Internet protocol multicast on passive optical networks
a technology of optical network and network protocol, applied in the field of internet protocol multicast on passive optical network, can solve the problems of reducing the effectiveness of such as streaming video, and inefficient for some types of media distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
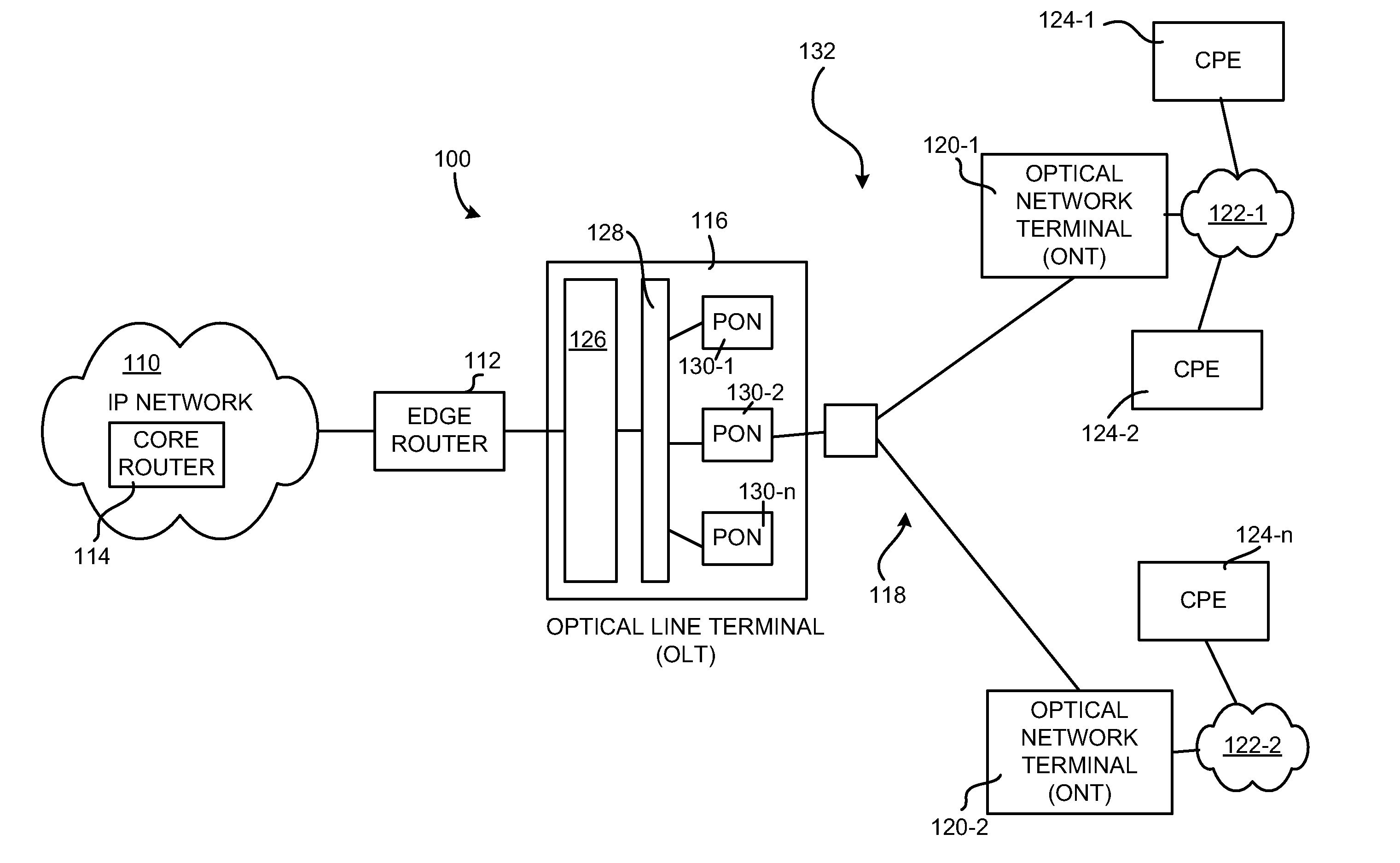
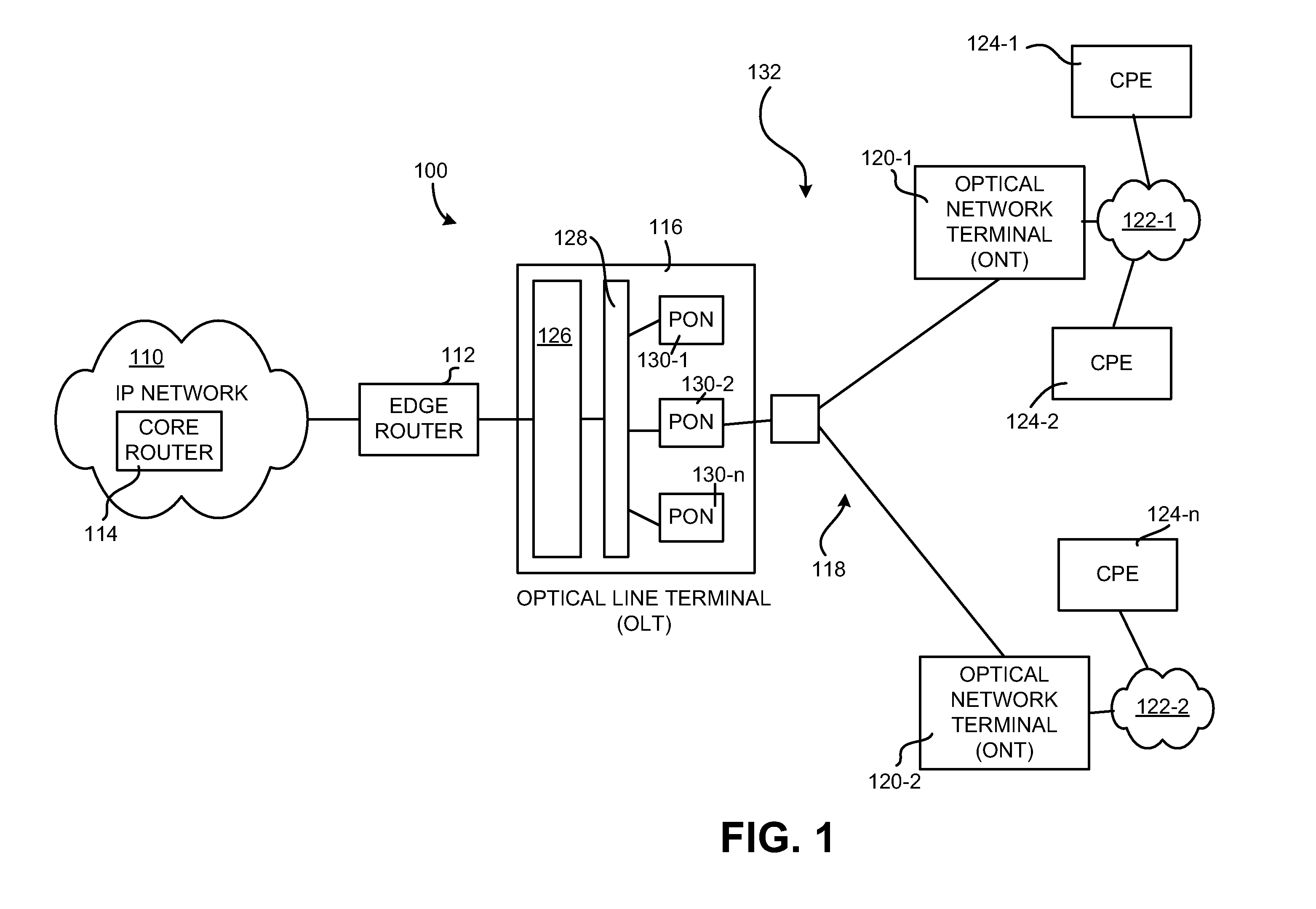
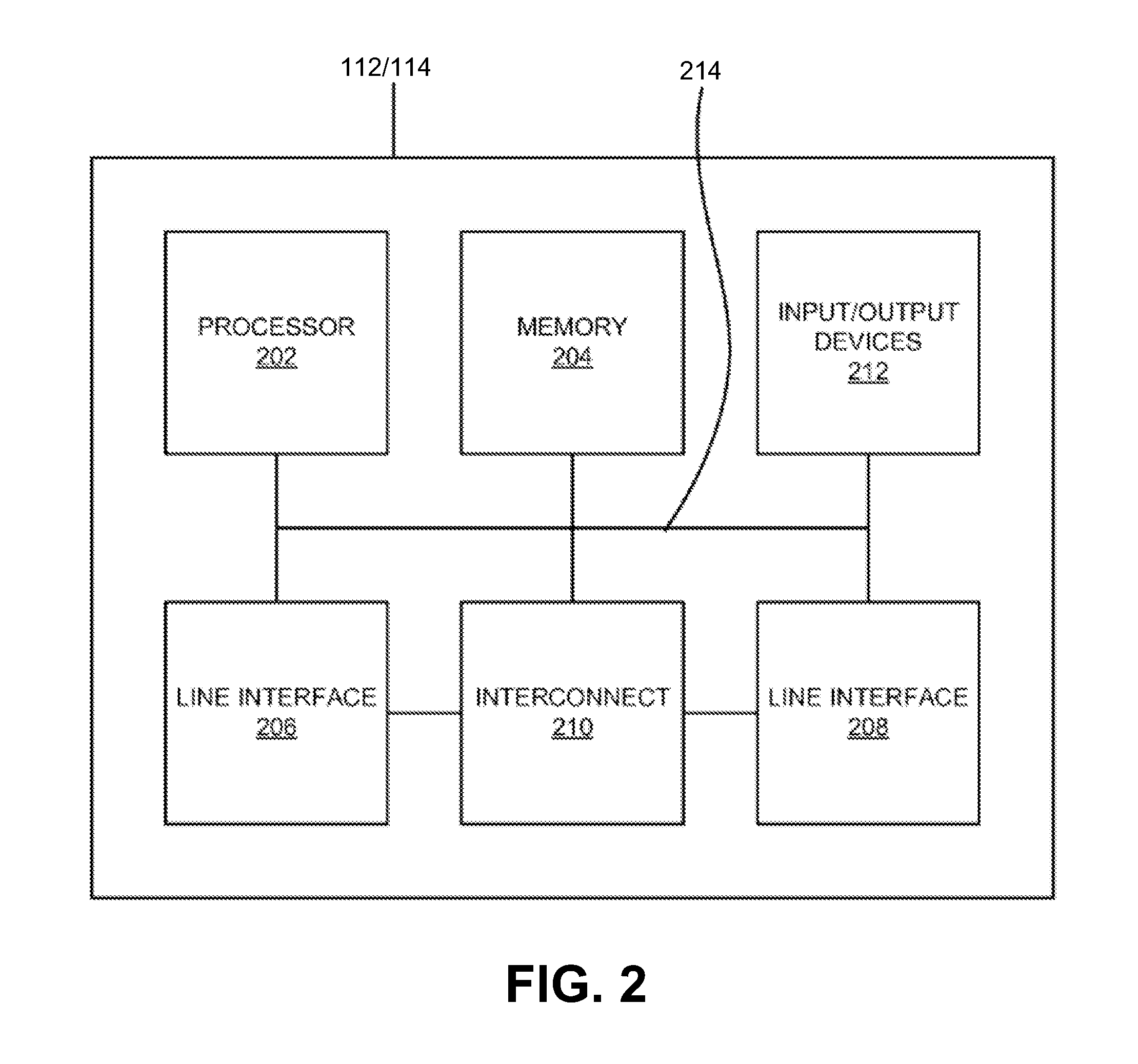
[0011]The following detailed description of exemplary embodiments refers to the accompanying drawings. The same reference numbers in different drawings may identify the same or similar elements. Also, the following detailed description does not limit the invention.
[0012]Implementations described herein provide for IP multicast on ATM-based PON systems without requiring the increased cost and latency introduced by segmentation and reassembly (SAR) of ATM cells and IGMP snooping processing. In one embodiment, an IP router upstream from the PON, upon receipt of an IGMP join (or leave) request message, captures address information associated with a requesting client. Logic on the IP router transmits (e.g., via a communication / control channel) the captured address information to the optical line terminal (OLT) to populate (or modify) one or more multicast state tables in the OLT, thereby indicating where multicast traffic is to be delivered.
[0013]Subsequently, the OLT may identify addres...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com