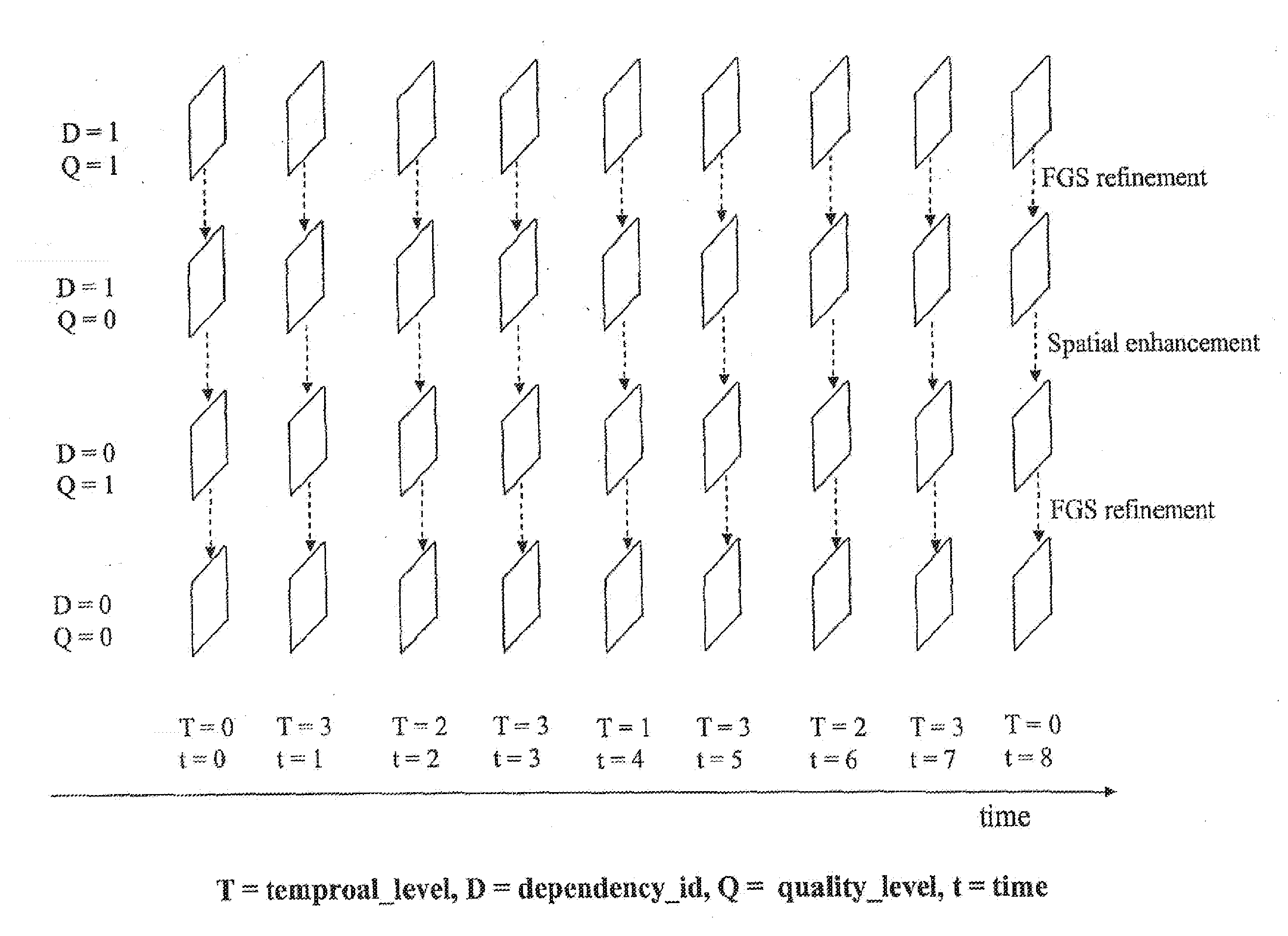
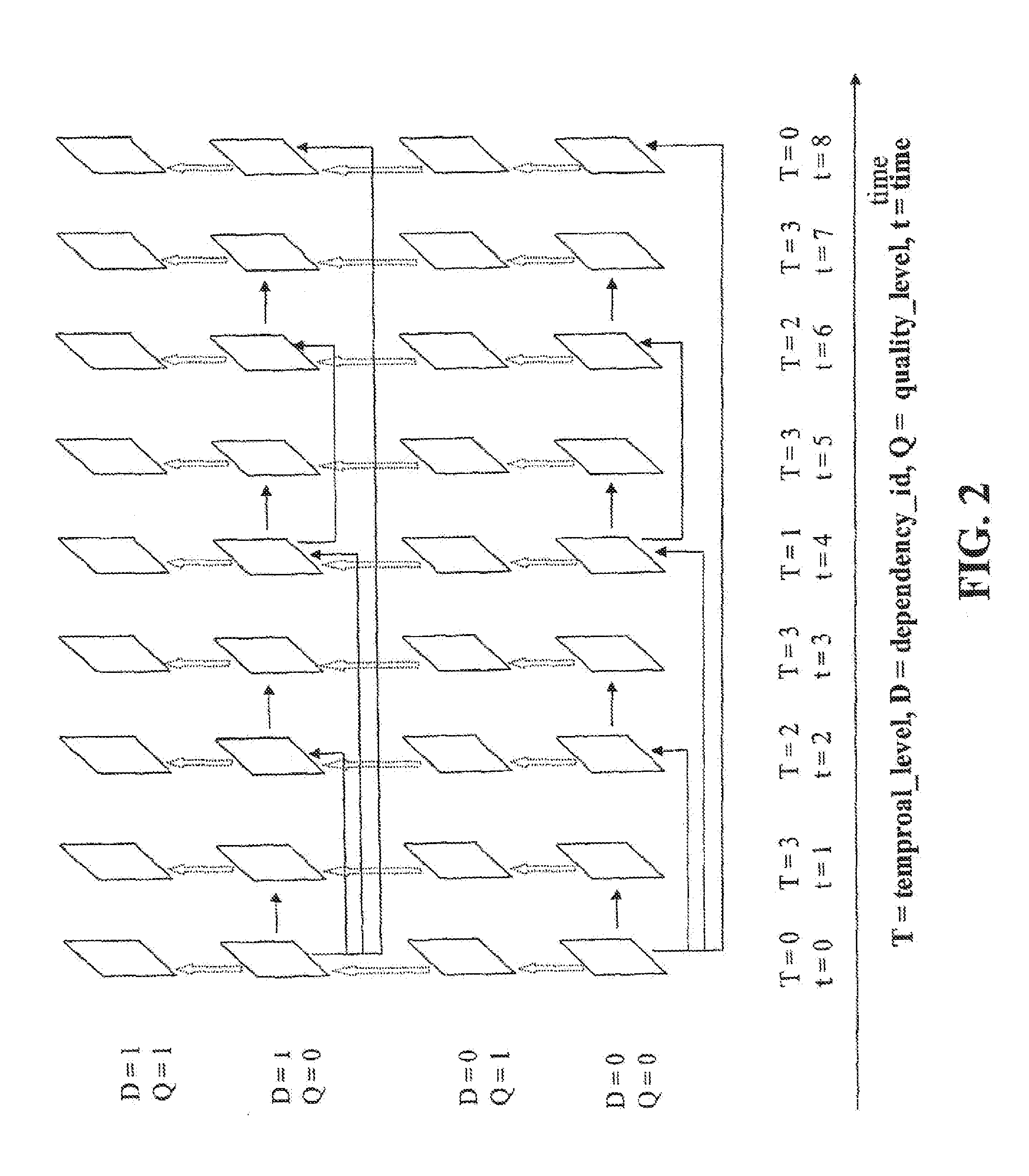
System and method for efficient scalable stream adaptation
a stream adaptation and scalable technology, applied in the field of media encoding, decoding, storage and transmission, can solve the problems of reducing coding efficiency, increasing transmission bandwidth, and using multiple streams at the same time, and achieves significant computational and implementation burden, simple and efficient low-to-high layer switching, and significant computational
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025]With reference to FIG. 6, a typical multimedia streaming system is described, which is one system for applying the procedure of the present invention.
[0026]A multimedia data streaming system typically comprises one or more multimedia sources 100, such as a video camera and a microphone, or video image or computer graphic files stored in a memory carrier. Raw data obtained from the different multimedia sources 100 is combined into a multimedia file in an encoder 102, which can also be referred to as an editing unit. The raw data arriving from the one or more multimedia sources 100 is first captured using capturing means 104 included in the encoder 102, which capturing means can be typically implemented as different interface cards, driver software, or application software controlling the function of a card. For example, video data may be captured using a video capture card and the associated software. The output of the capturing means 104 is typically either an uncompressed or ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com