Spacer and Associated Method for Laying Tile
a spacer and associated technology, applied in the field of tiles and slabs, can solve the problems of unattractive and undesirable tile surface, unfavorable tile surface, and inability to properly align adjacent tiles along a working surface during installation, and achieve the effect of facilitating additional alignment and leveling of tiles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
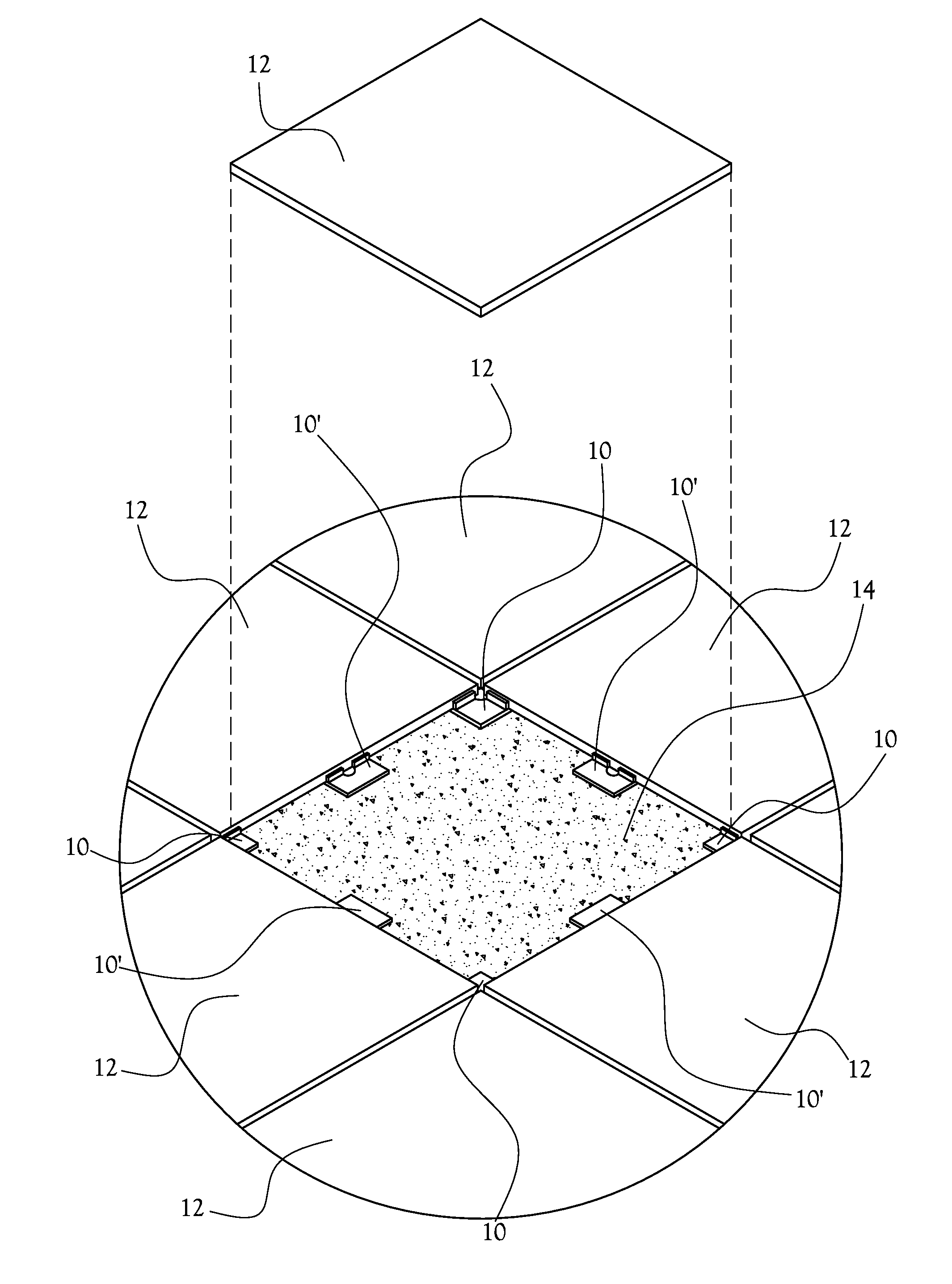
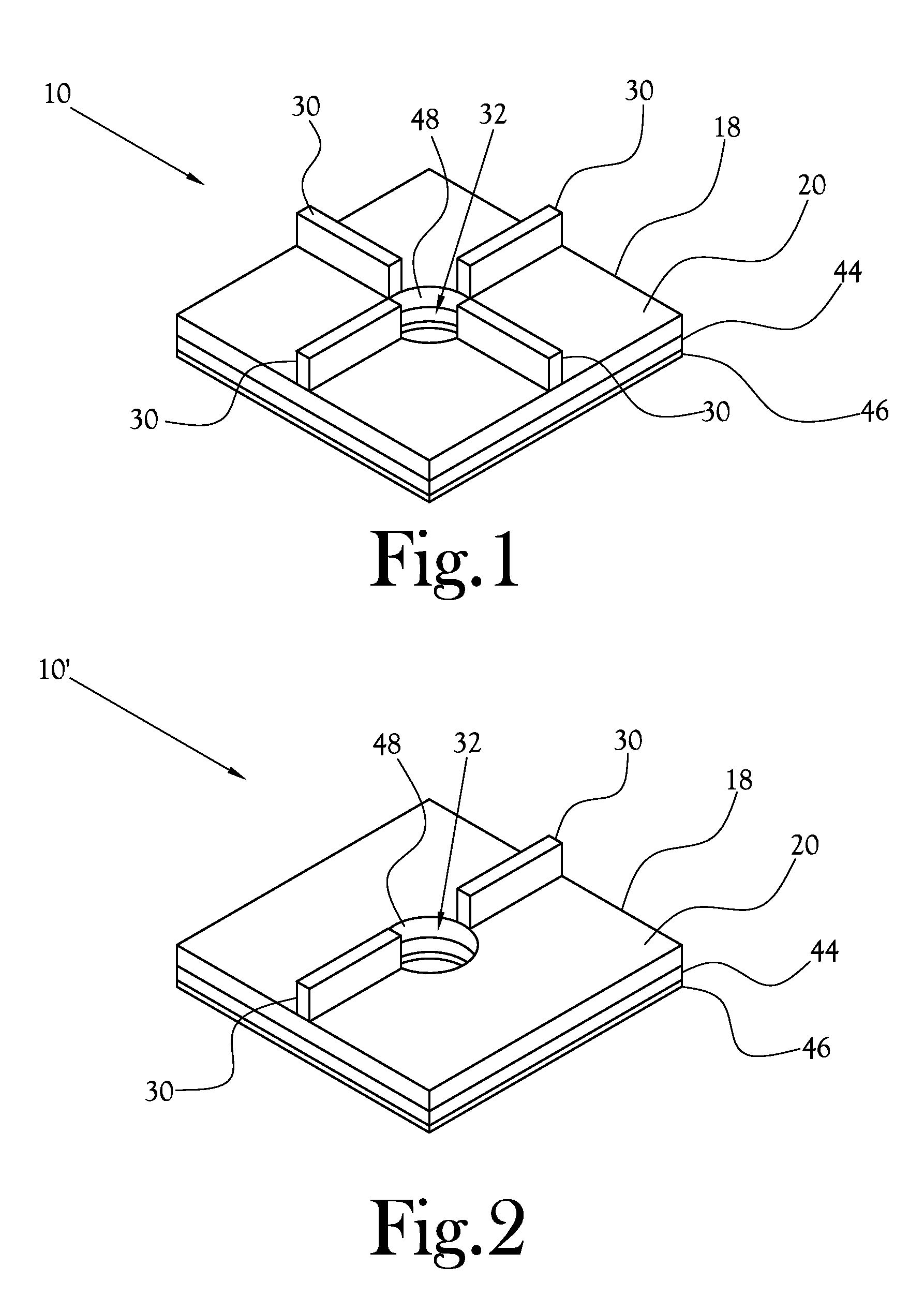
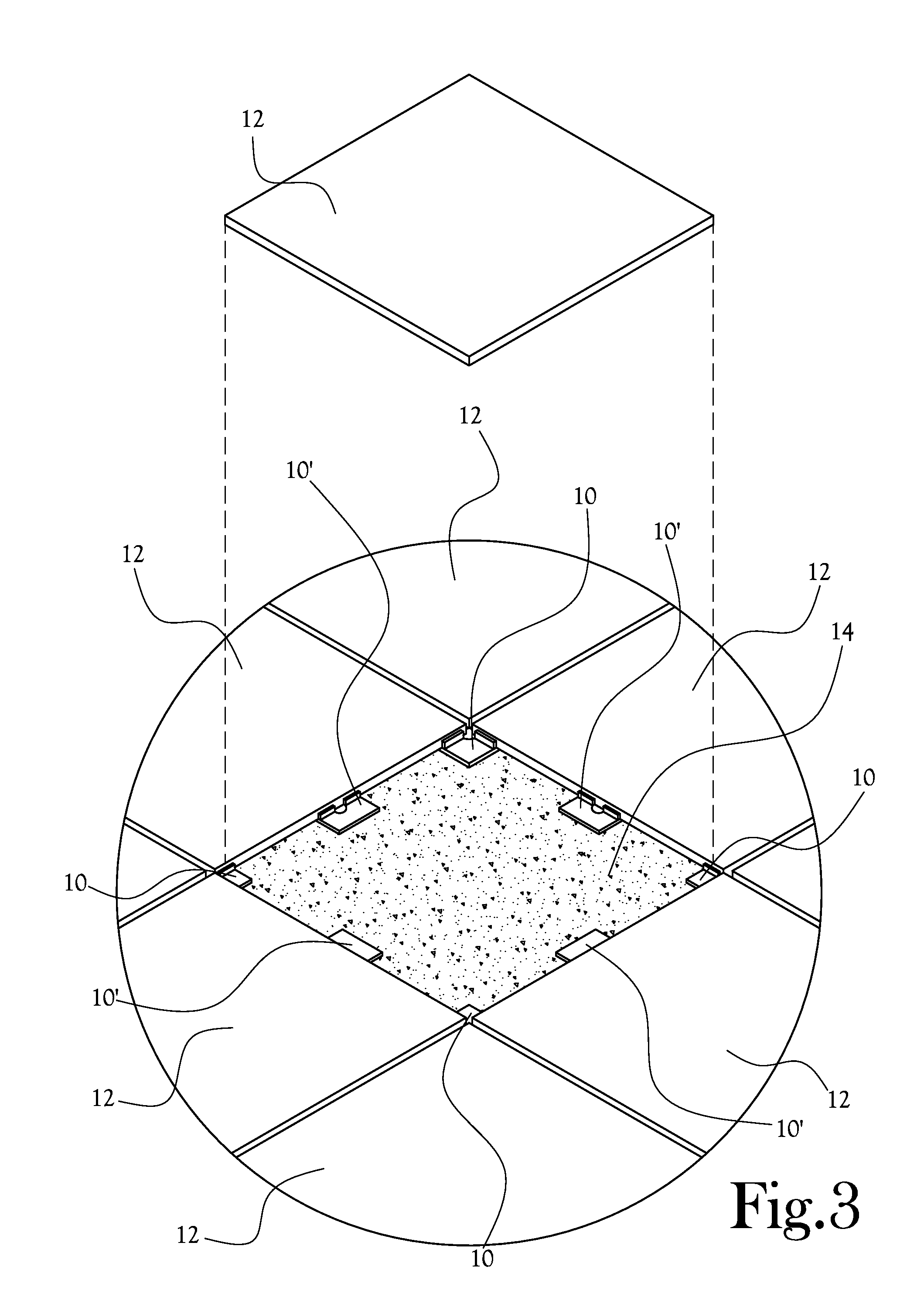
[0022]A spacer for laying tile 10 is disclosed herein and in the various figures. The spacer for laying tile, or spacer 10, is adapted to be interposed between adjacent tiles 12 of a plurality of tiles 12 and between the plurality of tiles 12 and a working surface 14 over which the tiles 12 are laid to assist in aligning and leveling the plurality of tiles 12 relative to each other and relative to the working surface 14. In several embodiments, the spacer 10 is helpful in promoting a co-planar arrangement of spaced apart tiles 12 such that a space is provided between each tile 12 and the working surface 14 sufficient to accommodate a substrate layer 26 of a desired thickness between each tile 12 and the working surface 14, and such that even spaces are provided between adjacent tiles 12 for receipt of mortar joints 16 therein.
[0023]With initial reference to FIGS. 1 and 4, one embodiment of the spacer 10 includes a planar base plate 18 which is dimensioned to extend along a working s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com