Method and apparatus for a hierarchical synchronization barrier in a multi-node system
a synchronization barrier and hierarchical technology, applied in the field of computer architecture, can solve the problems of long synchronization time, energy-inefficient system, power consumption,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
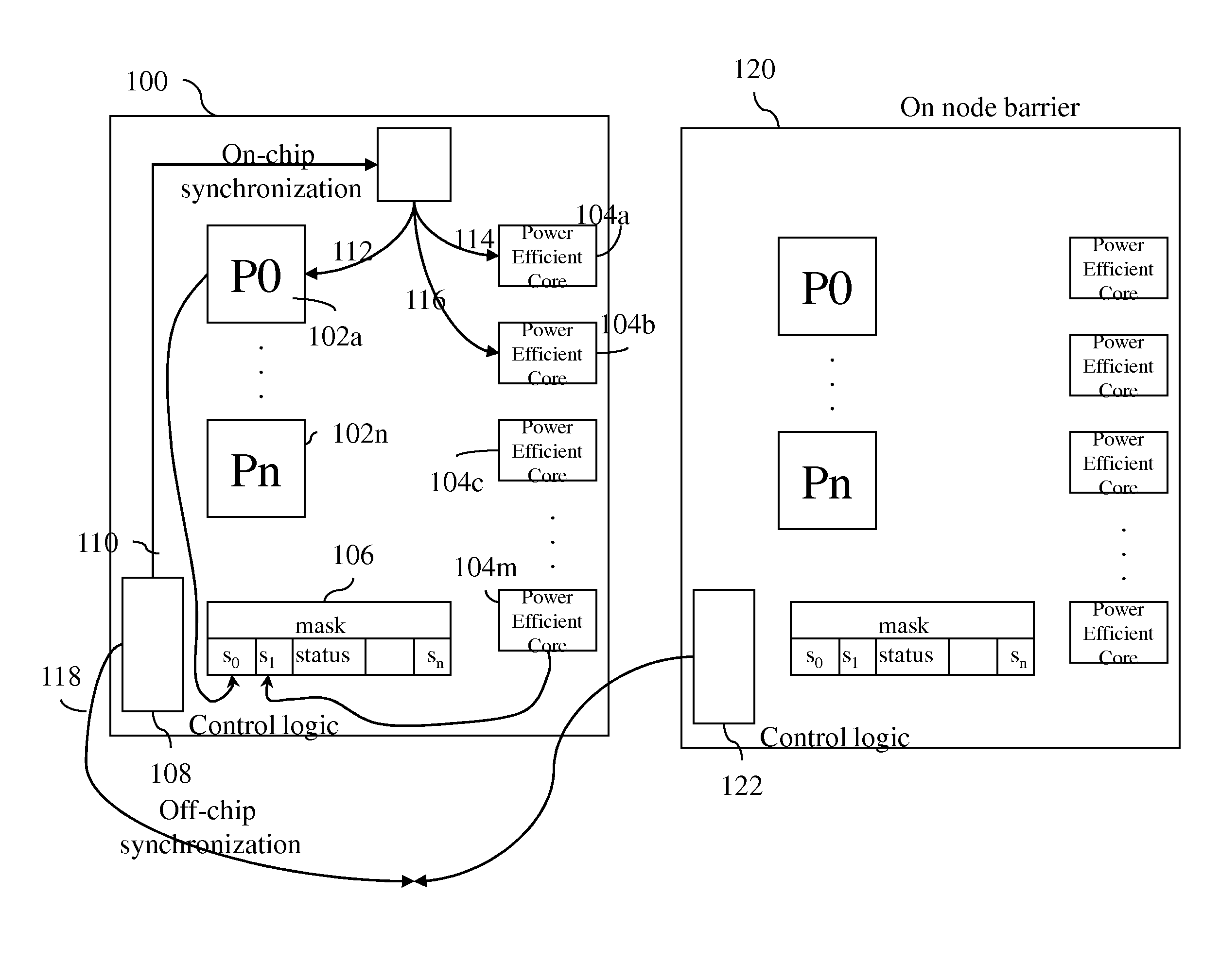
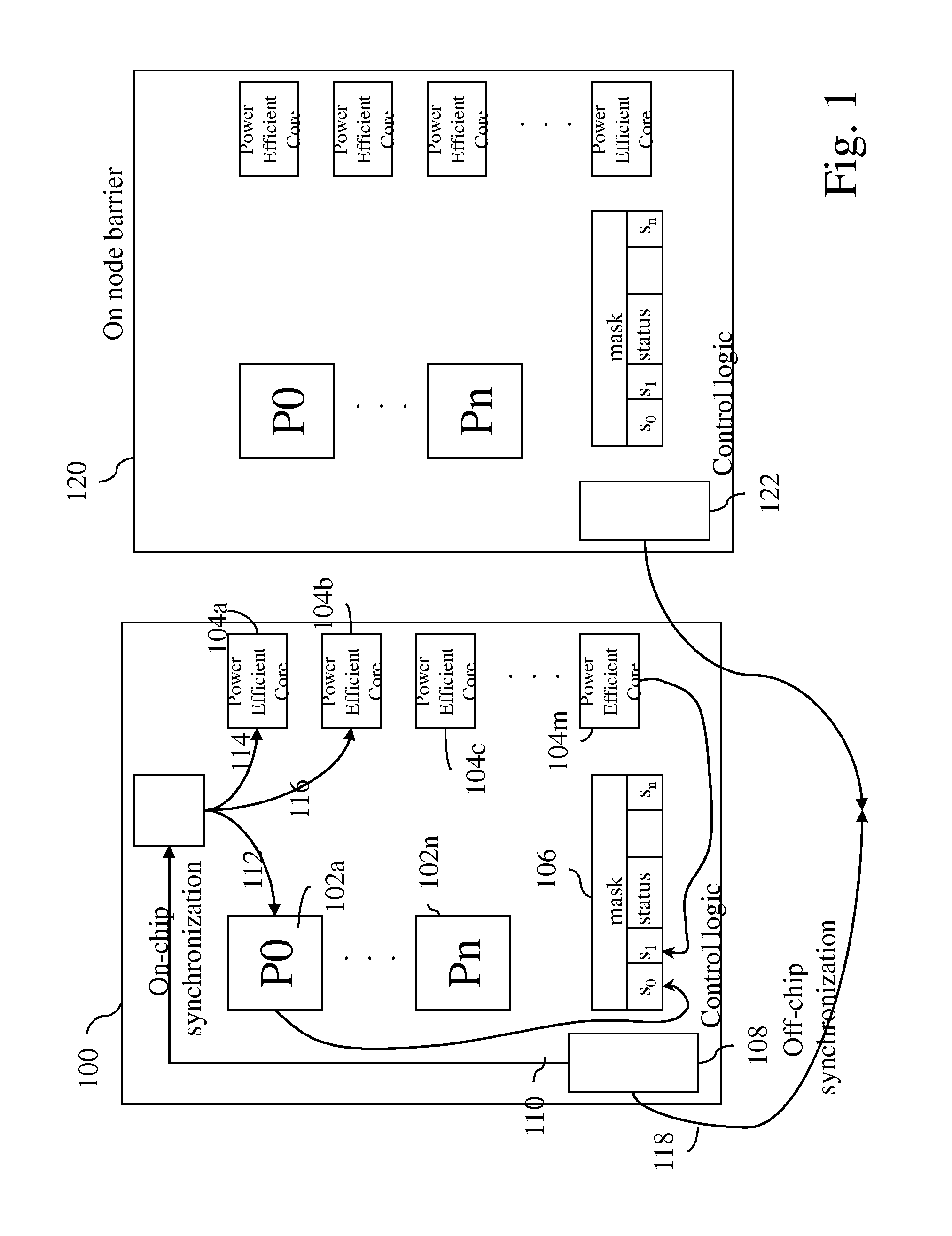
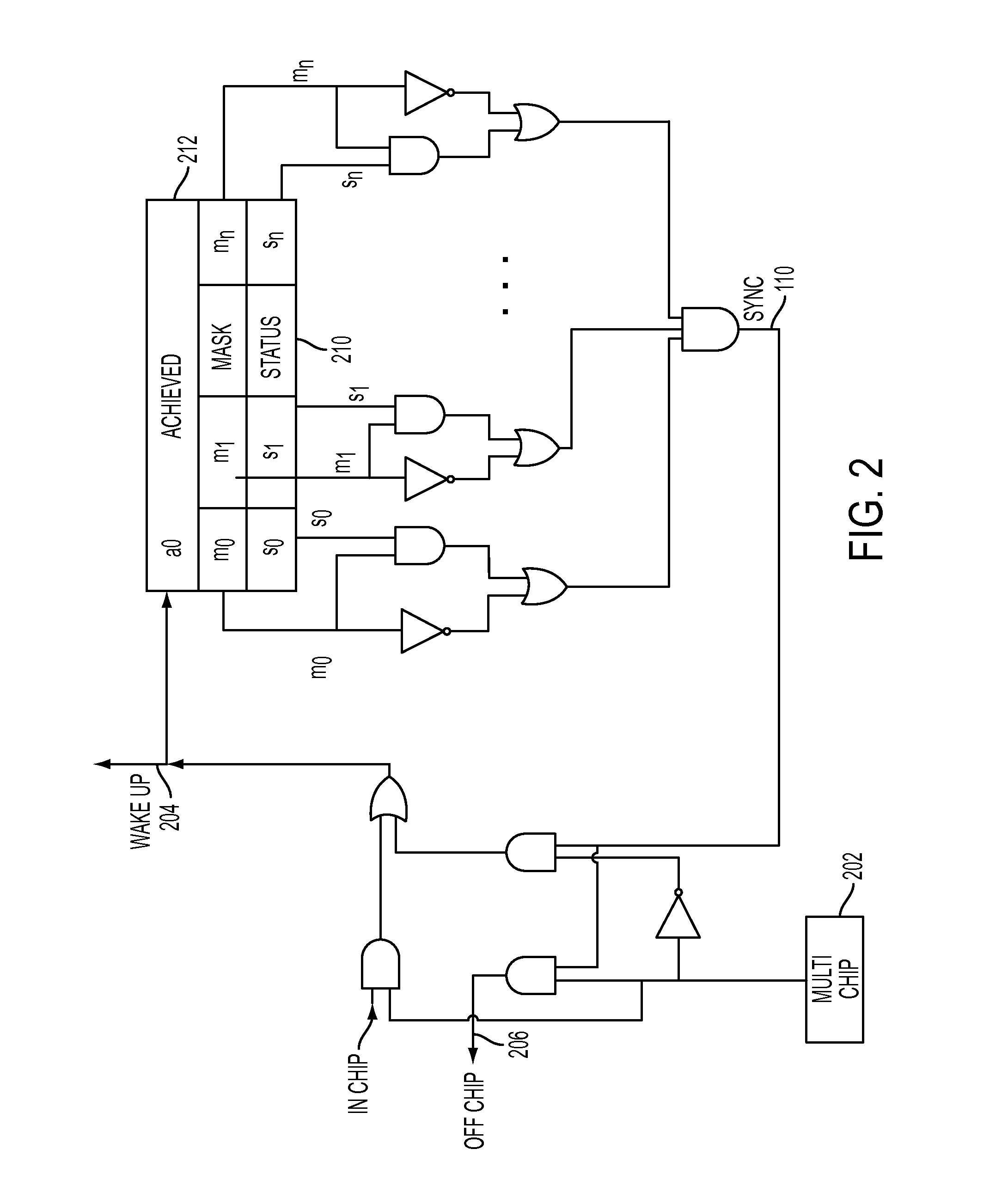
[0020]The present disclosure in one aspect describes a low-latency, low-overhead synchronization method which uses a symmetric software implementation for synchronizing nodes in a multiprocessor system. In the present disclosure, a node or chip refers to entity that is plugged into a socket and contains among other things computing cores. On a node are cores, or processor cores. On some architecture a core has one hardware thread; on other architecture the core may be an SMT (Symmetric Multi-Threaded) core and contain 2, 4, or possibly more hardware threads. Software threads get executed on top of the hardware thread. For the purposes of this document, thread is used to refer to hardware thread. In the event software thread is meant, the entire expression is written. A multiprocessor chip is referred to as a node. In another embodiment, a part of a chip can be referred to as a node, and a single chip can contain multiple nodes (or nodelets), which act as points of communication in t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com