Touch surface and method of manufacturing same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
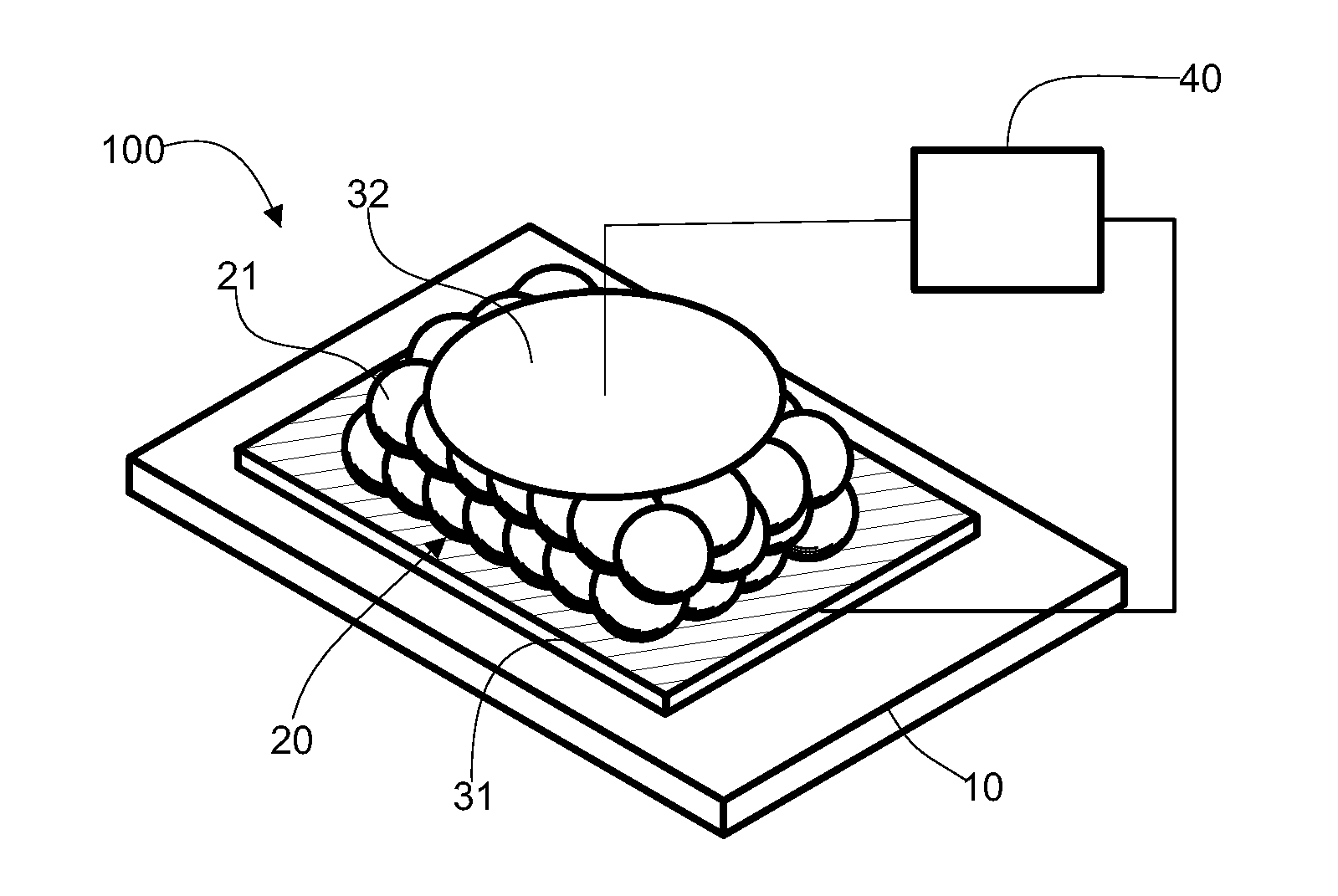
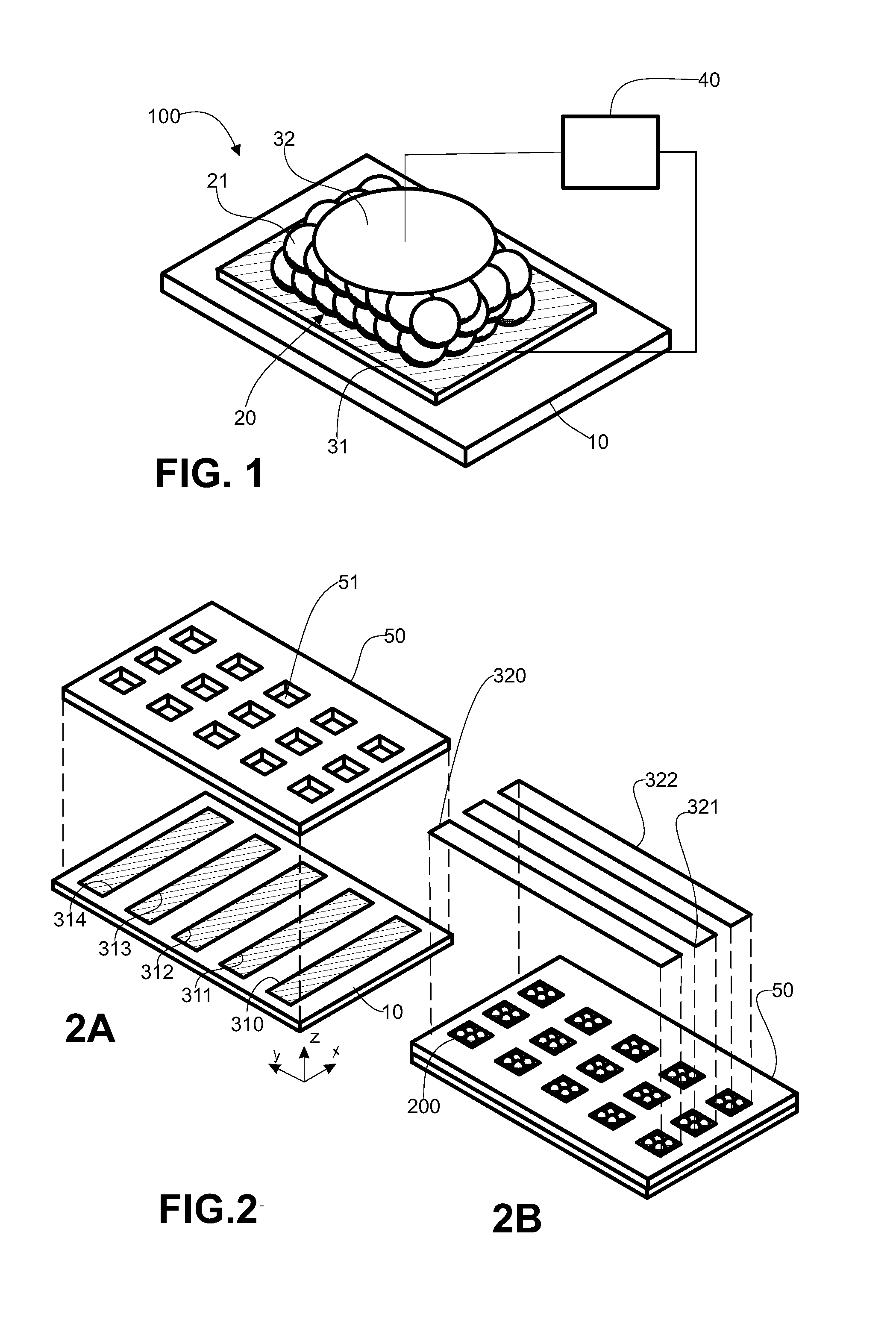
[0076]FIG. 3: the device that is the subject of the invention comprises an insulating substrate (10), on which is deposited a nanoparticles assembly (20) covering most of its surface. Said nanoparticles assembly can be single-layered or comprise several layers superimposed in a direction normal to the surface of the substrate (10).
[0077]A first ensemble of conductive strips (315, 316) is deposited on the substrate so as to form the first electrode, such that said strips extend between a portion of the substrate not covered by the nanoparticles assembly and said assembly in contact with the latter. A second ensemble of strips (323, 324), forming the second electrode, is deposited in the same way as the first strips, in symmetry with them in relation to the center of the center of the nanoparticles assembly. Finally, an insulating film (60) is deposited over everything.
[0078]FIG. 6: according to a variant of this embodiment, the discrete strips forming the first electrode are grouped...
third embodiment
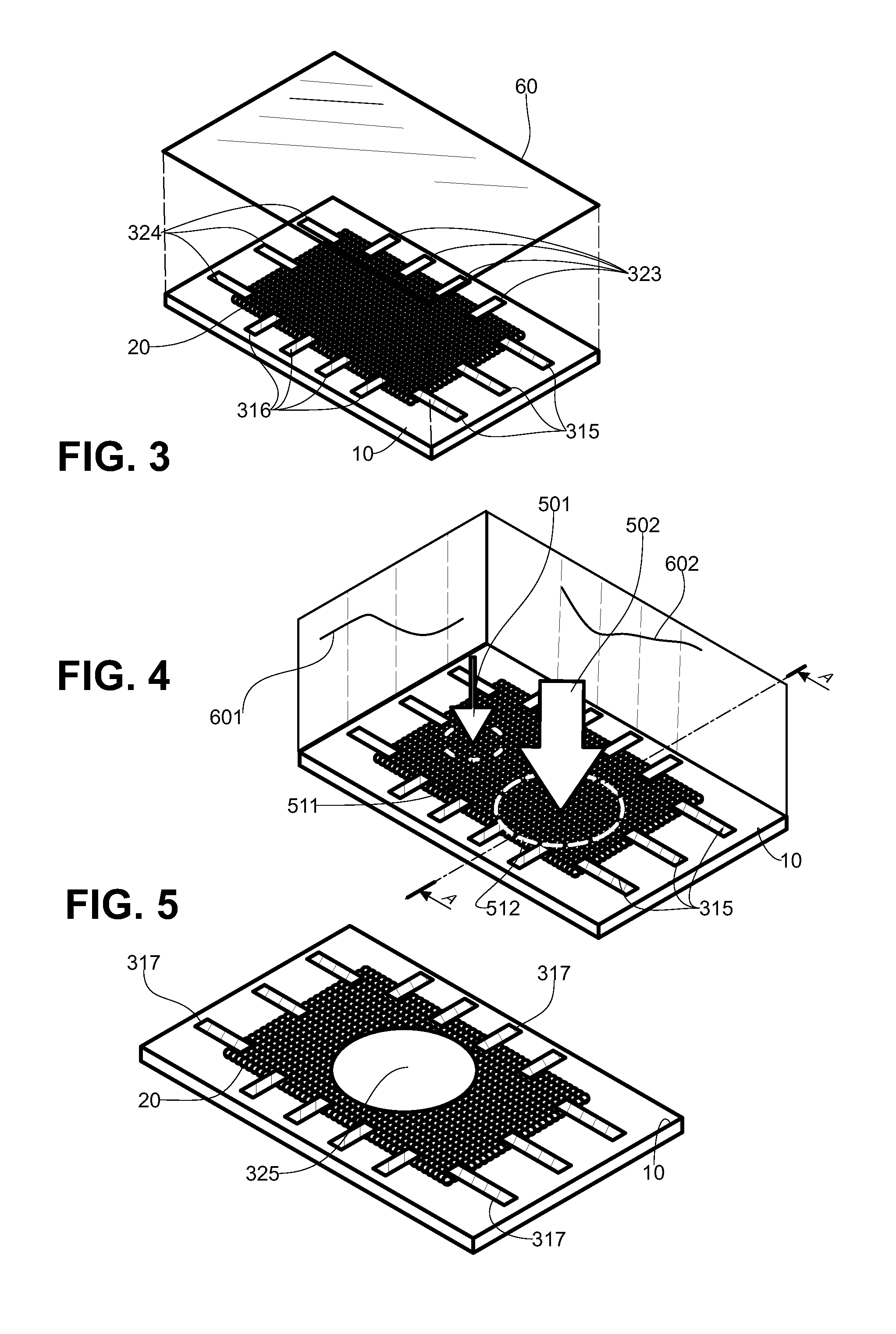
[0080]FIG. 5: the device that is the subject of the invention comprises an insulating substrate (10) on which a nanoparticles assembly (20) covering a portion of the surface of said substrate is deposited. The first electrode is formed of an ensemble of strips (317) deposited on the substrate and extending between a portion of the substrate that is not covered and the nanoparticles assembly (20), in contact with the latter. The second electrode (325) is placed on the nanoparticles assembly, the ensemble being covered by an insulating film (not shown). When a force is applied to the second electrode (325), both the normal and tangential components of said force change the distance between the nanoparticles of the assembly (20). The point of application of the force being known, i.e. substantially at the center of the second electrode (325), measuring an electrical property between said second electrode (325) and each of the strips (317) forming the first electrode makes it possible ...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap