Predicting the risks of multiple healthcare-related outcomes via joint comorbidity discovery
a risk prediction and risk technology, applied in the field of electrical, electronic and computer arts, can solve the problems of loss of crucial medical insights, inability to directly apply existing multi-task learning techniques to the problem of ehr-based risk prediction, and inability to identify single-task prediction models to identify these associations. , to achieve the effect of improving prediction accuracy and enhancing comorbidity identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
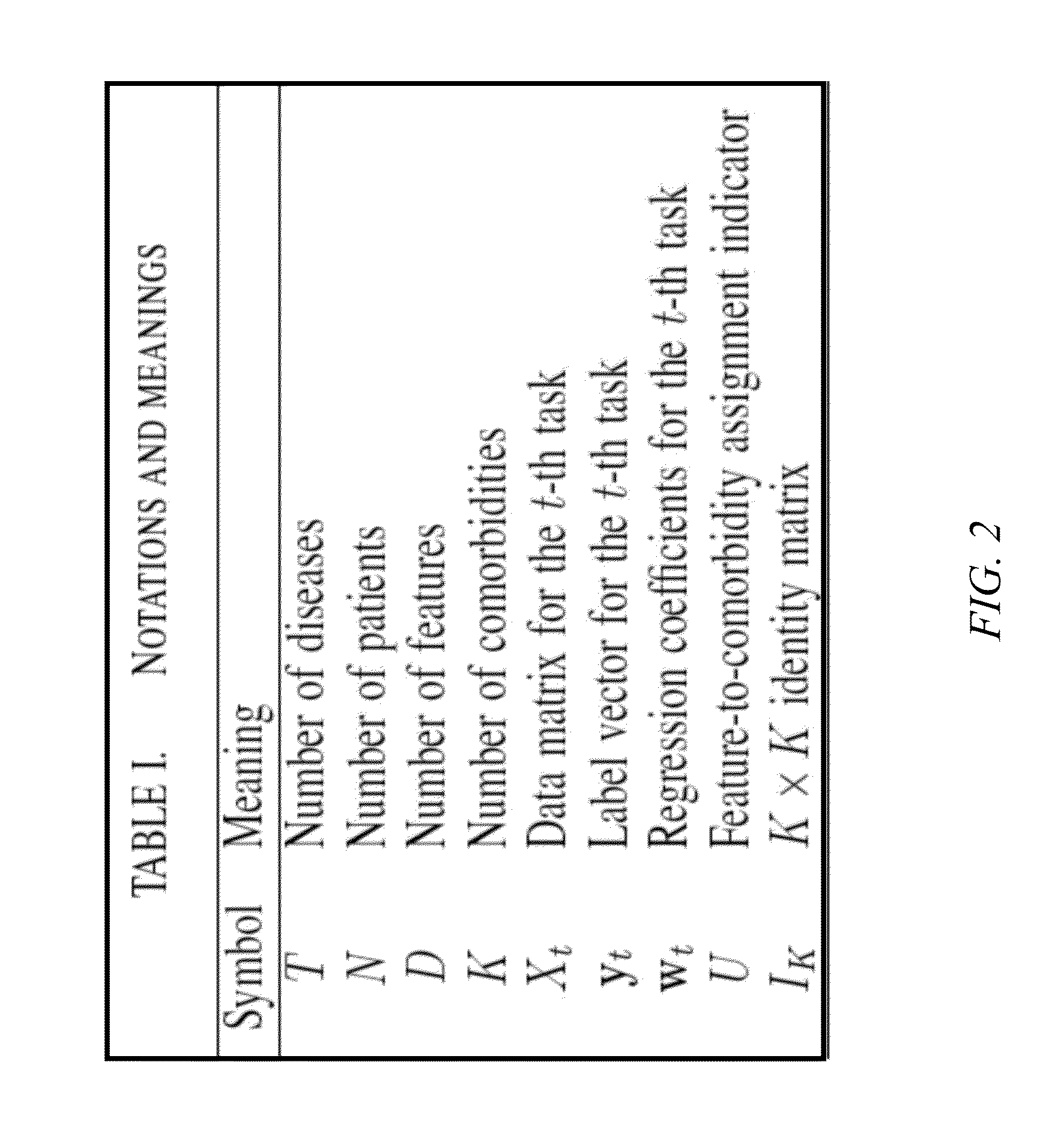
[0020]The framework of one or more embodiments of the present invention makes a mild assumption that will hold for a wide range of EHR data and diseases: The diseases share a small number of latent and distinct risk factors which can be represented by a combination of the medical features from the EHR database. The strength of the framework of the one or more embodiments of the invention comes from the fact that by combining multiple related diseases, noisiness and sparsity of the original medical features can be avoided to more accurately identify latent risk factors, which will in turn serve as better predictors for the target diseases.
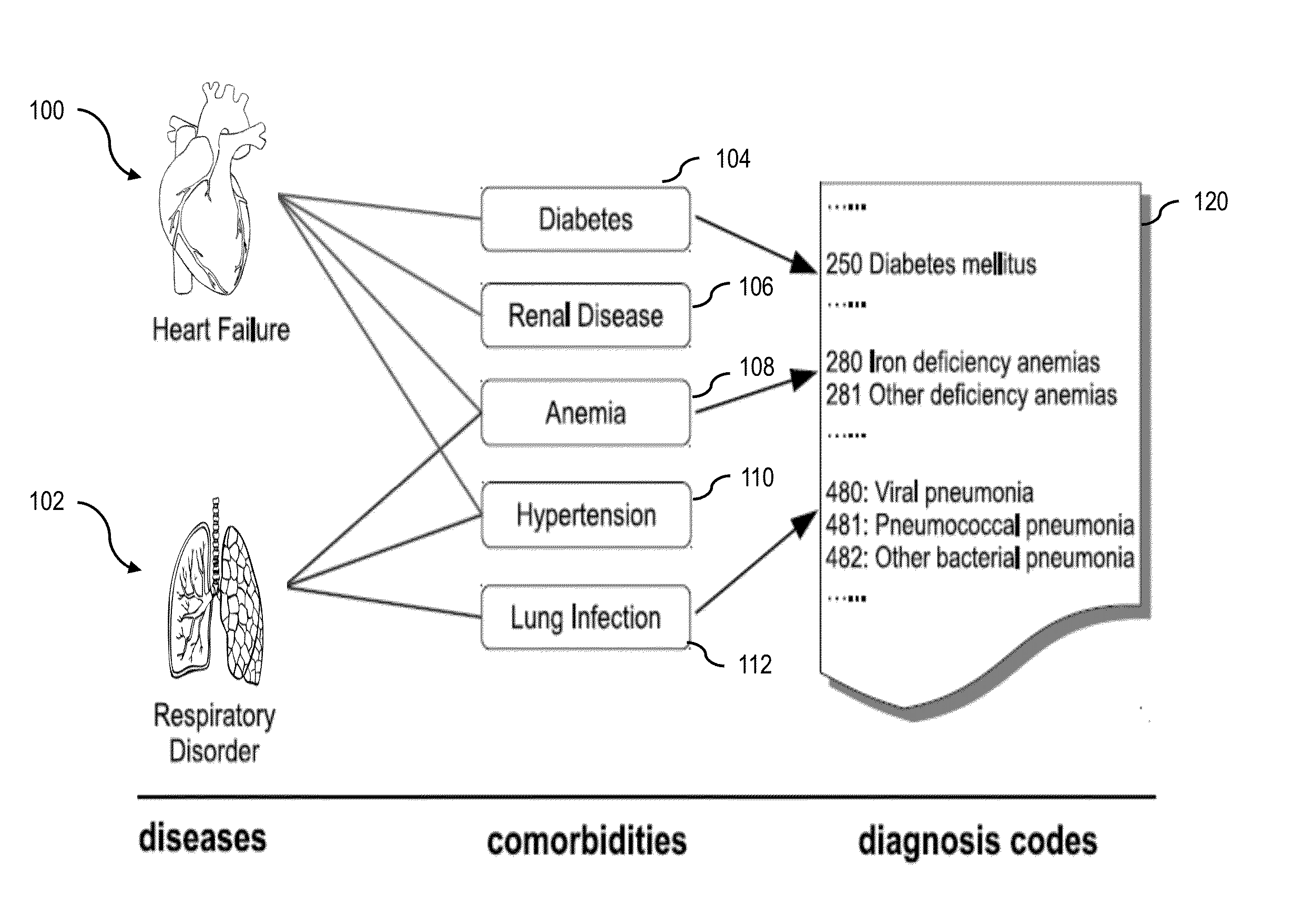
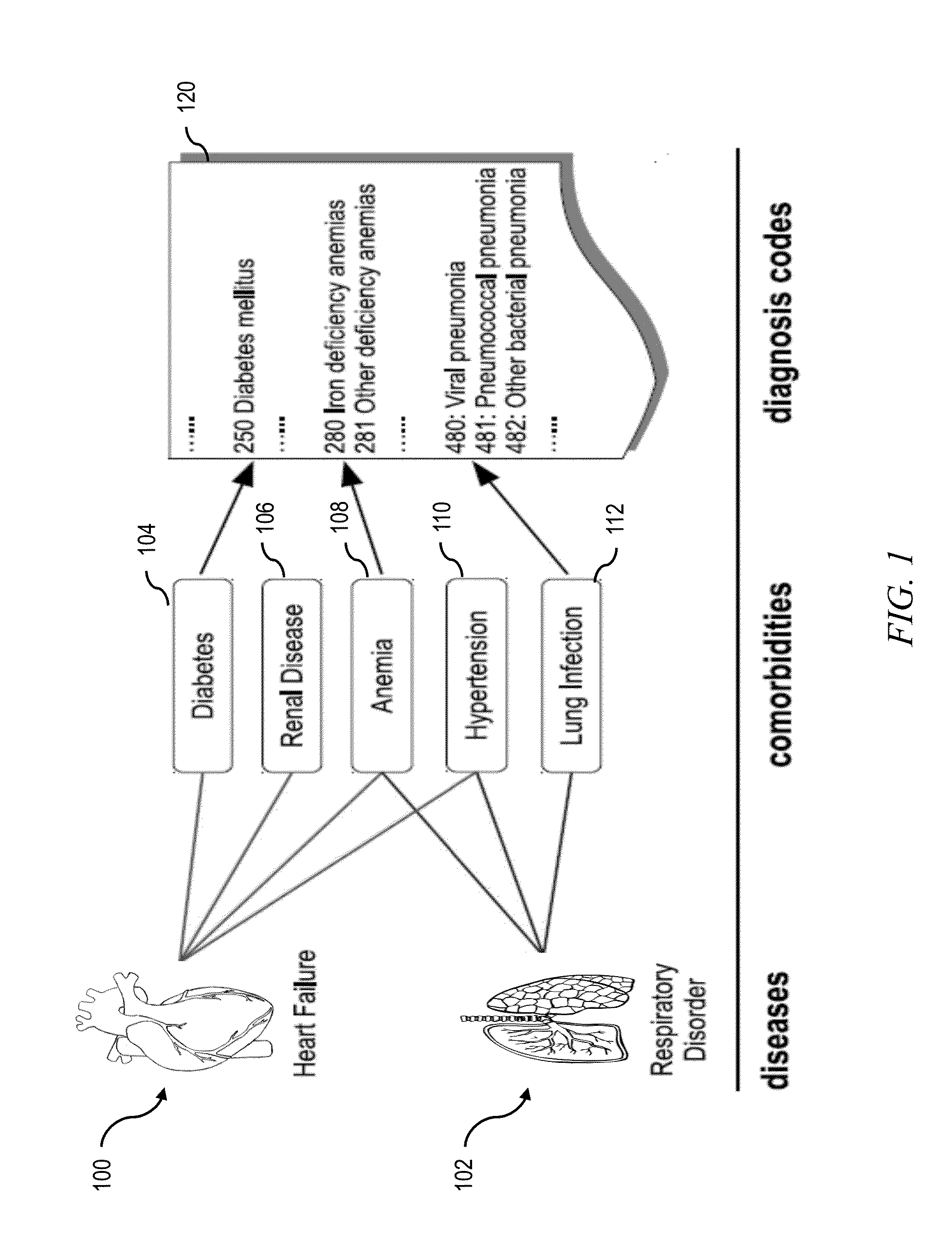
[0021]FIG. 1 shows relationships between individuals who are at risk of two diseases: heart failure 100 and respiratory disorder 102. Traditional risk models attribute the risks directly to the raw medical features from the EHR database 120, such as individual diagnosis codes, lab results, vitals, etc., which are often noisy and sparse. Under the fr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com