Stripping vessel for removing hydrocarbons entrained in catalyst particles
a technology of hydrocarbons and stripping vessels, which is applied in the field of stripping vessels, can solve the problems of large distance between the structure packing and the inlet to the stripping section, large surface area of catalyst particles employed in fcc processes, and large amount of hydrocarbons being withdrawn from the reaction zone with the catalyst, so as to reduce the impact of catalyst flow, reduce the impact of catalyst compression and mal-distribution, and reduce the effect of catalyst over accumulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
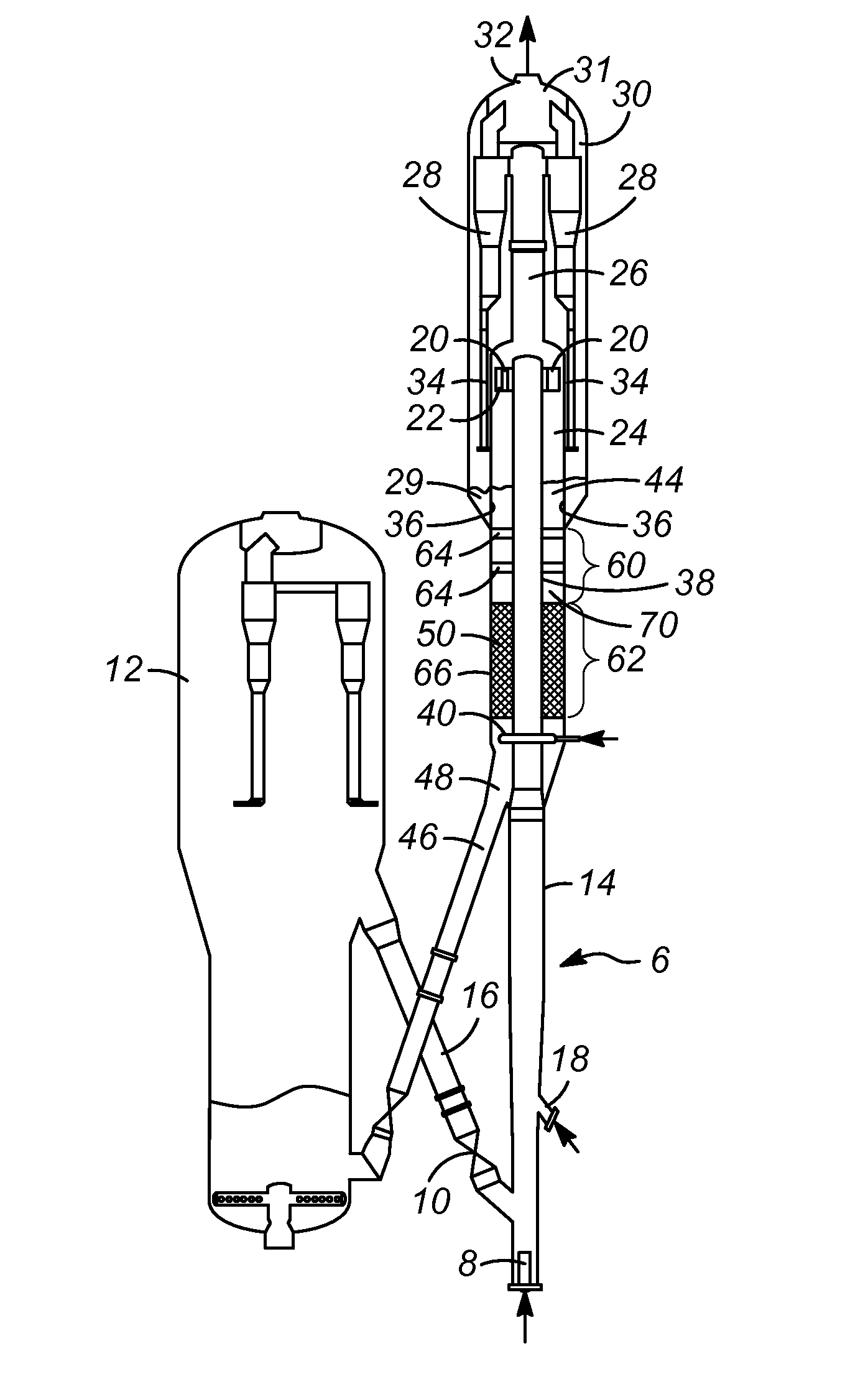
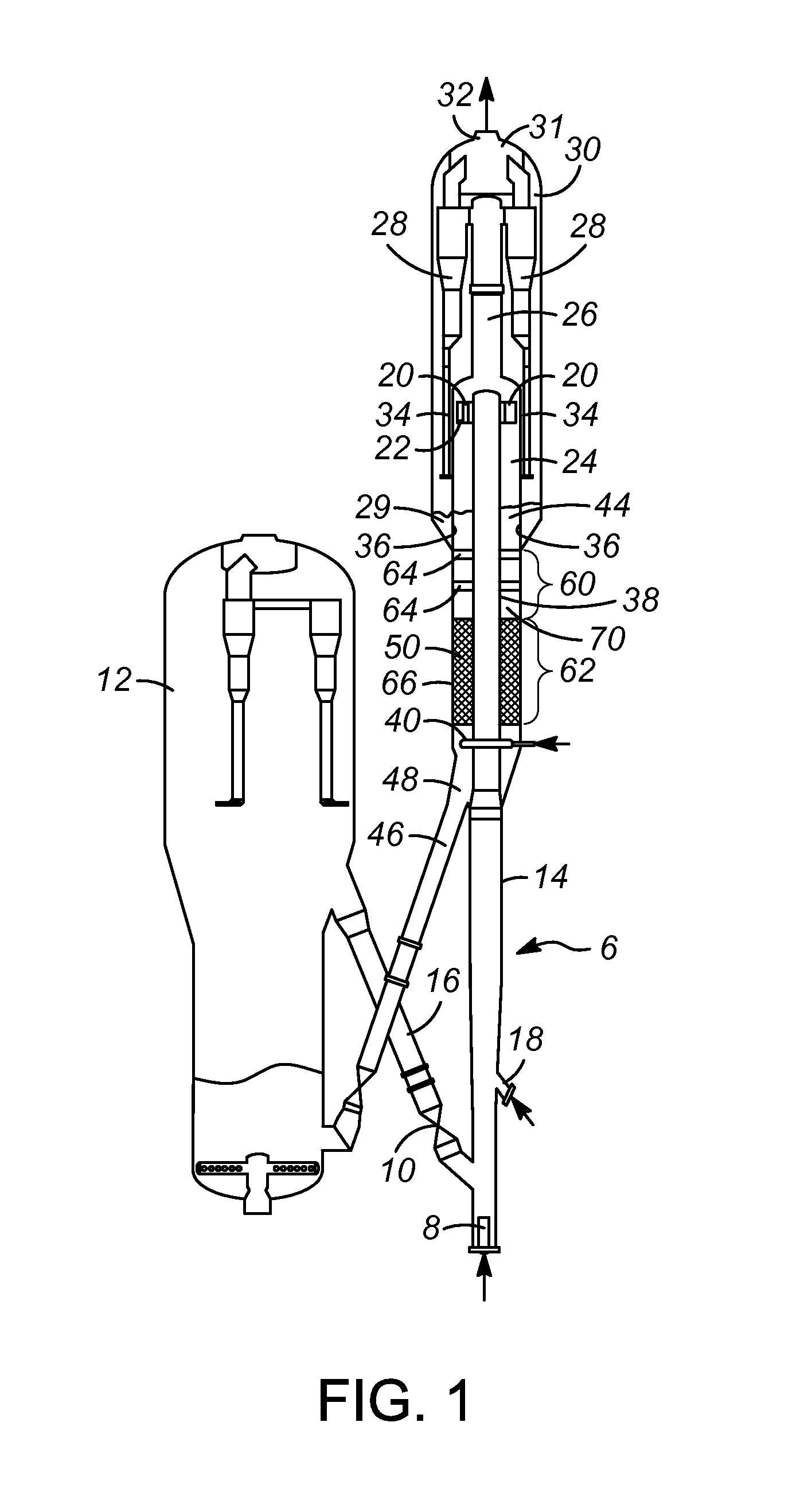
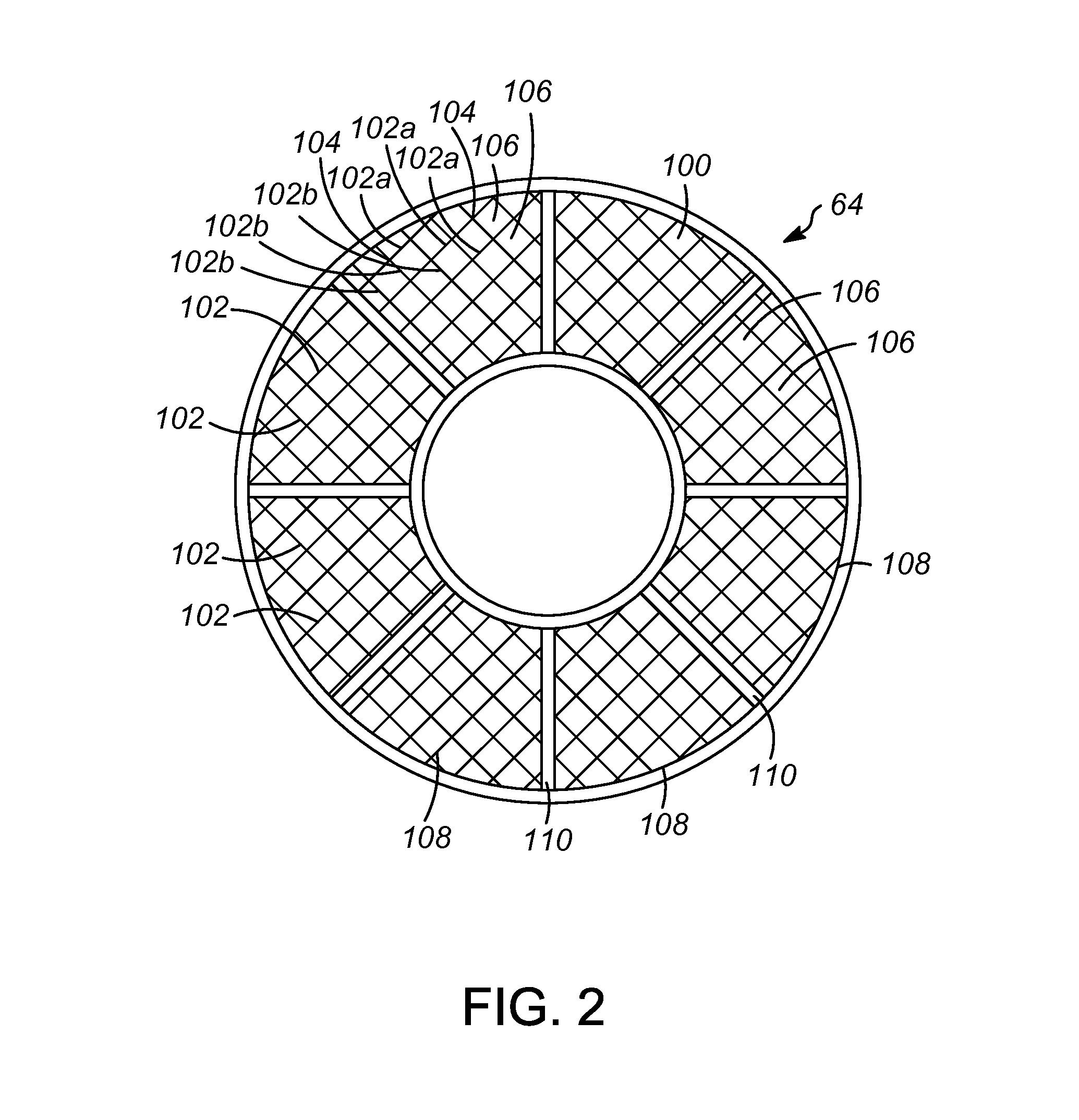
[0033]As discussed above, a design for a stripping vessel has been developed in which a grid or grids are disposed apart from a section of structure packing. The grid(s) will distribute catalyst that flows downward through the vessel, countercurrent to a stripping medium. The grids(s) will occupy the empty space above the inlet of the vessel to avoid over accumulation of the catalyst. It is contemplated that such a design is especially applicable to an FCC process and FCC process unit that is being retrofitted to include newer and more efficient stripping sections. The grids will occupy the empty space above or below the stripping section with structure packing and minimize the over accumulation of the catalyst.
[0034]With reference to the attached drawings, one or more embodiments of the present invention will now be described with the understanding that these embodiments are merely exemplary of the aspects and principles of the present invention.
[0035]The present invention comprise...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com