Patents
Literature
78results about How to "Simplified actuation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
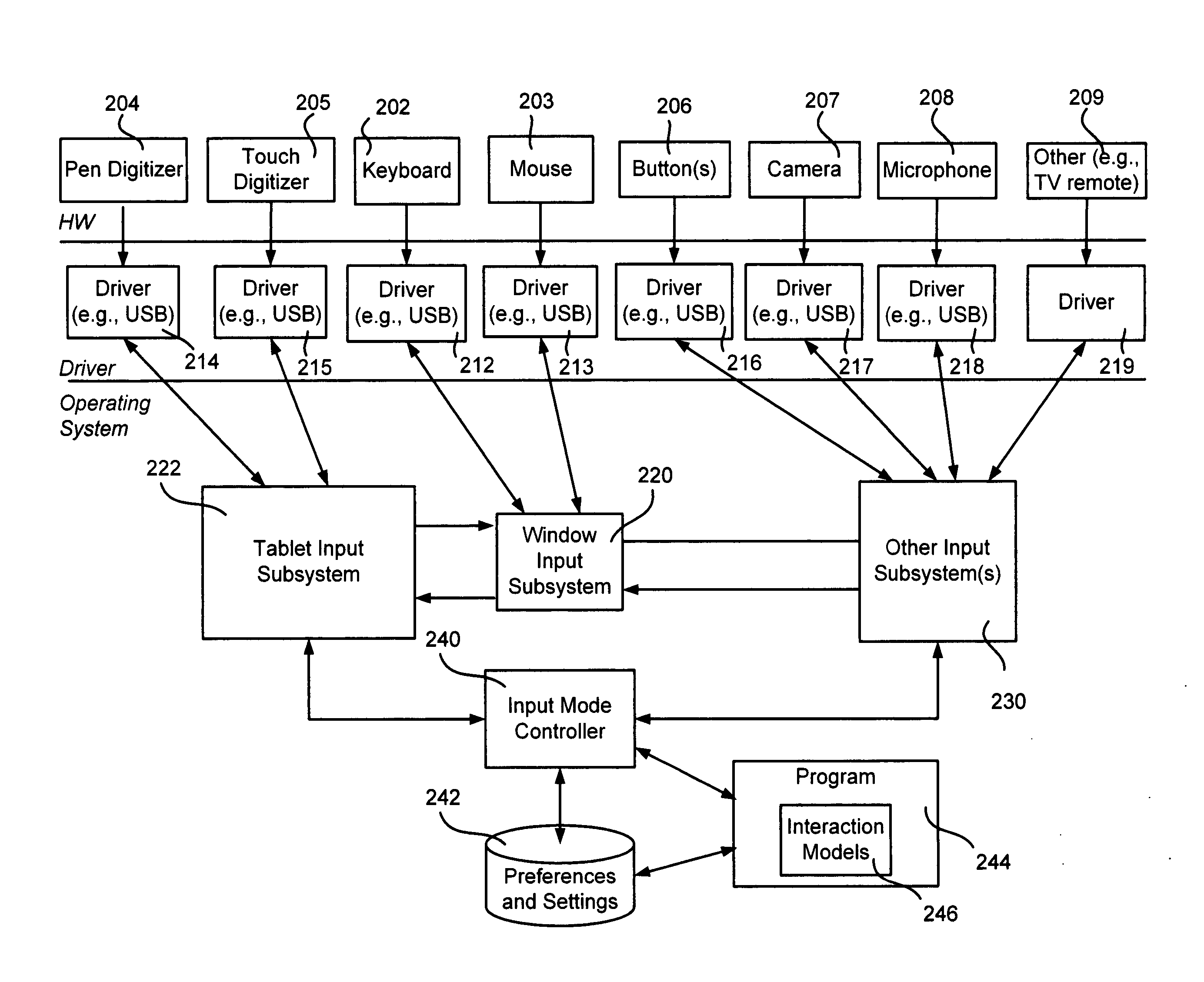
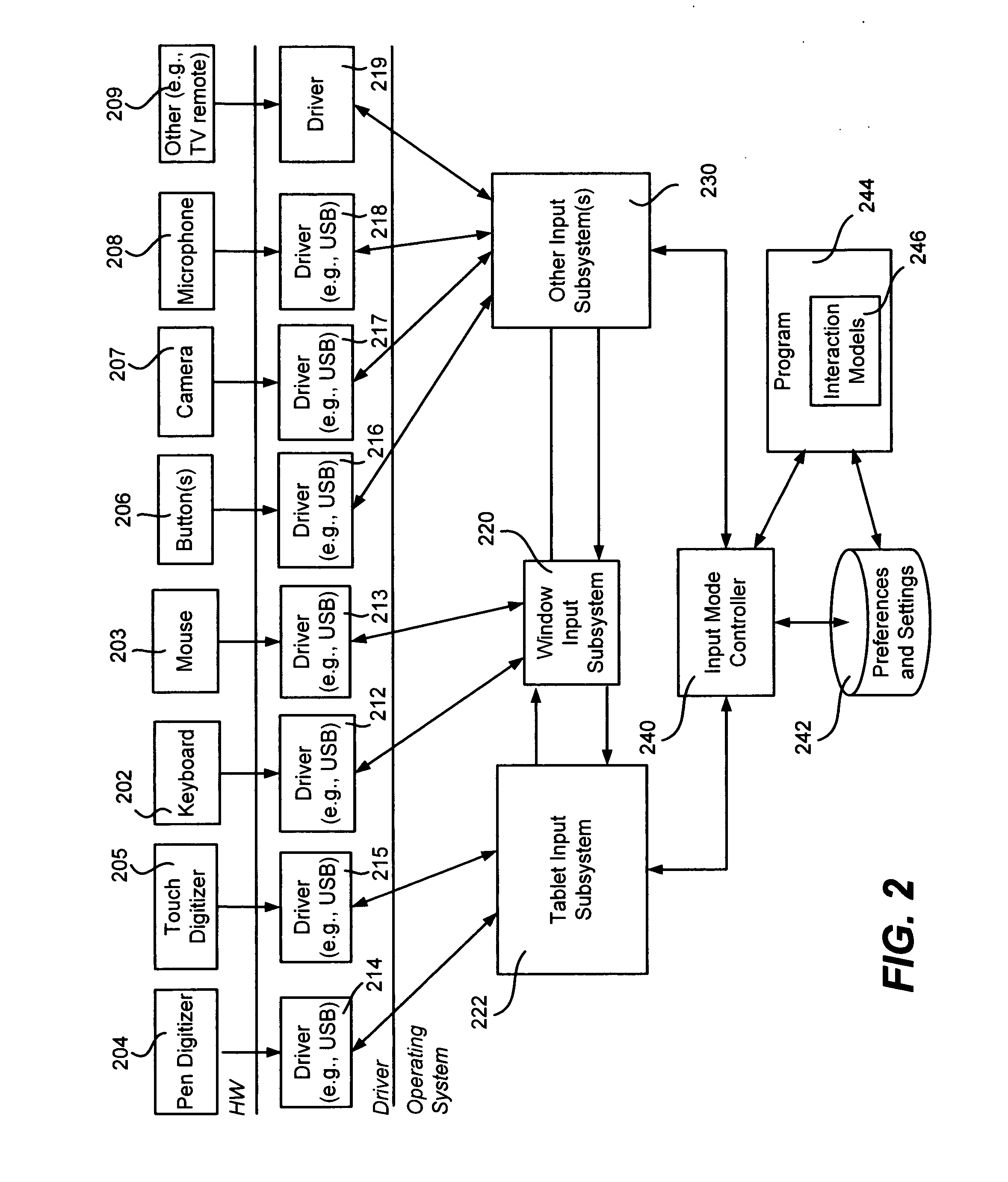
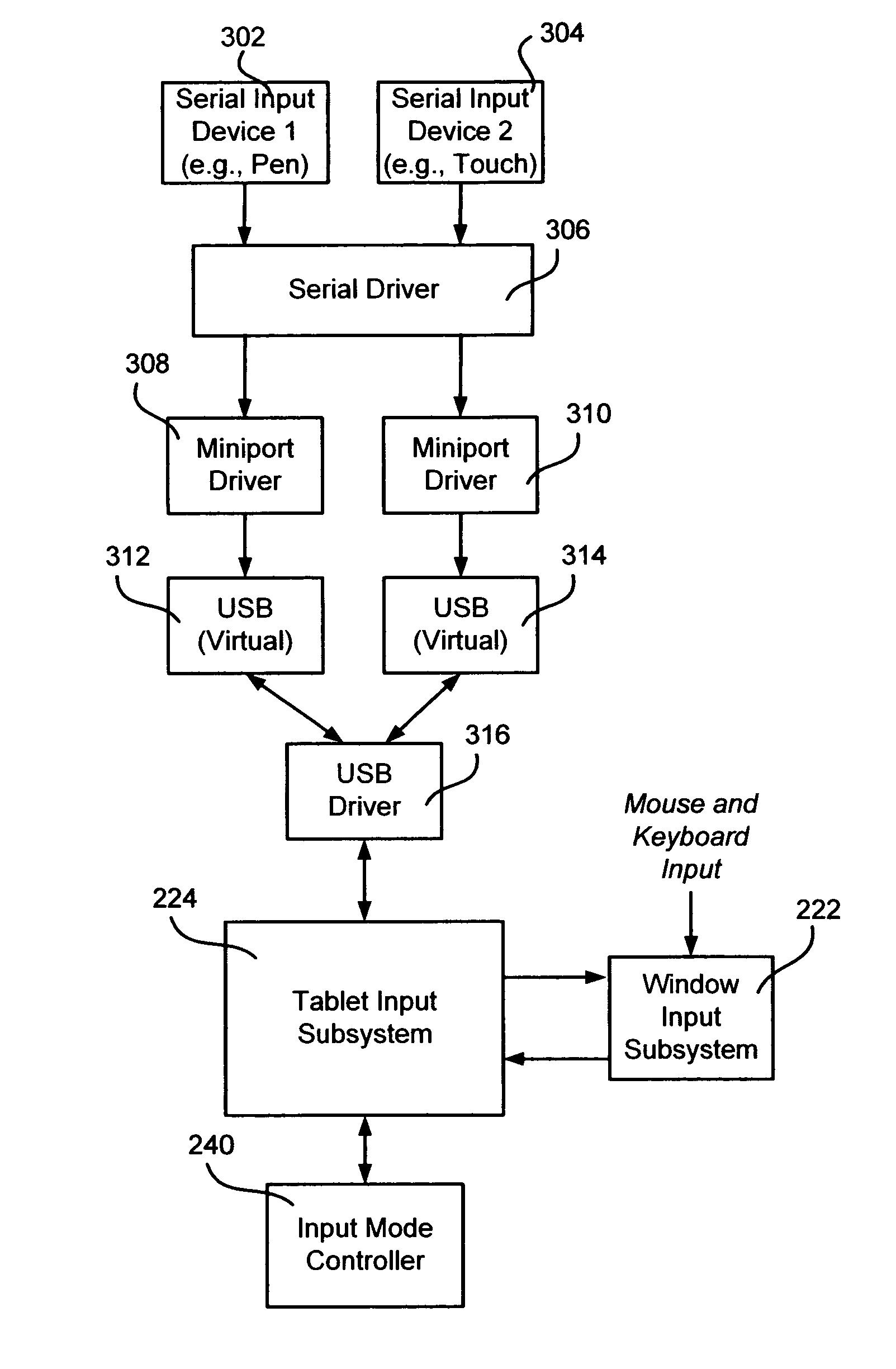
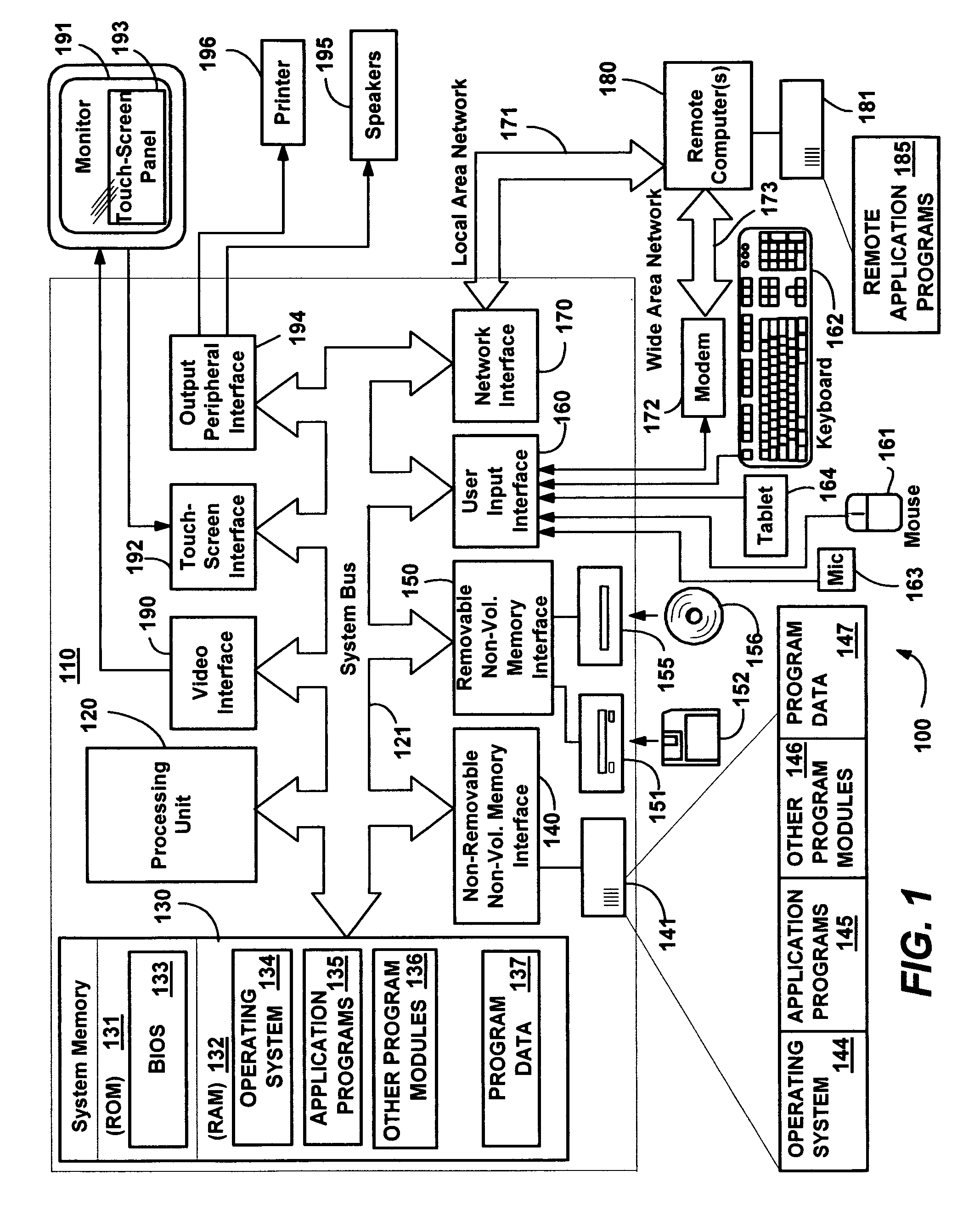
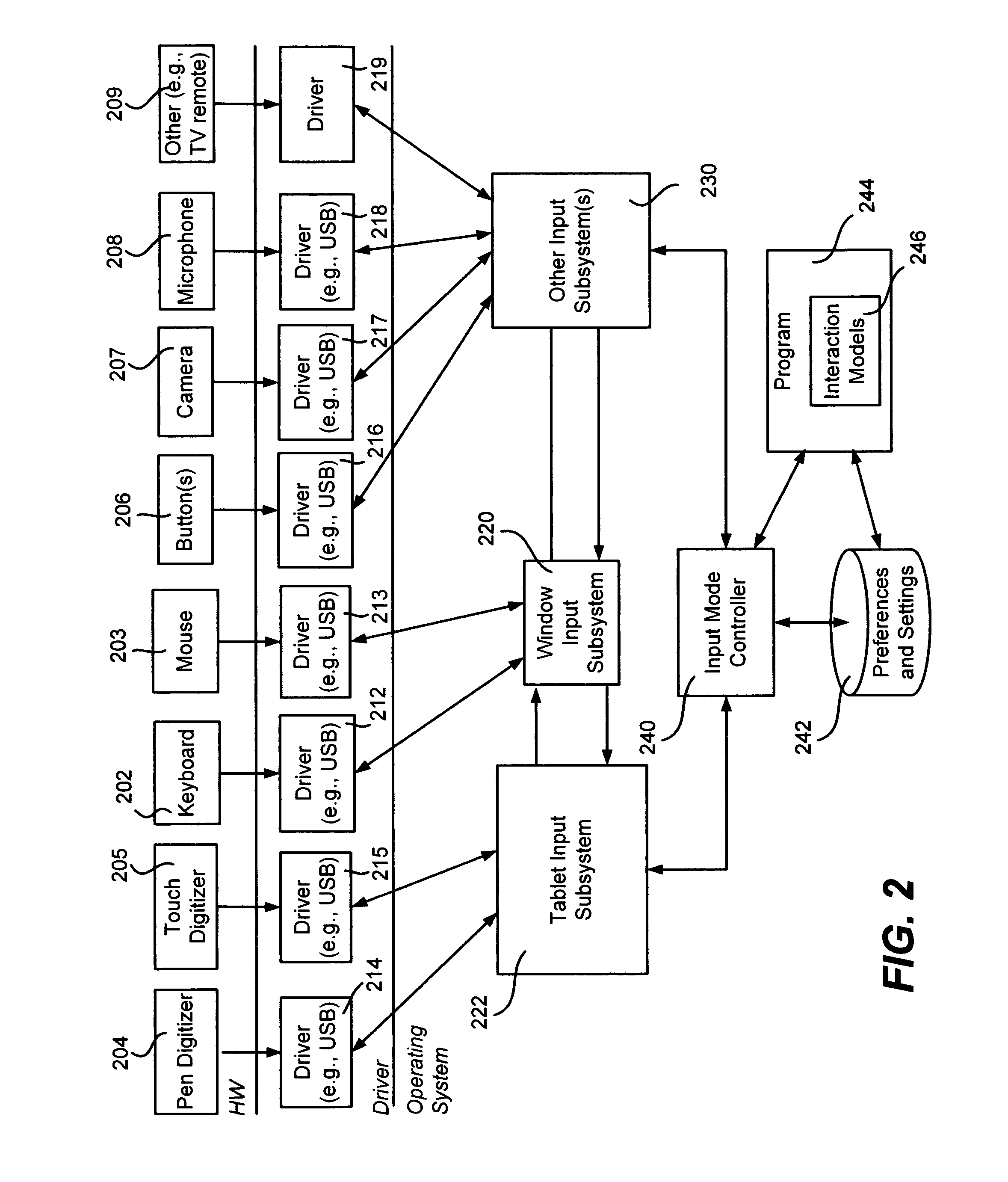
Computer interaction based upon a currently active input device
InactiveUS20060209016A1Improve interactive experienceEnhanced interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingSystems analysisHuman–computer interaction
Described is a computer-implemented system and method that dynamically detects which input device (e.g., pen or mouse) is currently in use, and based on the device, varies a program's user interaction model to better optimize the user's ability to interact with the program via that input device. A tablet input subsystem receives pen and touch data, and also obtains keyboard and mouse data. The subsystem analyzes the data and determines which input device is currently active. The active device is mapped to an interaction model, whereby different user interface appearances, behaviors and the like may be presented to the user to facilitate improved interaction. For example, a program may change the size of user interface elements to enable the user to more accurately scroll and make selections. Timing, tolerances and thresholds may change. Pen hovering can become active, and interaction events received at the same location can be handled differently.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
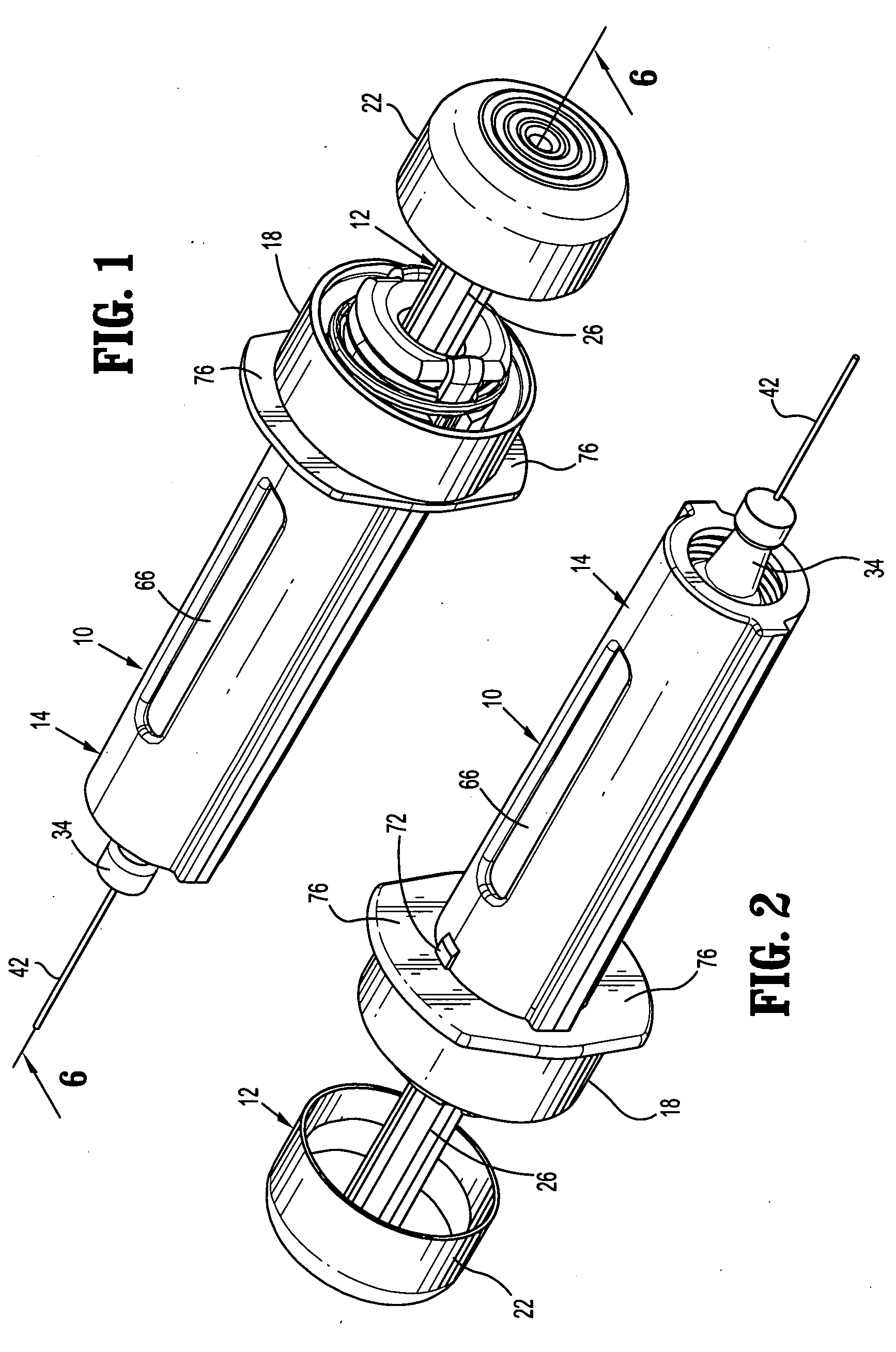
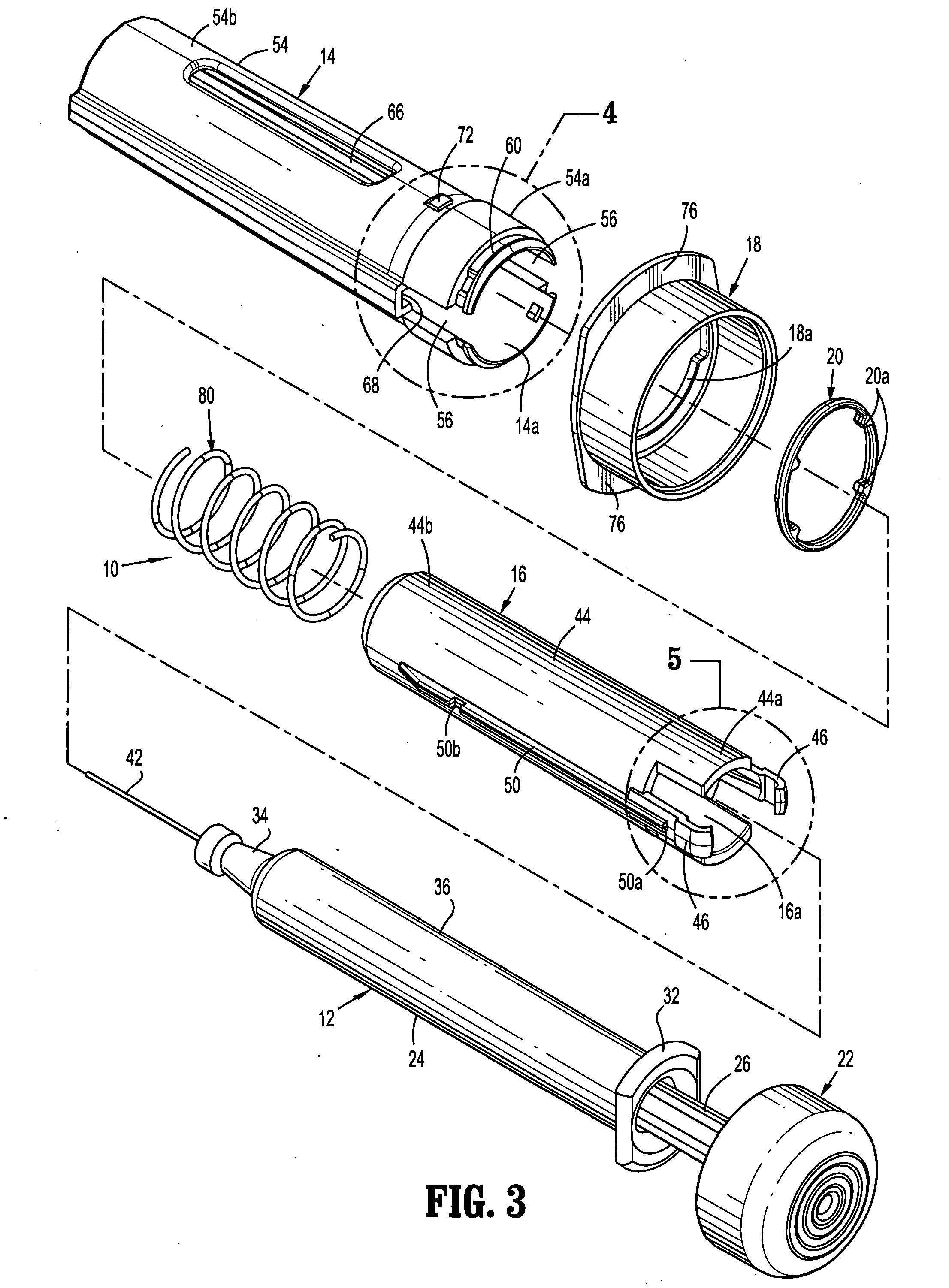
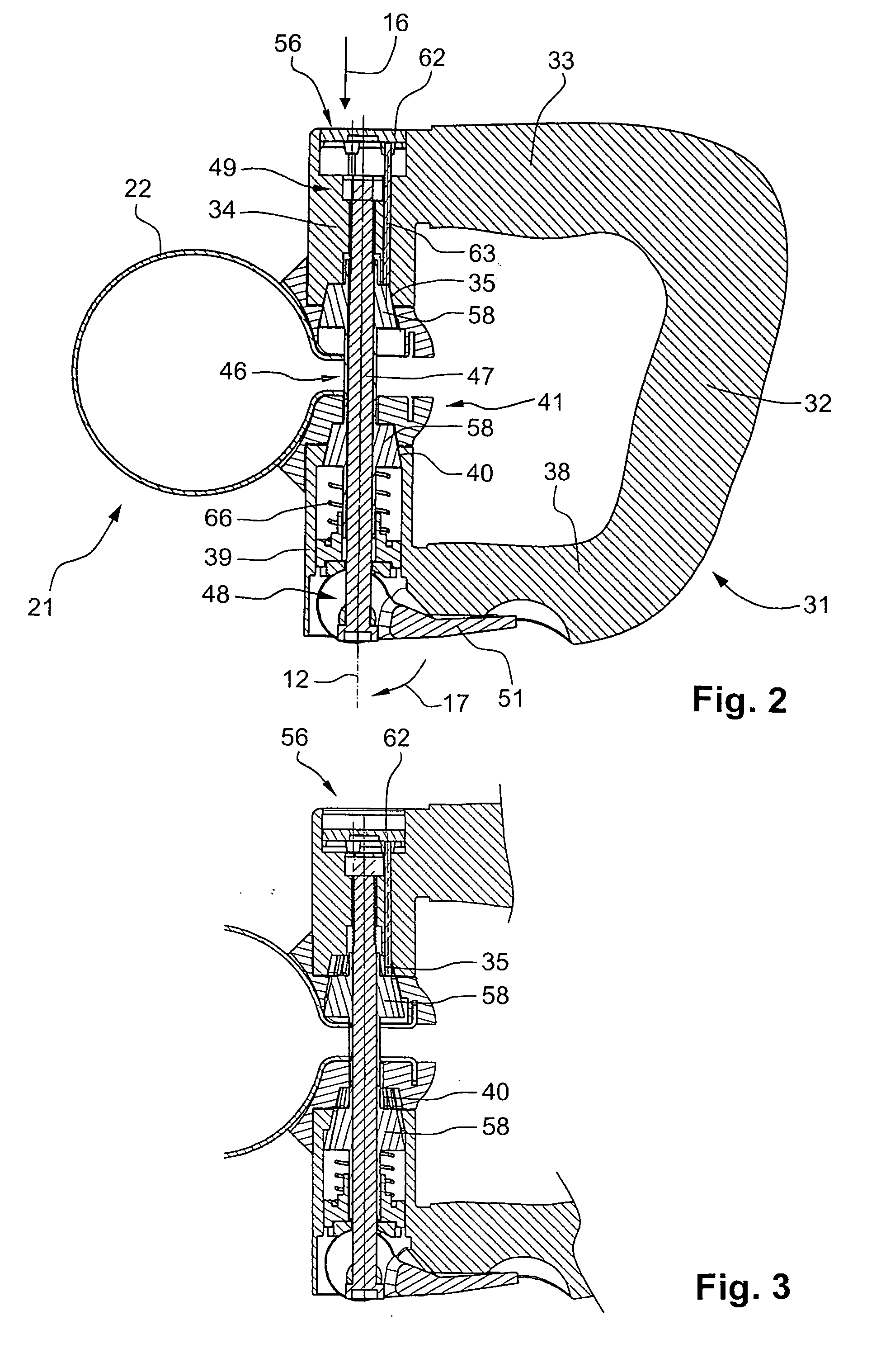
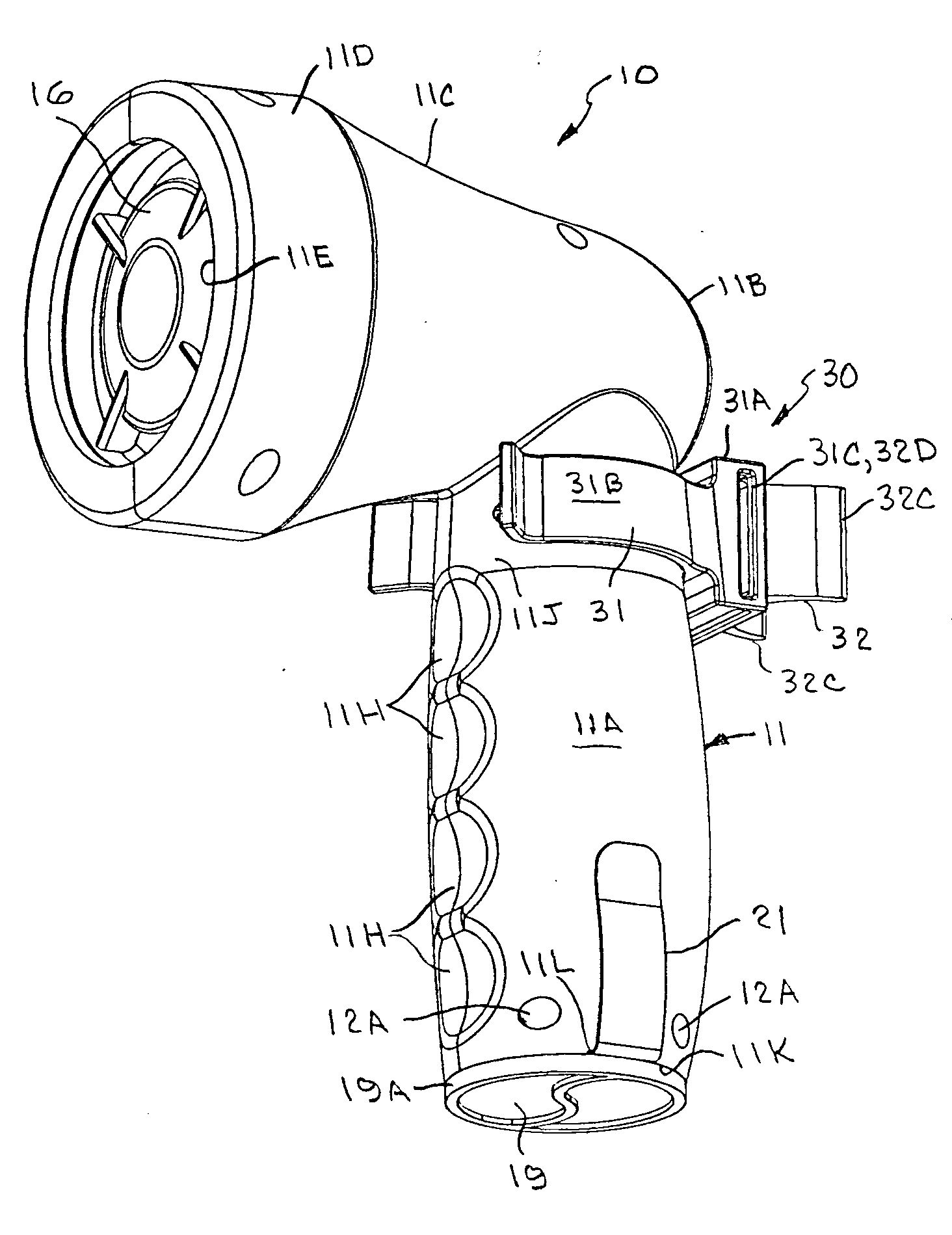
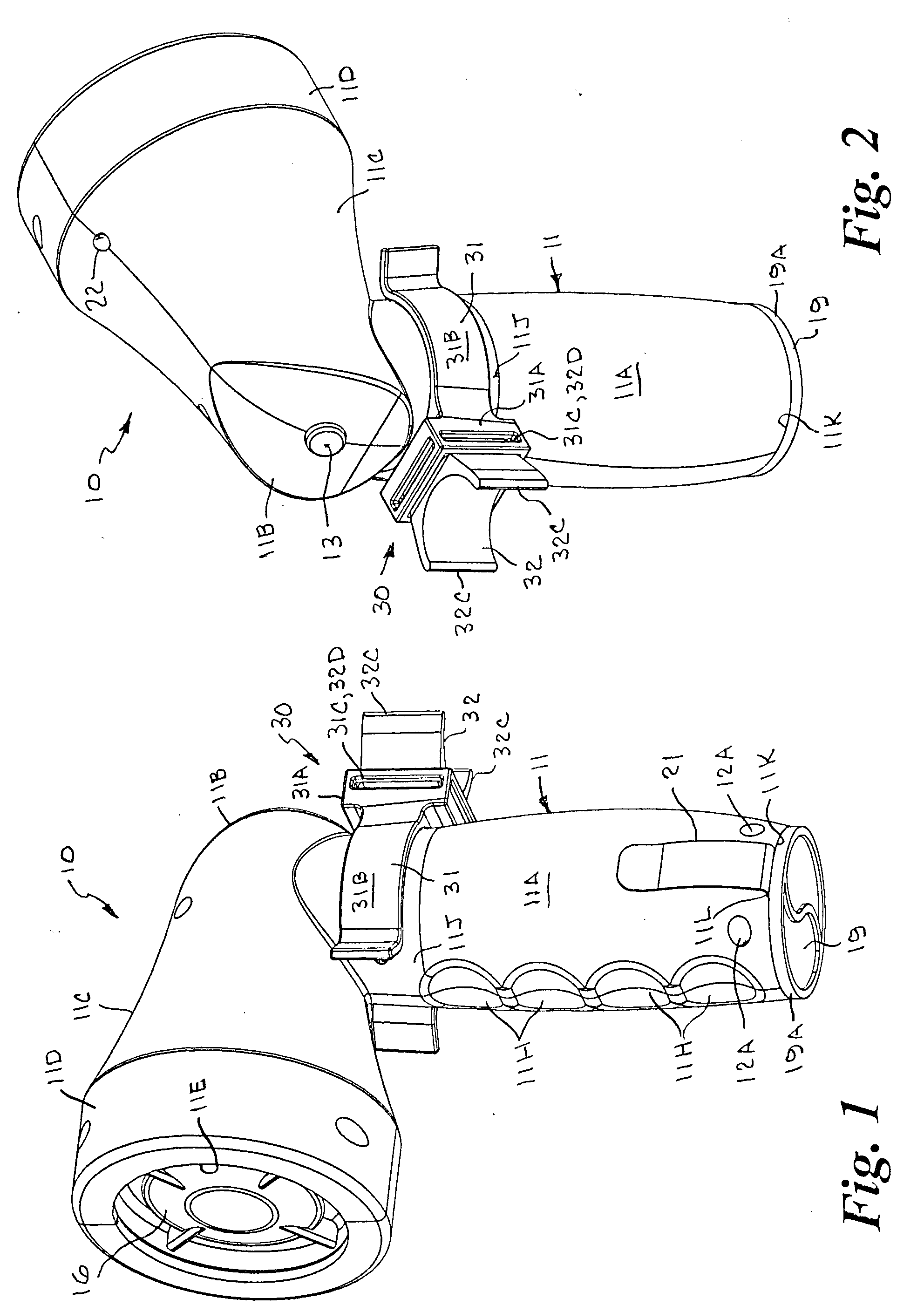
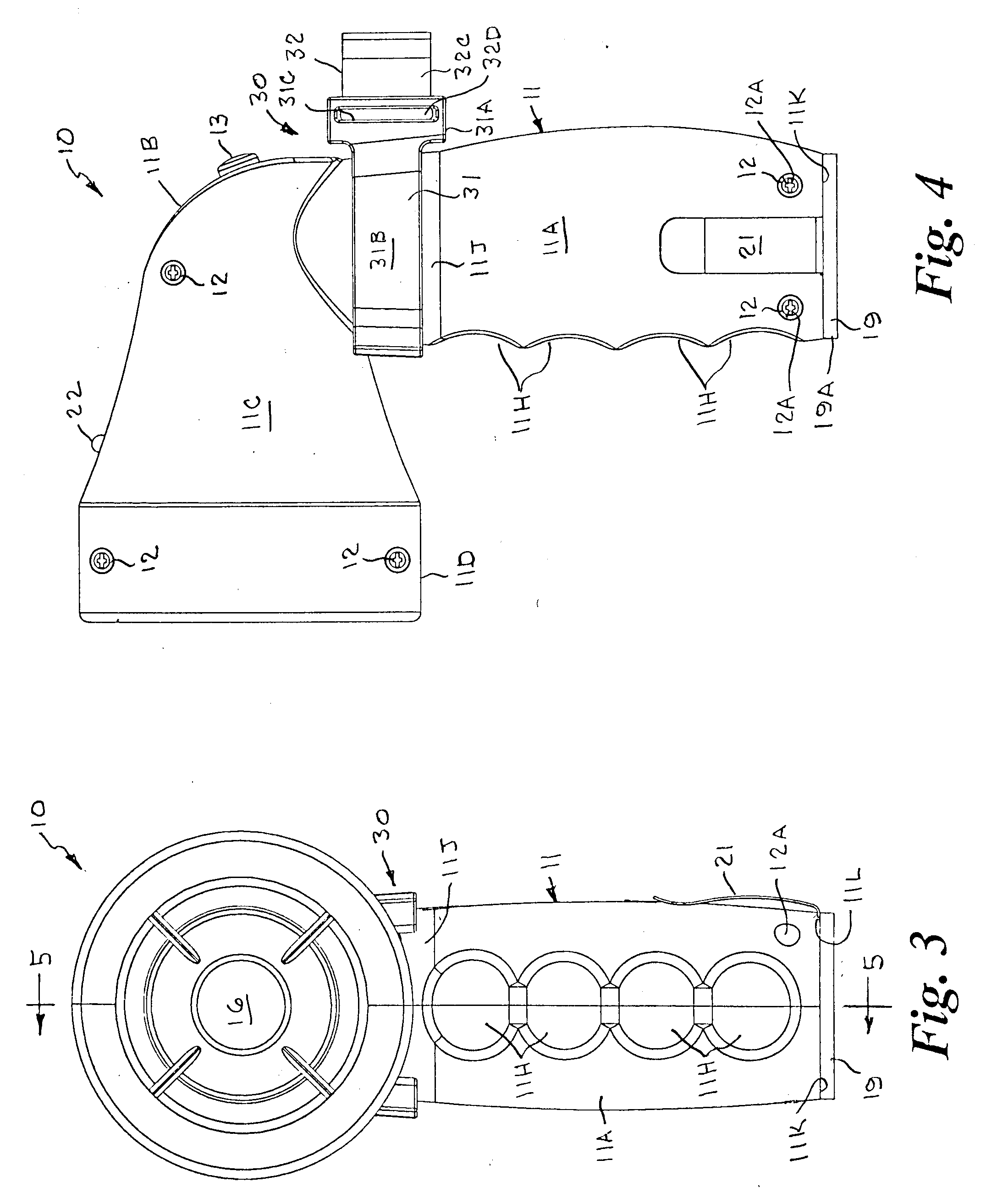
Passive latch ring safety shield for injection devices
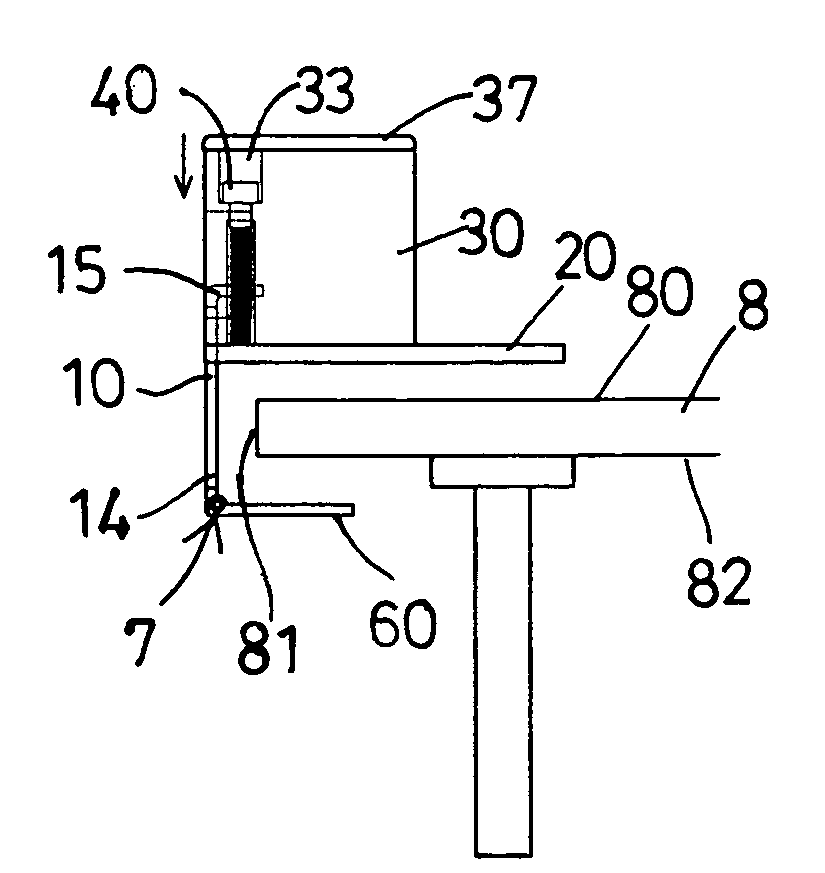
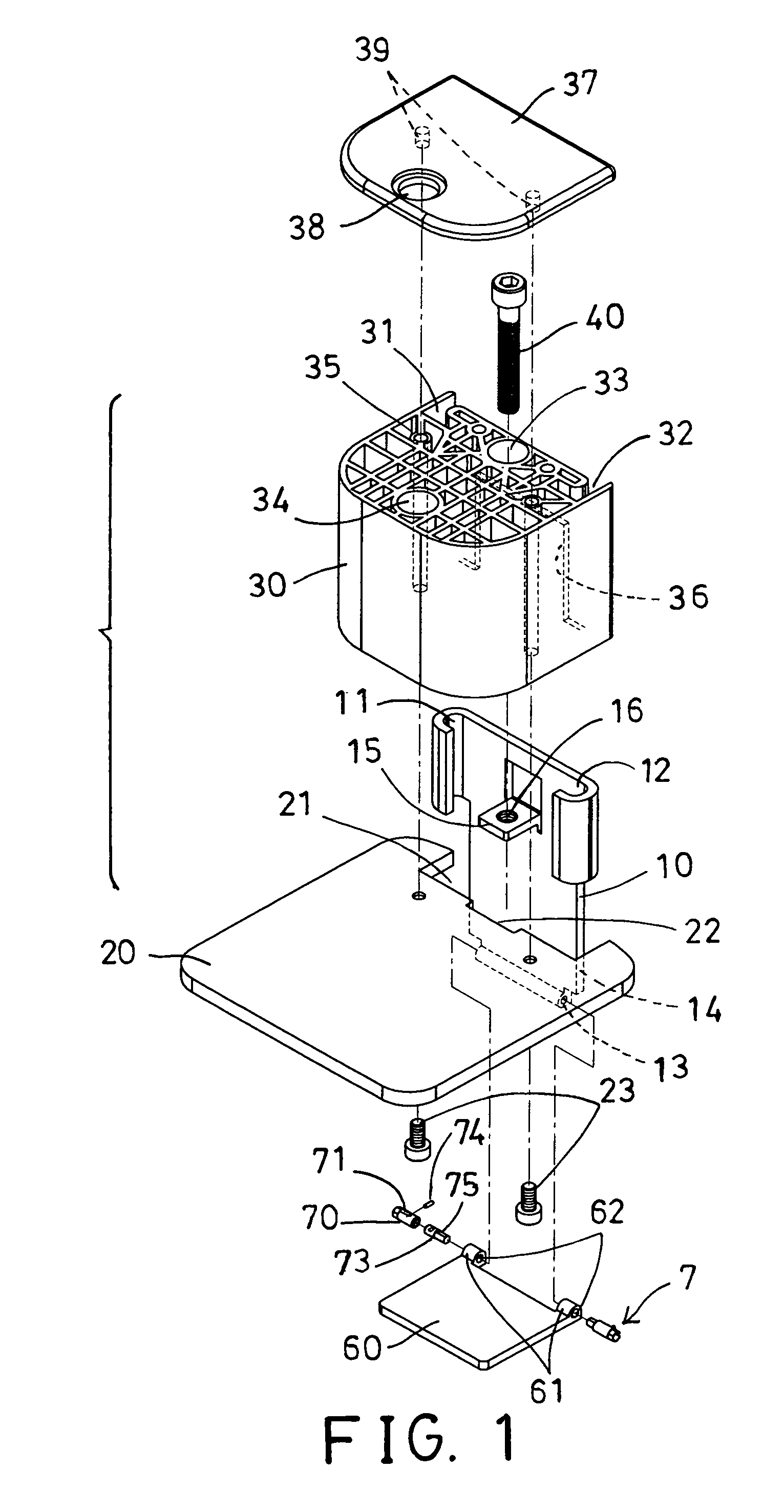
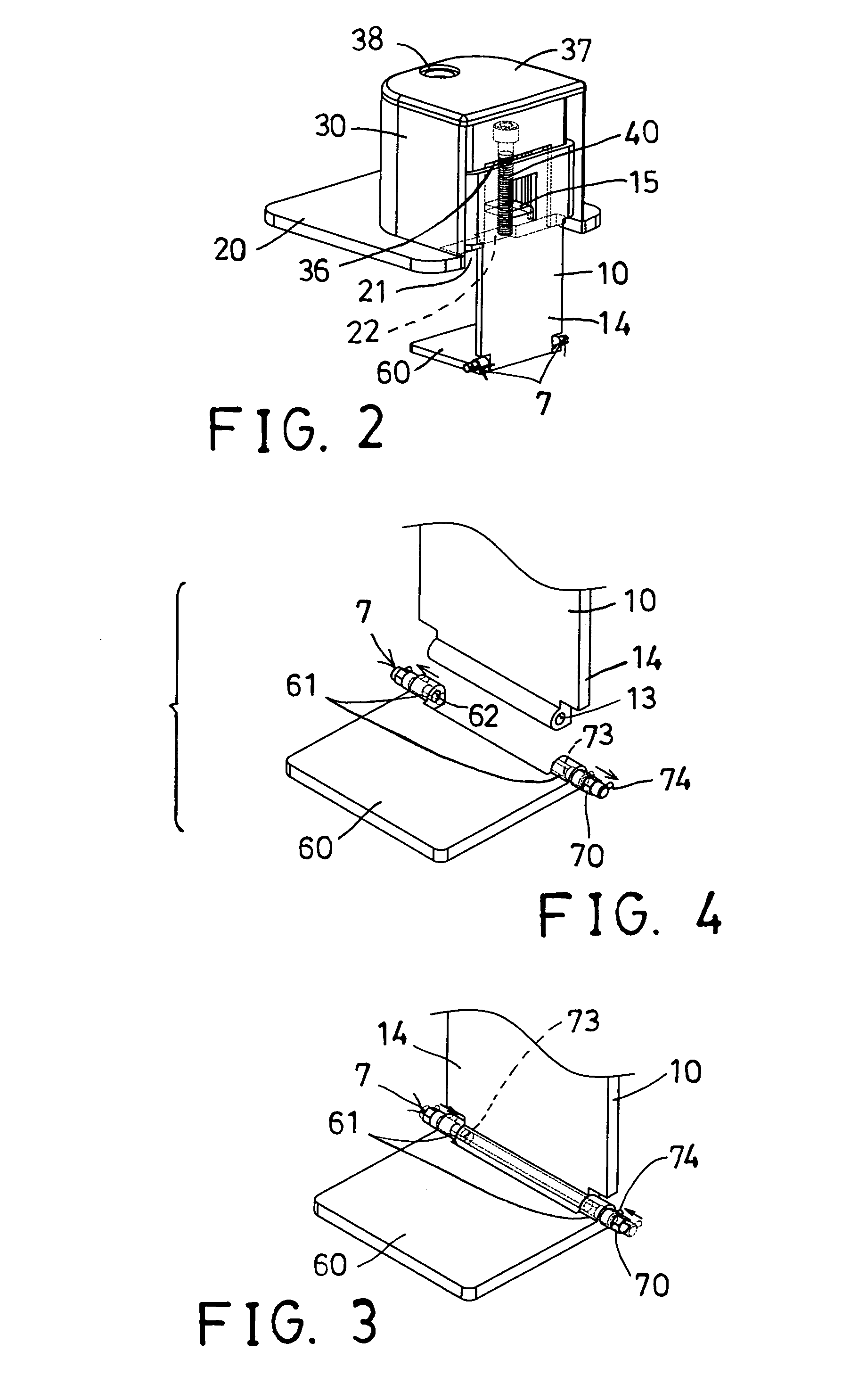
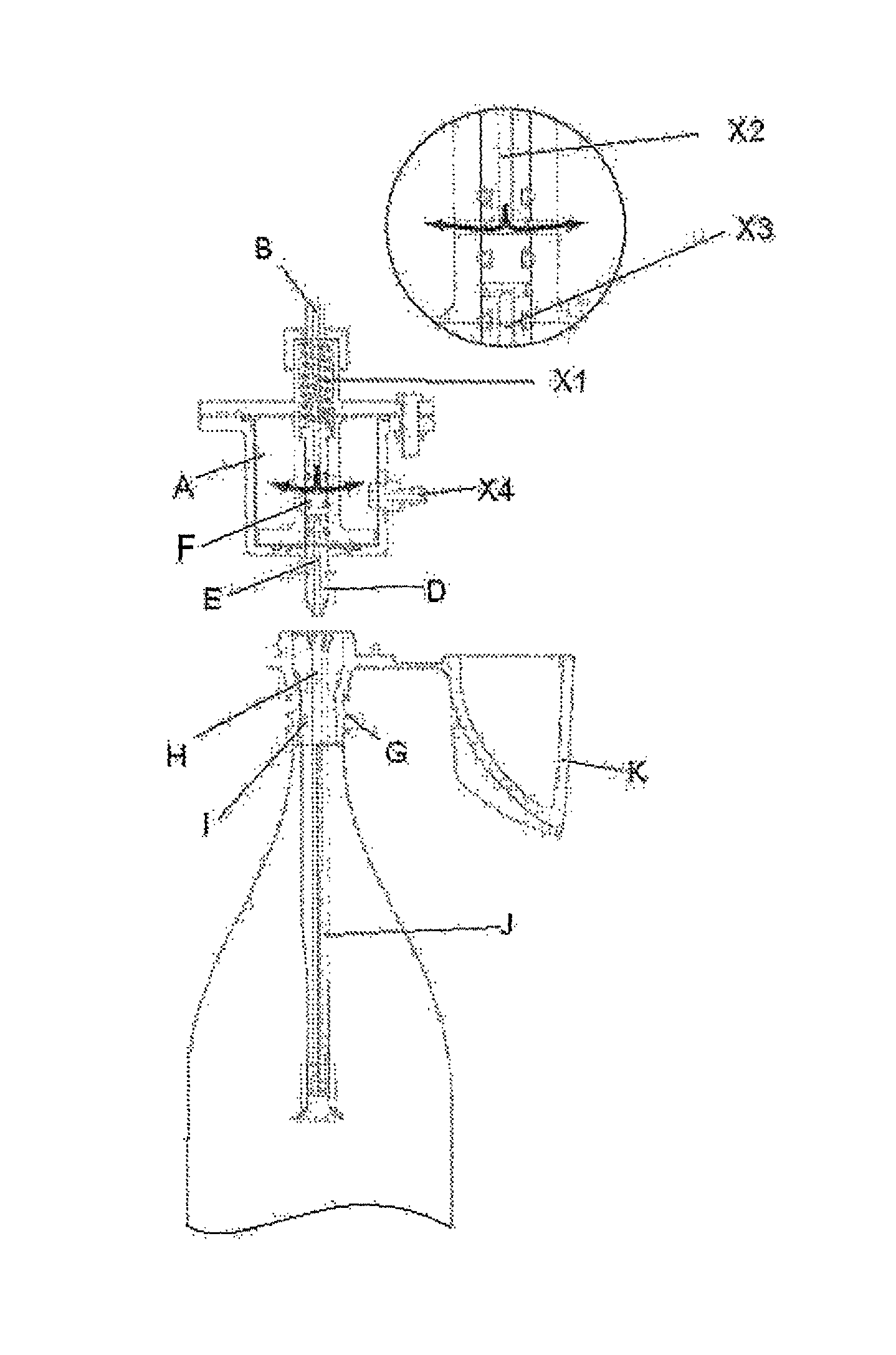
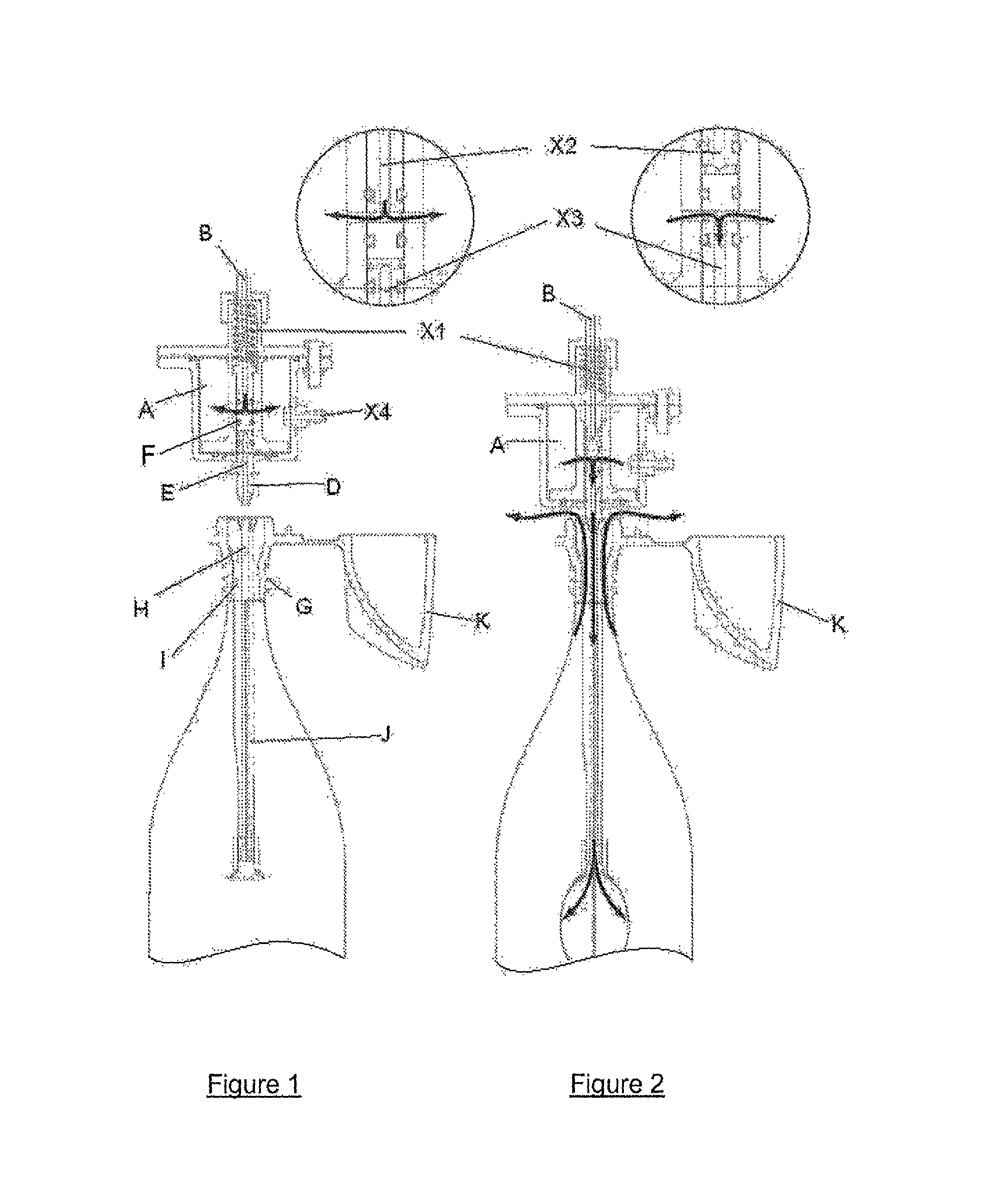
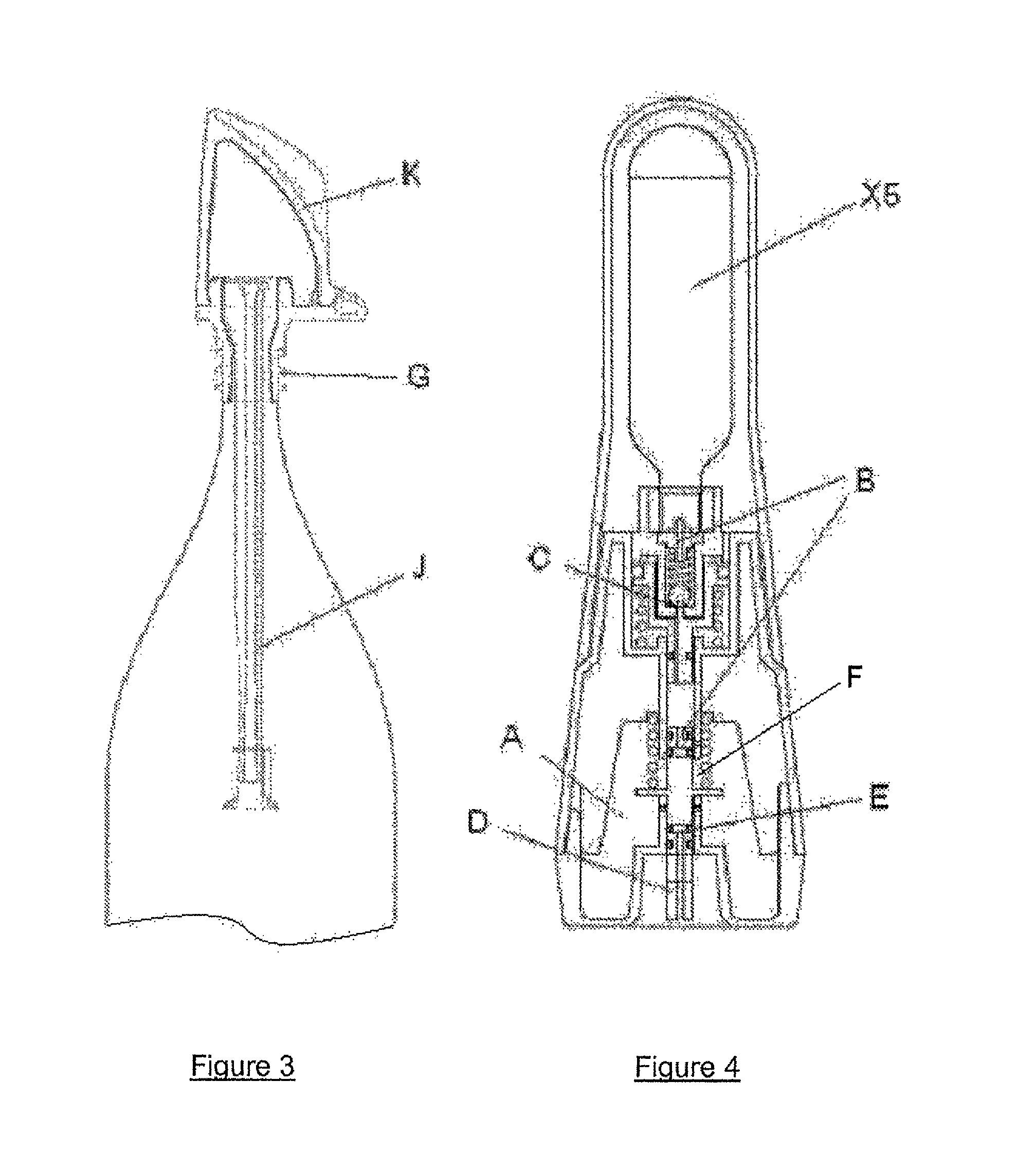
InactiveUS20070239117A1Easy to graspSimplified actuationInfusion needlesInjection deviceMedical treatment
A passive latch ring safety shield for use with medical injection devices is disclosed. The safety shield includes an inner sheath defining a channel which is dimensioned to receive an injection device and an outer sheath defining a channel which is dimensioned to slidably receive the inner sheath. A biasing member is provided between the inner and outer sheaths to urge the outer sheath in relation to the inner sheath from a retracted position to an advanced position. A resilient latch ring is supported on the safety shield in a position to prevent movement of the outer sheath in relation to the inner sheath from a retracted to and advanced position. The latch ring is deformable in response to actuation of the injection device to disengage the outer sheath from the inner sheath and allow the biasing member to move the outer sheath from the retracted position to the advanced position in relation to the inner sheath.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
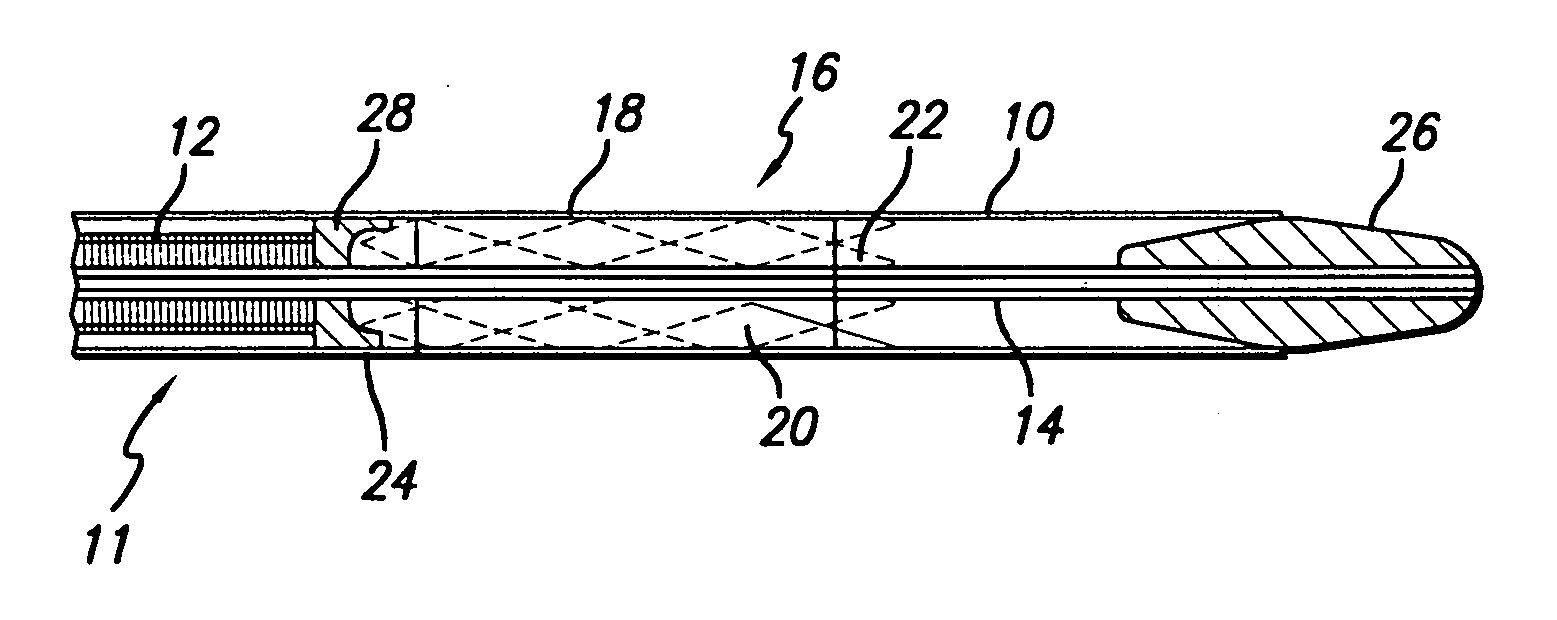
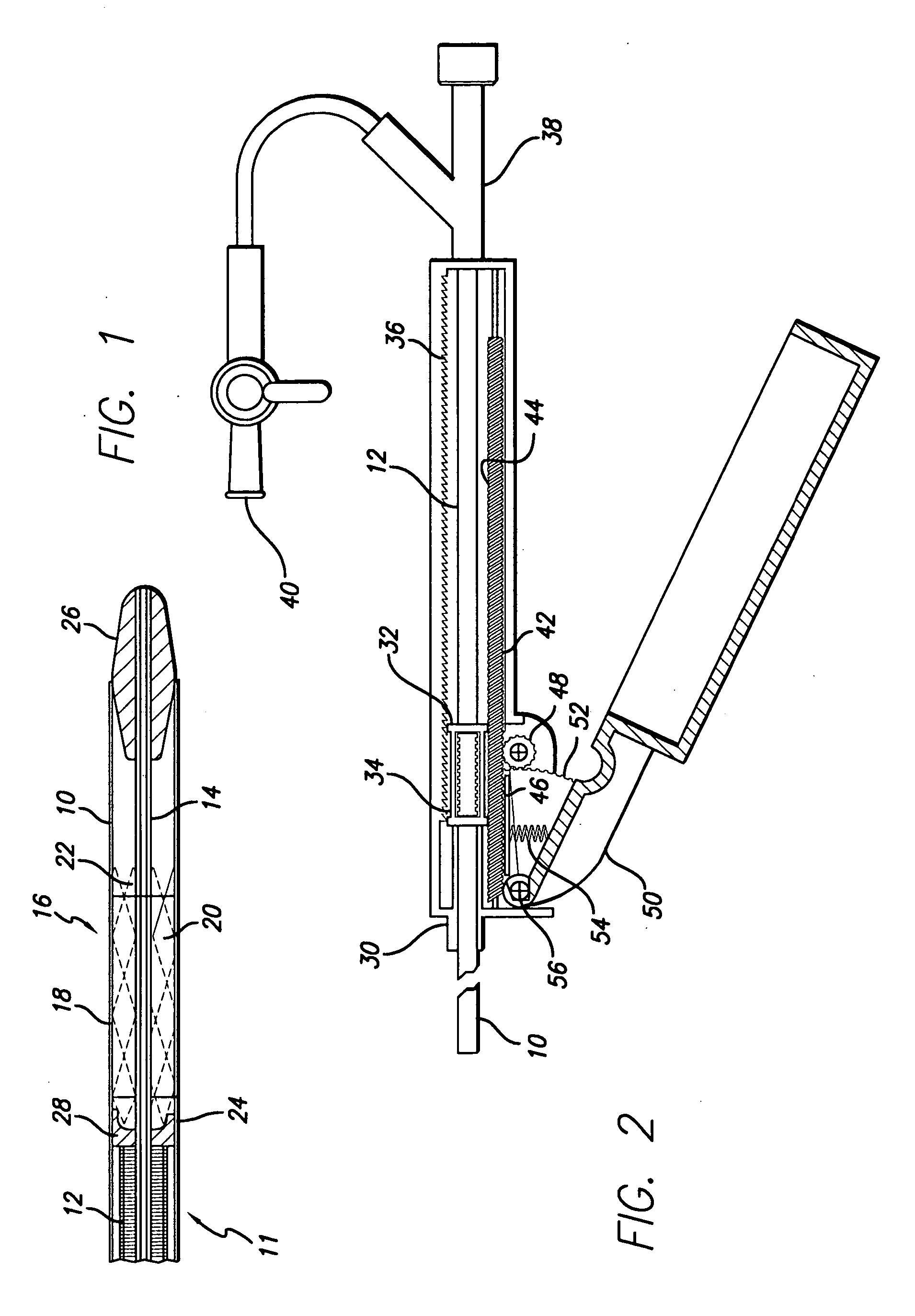
Delivery mechanism for implantable stent
A delivery system including an inner catheter with a reinforcing element and an outer catheter having a proximal end attached to a movable member. An abutment element may be attached to a distal end of the reinforcing element, configured to engage an implantable device disposed between the inner catheter and the outer catheter.
Owner:BARD PERIPHERAL VASCULAR
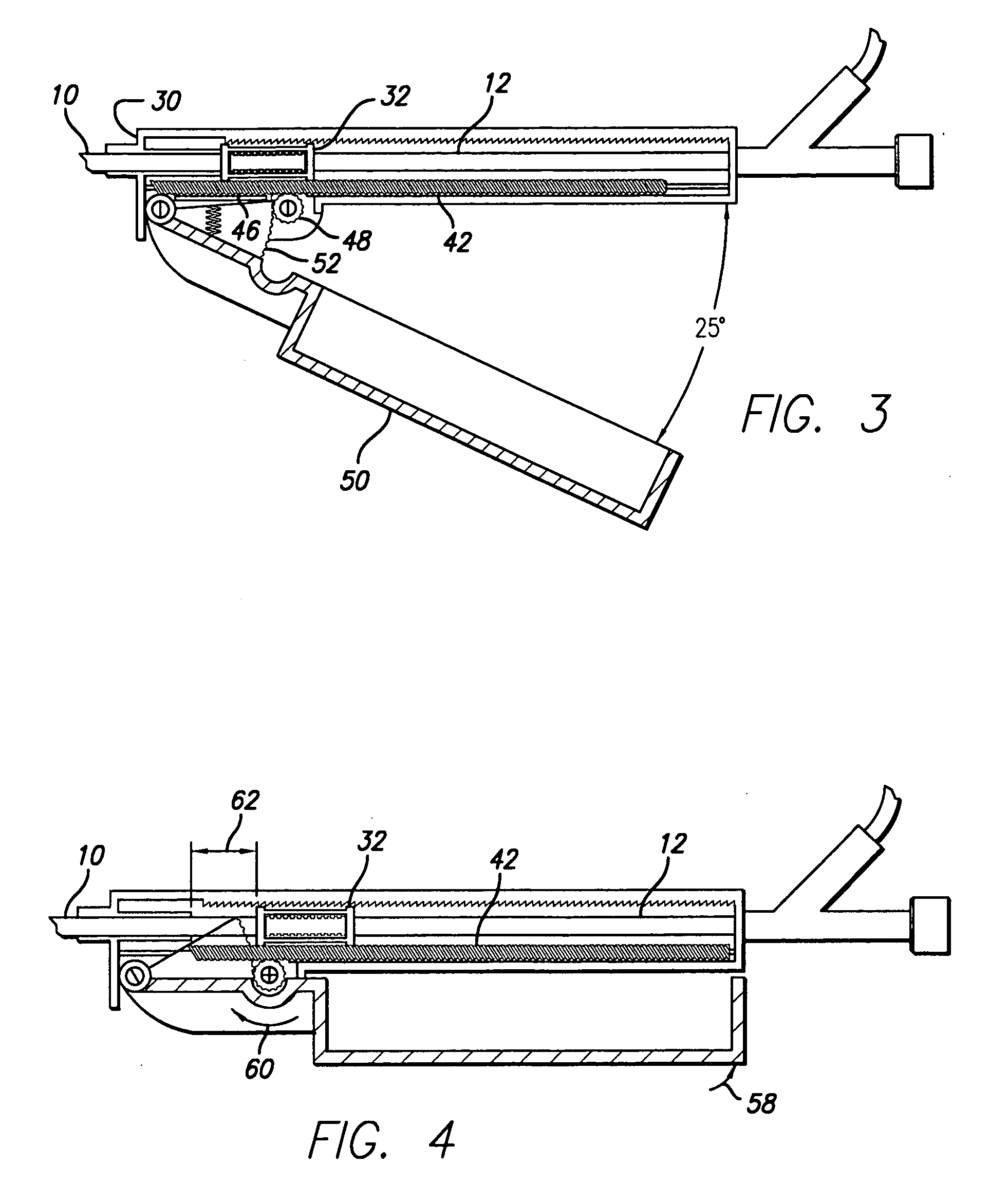
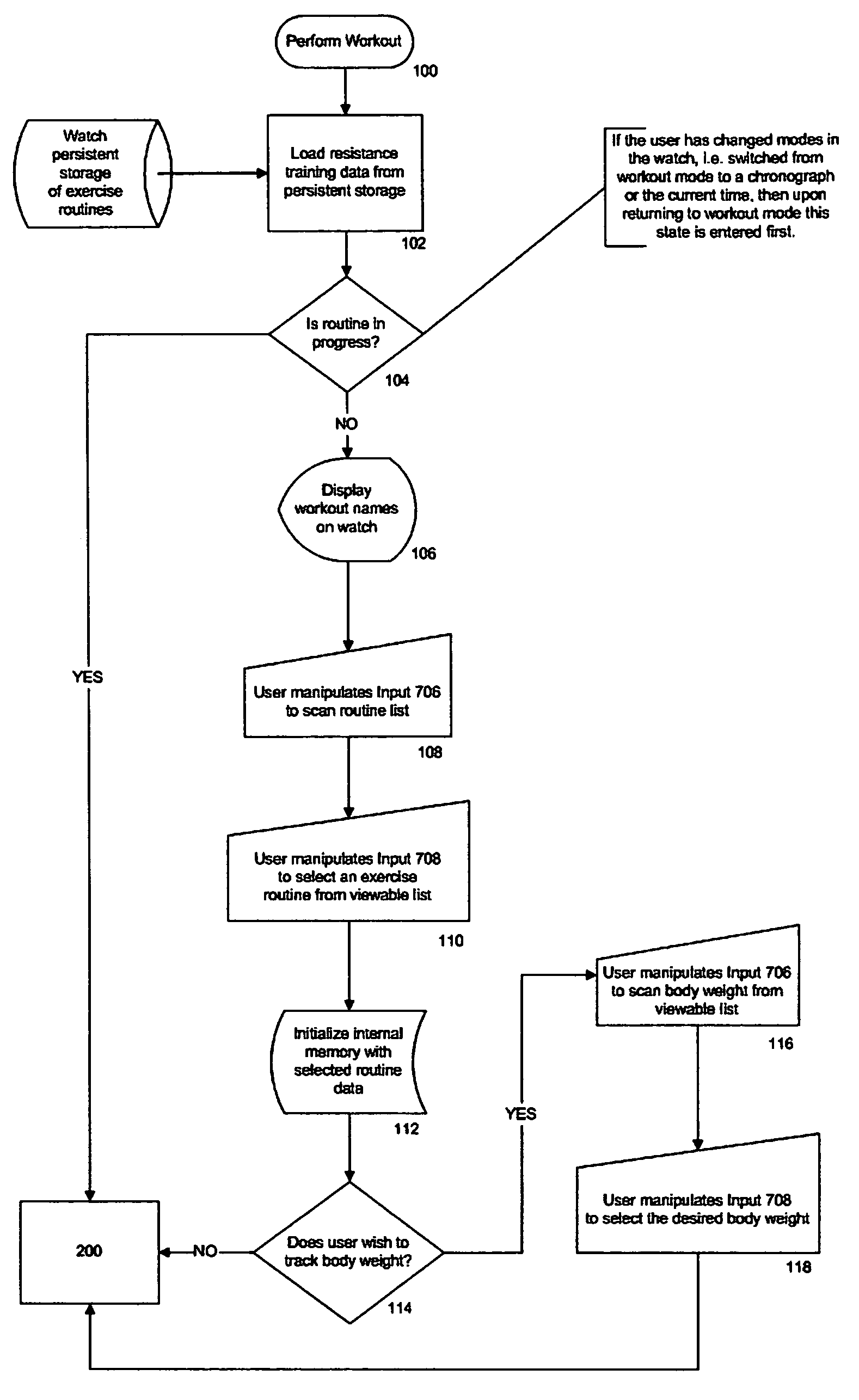
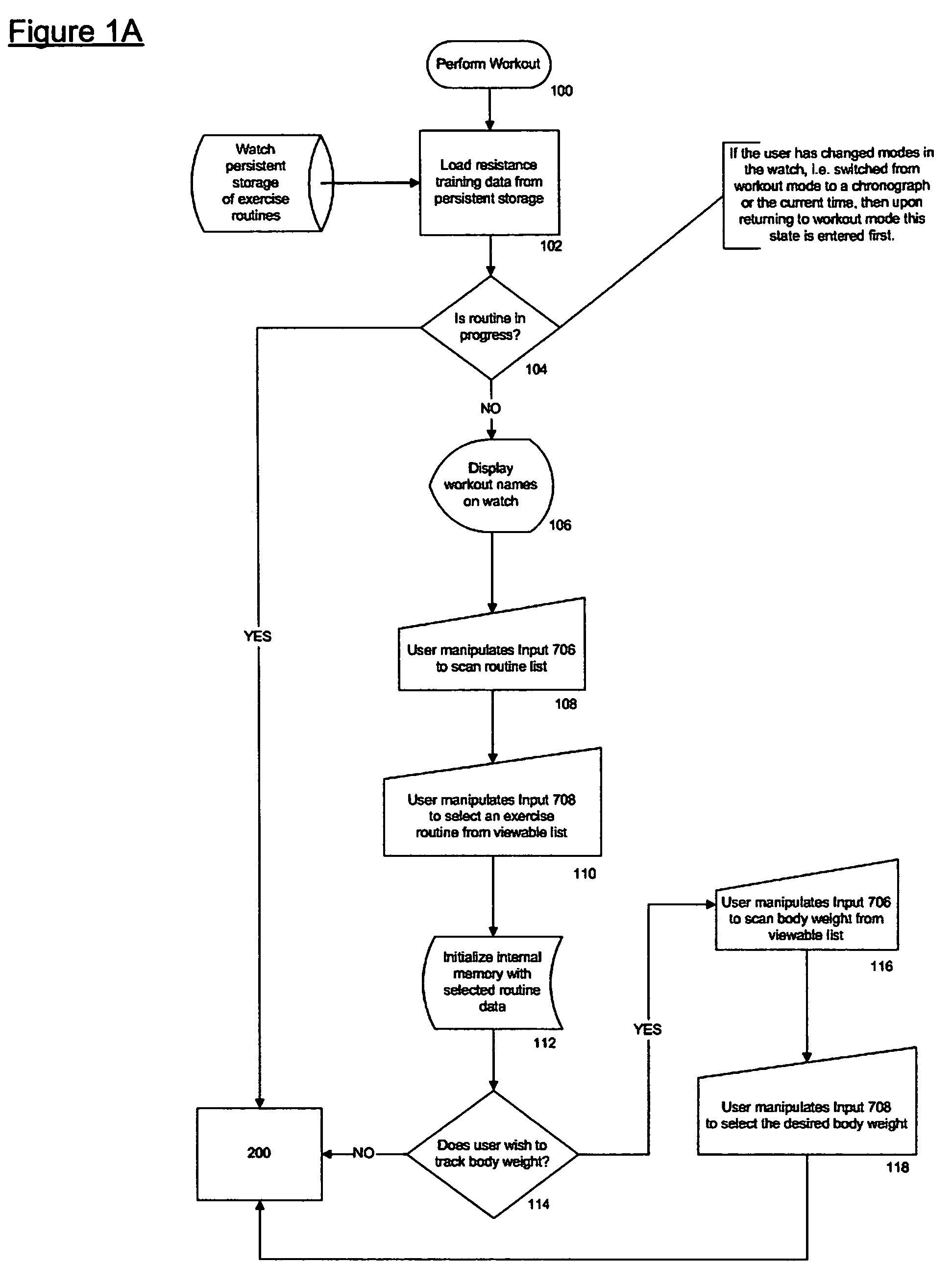
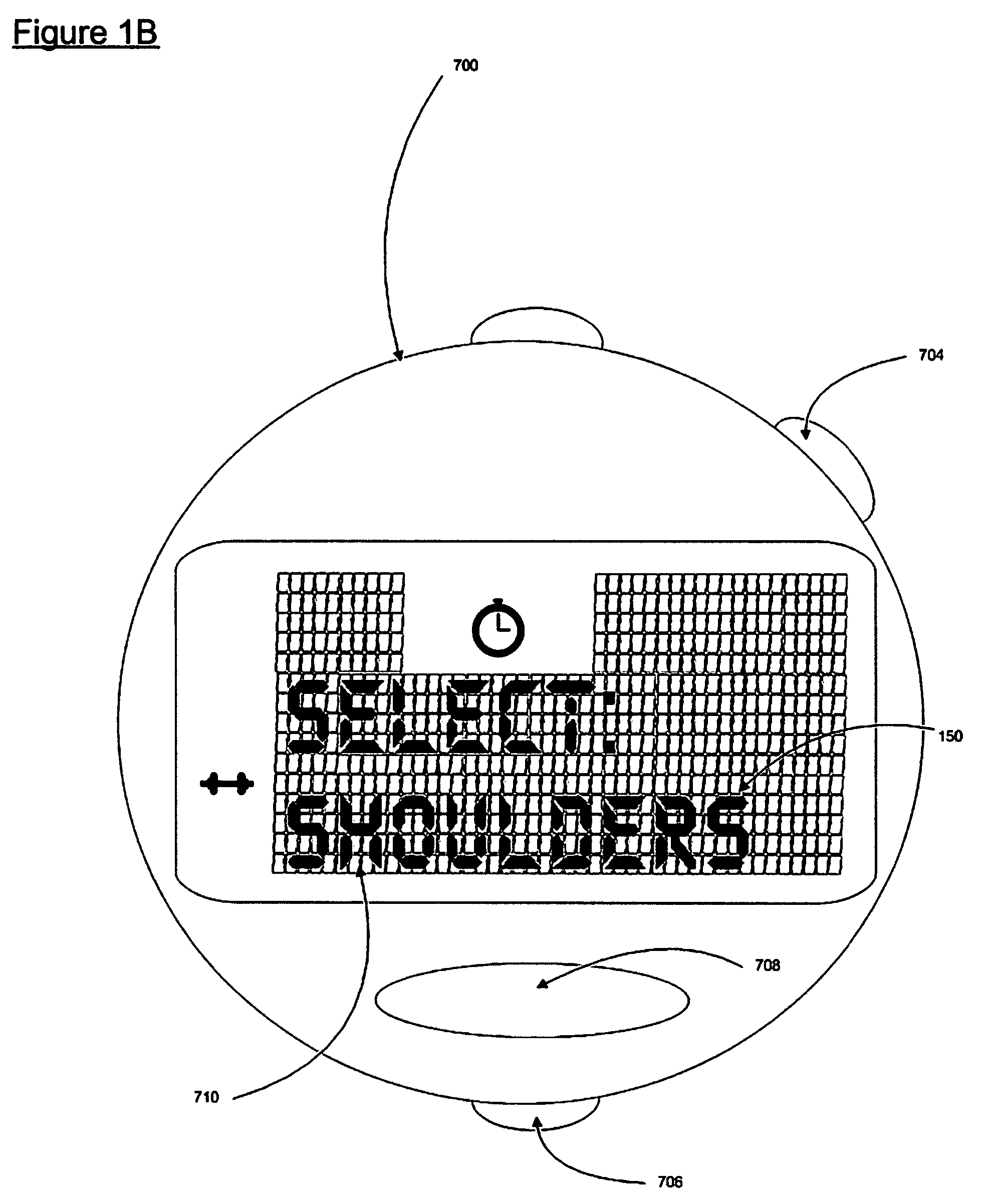
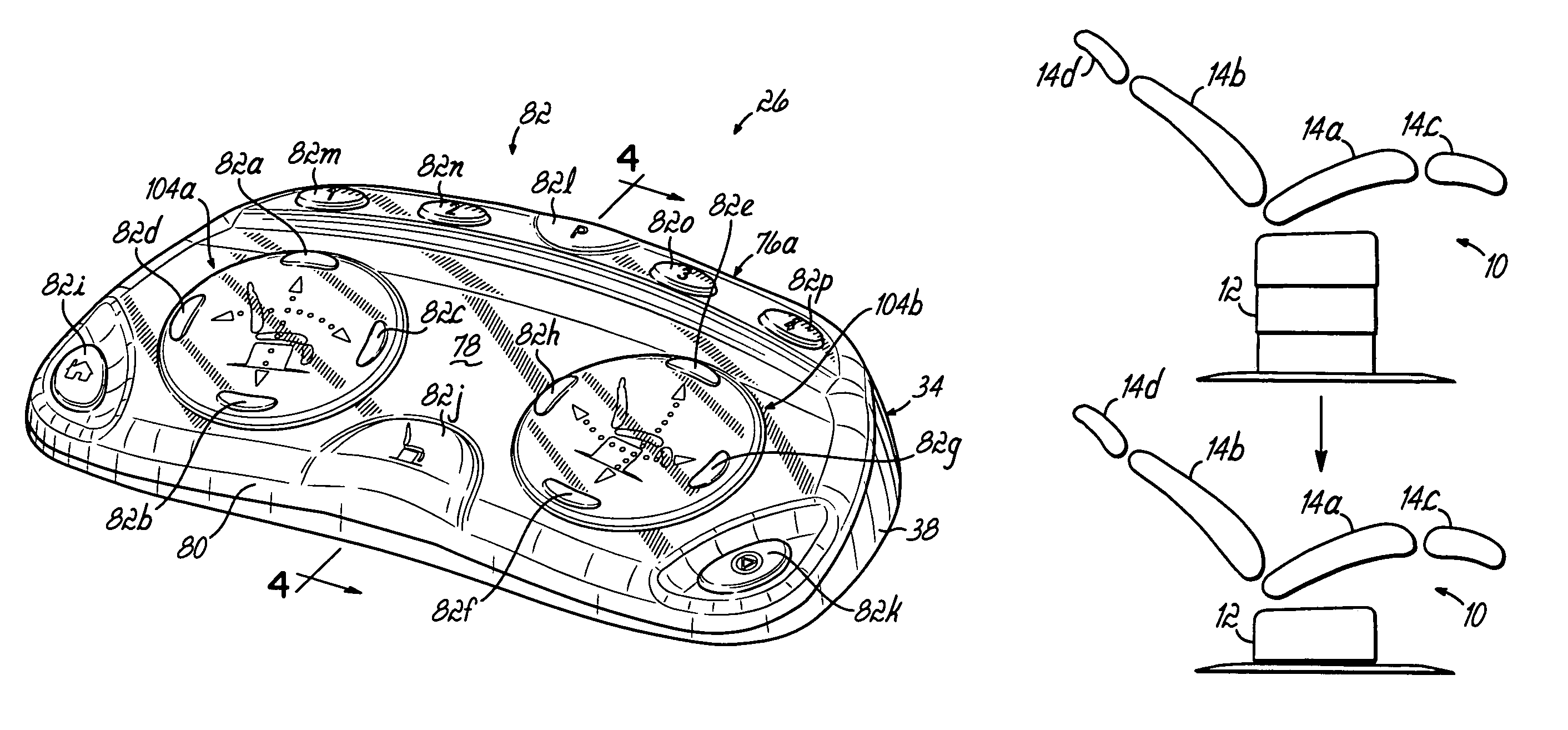
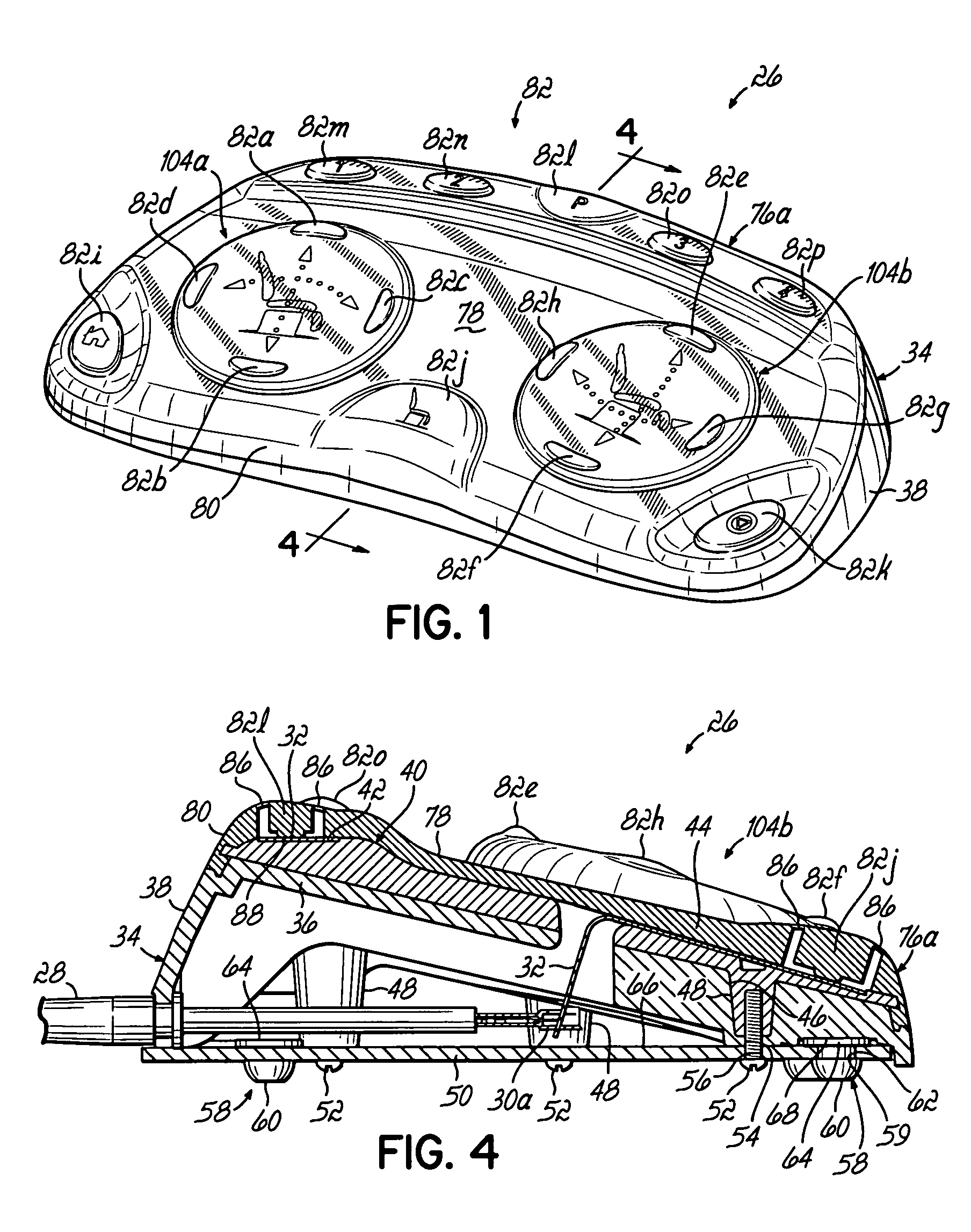
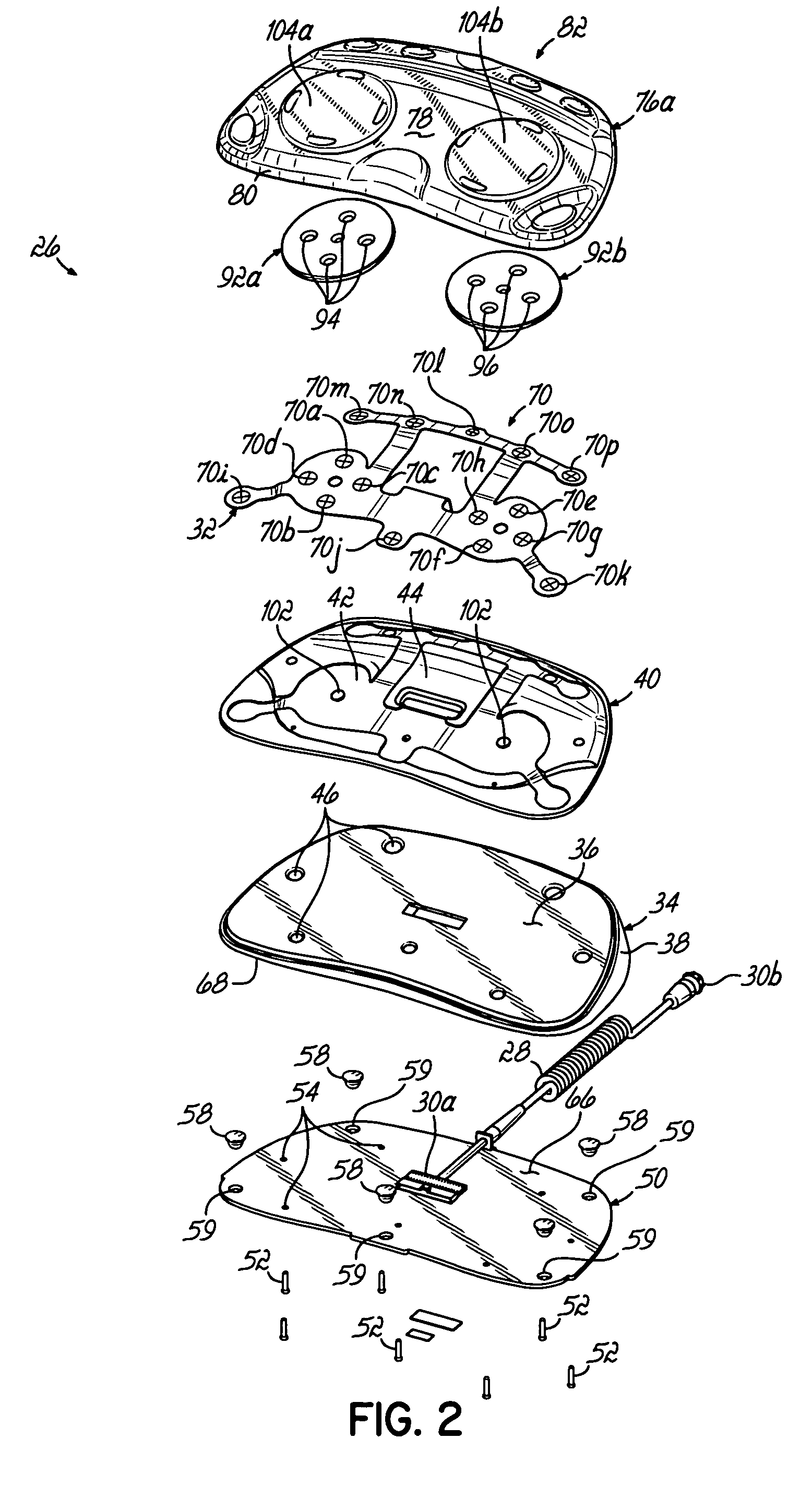
User interface for a resistance training device and method of use
InactiveUS7510508B2Easy to trackReduce trainingPhysical therapies and activitiesClubsResistance trainingUser interface
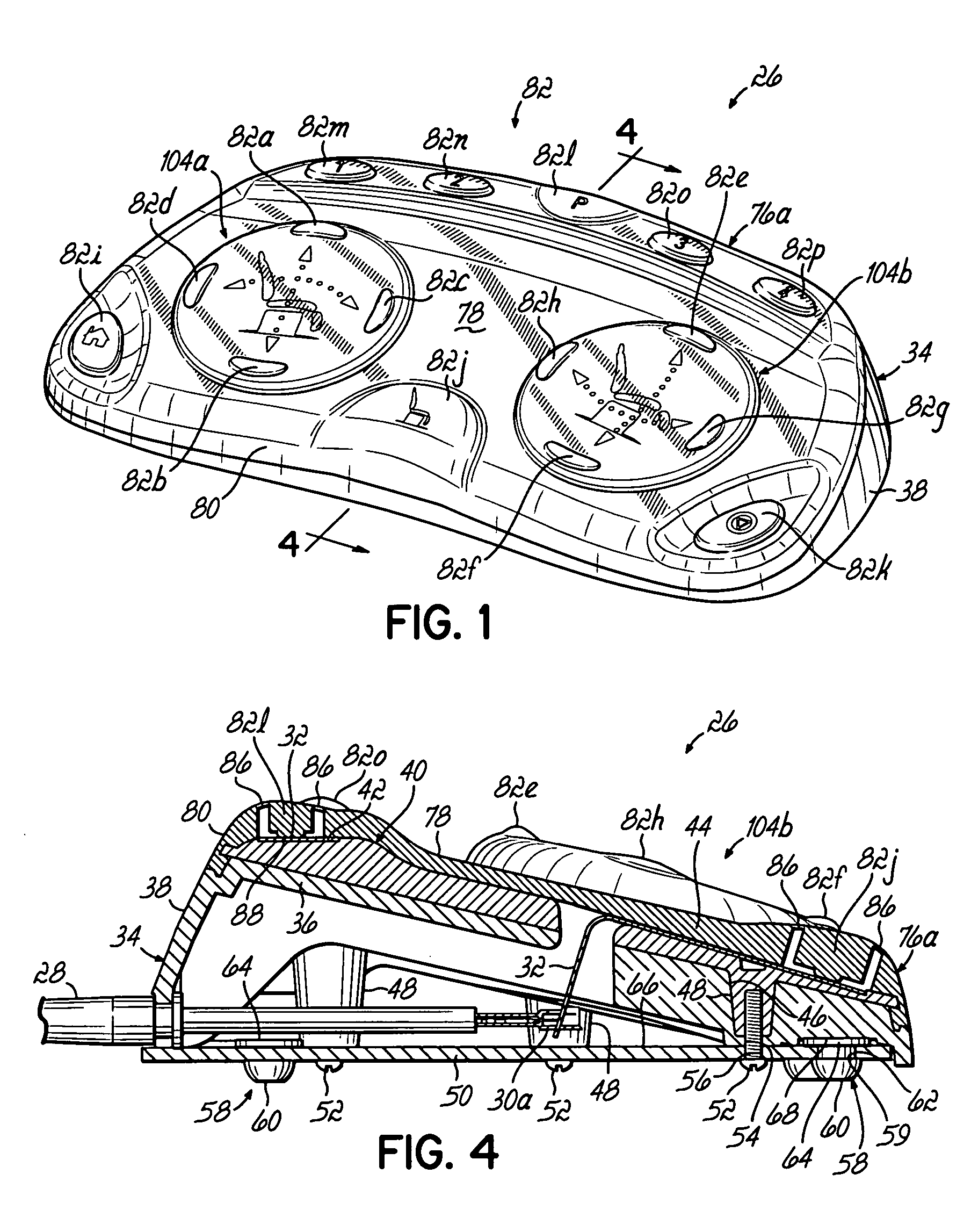
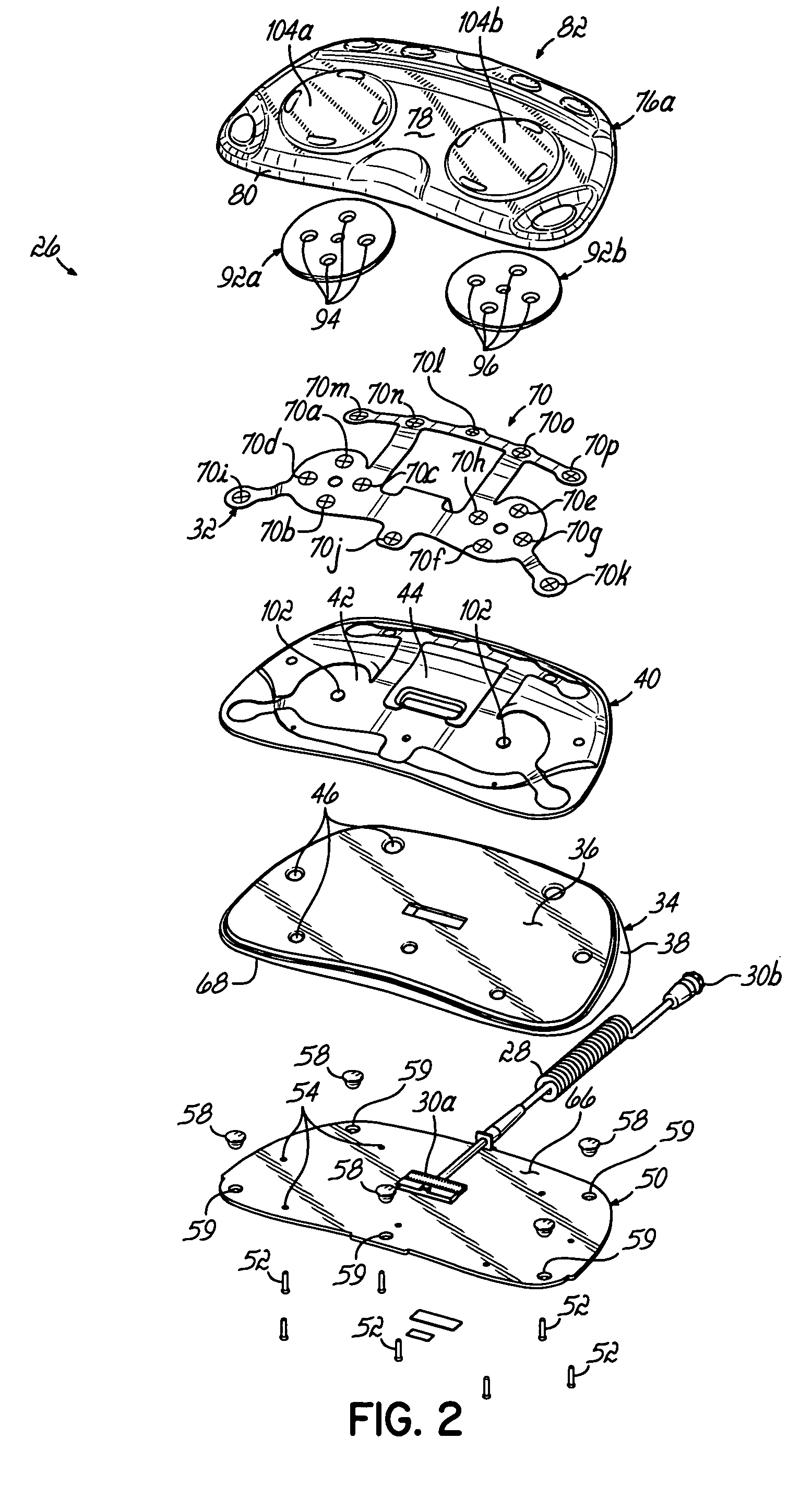
A system, method, and device for recording and tracking resistance training parameters in connection with a resistance training workout. A specially configured portable recording device has a very compact user interface having an input device with very few inputs. A user may record resistance training parameters directly on the recording device both quickly and easily with few and simple keystrokes, resulting in an improved recording process. A personal trainer or strength coach may track the workouts of multiple exercisers with increased convenience. In a particularly preferred embodiment, the recording device is provided in the body of a sport watch.
Owner:SANTOMASSIMO ROD N +1
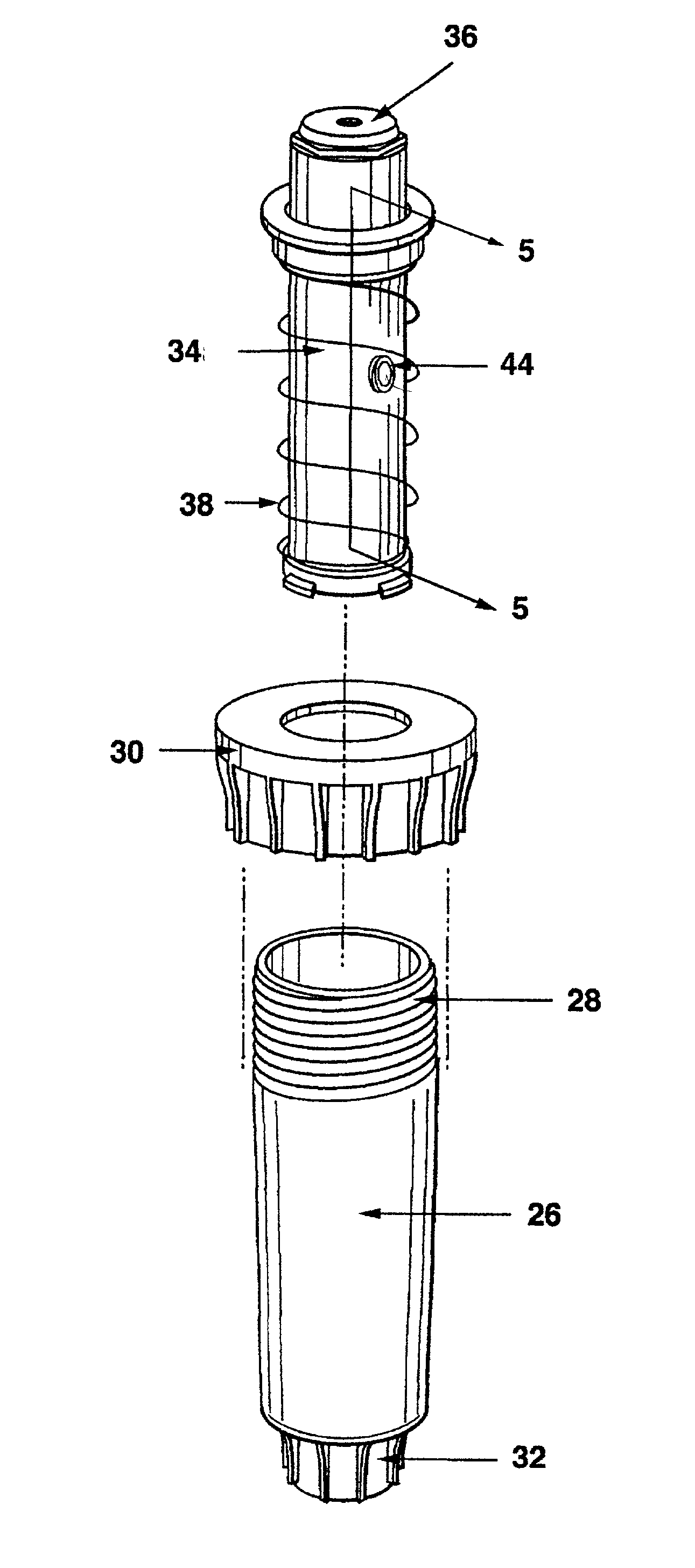
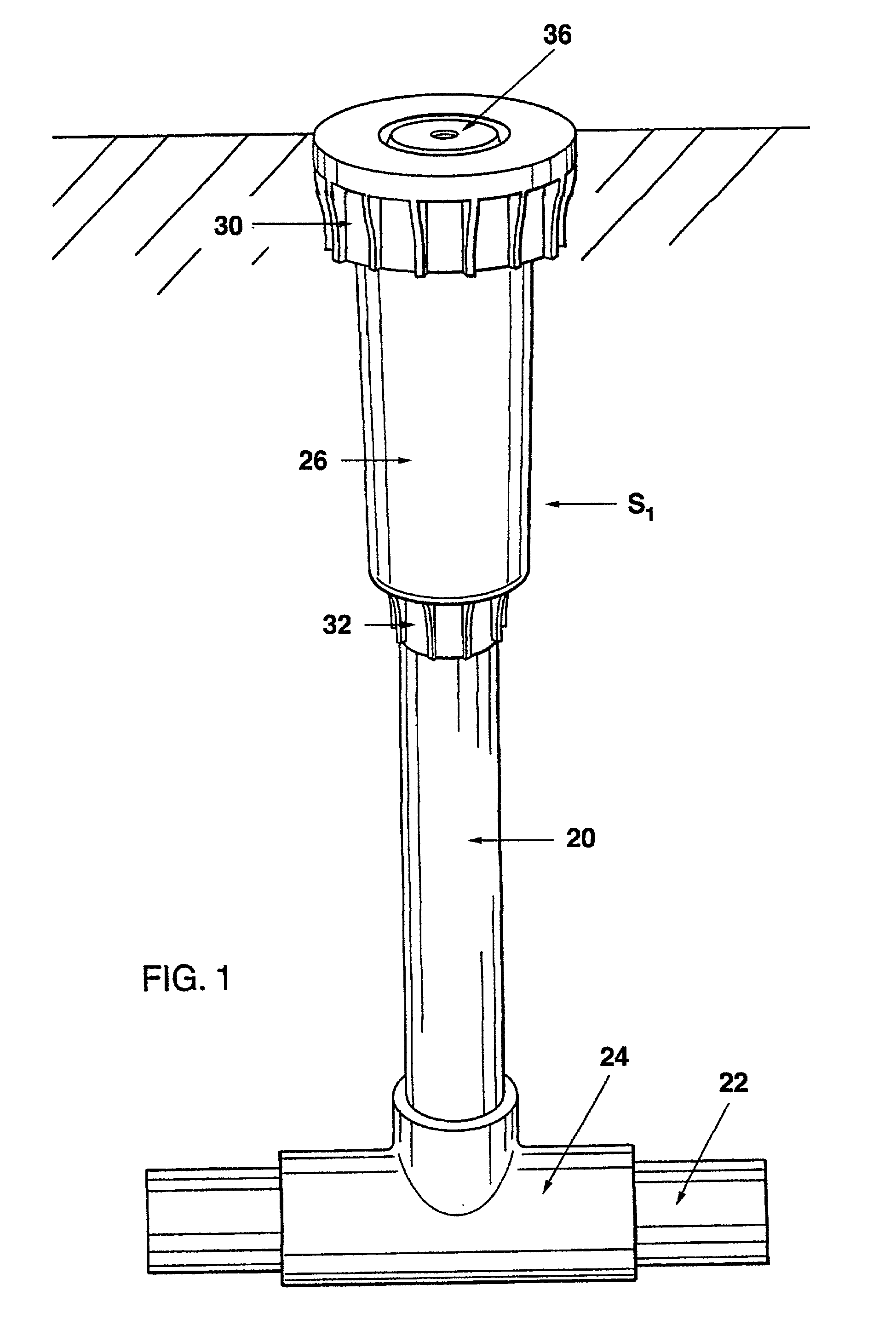
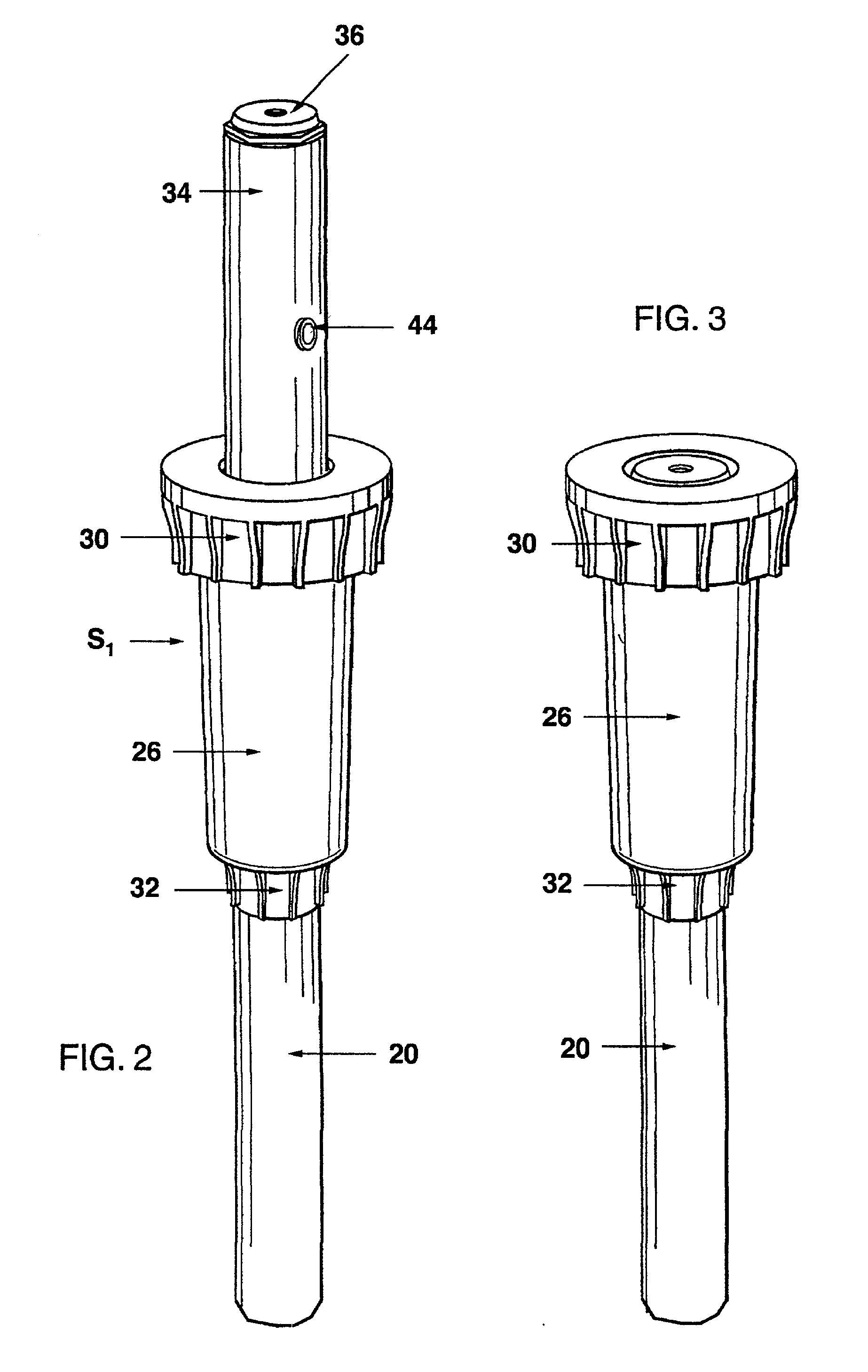
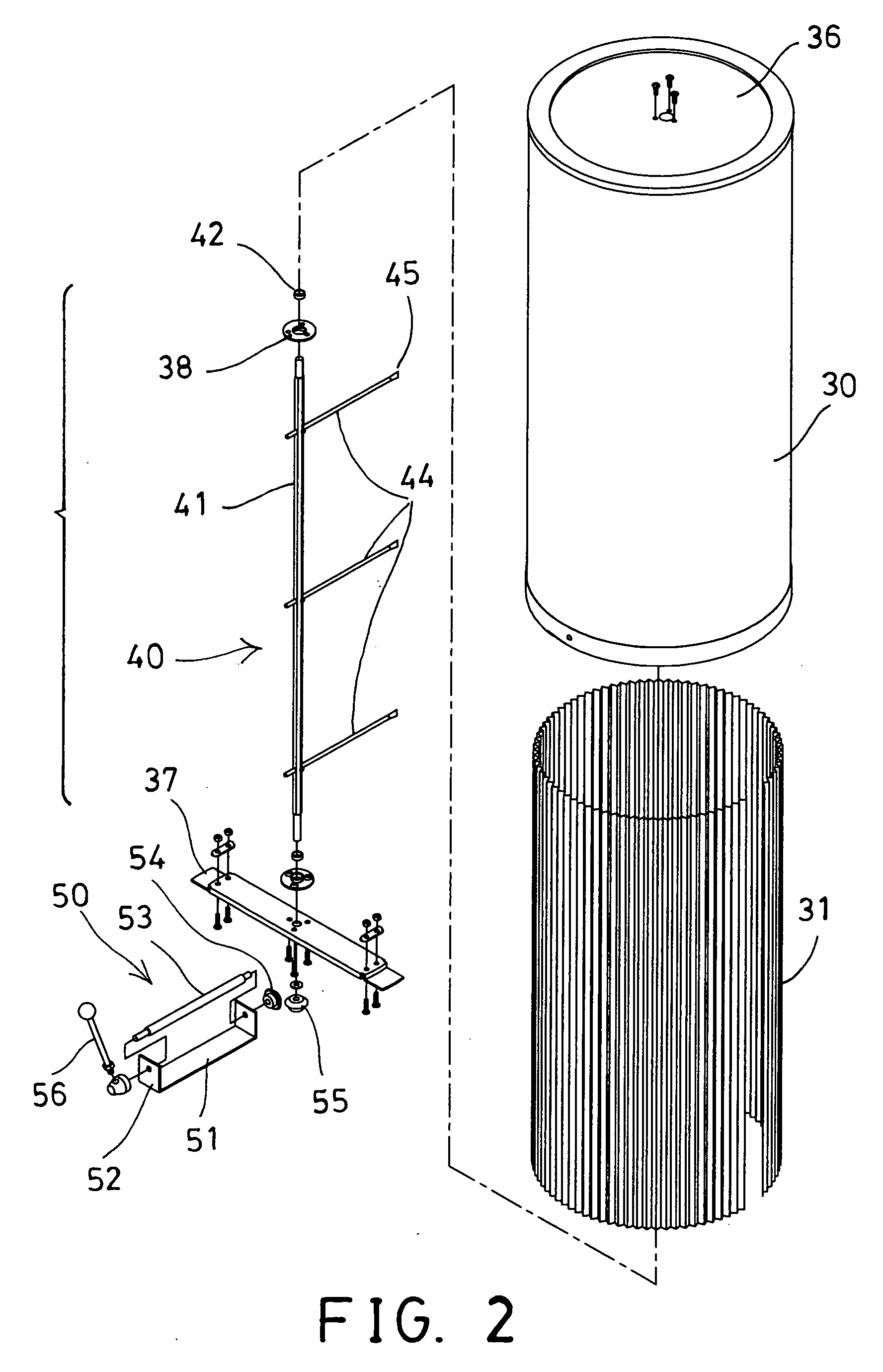
Water sprinkler head with integral off-on water flow control valve and adaptive fittings therefor
A sprinkler head assembly comprised of a base located at the upper end of a riser tube and which base carries an insert with an opening allowing for distribution of water. In accordance with the present invention, a control valve is located directly at the sprinkler head assembly. The control valve may be located in a stationary or shrub head which would be connected to a base or otherwise to a riser tube. The control valve could be located in a pop-up shaft, pop-up sprinkler head, or in a retrofit coupling or adapter located between a riser tube and sprinkler head. The control valve would rely upon a screw capable of being threadedly moved into a duct generally perpendicular thereto and which would have a diametral size somewhat larger than the duct. Moreover, the screw would be provided with an opening having a diameter approximately equal to that of the duct. The opening would be alignable with the duct in one position and when rotated would completely block the flow in another position. In this way, water flow to the sprinkler head assembly may be temporarily interrupted.
Owner:SIRKIN TEODORE
Foot control
ActiveUS20050172404A1Easy to startEasily interchangeableControlling membersMechanical apparatusControl powerMembrane switch
A foot control for controlling power-driven functions of a medical apparatus which positions a patient in a variety of examination and treatment positions. The foot control includes a membrane switch and a flexible keypad overlying the membrane switch. The flexible keypad is configured to actuate switch elements of the membrane switch in response to selective pressure applied on the keypad by a user's foot. Different configurations of keypads are interchangeable on the foot control to change the control functionality of the foot control while the membrane switch remains unchanged.
Owner:MIDMARK
Digital, self-calibrating proximity switch
ActiveUS20050209828A1Easy to trackPacked tightlyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsBiological activationComputer science
A signal processing system for detecting purposive signals includes an input receiving a signal having a signal characteristic subject to user manipulation. An activation detector compares a property of the signal characteristic to one or more signal characteristic property thresholds over time. A filter module determines whether the signal characteristic is purposively manipulated based on an amount of time preceding or following an occurrence of the property exceeding or falling below one or more signal characteristic property thresholds.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Measuring head for a coordinate measuring machine for determining spatial coordinates on a measurement object
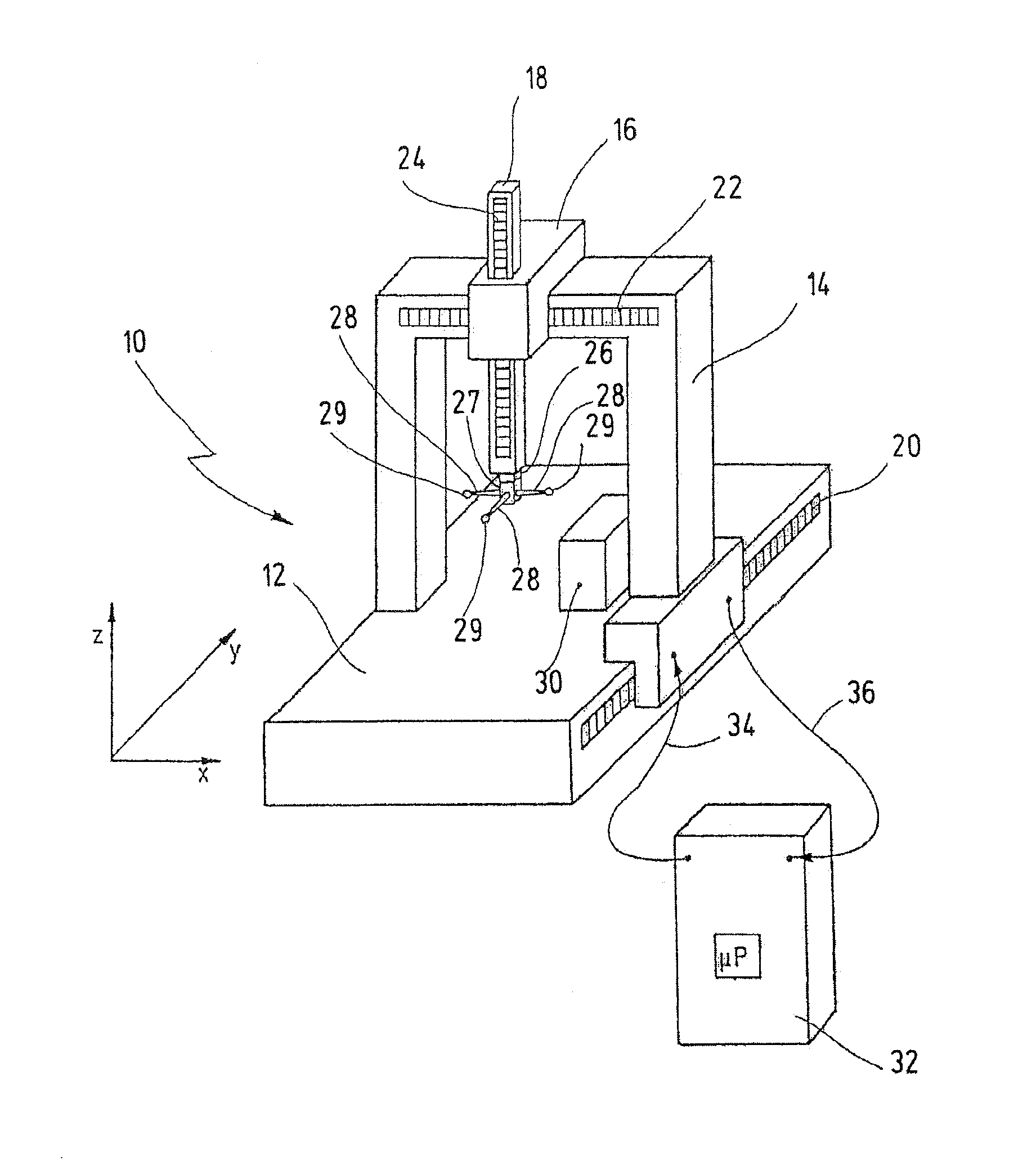
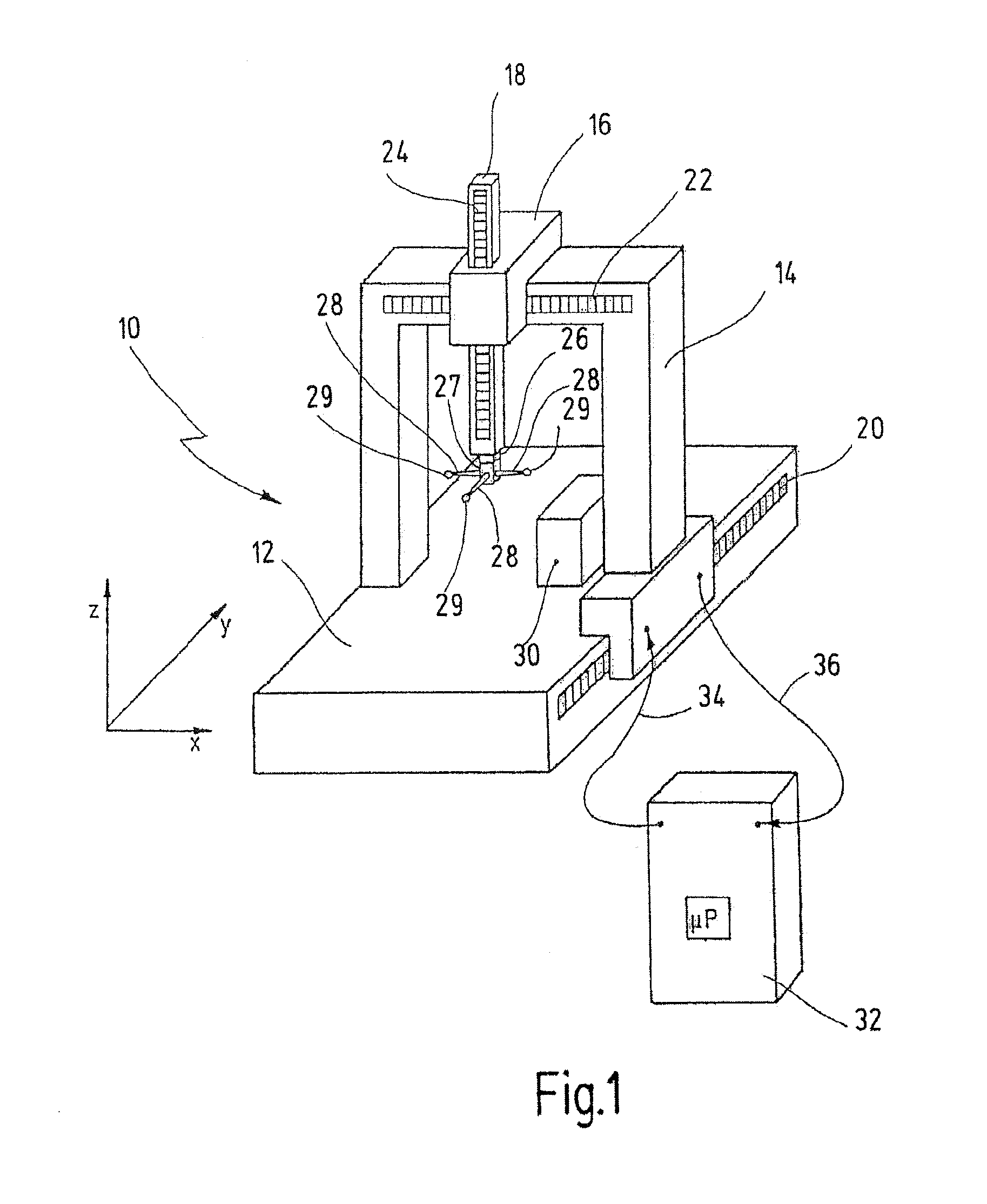
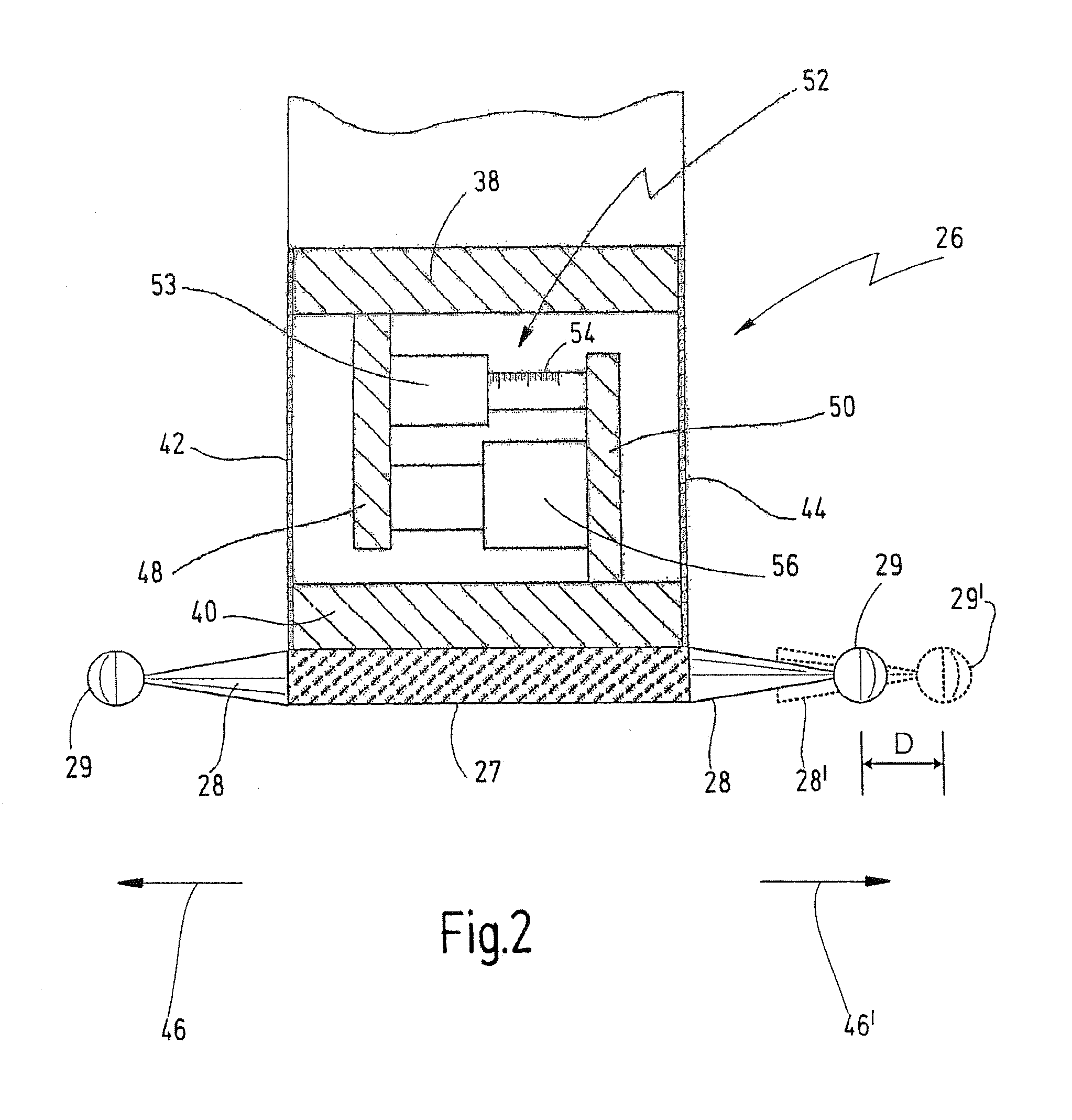
ActiveUS20140053423A1Simple and reliable openingSimple and reliable and closingMechanical measuring arrangementsEngineeringCoordinate-measuring machine
A measuring head for a coordinate measuring machine for determining spatial coordinates on a measurement object has a coupling part for detachably receiving a measurement tool. The coupling part has a number of first bearing elements, a magnet and a retaining pin. The measurement tool has a disk with a number of second bearing elements, an anchoring plate and at least one adjustable locking element. The magnet is configured to attract the anchoring plate so as to bring the first and second bearing elements into engagement with one another. The first and second bearing elements, in the engaged state, define a defined position of the measurement tool on the coupling part. The at least one locking element secures the measurement tool to the retaining pin. The anchoring plate is detachably secured to the disk and the at least one locking element retains the anchoring plate on the retaining pin.
Owner:CARL ZEISS IND MESSTECHN GMBH
Packaging and application device
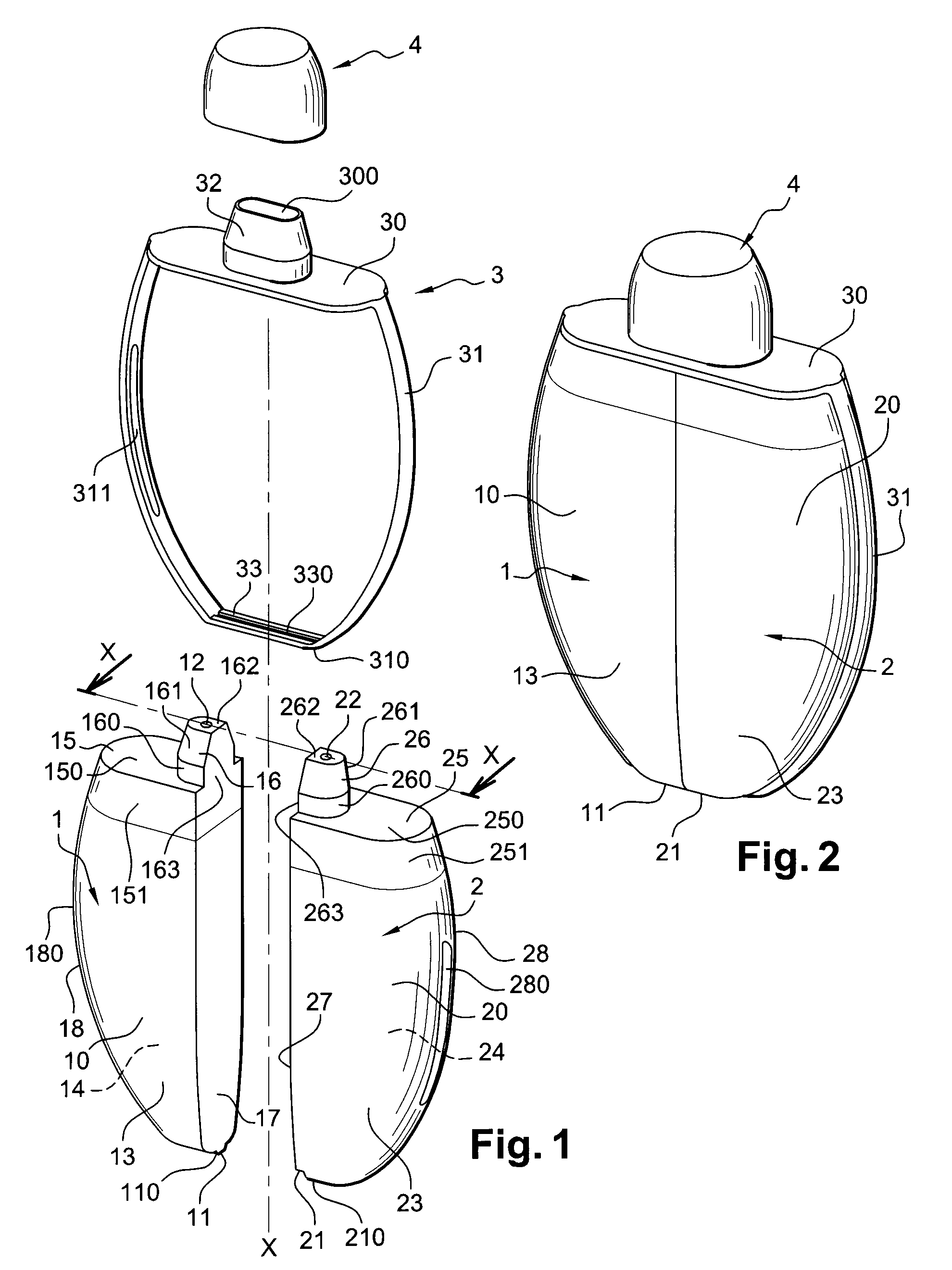
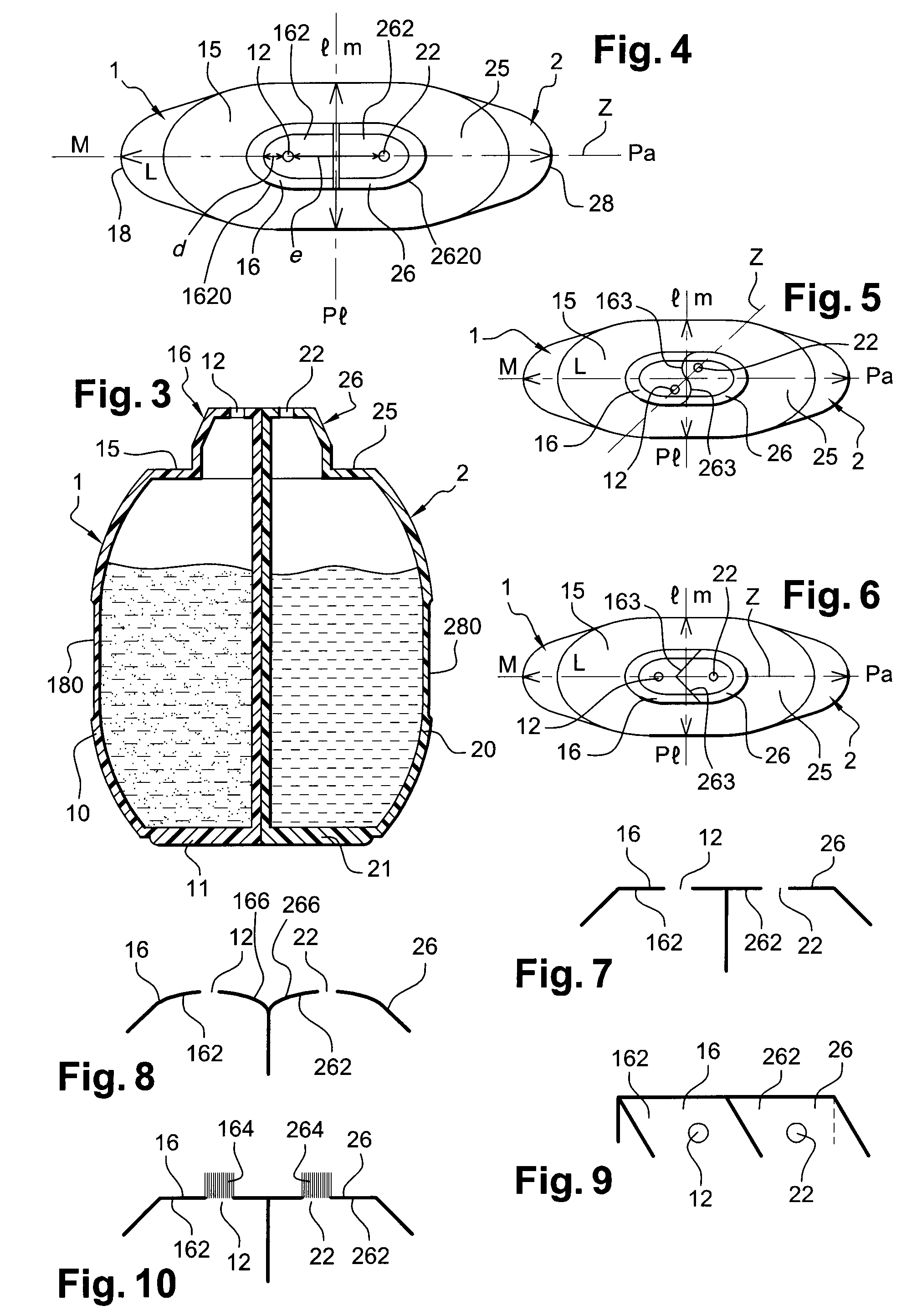
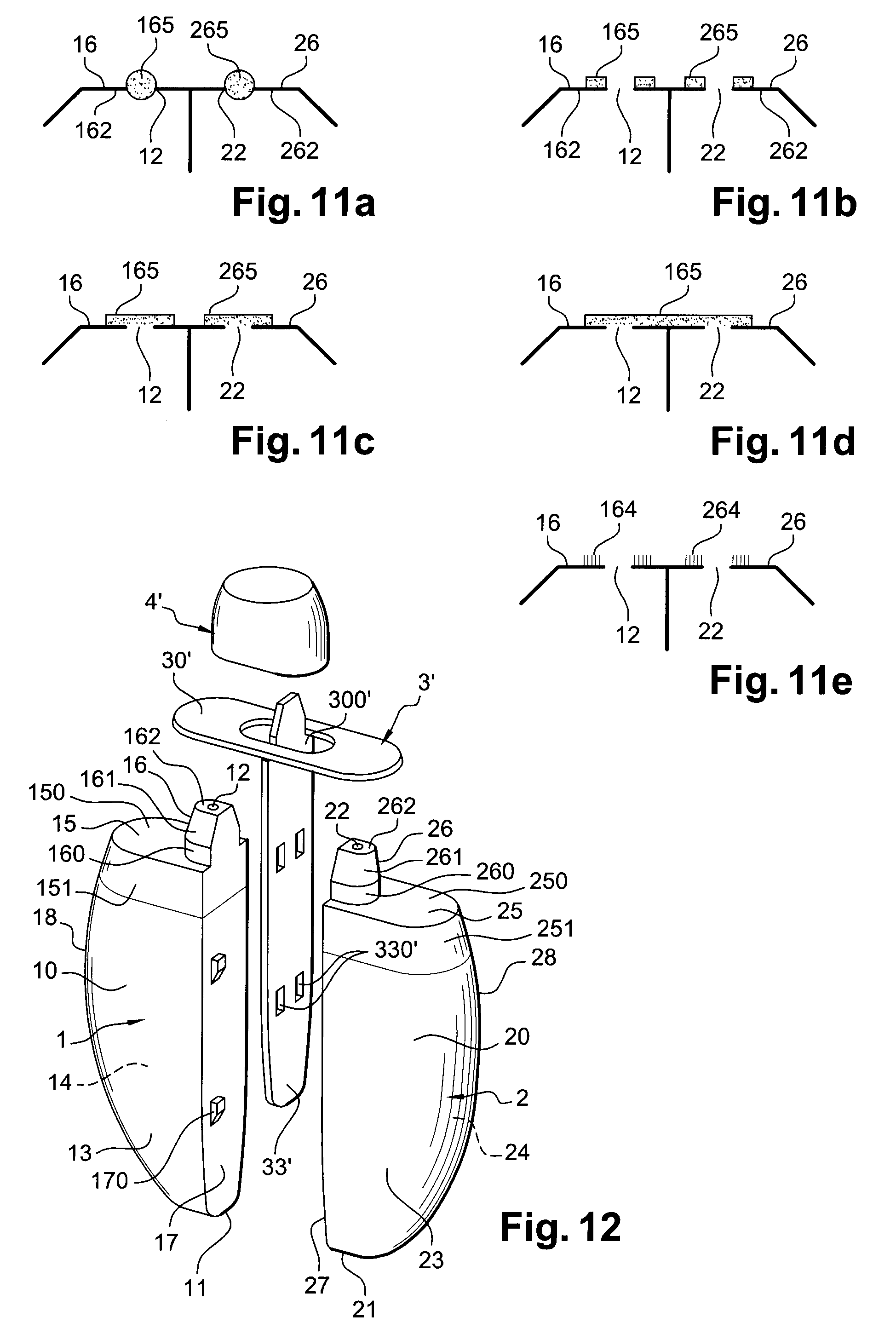
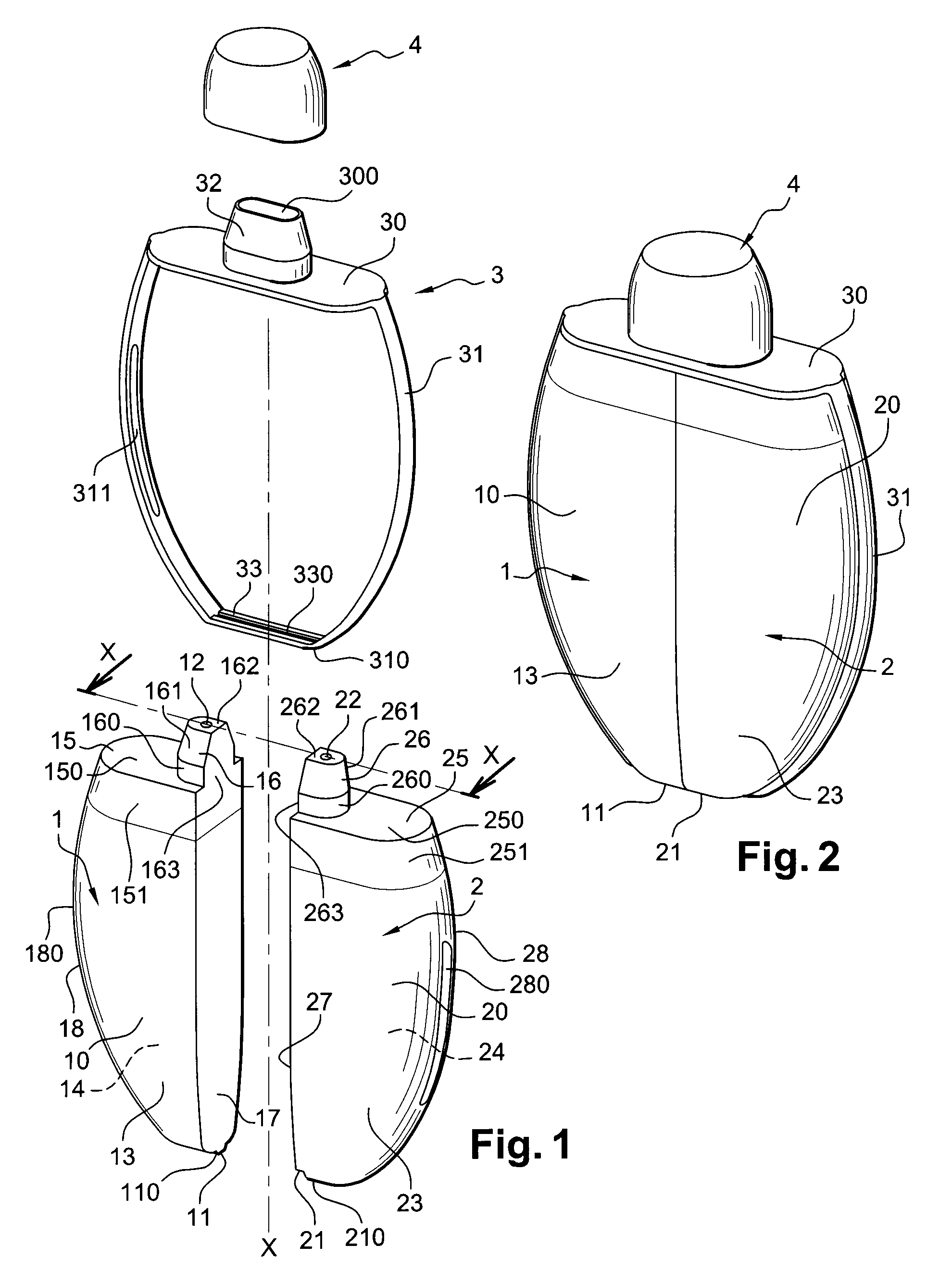
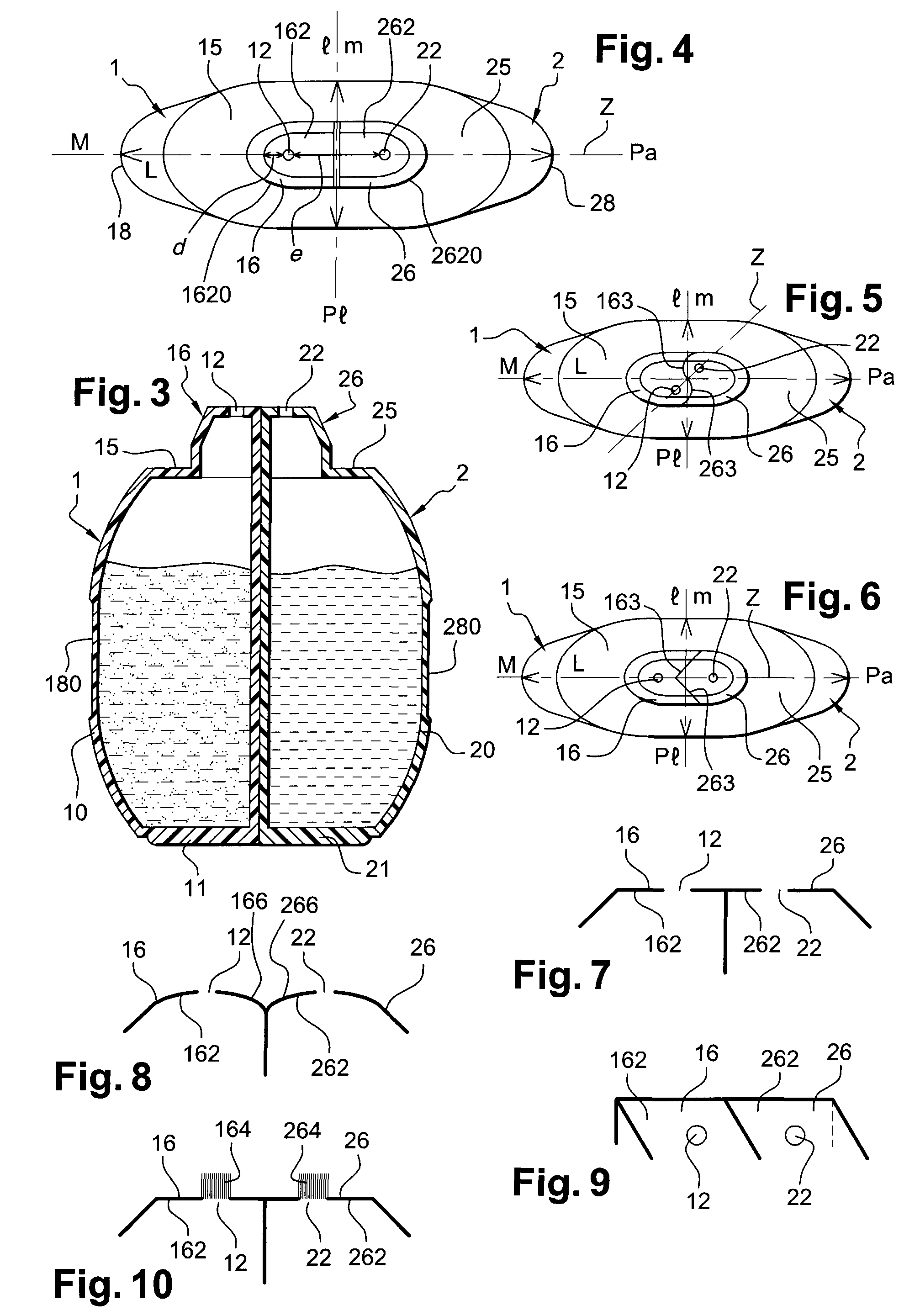
ActiveUS20080149126A1Easy to assembleEasy to manufactureCleaning machinesCurling devicesCouplingEngineering
A packaging and application device includes a first container which can contain a first product, with the first container including a deformable wall, so as to enable the first product to be dispensed through a first dispensing orifice. The device further includes a second container which can contain a second product, with the second container including a deformable wall, so as to enable the second product to be dispensed through a second dispensing orifice. According to an example, a coupling arrangement is mounted on the containers and joins the first and second containers together. The first and second dispensing orifices emerge separately at the level of a first application surface and a second application surface respectively, and the first and second containers are configured so as to be able to be actuated independently of one another.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Drive for pivoting a flap arranged on a vehicle body
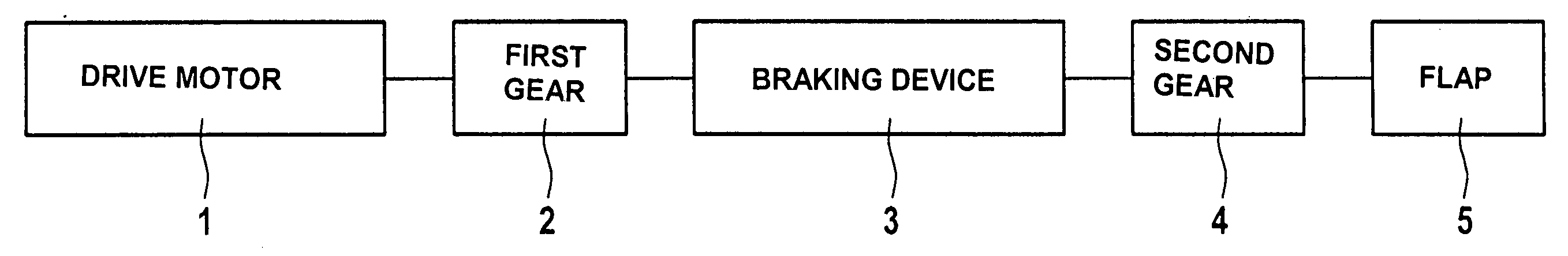
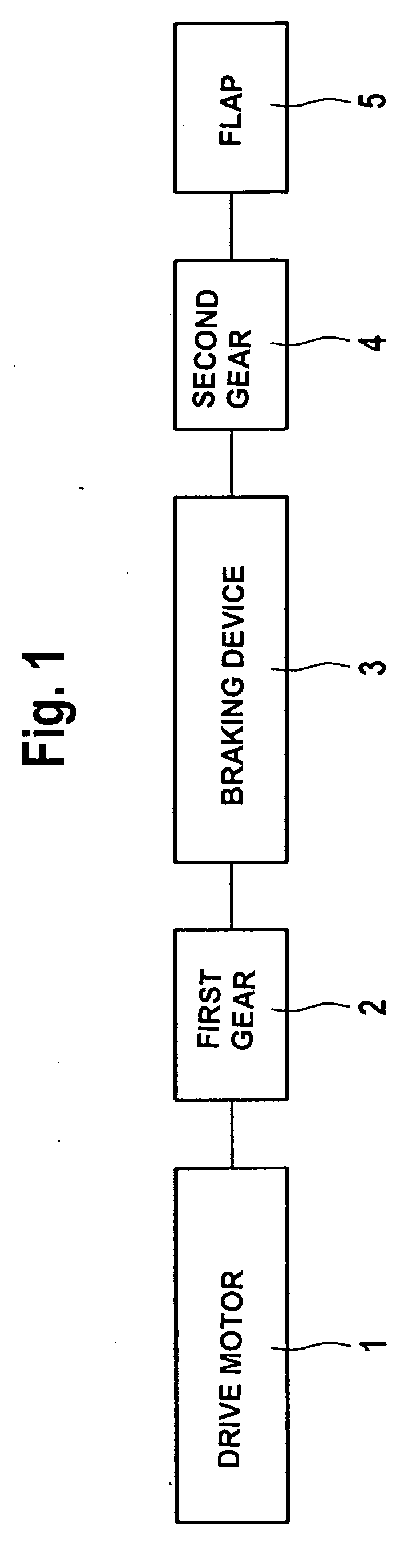
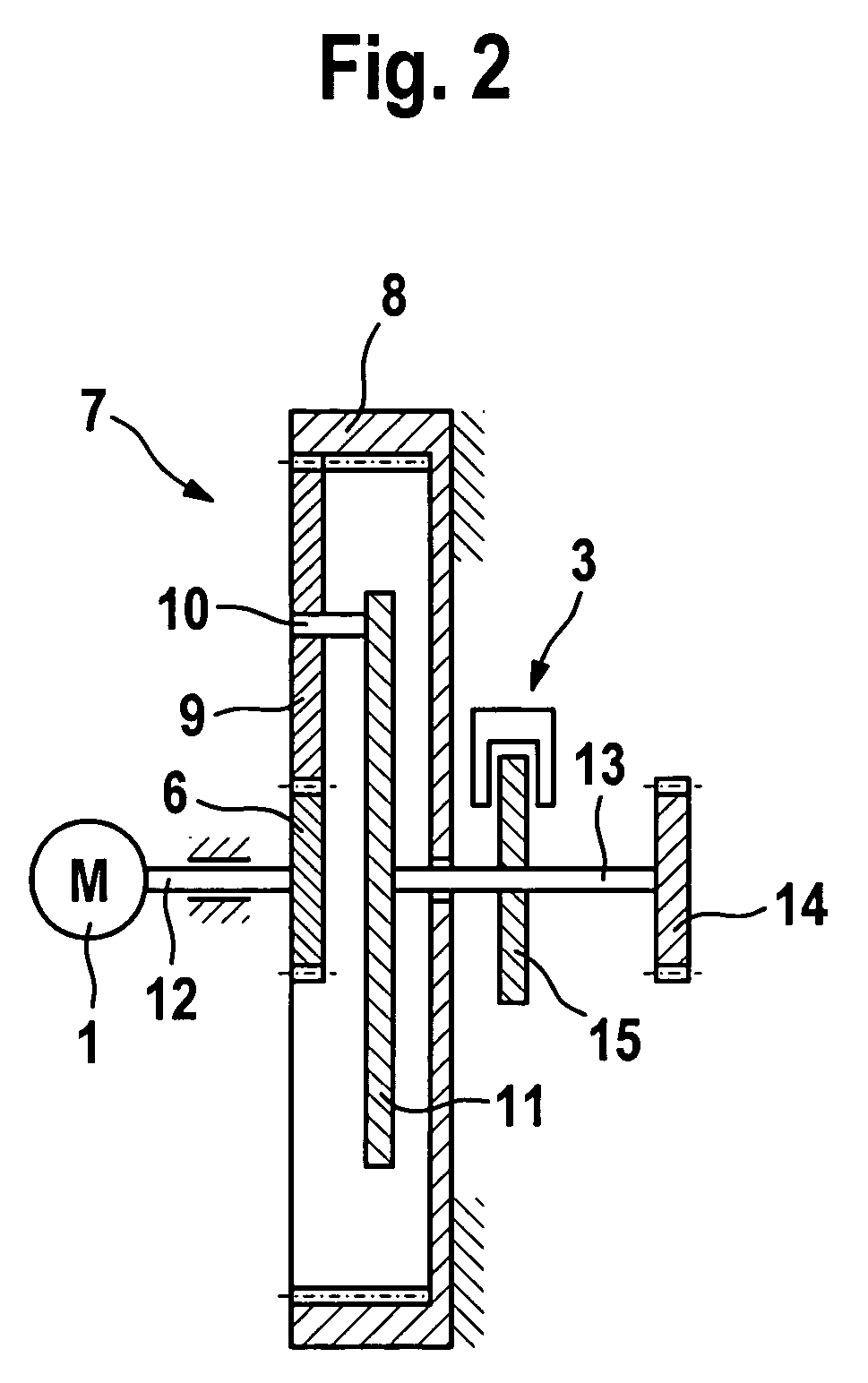
InactiveUS20060289821A1Large transmission ratioSimple and cost-effectiveOperating means/releasing devices for valvesBuilding braking devicesDrive motorSelf locking
A drive for pivoting a flap arranged on a vehicle body about a pivot axis includes a non-self locking electric motor and a drive train connecting the motor to the flap. The motor can be switched between a driving active state and a non-driving inactive state, the motor being moveable in the inactive state at least substantially without any resistance. A braking device blocks the drive train in the inactive state of the drive motor and unblocks the drive train in the active state of the motor.
Owner:STABILUS
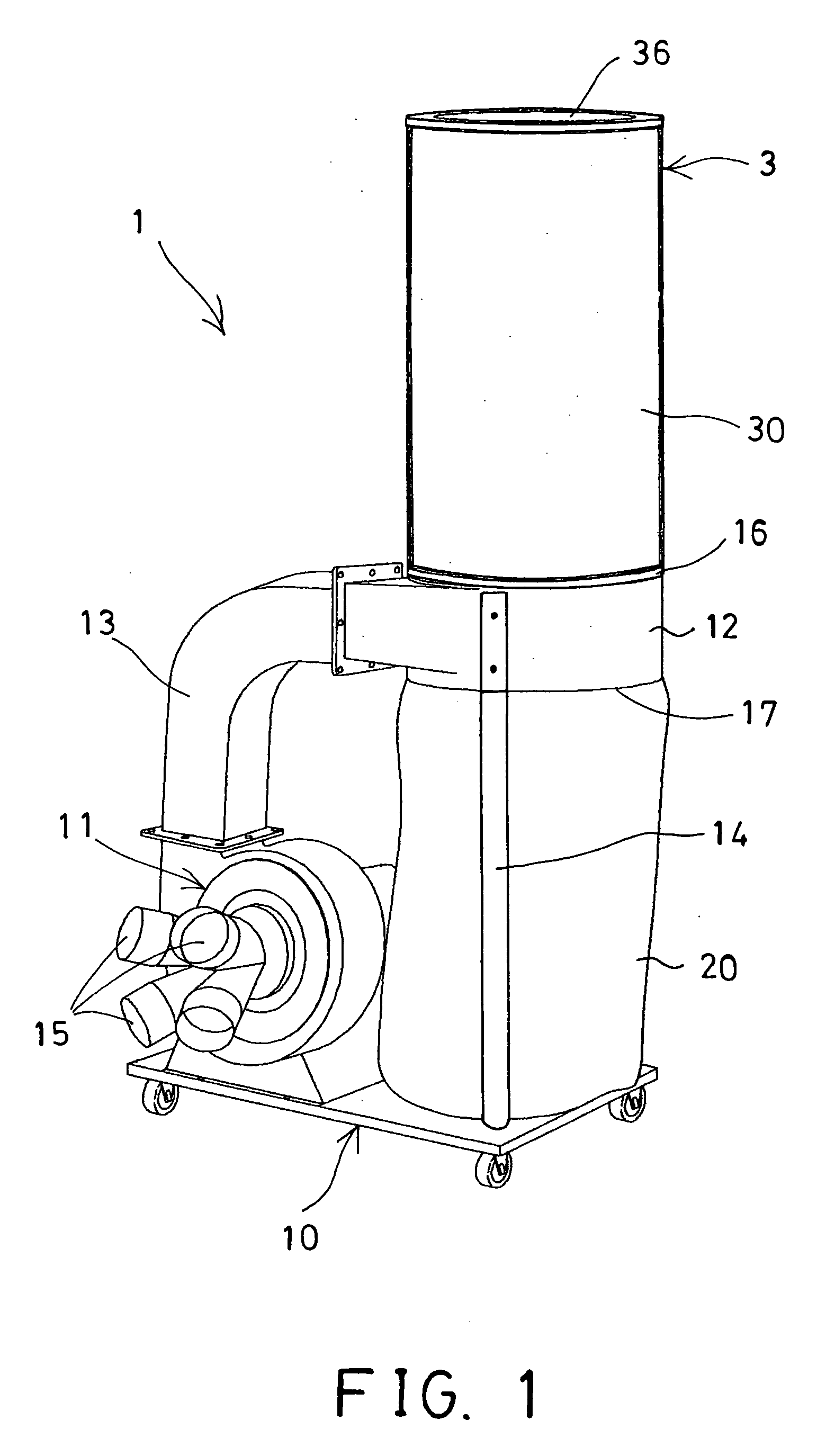
Dust removing device for dust collector
InactiveUS20090151306A1Easily collectEasy to collectDispersed particle filtrationTransportation and packagingEngineeringDust collector
A dust collector includes a filter housing, a filter member disposed in the filter housing, and a dust removing device disposed in the filter member for sweeping the filter member, to sweep of dirt from the filter member, and to allow the dirt to be removed from the filter member. The dust removing device includes one or more actuating members rotatably disposed in the filter member with such as a shaft for engaging with the filter member to sweep of dirt from the filter member when the actuating member is rotated relative to the filter member. A manually operating device is coupled to the shaft for rotating the shaft and the actuating member to sweep off the dust from the filter member.
Owner:CHENG TJER IND
Foot control
ActiveUS7058998B2Easy to startEasily interchangeableControlling membersMechanical apparatusControl powerMembrane switch
Owner:MIDMARK
Screw clamp having attached anchoring board
InactiveUS20130075565A1Simplified actuationEasy to operatePicture framesDomestic mirrorsMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:安歌科技(集团)股份有限公司
Packaging and application device
ActiveUS8523469B2Easy to assembleEasy to manufactureCarpet cleanersFloor cleanersCouplingEngineering
Owner:LOREAL SA
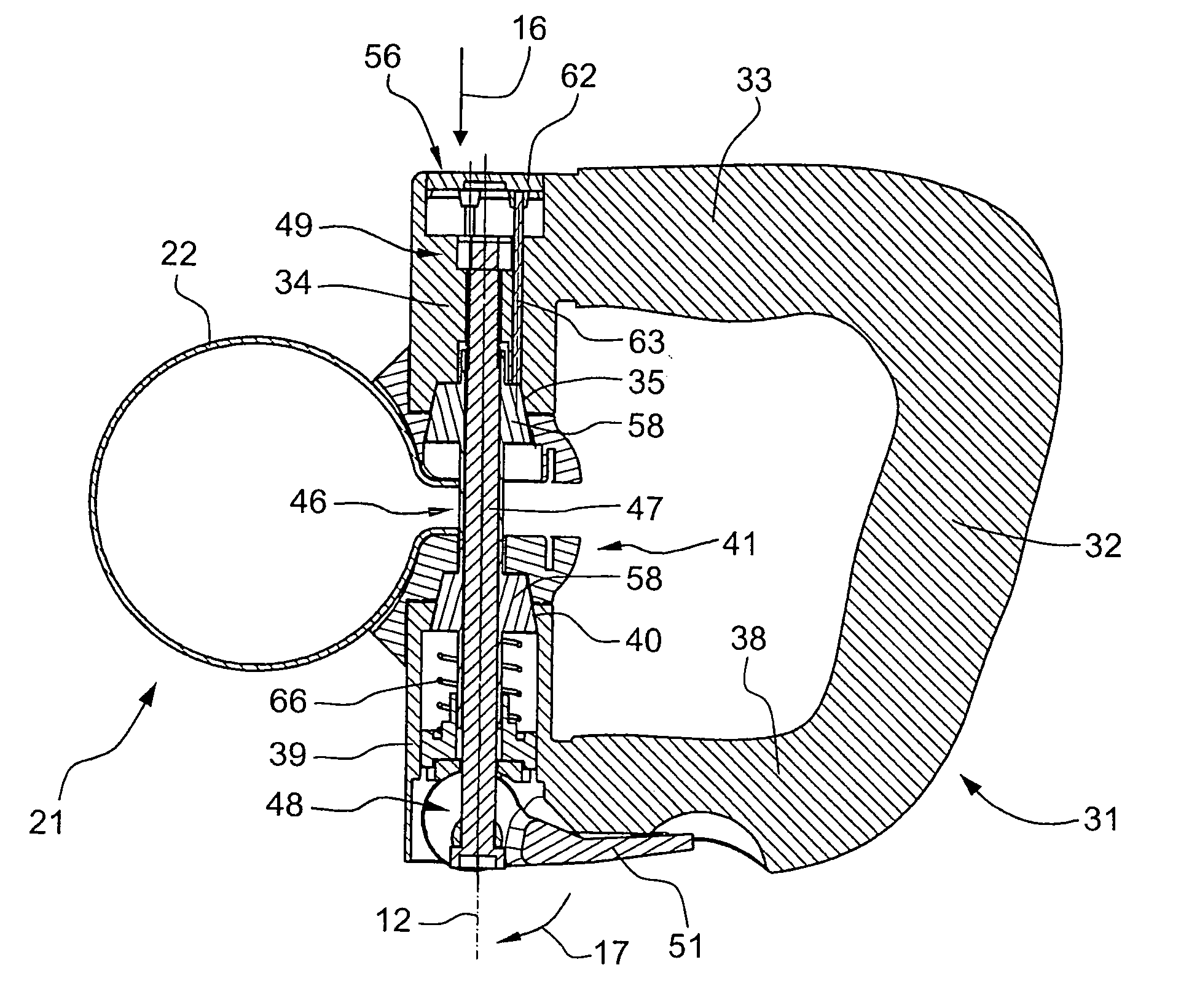
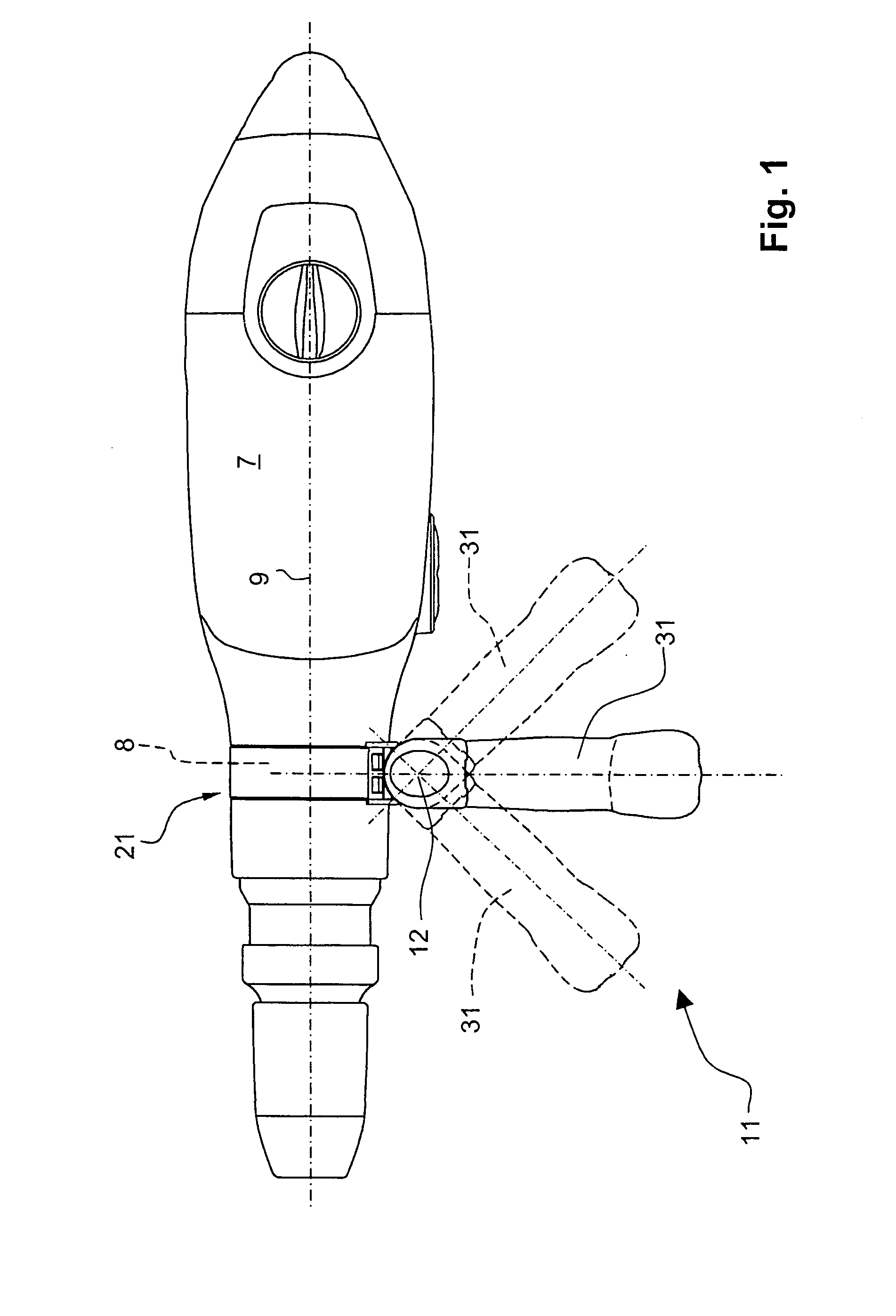
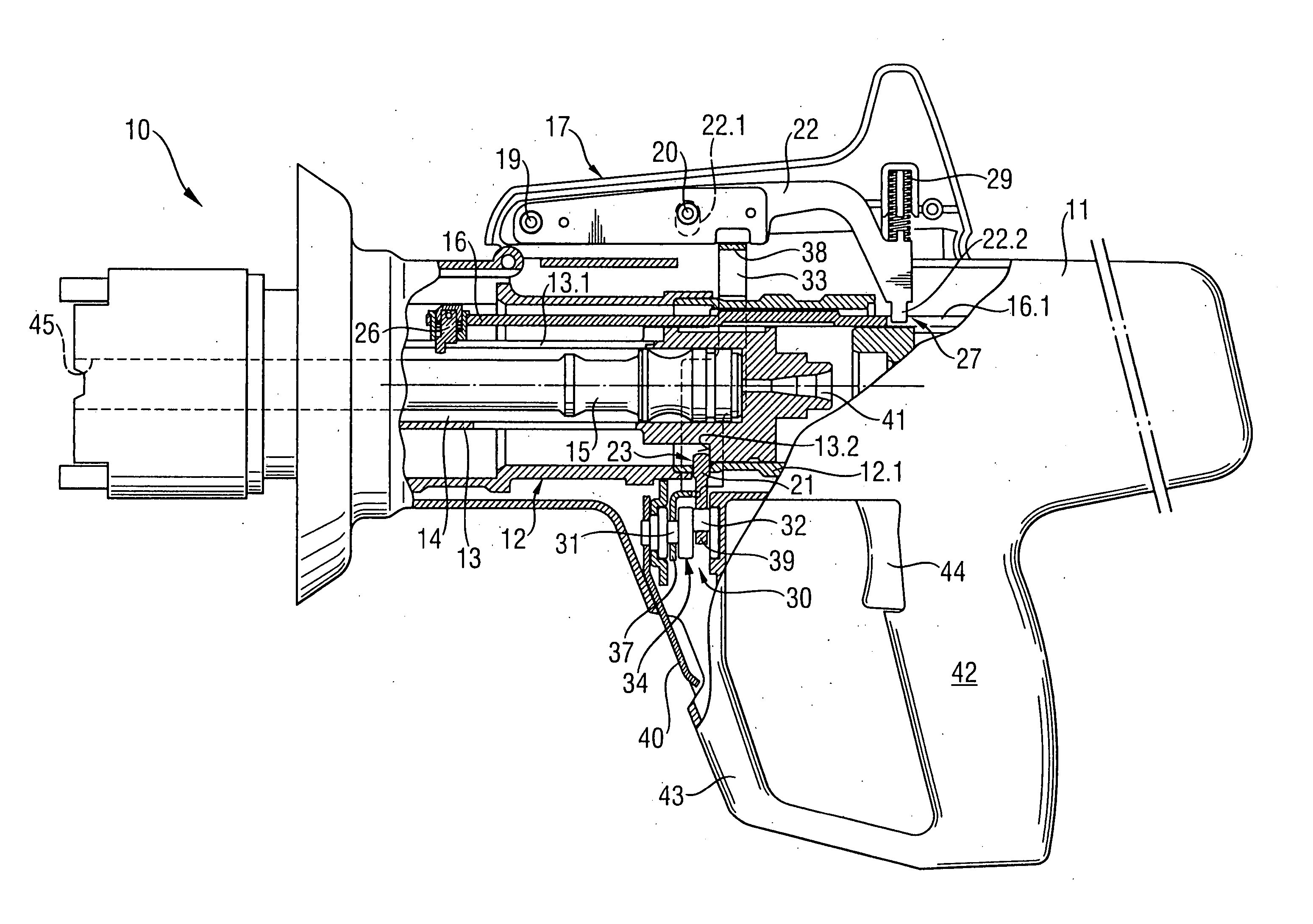
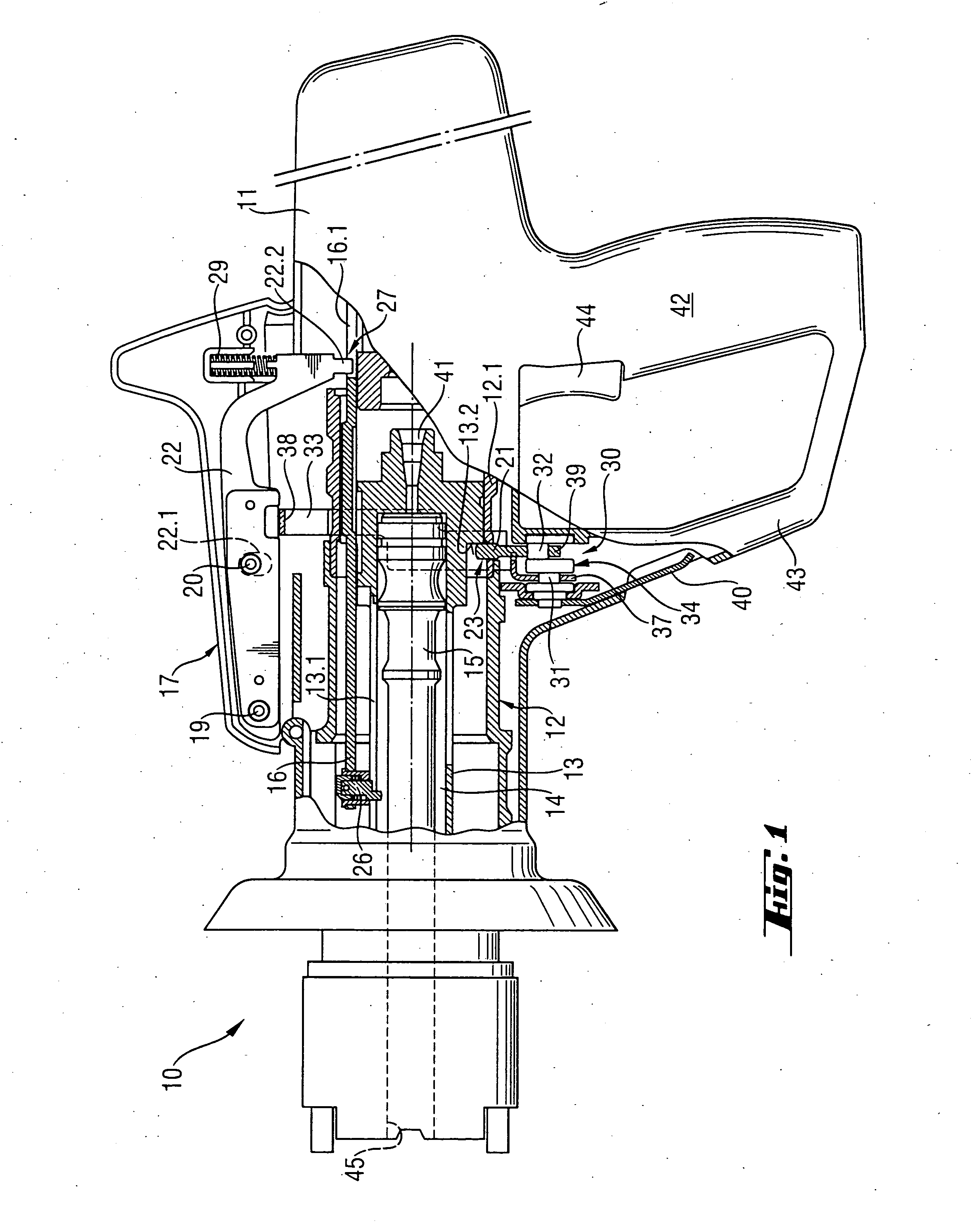
Auxiliary handle for hand-held power tool
An auxiliary handle for a hand-held power tool (7) includes a lockable lag hinge (46) provided between the clamping section (21) and the gripping member (34) and having a pivot pin (47), a tensioning member (51) for tightening and loosening the clamping section (21) and arranged on an end (48) of the pivot pin (47) of the lag hinge (46), a locking device (41) for locking and releasing the lag hinge (46), and an independent from the tensioning member (51), unlocking device (56) for releasing the locking device (41) and having an actuation member (62) upon actuation of which, the locking device (41) is displaced from its locking position in which the lag hinge (46) is locked to its release position in which the lag hinge (46) is released.
Owner:HILTI AG
Computer interaction based upon a currently active input device
InactiveUS7802202B2Enhanced interactionEnter exactlyCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingTablet computerSystems analysis
Described is a computer-implemented system and method that dynamically detects which input device (e.g., pen or mouse) is currently in use, and based on the device, varies a program's user interaction model to better optimize the user's ability to interact with the program via that input device. A tablet input subsystem receives pen and touch data, and also obtains keyboard and mouse data. The subsystem analyzes the data and determines which input device is currently active. The active device is mapped to an interaction model, whereby different user interface appearances, behaviors and the like may be presented to the user to facilitate improved interaction. For example, a program may change the size of user interface elements to enable the user to more accurately scroll and make selections. Timing, tolerances and thresholds may change. Pen hovering can become active, and interaction events received at the same location can be handled differently.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
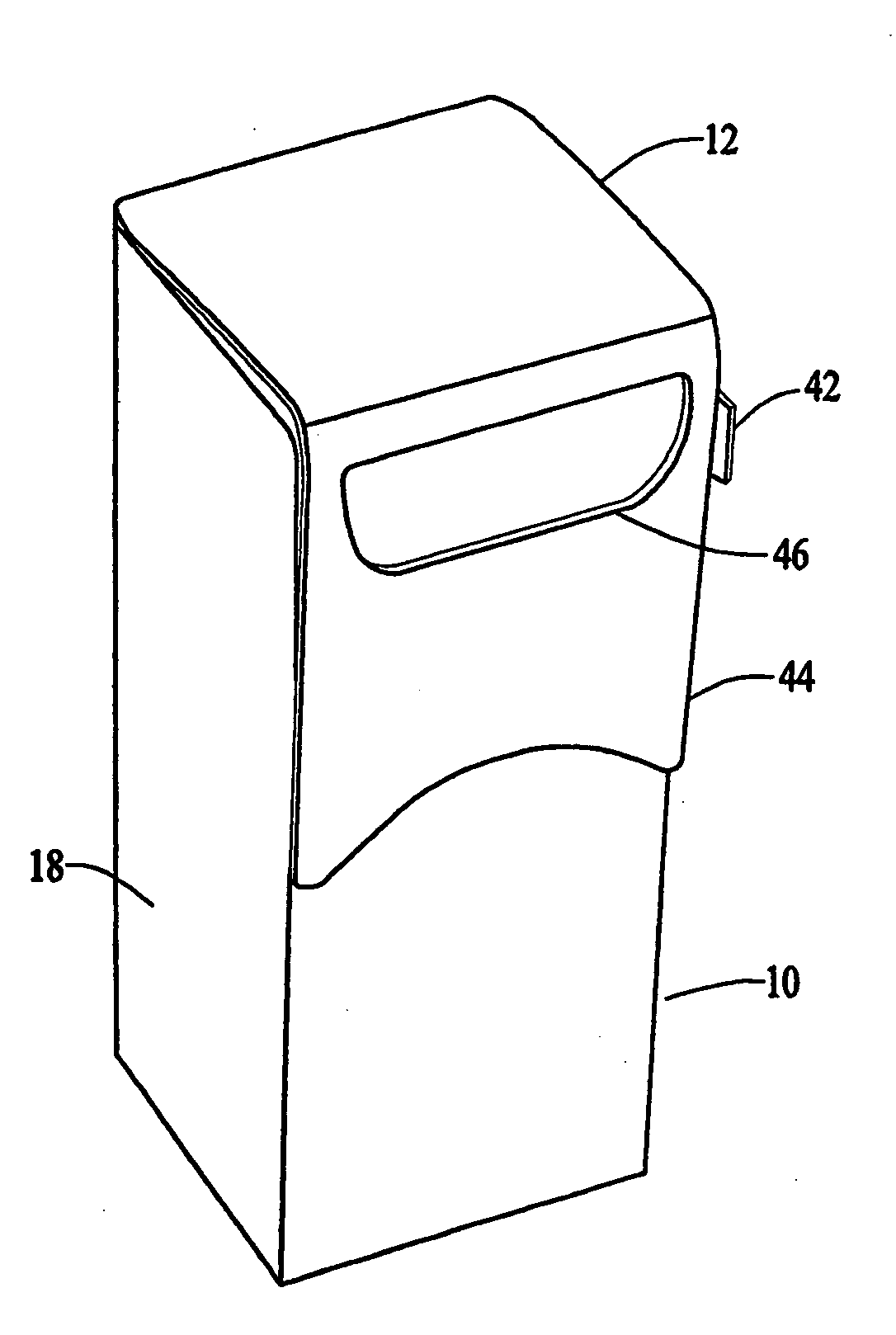
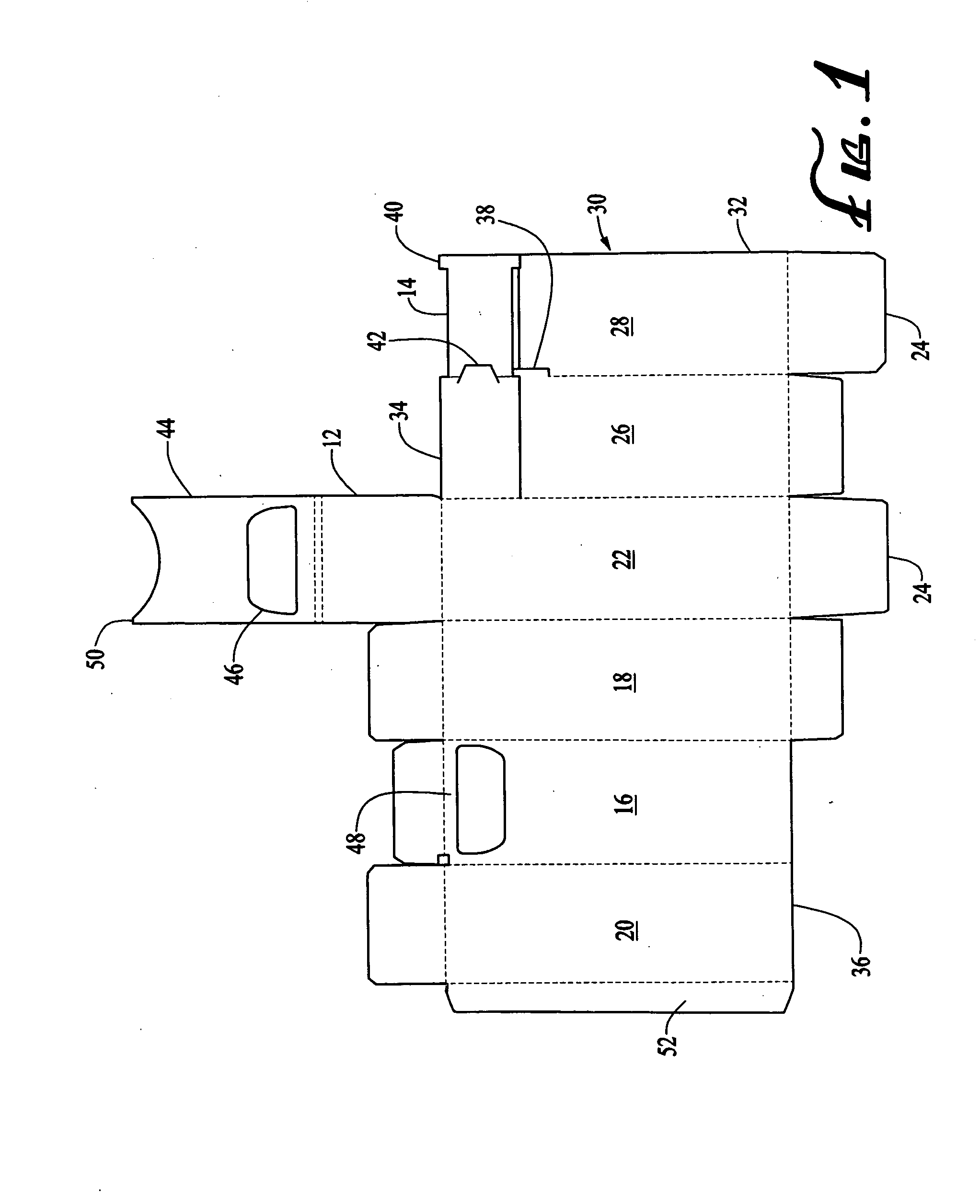
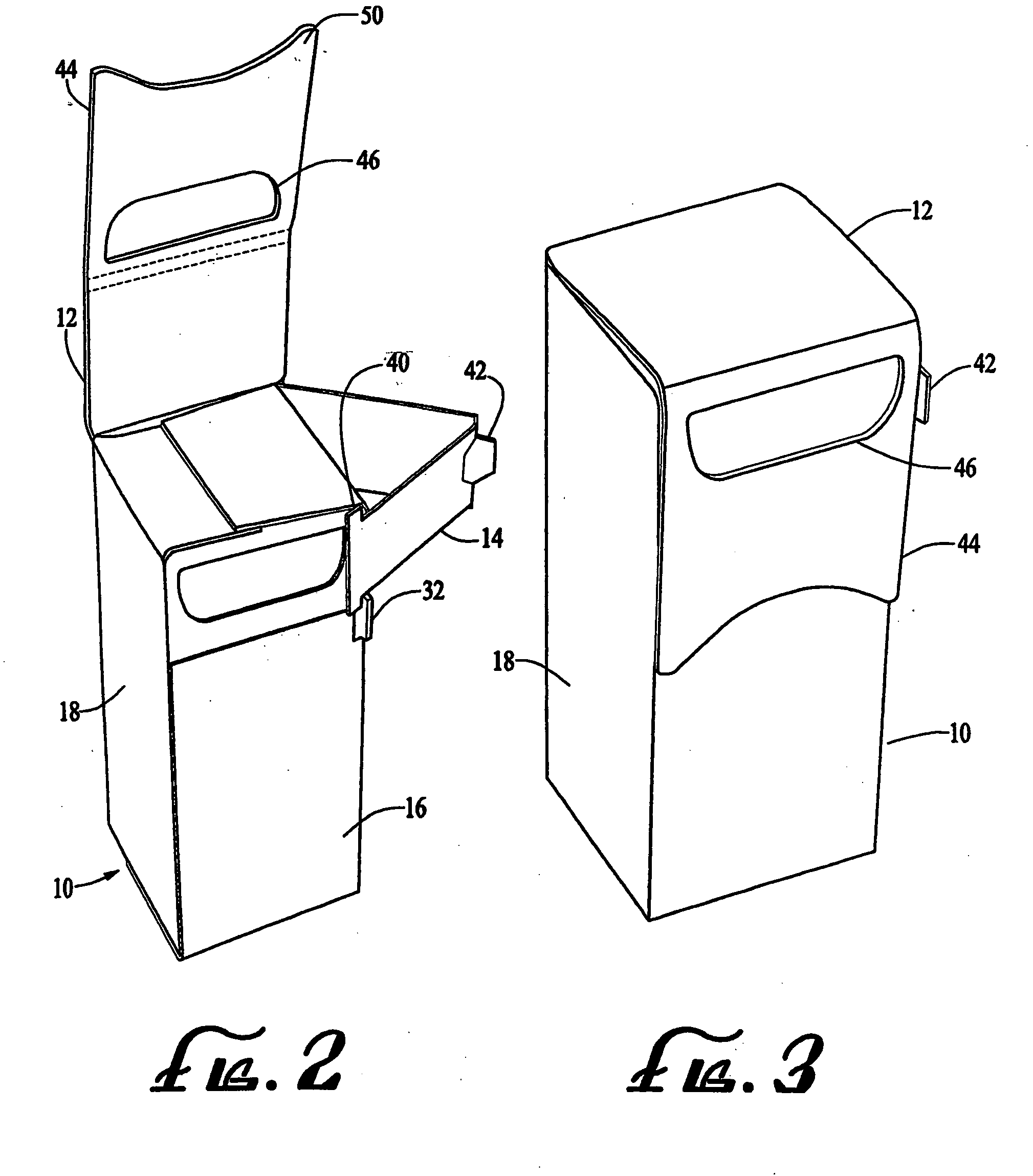
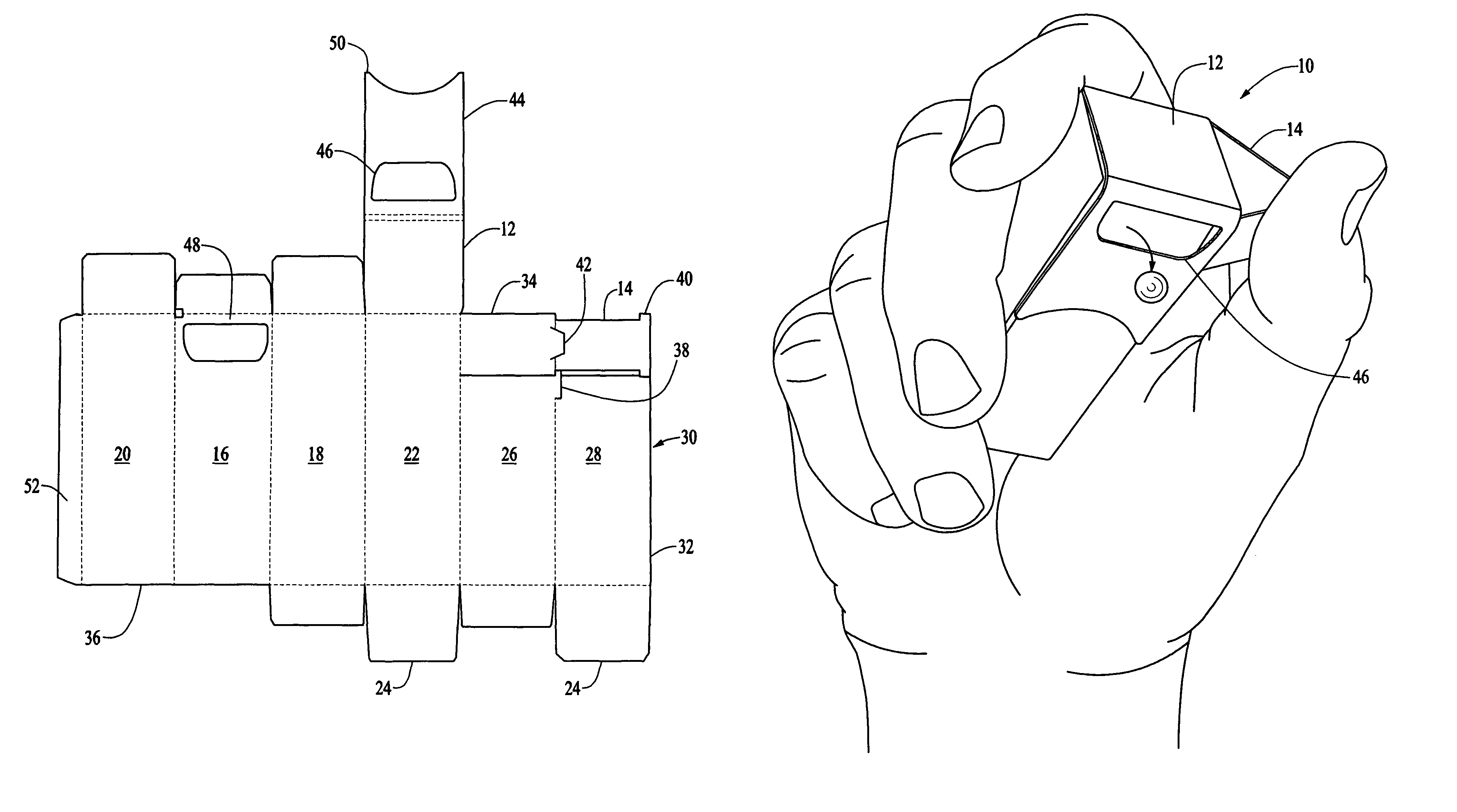
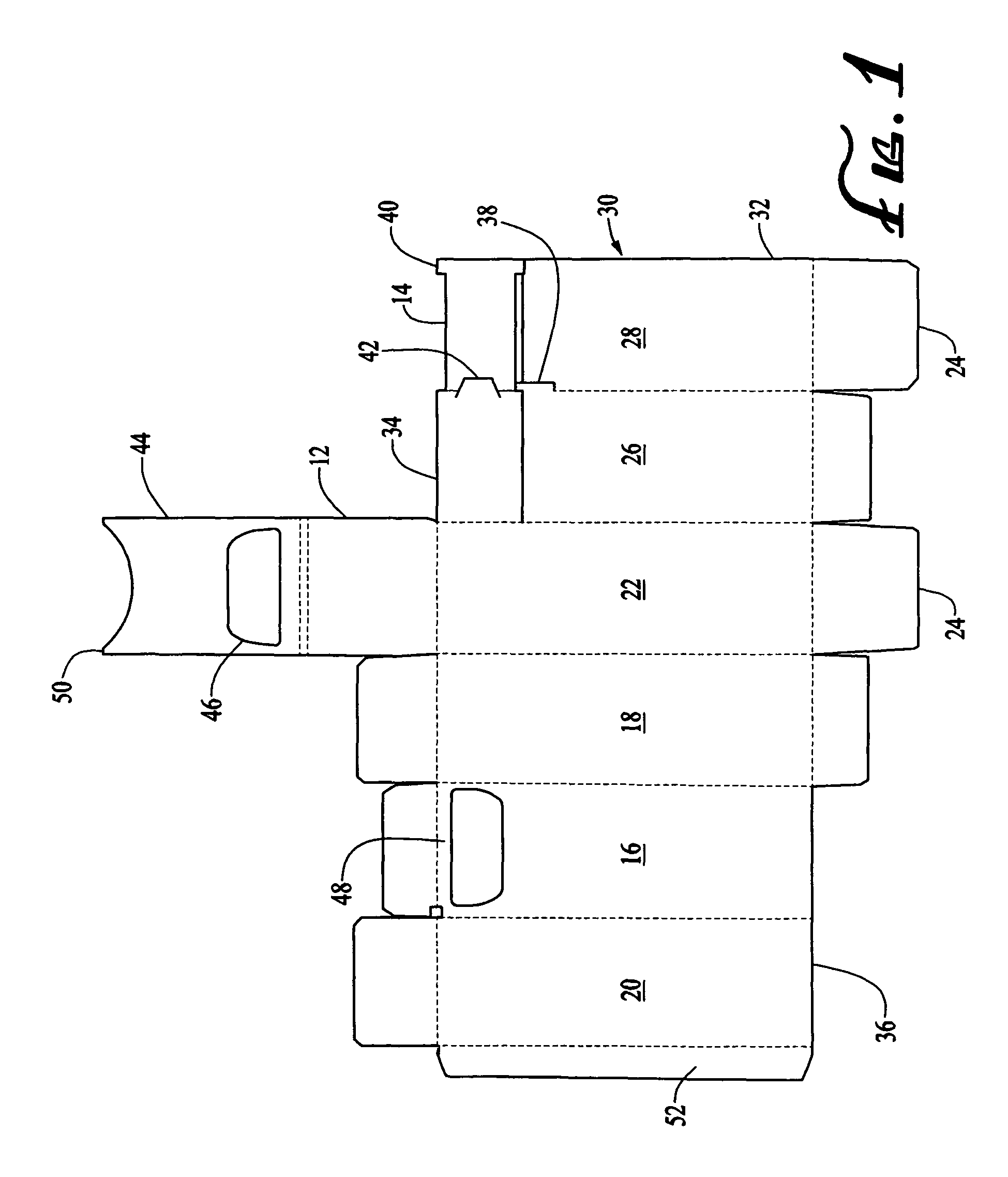
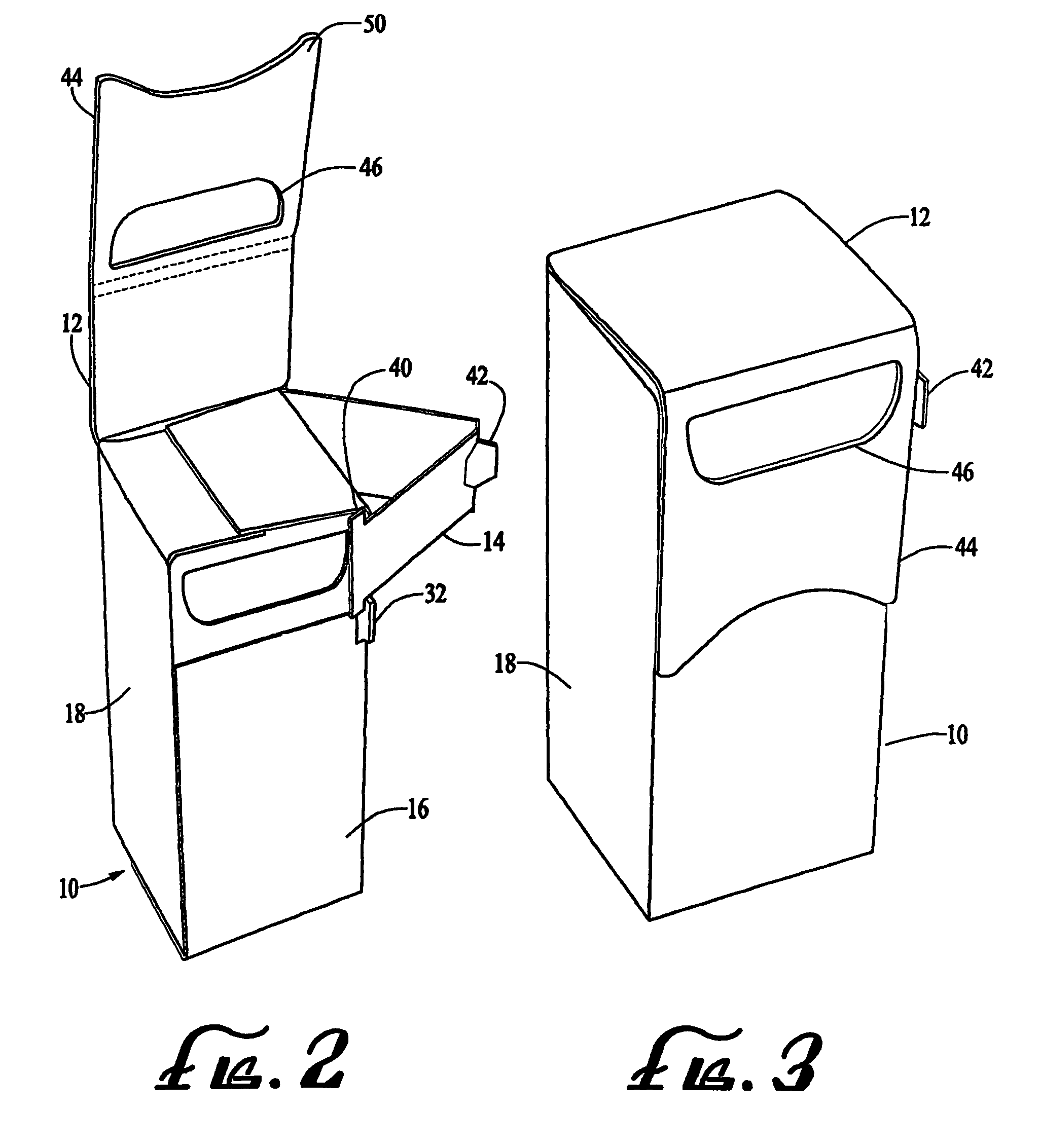
Thumb-actuated candy or mint box
A novel candy or mints box has an opening near the top of the box and an underlying slide that is moveable sideways across the opening. Preferably the top portion of the box includes a flap with an opening, and the flap extends over a corresponding opening in the front side such that the openings align, and the slide lies between the front side of the box and the top flap. The slide also preferably further includes a stop member and the box has a corresponding catch member, such that the slide is always contained within the box. Advantageously, the box is formed from a single blank piece of paper or cardboard stock, and folded in a particular sequence such that the slide ends up inside the box without the need for a separate insertion step.
Owner:HEGAMI DAVID TODJAR
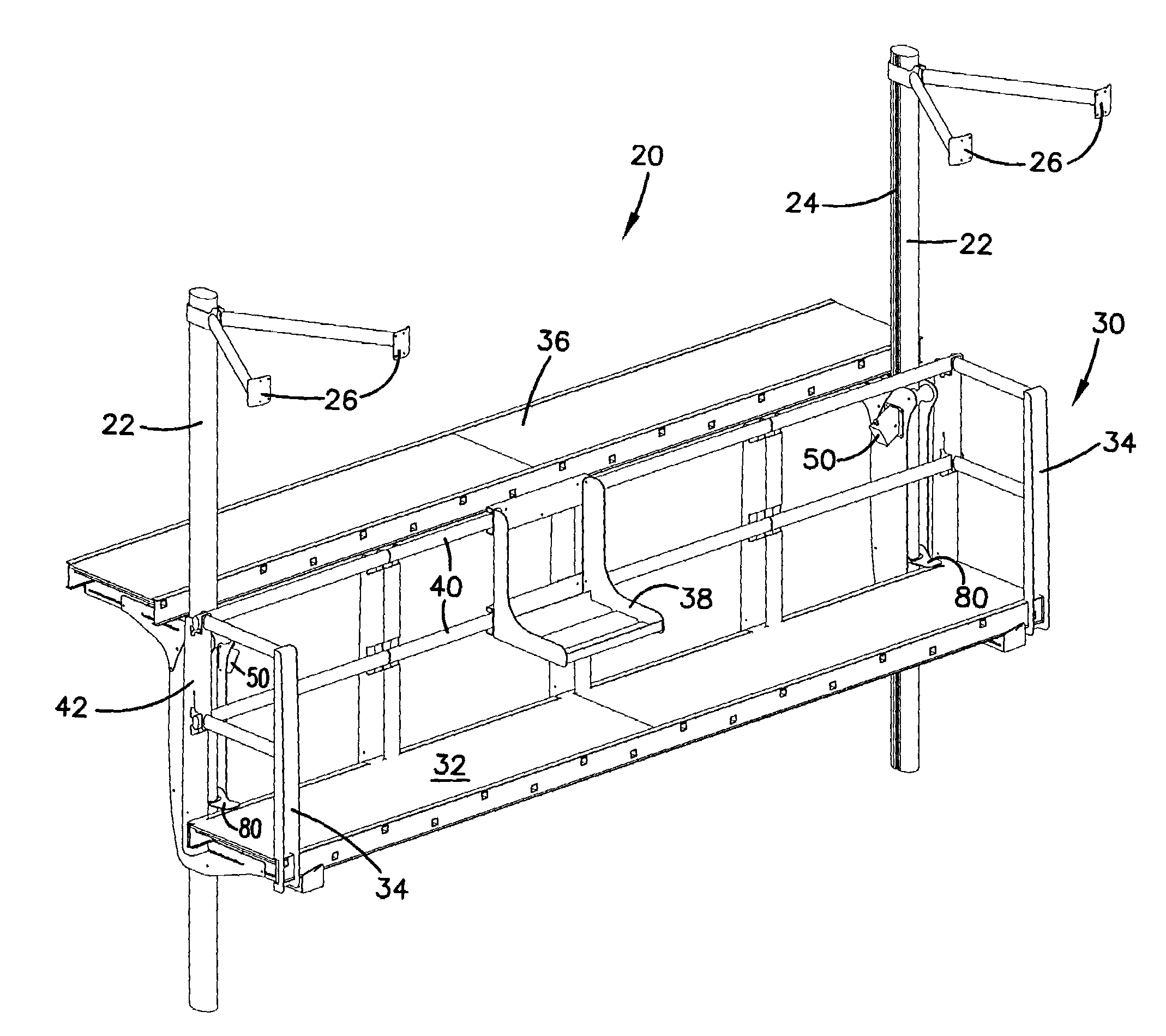
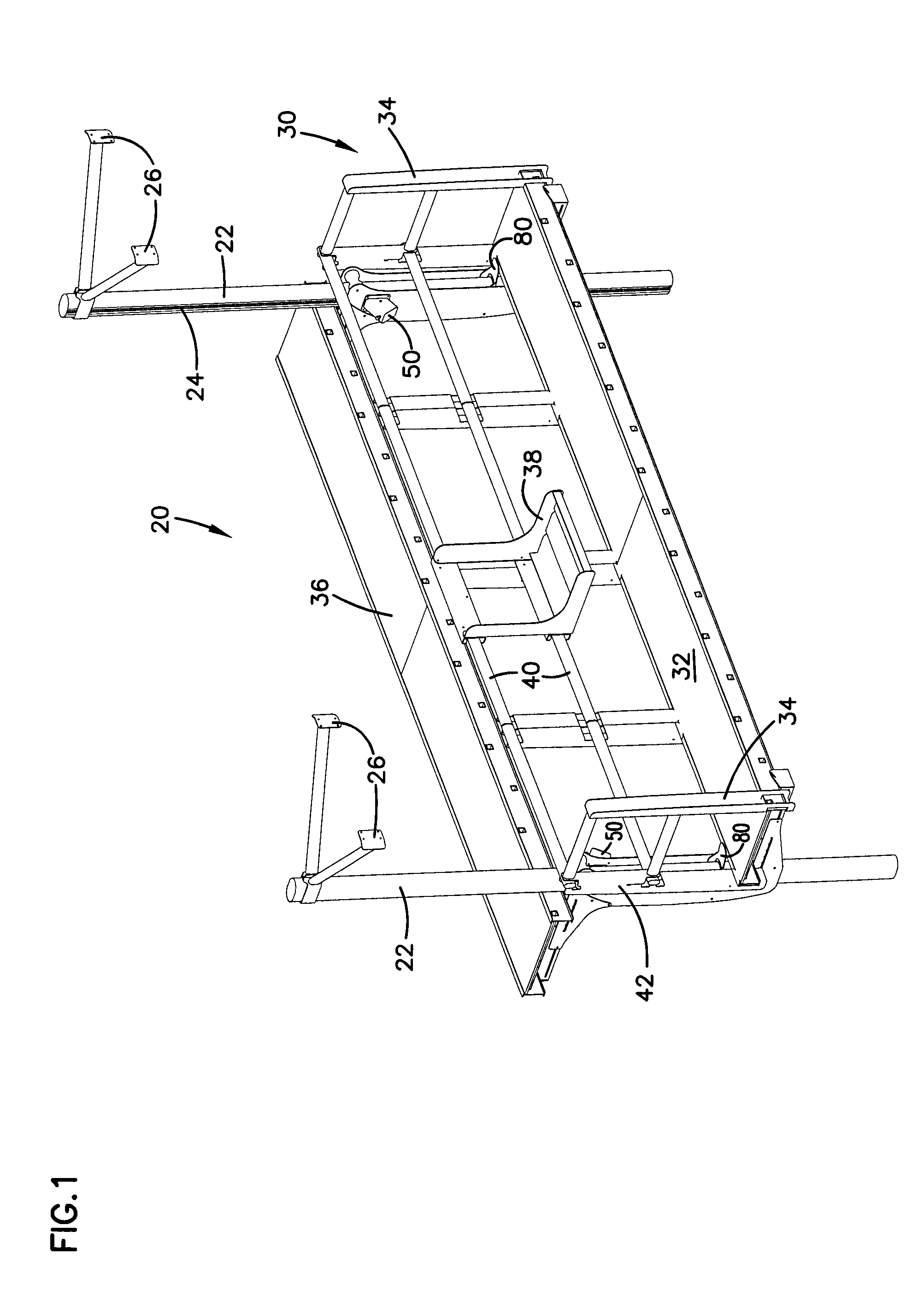
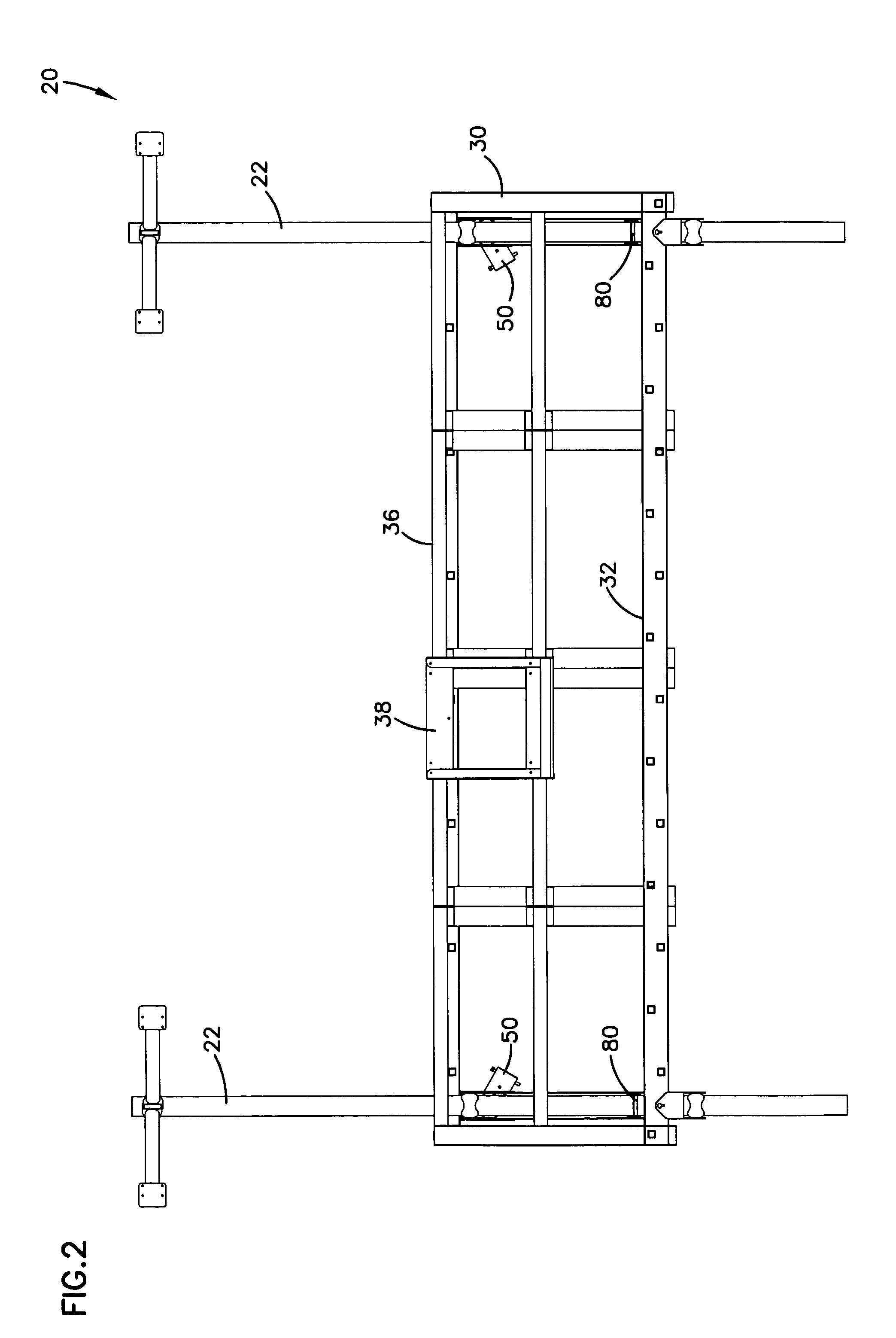
Scaffold lift system
InactiveUS6981573B2Easy to lowerEasily raisedToothed gearingsBuilding support scaffoldsEngineeringSprocket
A scaffolding system has a pair of vertical posts supporting a platform traveling vertically on the posts. A traveler device attaches to and engages each of the vertical posts and supports the platform. Each traveler device has a sprocket gear engaging a complementary track extending up the post so that rotation of the gear moves the traveler device along the vertical post and lifts and lowers the platform. The traveler device has a worm type drive gear configured for receiving a driver and meshing with the sprocket gear. The drive gear is operated with a power drill or a crank drive. The platform includes a foot operated brake device providing a back up system to prevent the platform from accidentally dropping.
Owner:REECHCRAFT
Setting tool
ActiveUS20050051592A1Conveniently dismountReduce modification costNailing toolsMotion transferEngineering
A setting tool for driving in fastening elements includes a piston guide (13) located in the receptacle (12) and having a hollow chamber (14) in which a setting piston (15) is displaceably arranged, a safety element (21), a piston return element (16), an operational member (17) for operating the piston return element (16), a transmission member (22) for transmitting movement of the operational member (17) to the piston return element (16), and a manually actuatable actuation element (30) having a first adjustment section (31) connected with the safety element (21) and a second adjustment section (32) connected with the transmission member (22) for simultaneous displacement of the safety element (21) and the transmission member (22) in their respective release positions (24, 28) or their safety position (23) and the transmission position (27), respectively.
Owner:HILTI AG
Screw clamp having pivotal anchoring board
InactiveUS20130075564A1Simplified actuationEasy to operatePicture framesDomestic mirrorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:安歌科技(集团)股份有限公司
Electromechanical Horn For Deterring Animals
ActiveUS20120272923A1Small sizeConsumes less electric powerAnimal repellantsTaming and training devicesElectricityHarmonic
An electromechanical horn having a sound generating system including a piezoelectric speaker generates a series of short, audible sound signals in a repetitive pattern, the generated sound signals having fundamental frequencies with associated harmonic component frequencies and decibel levels that fall within a frequency range of greatest hearing sensitivity of the animal to disperse or deter an aggressive animal in a non-detrimental manner. The generated sound signals have fundamental frequencies with associated harmonic component frequencies that fall within a frequency range of from about 3 kHz to about 10 kHz, and decibel levels in a range of from about 75 dB to about 115 dB (SPL) at 1 meter. The horn device can be hand-held, attached to a user's belt or clothing, or removably attached to a bicycle, motorcycle, stroller, or other conveyance or object and can be actuated while attached or quickly removed and actuated when needed.
Owner:STEPHENS LEAH +1
Ladder support bracket
A ladder support bracket comprises a first clamp for clamping to an immovable structure connected to a second clamp for clamping to the ladder stile, the first clamp having a fixed and moveable jaw moving on a hinge shaft, and the second clamp comprising a clamping pad mounted on the hinge shaft distally from the first clamp for frictional engagement with the ladder stile upon rotation of the pad.
Owner:AVENKO
Container-Treatment Installation Having Holder Devices Configured to Co-Operate Mutually
ActiveUS20140318079A1Simplified actuationSimplify cleaningSynchronising machinesConveyorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SERAC GROUP
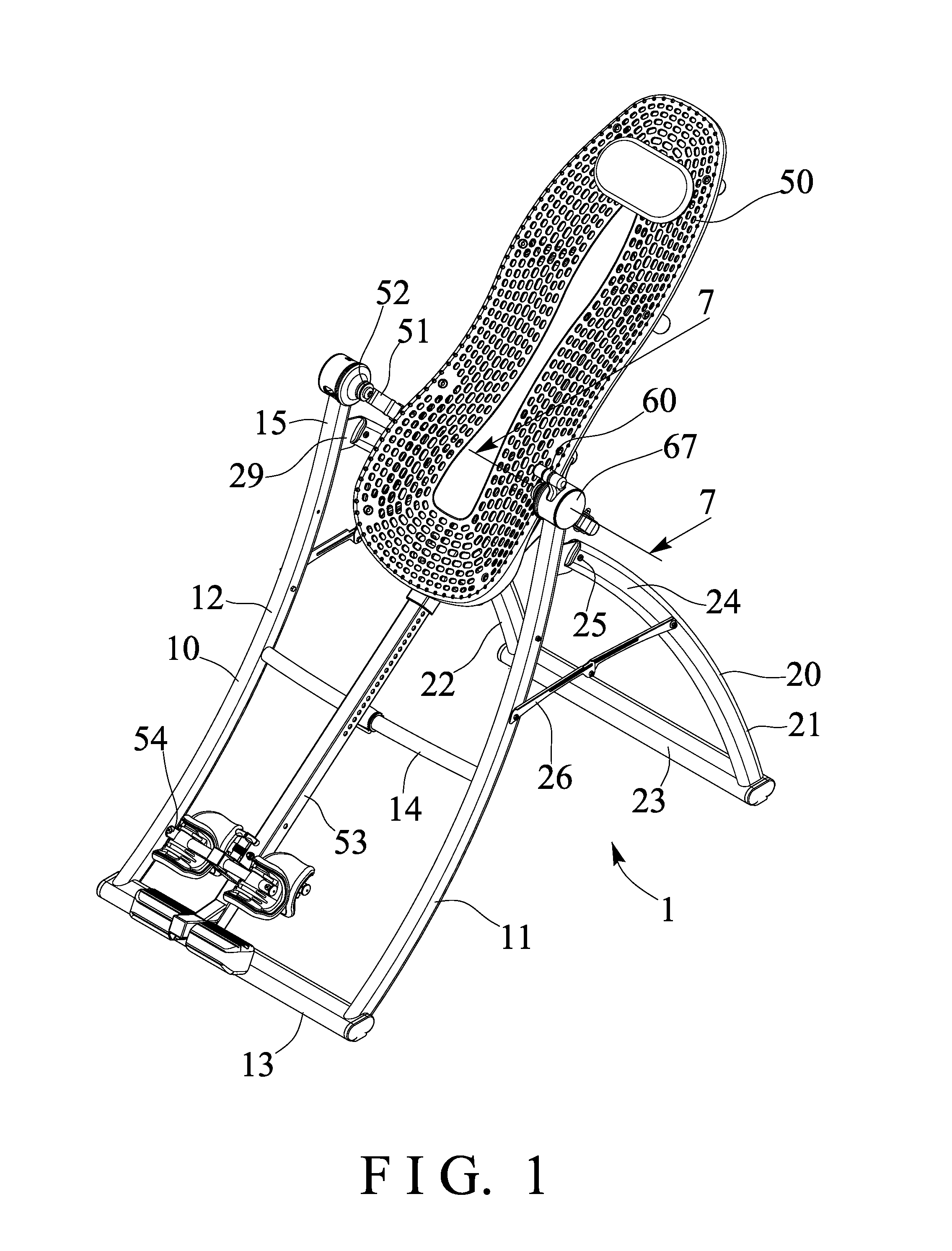
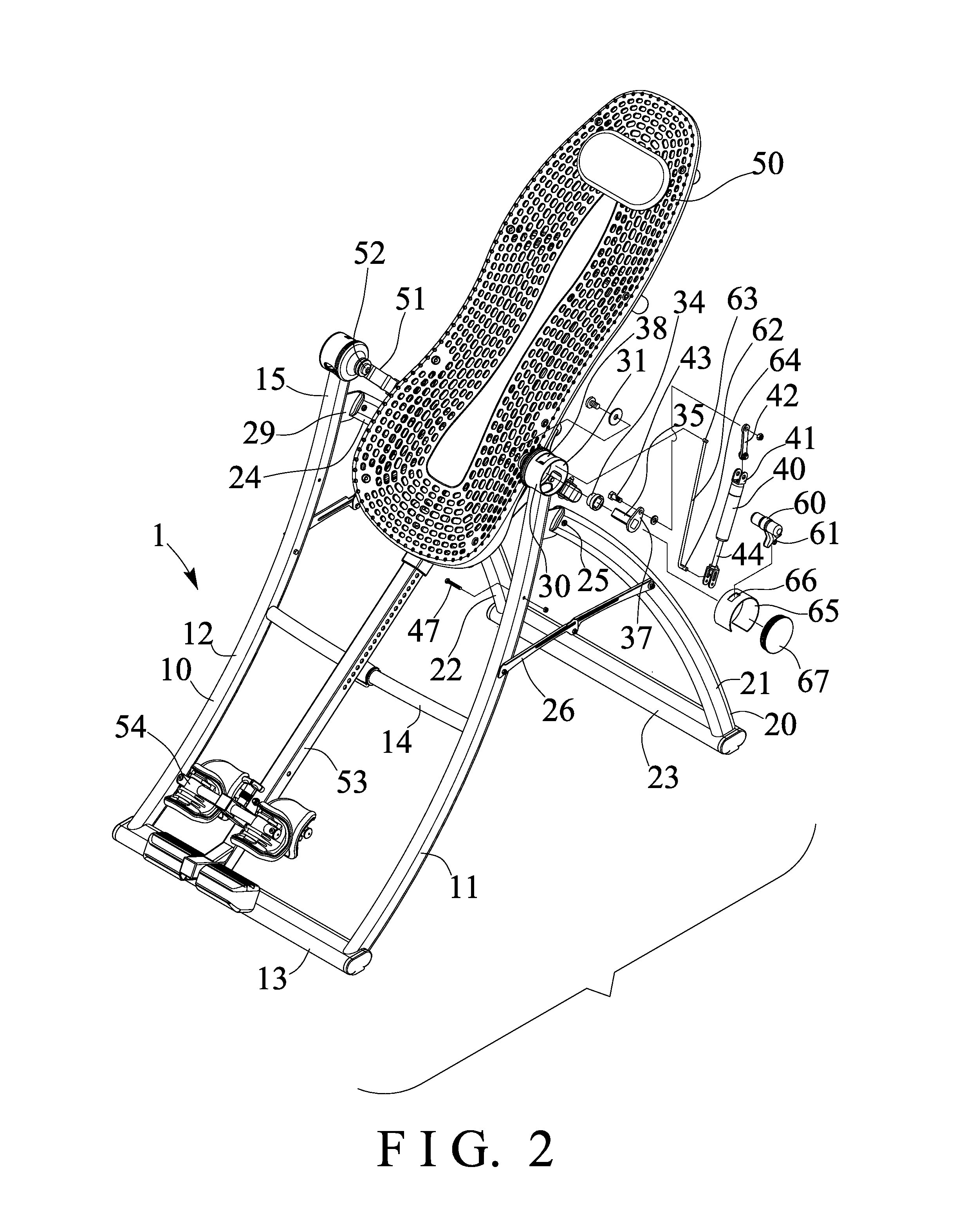
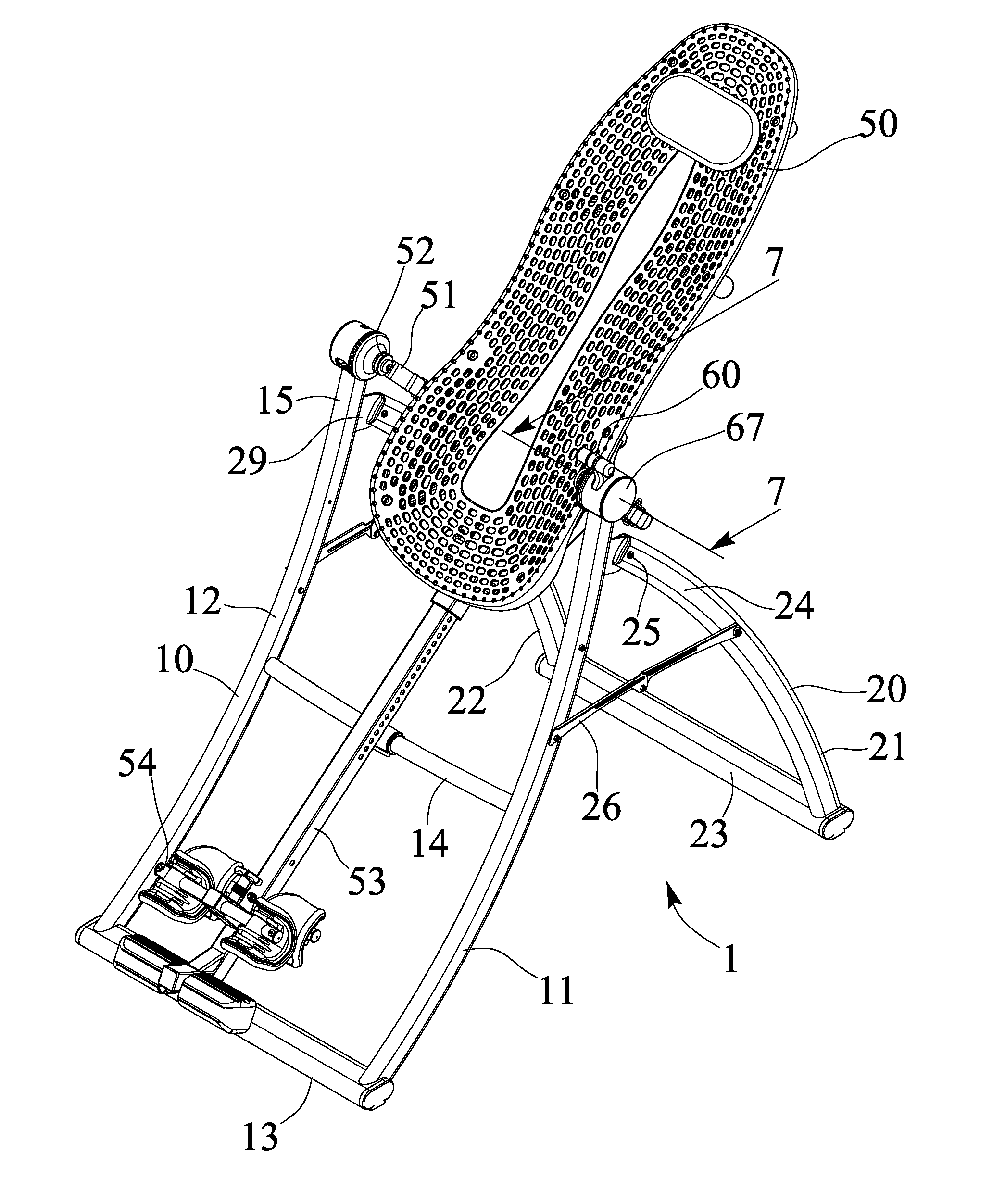
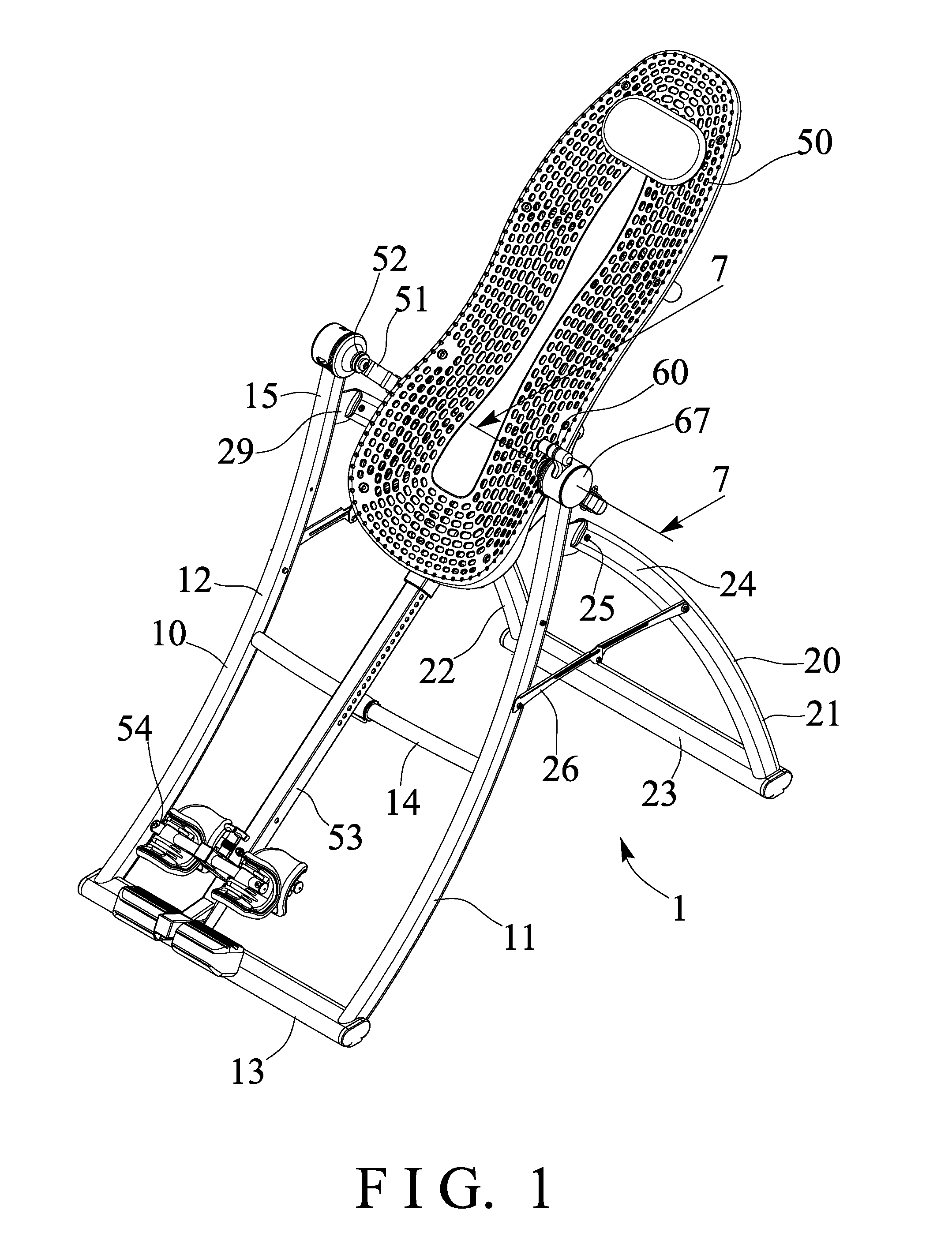
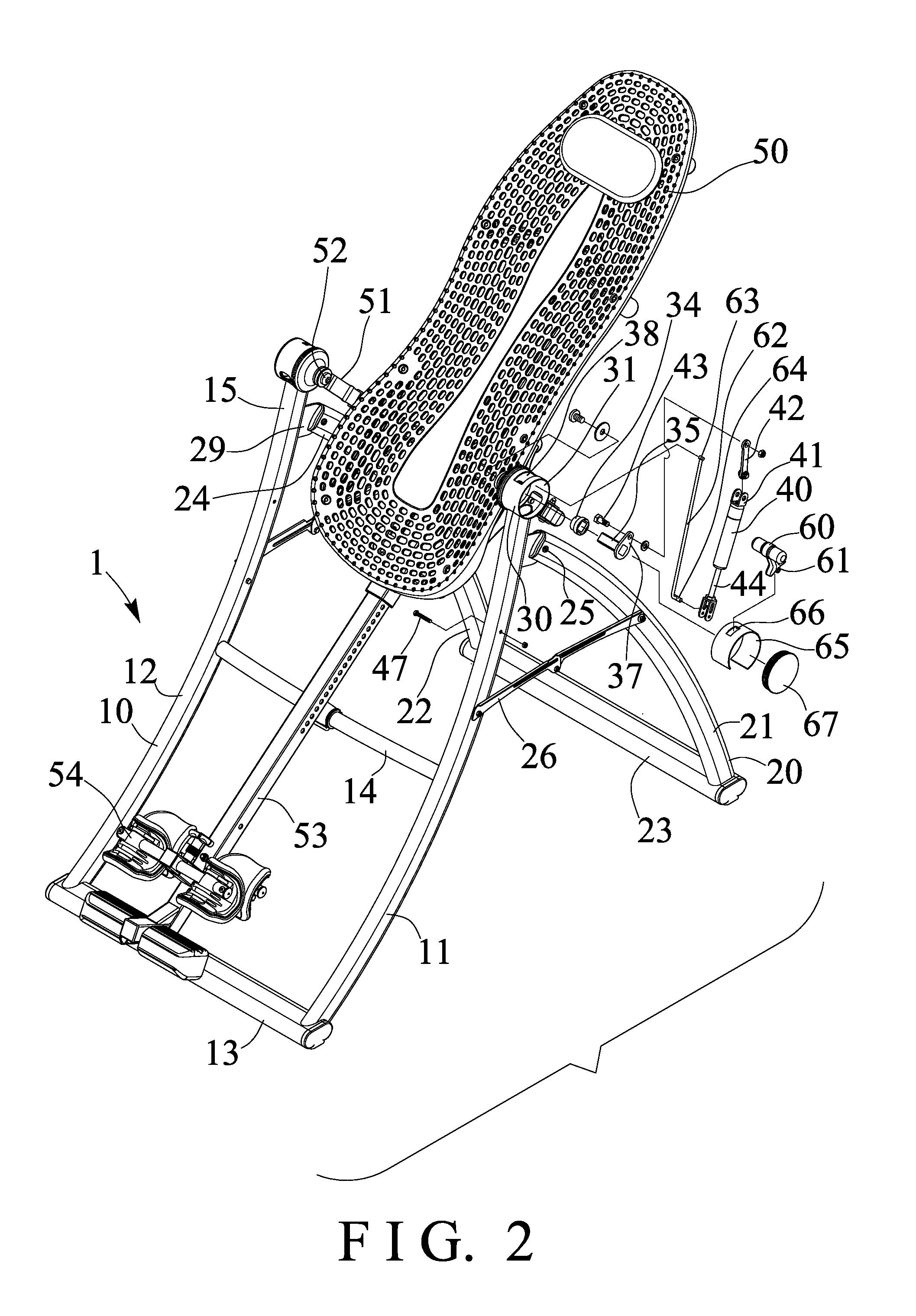
Tilting inversion exerciser
ActiveUS9526667B1Giving some security to the userSimplified actuationChiropractic devicesStiltsEngineeringActuator
Owner:BETO ENG & MARKETING
Preservation device and container stopper for use therewith
A device and method for preservation of an oxidizable substance, e.g. a liquid such as a beverage of which wine is an example, is described. In a first aspect, a device is described for controlling the delivery of a predetermined amount of inert gas into a container with a single opening such as a wine bottle at a pre-determined pressure, suitable for an efficient delivery of the inert gas, with a simultaneous displacement of the air present in the top space of the container or bottle, in a simple actuation. In a second aspect, an improved container or bottle stopper is described with simple features that allow easy and cheap manufacture significantly reducing the cost of the stopper. In a third aspect to an efficient and cost-effective method is described for the preservation of a degradable substances especially liquids such as beverages of which wine is an example.
Owner:DULST MARC
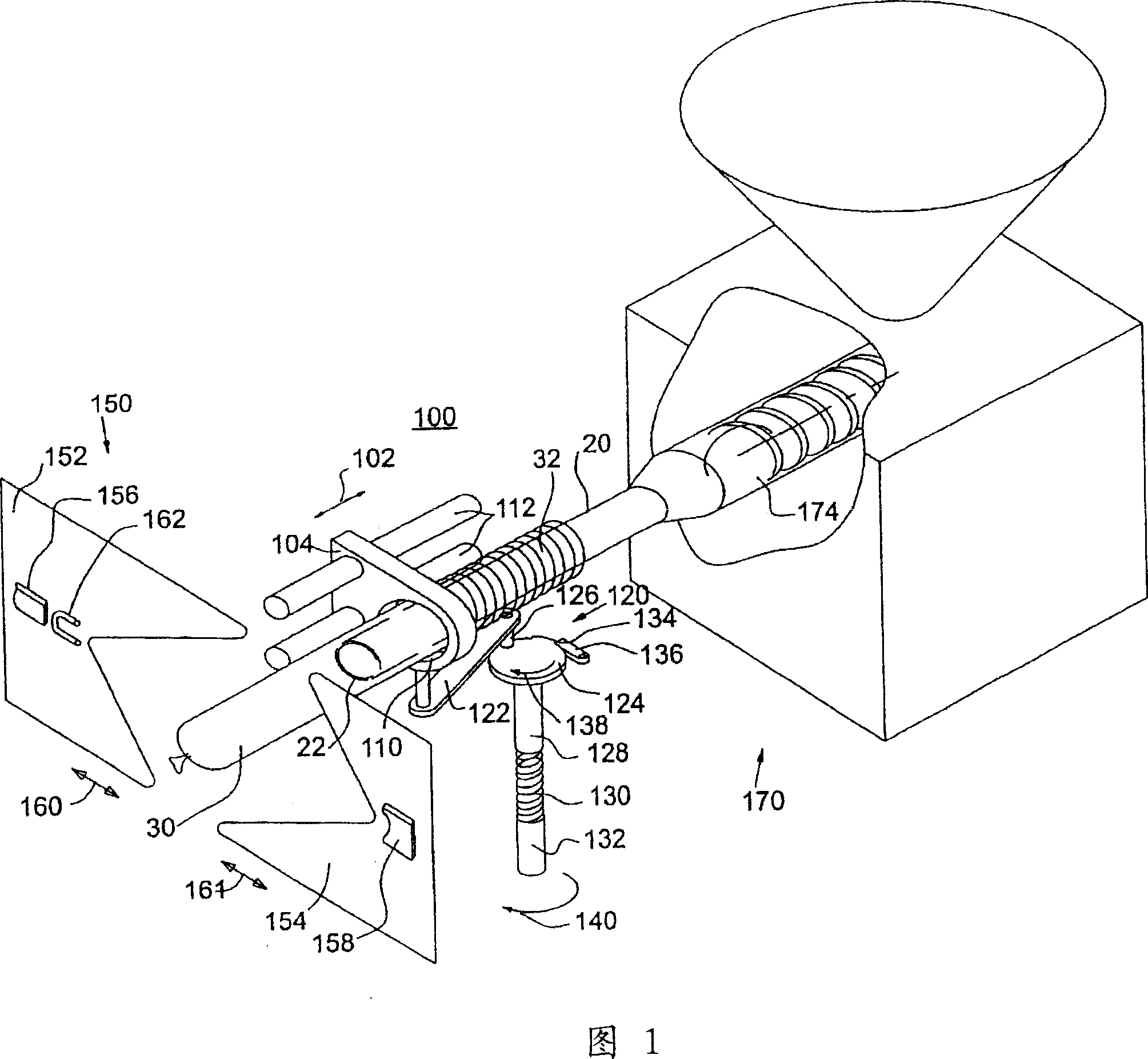
Device and method for portioning and packaging
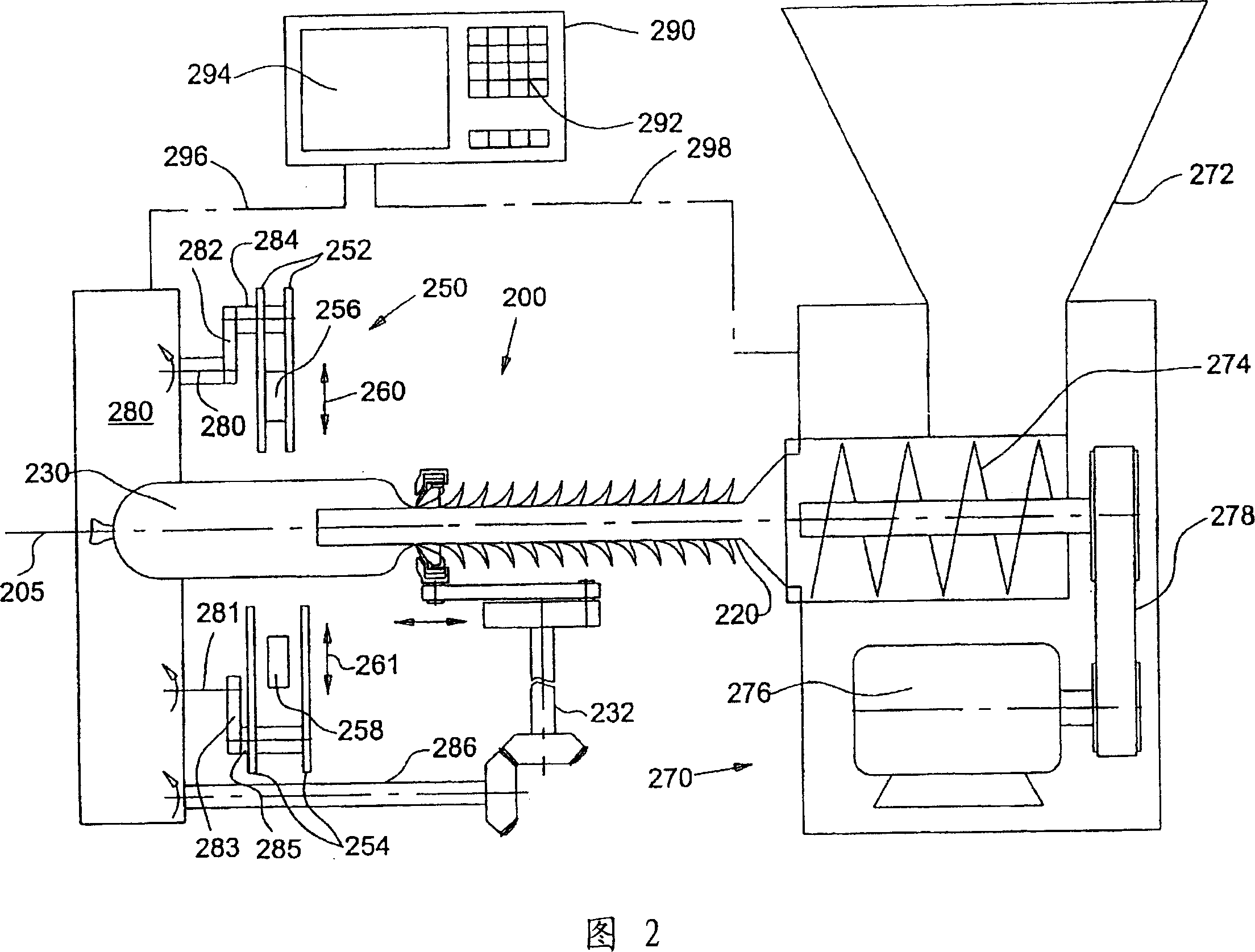
InactiveCN1934961ASimplified actuationAllows for increased efficiencySausage skin tying apparatusSausage filling/stuffing machinesPortion sizeFilling materials
Portioning and packaging device comprises a conveying device (170, 270) for filling material that has a pump for generating a continuous volume and is connected to a filling pipe (20, 220) supplying a reservoir of a tube-shaped packing sleeve (30, 230) so that this can be removed with filling material from the filling tube, and a sealing device (150, 250) that ties the end of the filled tube and seals it with a sealing element(162). The sealing device has a control device (290) that generates a control signal during the tying and sealing step based on a selected portion size and the continuous volume flow and sends it to a drive of the sealing device. An independent claim is also included for a portioning and packaging process.
Owner:POLY CLIP SYST
Pistol-grip for intuitive control of a robotic or virtual hand
InactiveUS9020644B2Facilitates intuitive controlImprove functionalityProgramme controlManual control with multiple controlled membersSimulationRobot end effector
An end effector controller that is gripped by an operator in one hand, including a pistol-grip housing configured to fit in the palm of an operator's hand when gripped and having mounted thereon a plurality of switching mechanisms with pivoting, dual-acting switch triggers each configured for independent actuation by multiple fingers of the hand when said controller is gripped, and a method for controlling a robotic end effector remotely using the operator hand-gripped controller, the method including switching between preset operating modes of the end effector using a single, control input element, easily actuated by a finger in the operator's gripping hand; and providing continuous fine adjustment between preset modes using a second, control input element also easily actuated by a finger on the operator's gripping hand.
Owner:BARRETT TECH LLC
Thumb-actuated candy or mint box
ActiveUS7743973B2Simplified actuationEasy to holdNon-removalbe lids/coversPackaging sweetsCardboardEngineering
A novel candy or mints box has an opening near the top of the box and an underlying slide that is moveable sideways across the opening. Preferably the top portion of the box includes a flap with an opening, and the flap extends over a corresponding opening in the front side such that the openings align, and the slide lies between the front side of the box and the top flap. The slide also preferably further includes a stop member and the box has a corresponding catch member, such that the slide is always contained within the box. Advantageously, the box is formed from a single blank piece of paper or cardboard stock, and folded in a particular sequence such that the slide ends up inside the box without the need for a separate insertion step.
Owner:HEGAMI DAVID TODJAR
Portable pump and method for producing same
InactiveUS20160263312A1Simplified actuationLow production costInfusion syringesMedical devicesHypodermoclysisBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a miniature portable pump with mechanical actuation, preferably without a motor, provided with a bowed piston for injecting fluid by manual dosing and / or continuously. The pump consists of a small number of parts with very low production cost, for injecting medication, preferably subcutaneously.
Owner:SWISSINNOV PROD SARL
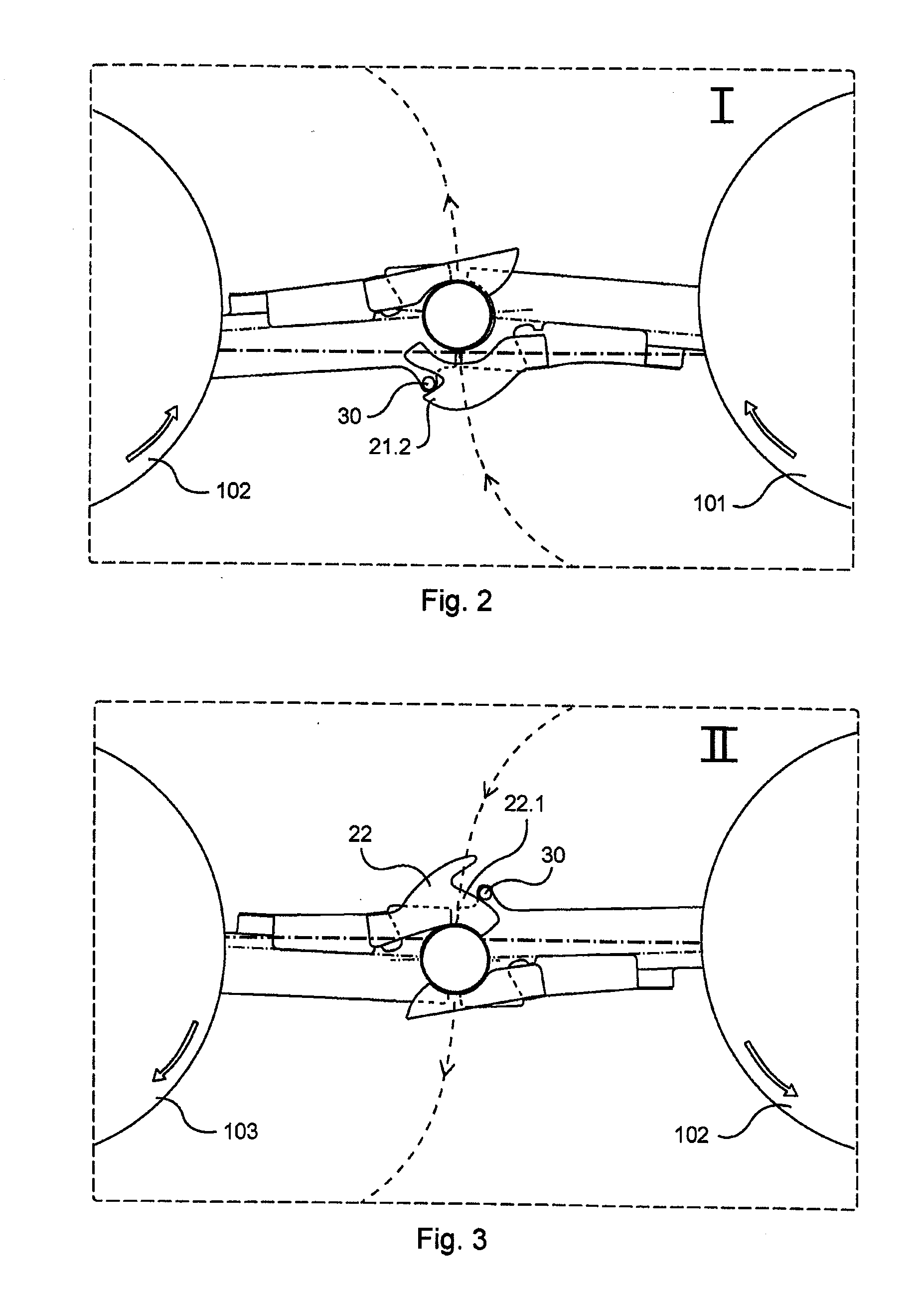
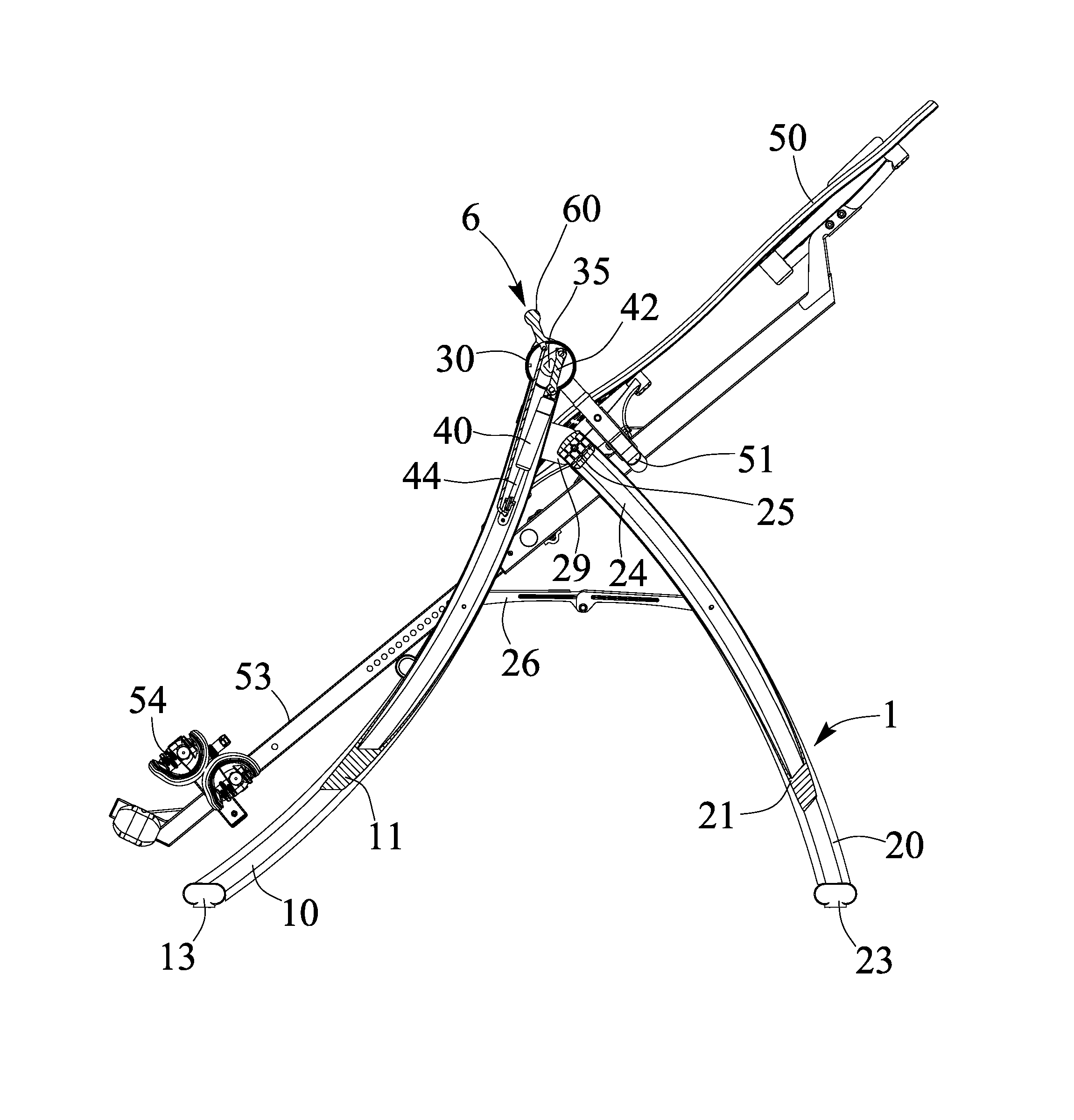
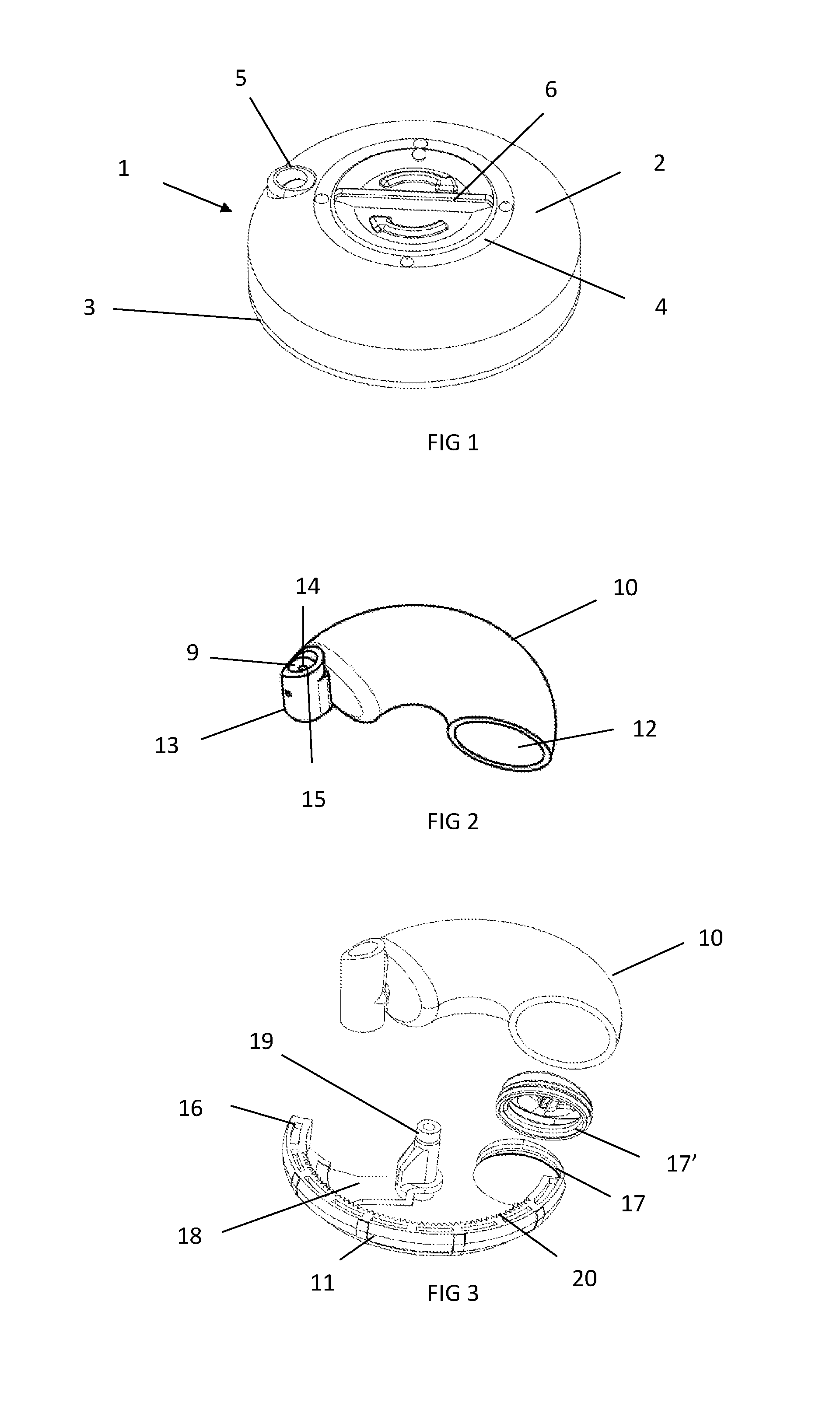
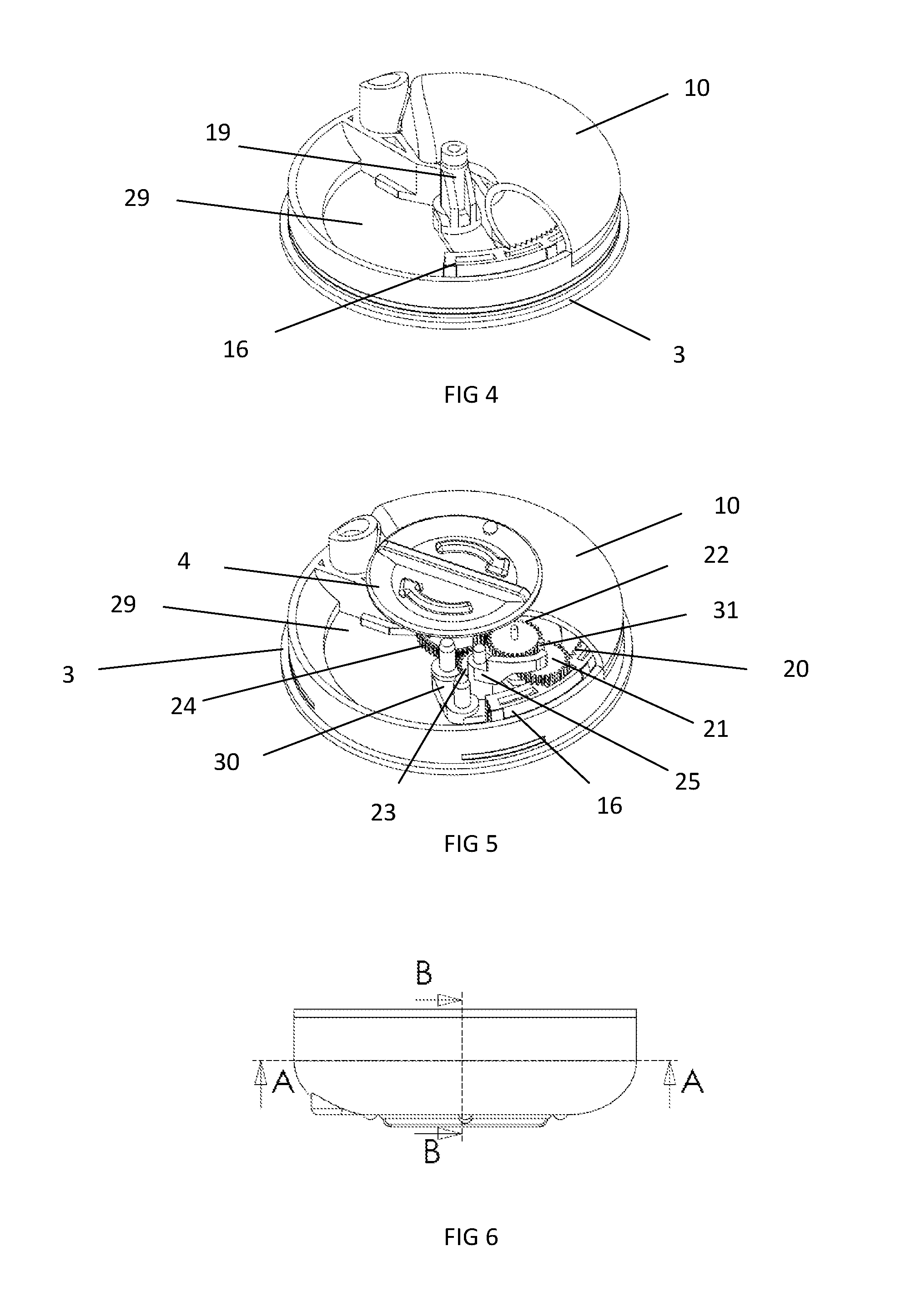
Tilting inversion exerciser
ActiveUS20160361586A1Giving some security to the userSimplified actuationChiropractic devicesMuscle exercising devicesEngineeringActuator
A tilting inversion exerciser includes a supporting stand having a primary frame and an auxiliary frame, the primary frame includes two posts, two barrels on the posts, two shafts attached to the barrels, a carrier attached to the shafts for supporting a supporting table, and an actuator is coupled between one of the shafts and one of the posts and includes a release valve for releasing the actuator when the release valve is depressed and actuated, and for locking the actuator when the release valve is released. The user may easily actuate the release valve to release and to lock the actuator without applying much force or energy to rotate the carrier and the supporting table relative to the supporting stand.
Owner:BETO ENG & MARKETING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com