is composed of ultra thin stone veneer 11 and a light base board 12 sticking to the rear surface of the stone veneer 11, and the four connecting batten 2 separately fasten the four bottom edges of the composite body 1. The thickness of the stone veneer 11 ranges from 12 mm to 5 mm, and the light base board 12 is aluminum beehive plate. But no limitation to it, the light base board 12 can apply with other existing light hard materials.
[0024]Refer to FIG. 1 to FIG. 3, the central of the side surface of the stone veneer 11 has anchorage groove 11a in a loop. It applies high speed diamond microtome to cut the anchorage groove 11a, which settles the problem of easy fragile, defective edge, and irregularities in thickness of the ultra thin stone veneer when cutting the grooves.
[0025]Refer to FIG. 1, FIG. 2 and FIG. 4,...
embodiment 2
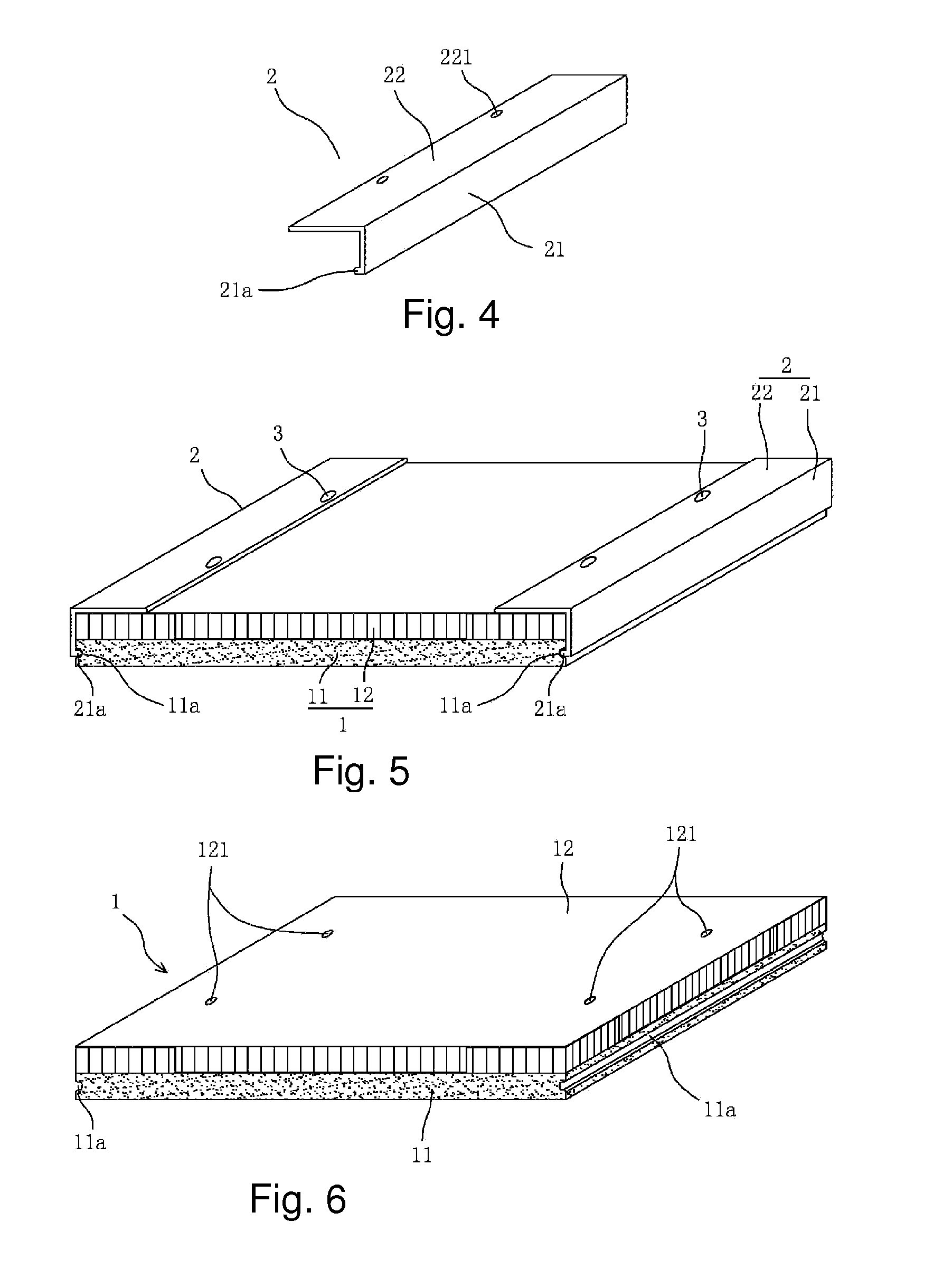
[0026]Refer to FIG. 5 and FIG. 6, the differences between the embodiment 1 and the embodiment 2 are:
[0027]Only a pair of the opposite side surface of the stone veneer 11 has anchorage groove 11a, the two bottom edges of the composite board body 1 in correspond with the anchorage groove 11a have connecting batten 2, the length of the connecting batten 2 is the same with the length of the edge of the composite board body 1, another two bottom edges have not connecting batten. With the connecting batten 2 in FIG. 5, the stone veneer 11 and the light base board 12 are fixed together. The rest structure is the same as that of the embodiment 1, which will not be detail described here.
embodiment 3
The Differences Between the Third Embodiment and the First Embodiment are
[0028]Refer to FIG. 7 to FIG. 10, the thickness of the stone veneer 11 of the composite board body 1 range from 12 mm to 3 mm. The side surfaces of the stone veneer 11 have not anchorage groove, and the front plate of the connecting batten have not stone hook, but the central of two sides of the front plate 21 of the connecting batten which is laid against the bottom edge of the stone veneer has punch 21b, the side surface of the stone veneer 11 has connecting blind hole 11b in correspond with the punch 21b; falling-prevention thread nail 5 insert to the punch 21b and the connecting blind hole 11b, the end of the thread nail 5 and the inner of the connecting blind hole 11b are fixed together by adhesive matter, so that the front plate 21 of the connecting batten 2 and the stone veneer are fixed together. With the mechanical power of the connecting batten 2, the stone veneer 11 and the light base board are fixed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com