Endoscopic instrument
a technology of endoscopic instruments and shank tools, applied in the field of endoscopic instruments, can solve the problems of not only being used therapeutically, but also merely diagnosing, and reducing the risk and achieving the effect of avoiding the danger of injury due to sharp-edged tool heads and being easy to position and actuate the shank tools by a single user
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
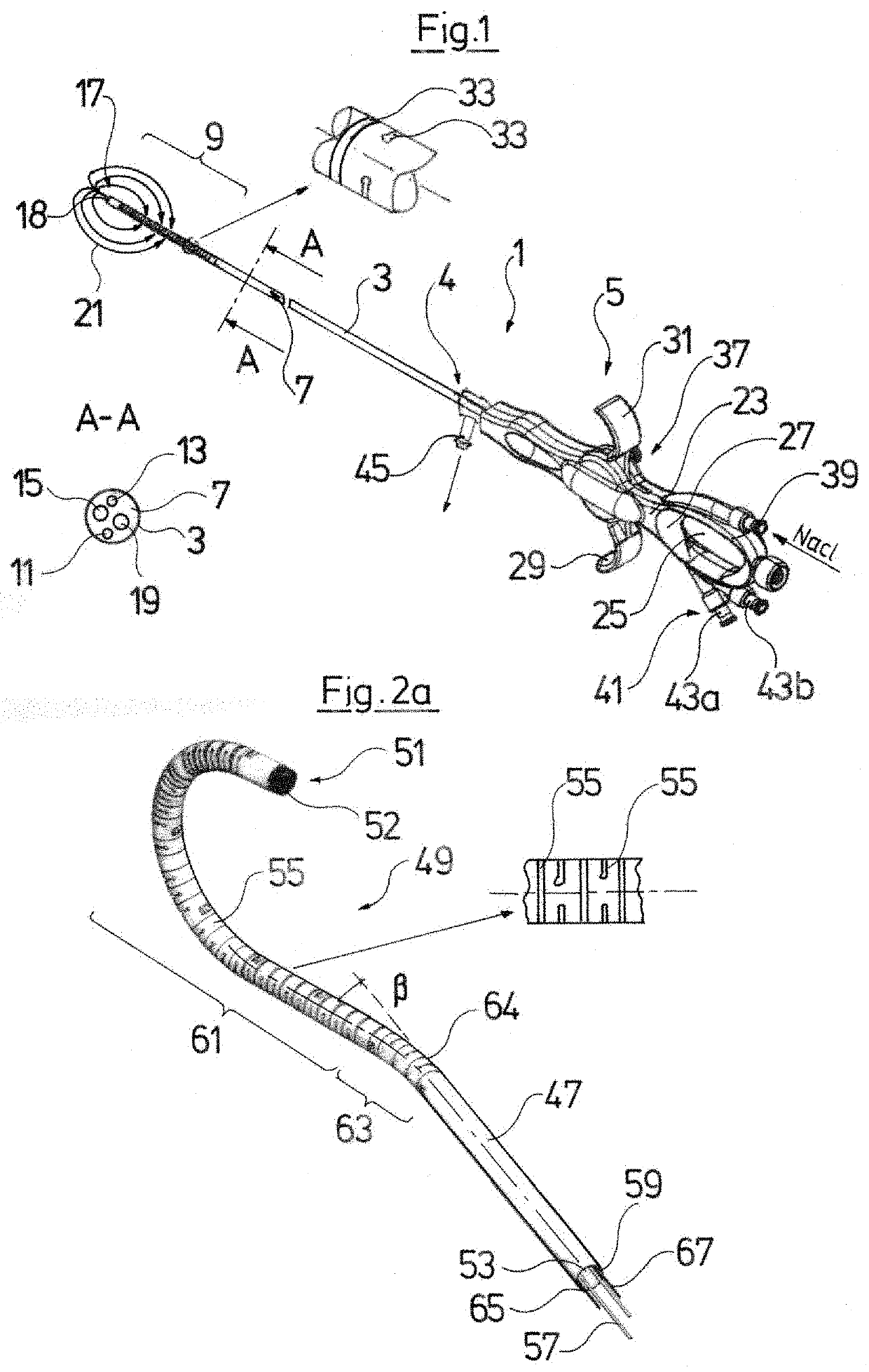
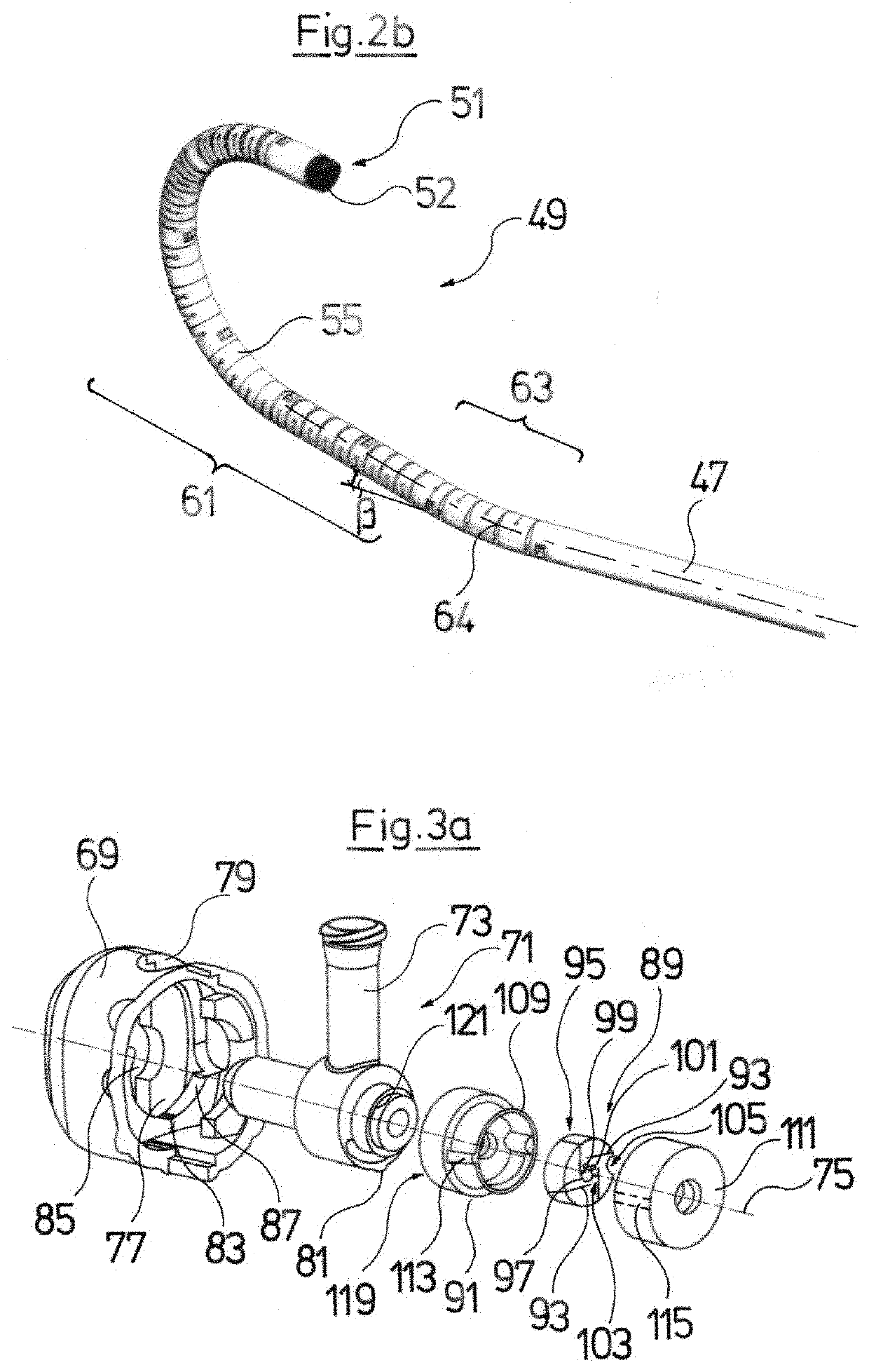
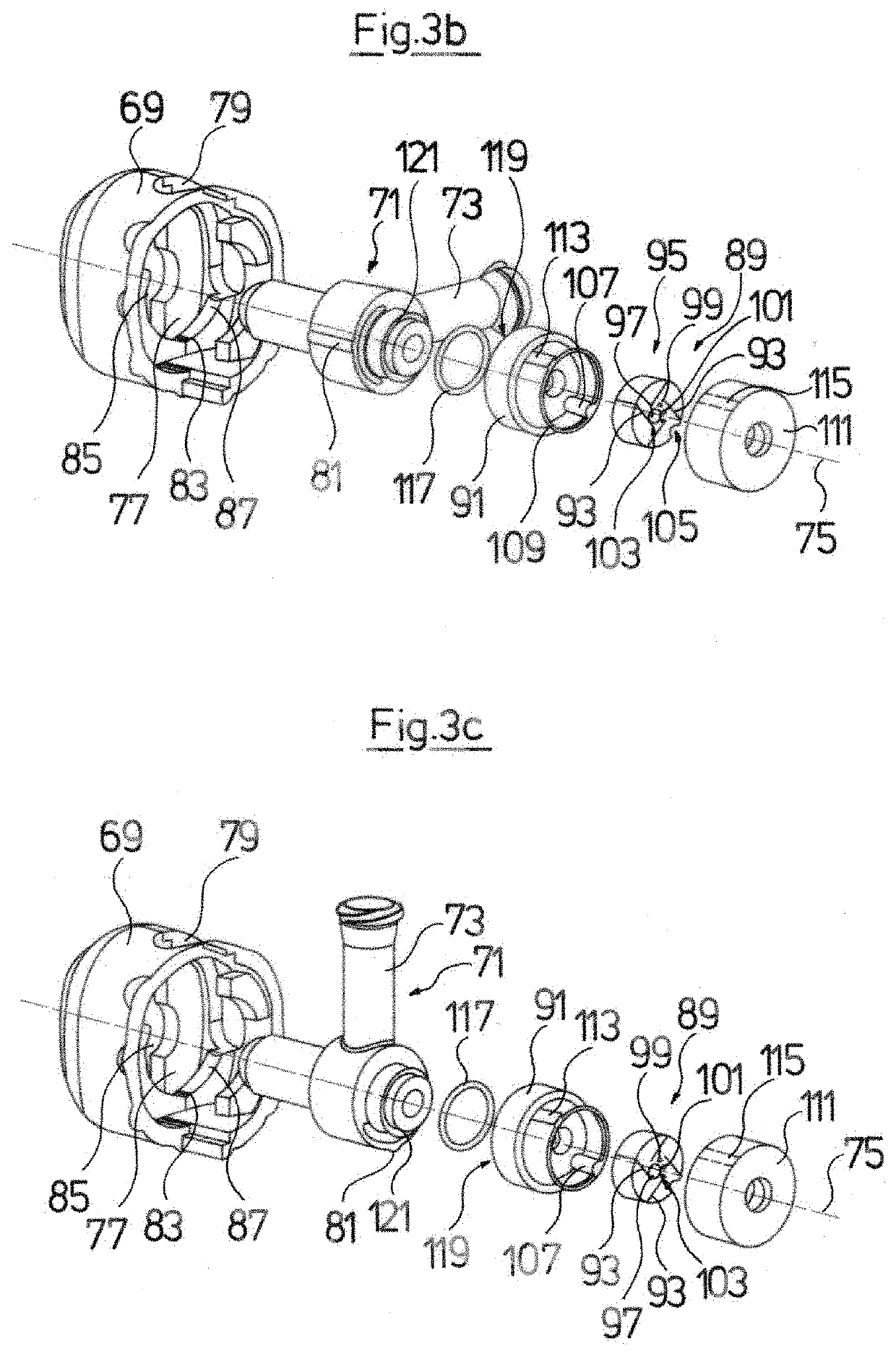
[0064]Referring to the drawings, FIG. 1 by way of example shows an endoscopic instrument 1 which comprises a tubular shank 3 for insertion into a body cavity. The shank 3 is connected to a handling device 5 at a proximal end 4 and in its inner lumen forms a fluid channel 7. The shank 3 furthermore at a distal, bendable shank section 9 is configured in at least partly flexible manner, in order when necessary to be bent by way of the action of the handling device 5.
[0065]It is evident in a part-section A-A through the shank 7 that by way of example a first optical and / or electrical lead 11 for the illumination at the distal shank end 17, a second optical and / or electrical lead 13 for taking pictures at the distal shank end 17, a first working channel 15 and a second working channel 19 run in the fluid channel 7. An LED as a light source can be arranged at the distal end of the first lead 11, wherein the lead 11 serves as an electrical electricity supply lead to the LED. Alternatively ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com