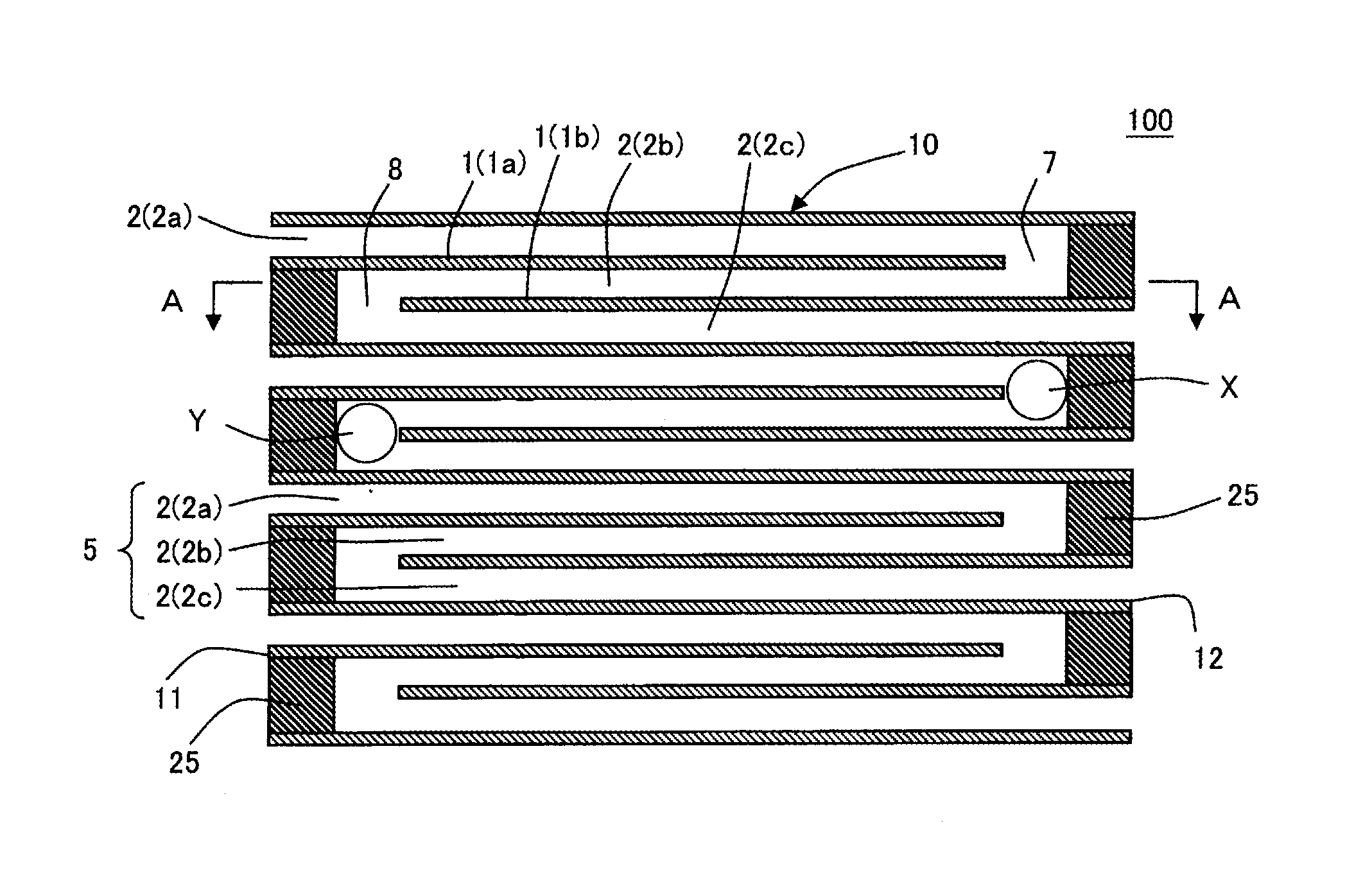
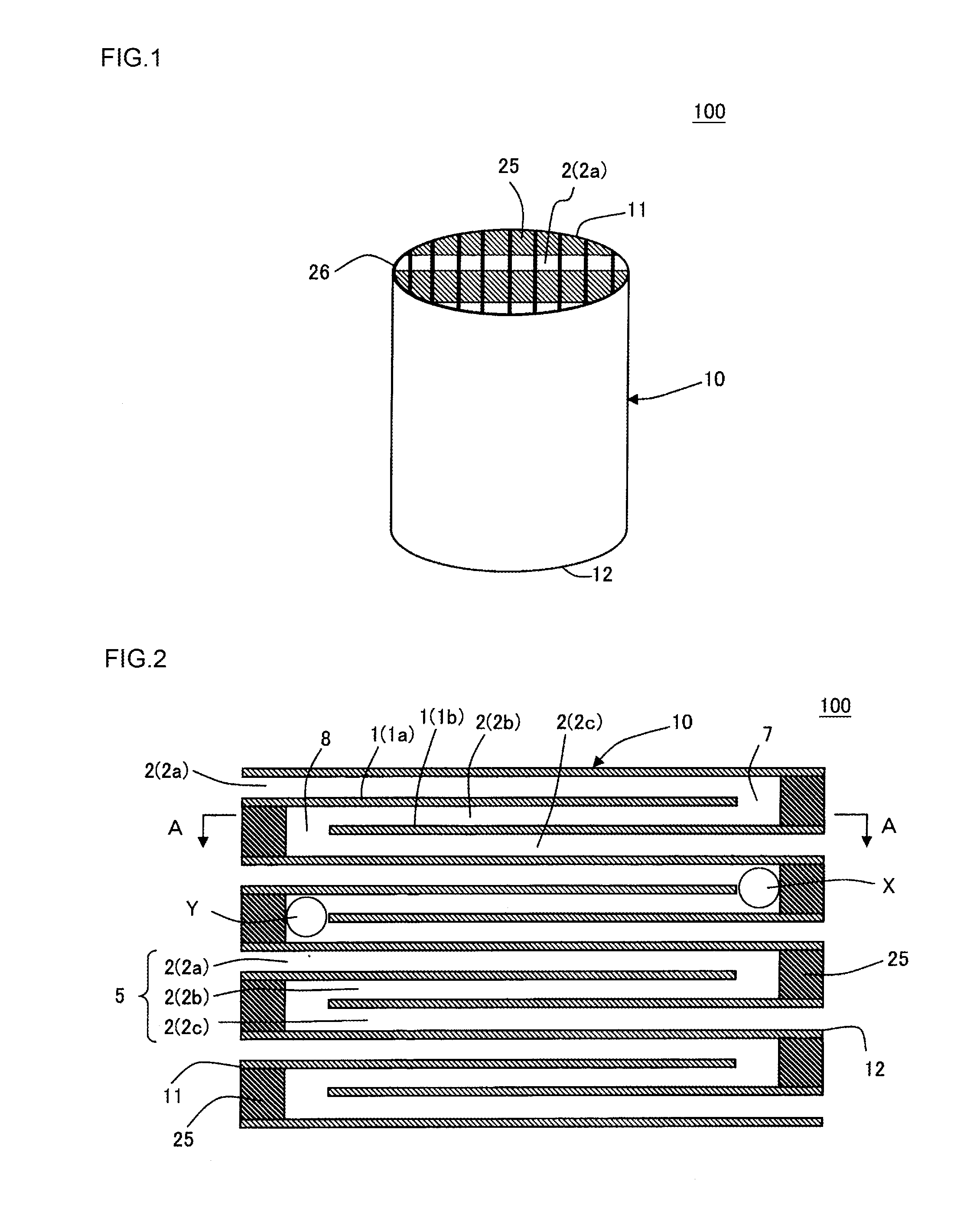
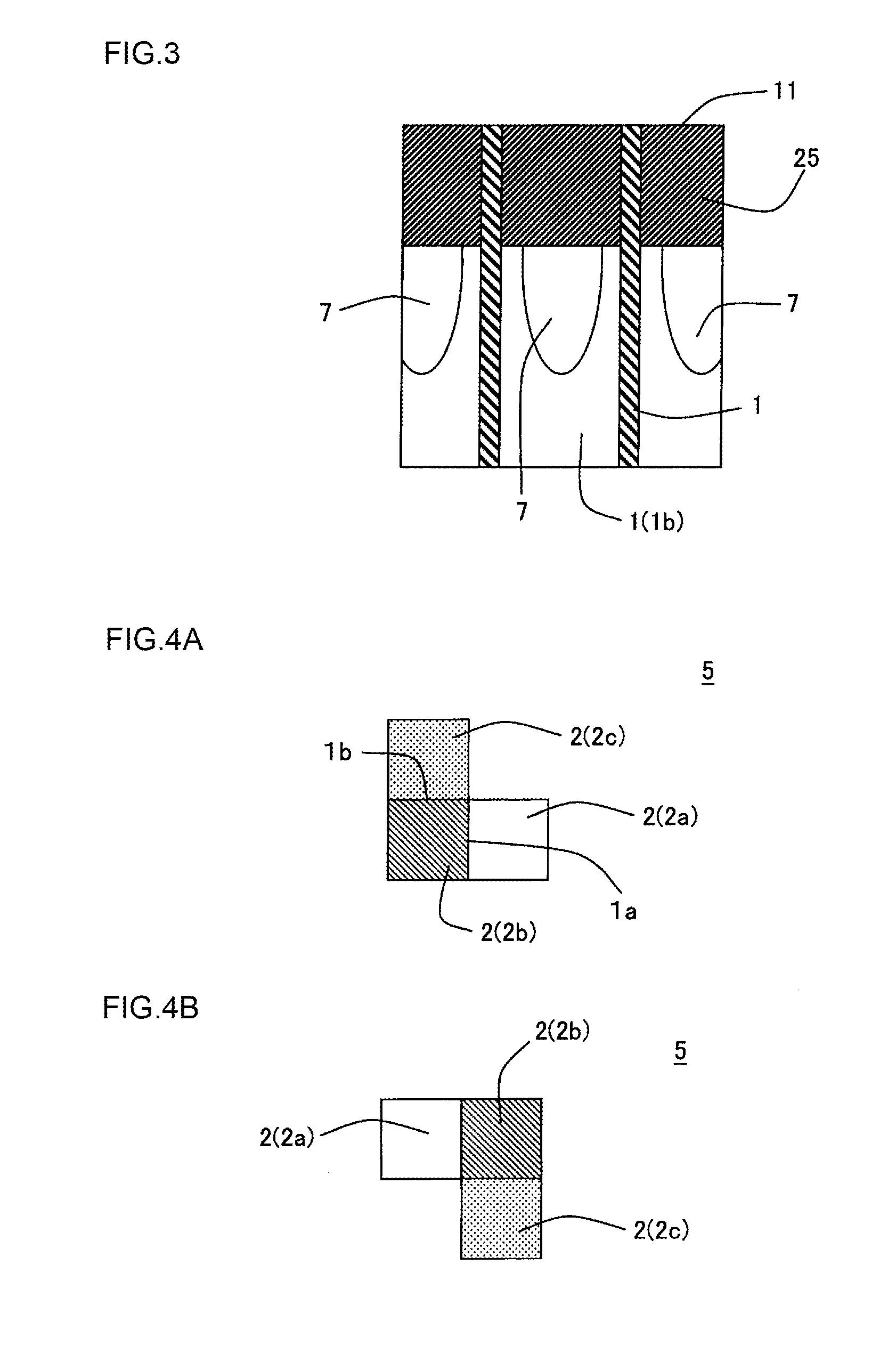
Honeycomb structure
a honeycomb and structure technology, applied in the field of honeycomb structure, can solve the problems of affecting the efficiency of honeycomb structure, and difficult to discharge ash accumulated from the honeycomb structure, etc., to inhibit the increase of pressure loss and excellent trapping efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0106]A pore former, an organic binder and water were added to a cordierite forming raw material to obtain a forming raw material. The forming raw material was mixed and kneaded to prepare a columnar kneaded material. As an organic binder, methylcellulose was used, and 5 parts by mass of methylcellulose was added to 100 parts by mass of the cordierite forming raw material. The water was added as a dispersing medium as much as 10 mass % to the whole forming raw material. The cordierite forming raw material is a raw material which becomes cordierite when fired. Specifically, the cordierite forming raw material is a ceramic raw material obtained by mixing “predetermined raw materials” to obtain a chemical composition in which silica (SiO2) is in a range of 42 to 56 mass %, alumina (Al2O3) is in a range of 30 to 45 mass %, and magnesia (MgO) is in a range of 12 to 16 mass %. “The predetermined raw materials” are raw materials selected from the group consisting of talc, kaolin, calcinate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com