System, method, and apparatus for modeling project reliability
a project reliability and modeling technology, applied in the field of project reliability prediction, can solve the problems of not providing early prediction of failure rate, software or hardware, and not describing making early reliability predictions
Inactive Publication Date: 2015-01-22
RAYTHEON CO
View PDF0 Cites 16 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
The present patent disclosure uses mathematical functions to predict the reliability growth of software and hardware in the future. It also mentions various models, such as the power-law model, for reliability growth analysis. However, none of these models have been used to make early predictions of failure rates from the known conditions of software or hardware. The patent aims to provide a solution by incorporating early reliability predictions from historical data to improve the reliability of software and hardware systems.
Problems solved by technology
None of them, however, describes making early reliability predictions from the historically known conditions for software or hardware, or software and hardware together.
Accordingly, prior art models only considered analyzing failures after design completion, and did not provide early prediction of failure rate.
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
example 1
New Software Failure Rate at the Maturity Time
[0080]KSLOC count: 208
[0081]Acceleration factor: A=1
[0082]SEI level 4=1.0 fault / KSLOC
N0=1.0·208=208 faults
[0083]With the assumptions of t1=1 sec.= 1 / 3,600 hour; T=4 years, p=0.03
t1=2.778·10−4
T=4·8,760=3.504·104
{circumflex over (β)}=0.285
{circumflex over (λ)}=10.286
The final failure rate at the maturity time:
ω^(TP)=λ^·β^·tβ^-1=1.637·10-3failureshour
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
A system, method and apparatus arranged for early-stage reliability-growth models for predicting project reliability at an early stage. These predictions can integrate with an overall system reliability model. Embodiments include predicting reliability of hardware, software, or any other engineering project.
Description
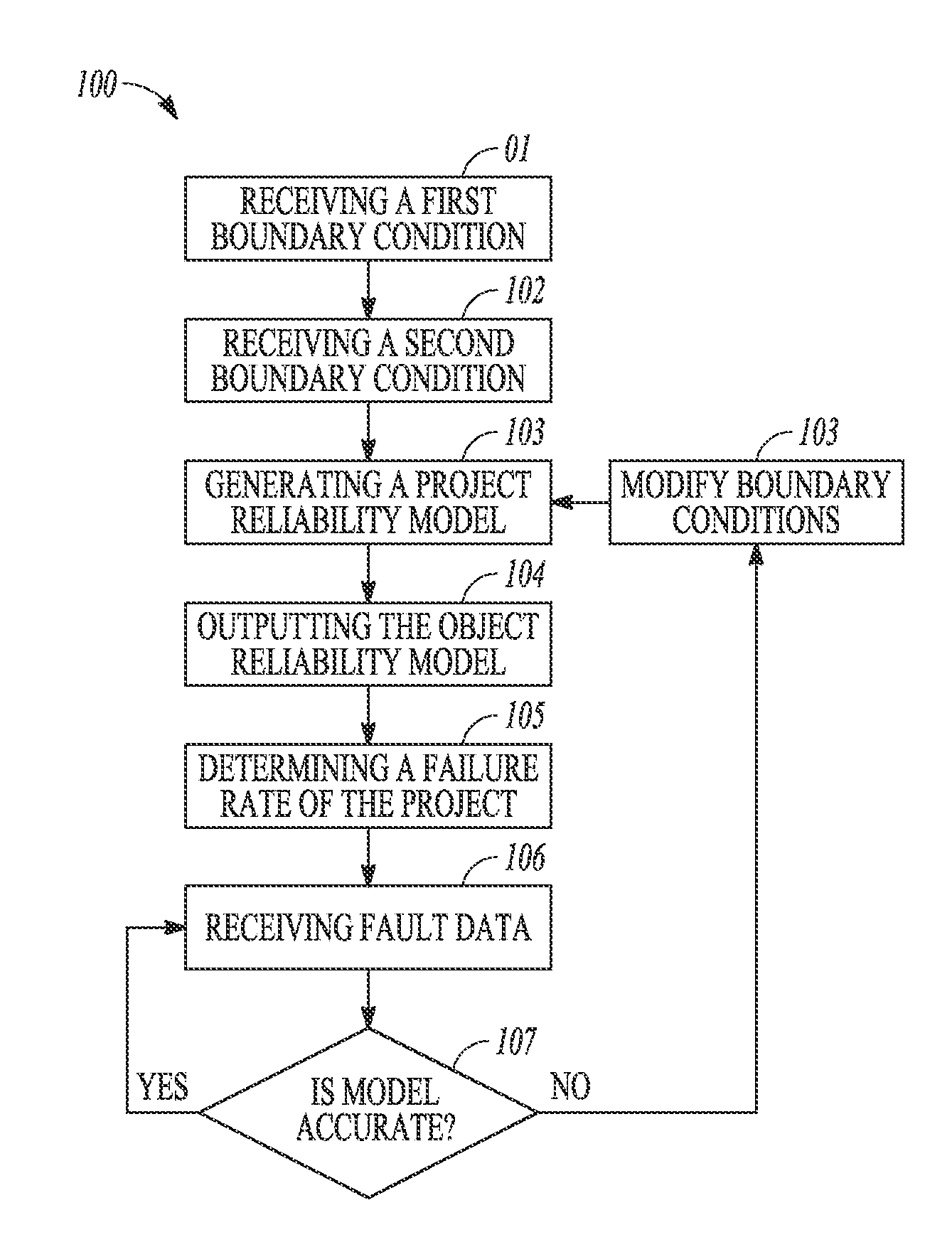
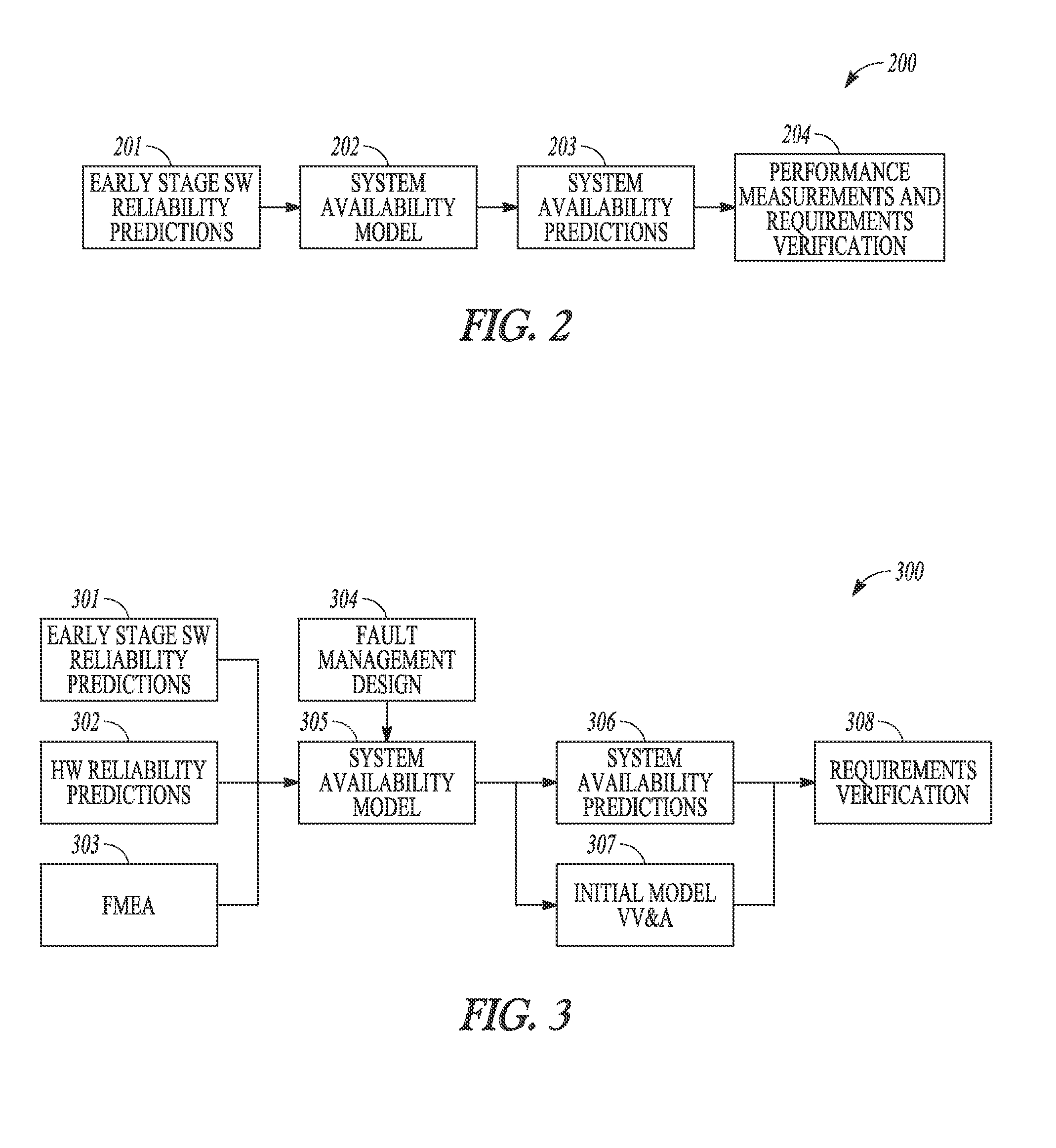
GOVERNMENT LICENSE RIGHTS[0001]This invention was made with government support under government contract no. FA8807-10-C-0001 awarded by the United States Air Force. The government has certain rights in the invention.FIELD[0002]Embodiments pertain to predicting project reliability. Exemplary projects include hardware, software, or both.BACKGROUND[0003]Software developers and users desire early reliability estimates for projects or products. Faults (also called bugs or defects) lead to failures, e.g., a system malfunction. Current models for providing early failure rate or reliability estimates are not mathematically accurate. Current models extrapolate the number of remaining faults based on their assumed statistical distribution when appearing as failures. The prior models, which use continuous statistical distributions are mathematically or physically incorrect, and do not provide early reliability estimates. Thus, prior art reliability estimates are unreliable.[0004]Additionally,...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Applications(United States)
IPC IPC(8): G06F17/50G06F11/00
CPCG06F17/5009G06F11/008G06Q10/0637
Inventor PETERSON, JON R.KRASICH, MILENA
Owner RAYTHEON CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com