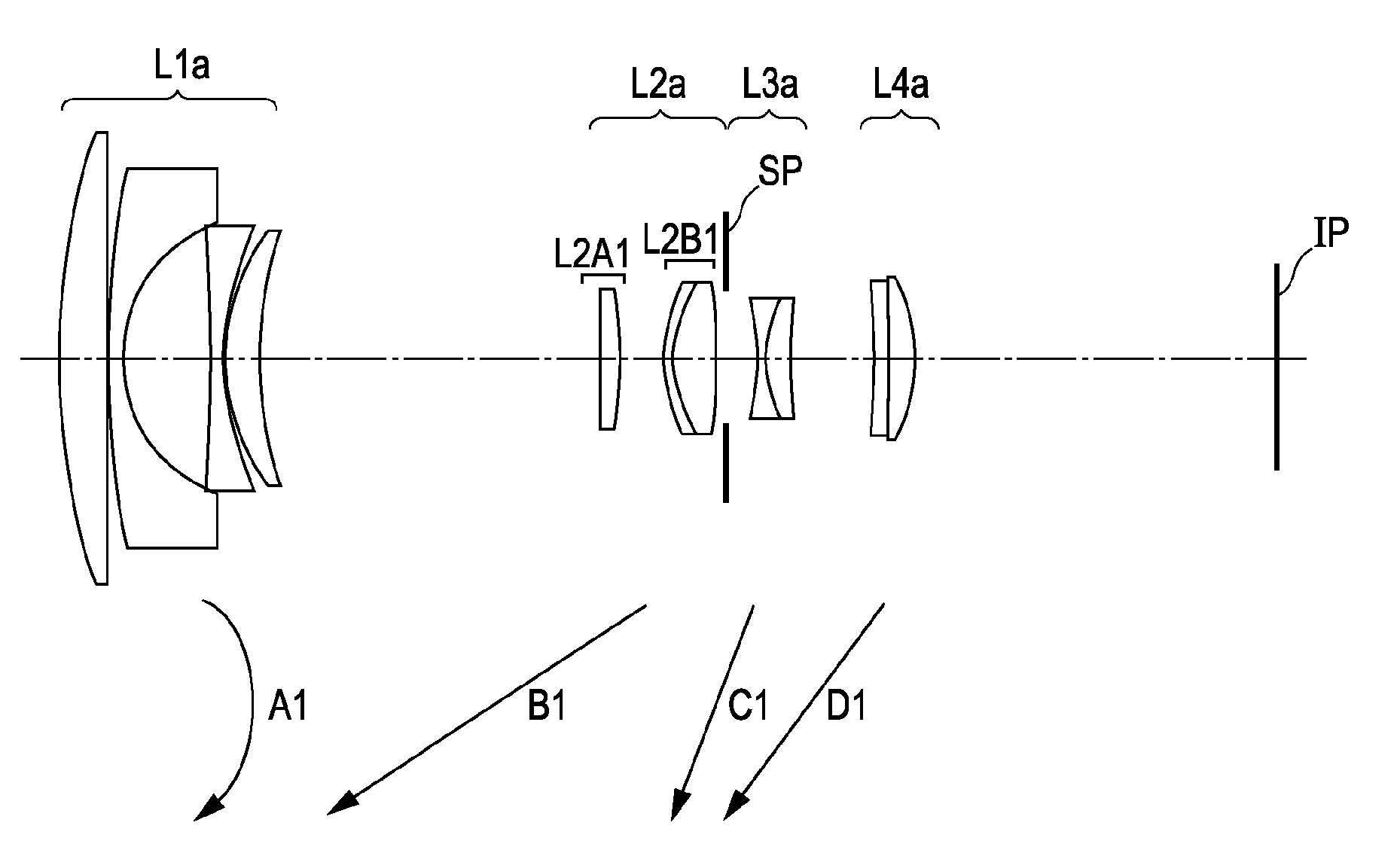
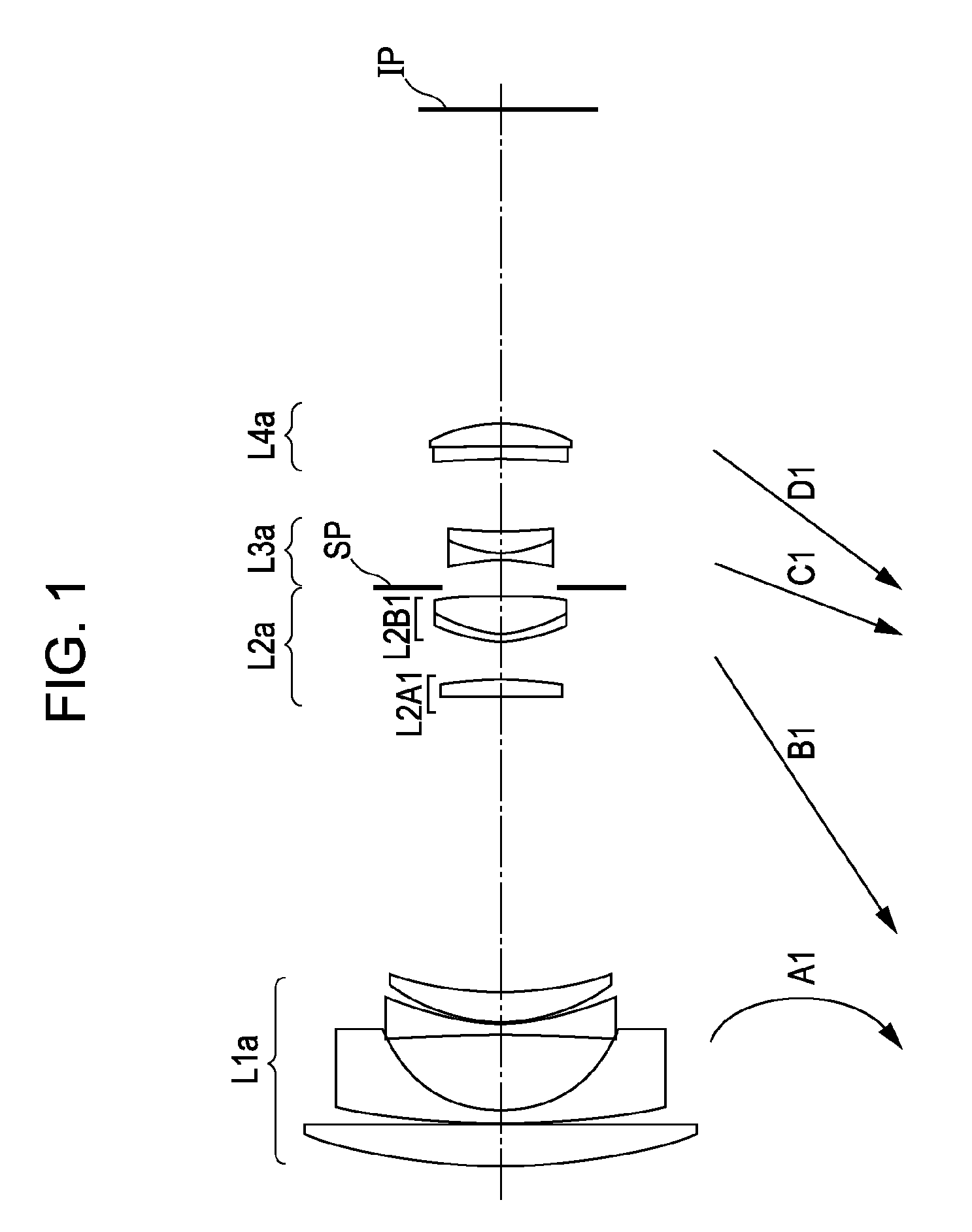
Zoom lens and image-pickup apparatus having the same
a technology of zoom lens and image pick-up apparatus, which is applied in the field of zoom lens, can solve the problems of difficult to suppress the variations of aberration due to zooming, the entire lens system is difficult to be miniaturized, and the increase of aberration due to vibration compensation, etc., and achieve the effect of efficient compensation for vibration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
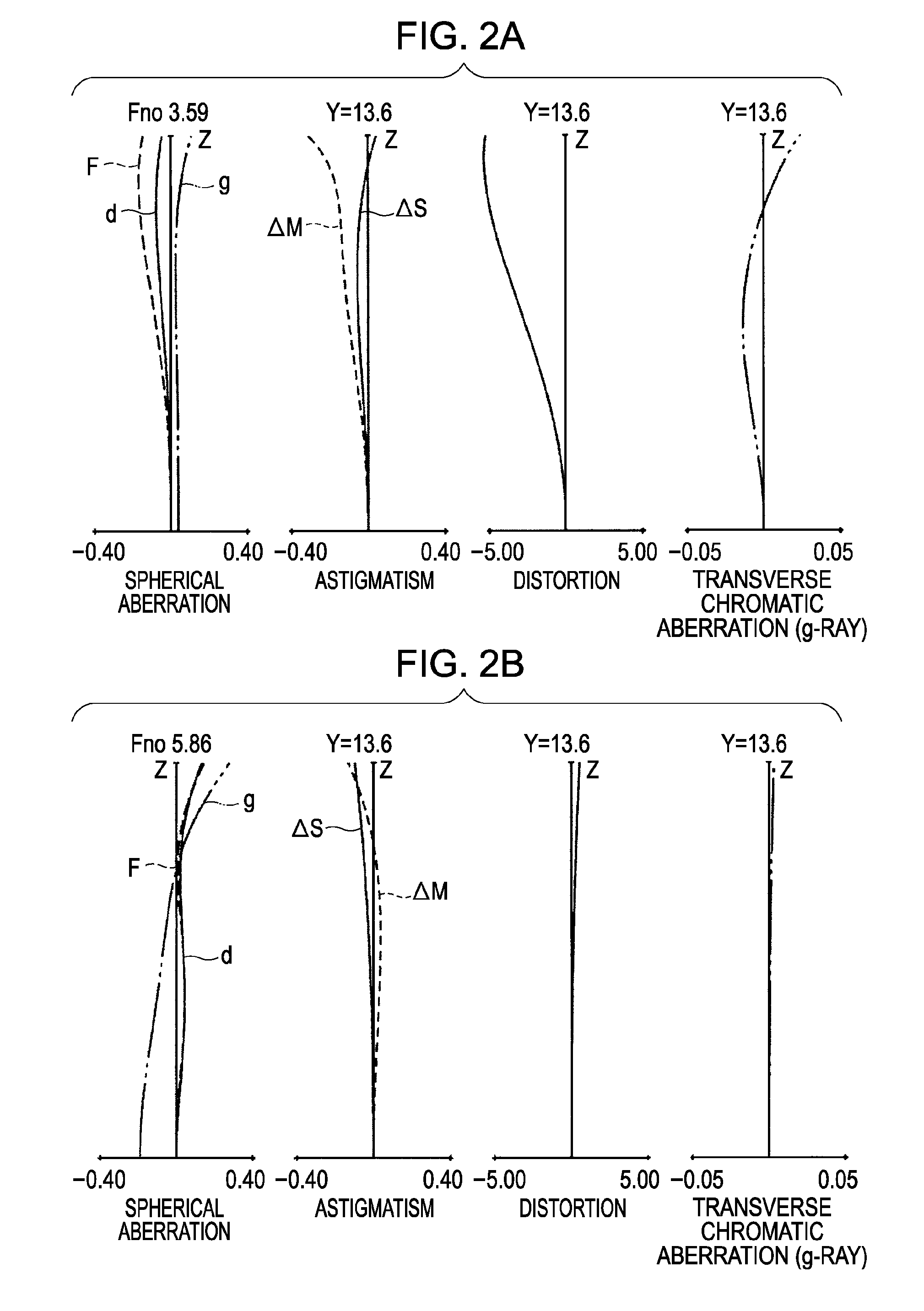
numerical examples 1
f=17.50˜53.00 Fno=3.59˜5.86 2ω=75.8°˜28.8°
R 1=74.641 D 1=4.50 N 1=1.516330 ν 1=64.1
R 2=−3856.041 D 2=0.15
R 3=98.417 D 3=1.60 N 2=1.622992 ν 2=58.2
R 4=14.489 D 4=8.52
R 5=−127.608 D 5=1.20 N 3=1.622992 ν 3=58.2
R 6=27.528 D 6=0.15
R 7=21.526 D 7=3.40 N 4=1.846660 ν 4=23.8
R 8=42.071 D 8=VARIABLE
R 9=−531.961 D 9=1.70 N 5=1.518229 ν 5=58.9
R10=−36.156 D10=4.53
R11=16.829 D11=0.80 N 6=1.846660 ν 6=23.9
R12=12.056 D12=4.20 N 7=1.487490 ν 7=70.2
R13=−71.553 D13=1.00
R14=APERTURE STOP D14=VARIABLE
R15=−28.778 D15=0.75 N 8=1.647689 ν 8=33.8
R16=12.243 D16=2.40 N 9=1.761821 ν 9=26.5
R17=51.593 D17=VARIABLE
R18=−62.665 D18=1.30 N10=1.491710 ν10=57.4
[0119]R19=−140.261 D19=−0.07
R20=1237.920 D20=2.69 N11=1.487490 ν11=70.2
R21=−17.585
\FOCAL LENGTH 17.50 31.07 53.00 VARIABLE SPACE\
D 8 33.74 13.03 3.04
D14 3.30 6.68 10.13
D17 8.24 4.86 1.41
numerical examples 2
f=18.69˜53.27 Fno=3.63˜5.86 2ω=72.2°˜28.7°
R 1=80.198 D 1=3.40 N 1=1.516330 ν 1=64.1
R 2=1485.520 D 2=0.15
R 3=74.916 D 3=1.60 N 2=1.622992 ν 2=58.2
R 4=14.601 D 4=7.99
R 5=−141.698 D 5=1.20 N 3=1.622992 ν 3=58.2
R 6=25.795 D 6=0.15
R 7=21.179 D 7=3.40 N 4=1.805181 ν 4=25.4
R 8=46.880 D 8=VARIABLE
R 9=−302.692 D 9=1.90 N 5=1.487490 ν 5=70.2
R10=−34.091 D10=4.20
R11=16.673 D11=0.80 N 6=1.846660 ν 6=23.9
R12=12.277 D12=4.50 N 7=1.487490 ν 7=70.2
R13=−73.294 D13=1.00
R14=APERTURE STOP D14=VARIABLE
R15=−29.161 D15=0.75 N 8=1.639799 ν 8=34.5
R16=12.672 D16=2.60 N 9=1.784723 ν 9=25.7
R17=43.512 D17=VARIABLE
R18=−96.235 D18=1.50 N10=1.583060 ν10=30.2
[0120]R19=−437.245 D19=0.03
R20=417.340 D20=3.80 N11=1.487490 ν11=70.2
R21=−18.474
\FOCAL LENGTH 18.69 32.08 53.27 VARIABLE SPACE\
D 8 33.62 13.53 3.23
D14 3.30 6.19 8.96
D17 7.34 4.45 1.68
ASPHERIC FACTOR
19 FACE: A=0.00000e+00 B=3.76648e−05 C=3.00374e−08
D=7.60709e−10 E=−8.99719e−12 F=0.00000e+00
numerical examples 3
f=18.62˜53.32 Fno=3.63˜5.86 2ω=72.4°˜28.7°
R 1=70.299 D 1=3.40 N 1=1.516330 ν 1=64.1
R 2=601.574 D 2=0.15
R 3=85.189 D 3=1.60 N 2=1.622992 ν 2=58.2
R 4=14.573 D 4=8.08
R 5=−131.403 D 5=1.20 N 3=1.622992 ν 3=58.2
R 6=26.414 D 6=0.15
R 7=21.357 D 7=3.40 N 4=1.805181 ν 4=25.4
R 8=48.045 D 8=VARIABLE
R 9=−212.350 D 9=1.90 N 5=1.516330 ν 5=64.1
R10=−33.748 D10=4.20
R11=16.638 D11=0.80 N 6=1.846660 ν 6=23.9
R12=12.089 D12=4.50 N 7=1.487490 ν 7=70.2
R13=−67.351 D13=1.00
R14=APERTURE STOP D14=VARIABLE
R15=−27.965 D15=0.75 N 8=1.639799 ν 8=34.5
R16=12.432 D16=2.60 N 9=1.784723 ν 9=25.7
R17=43.001 D17=VARIABLE
R18=−97.655 D18=1.50 N10=1.583060 ν 10=30.2
[0121]R19=−332.527 D19=0.04
R20=1043.264 D20=3.76 N11=1.487490 V11=70.2
R21=−17.869
\FOCAL LENGTH 18.62 31.88 53.32 VARIABLE SPACE\
D 8 32.81 13.04 2.78
D14 3.30 6.07 8.95
D17 7.20 4.43 1.55
ASPHERIC FACTOR
19 FACE: A=0.00000e+00 B=3.81779e−05 C=2.00413e−08
D=6.78143e−10 E=−4.60818e−12 F=0.00000e+00
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com