Electromotive chain saw
a technology of electromagnetism and chain saw, which is applied in the direction of motor/generator/converter stopper, dynamo-electric converter control, metal sawing accessories, etc., can solve the problems of inability to go to the subsequent steps of work, inadvertent damage to material in process, and rotation of cutting chain for several seconds, so as to improve the durability of the clutch mechanism and enhance the durability of the engagement detent and other clutch components.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
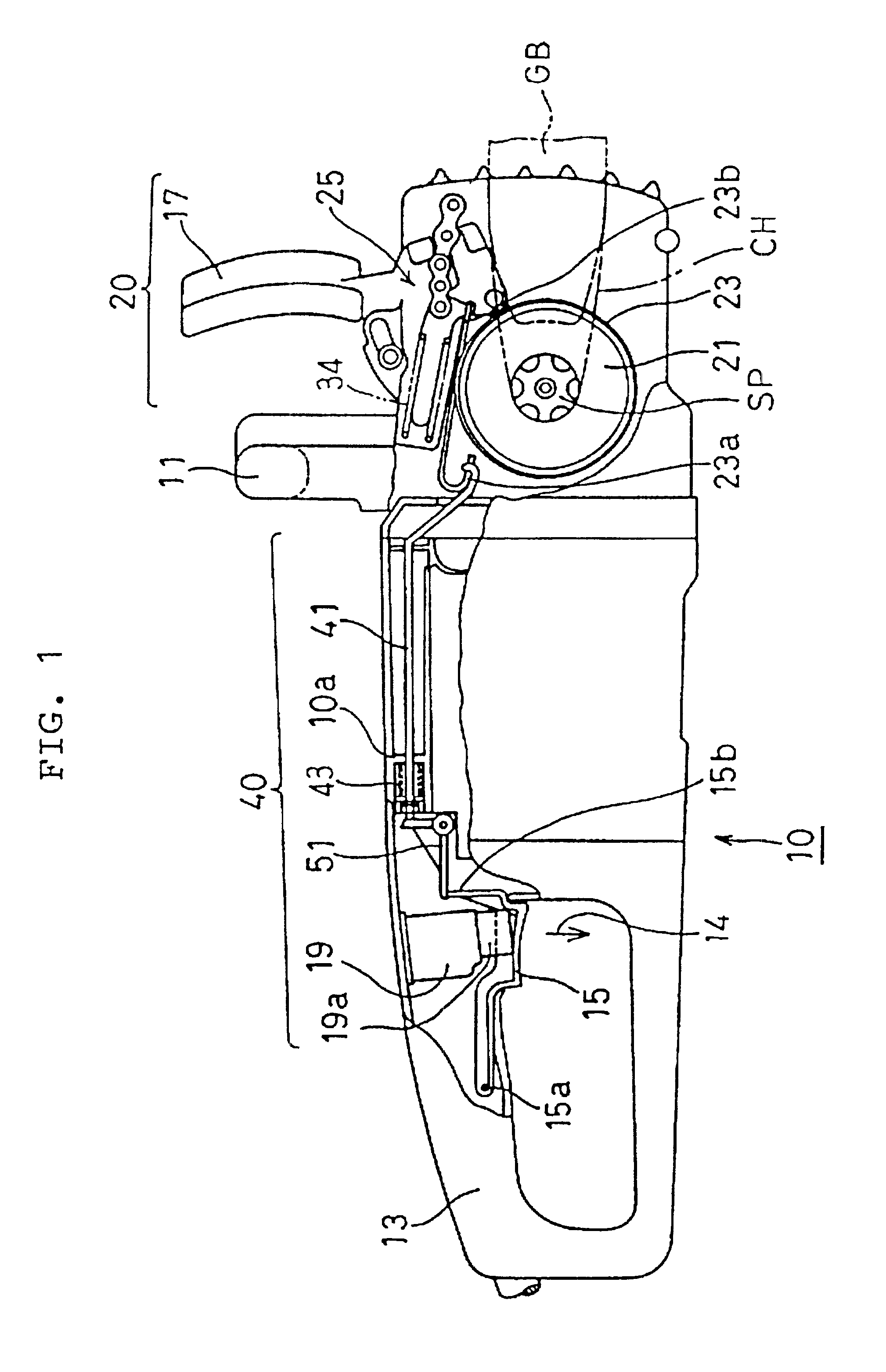
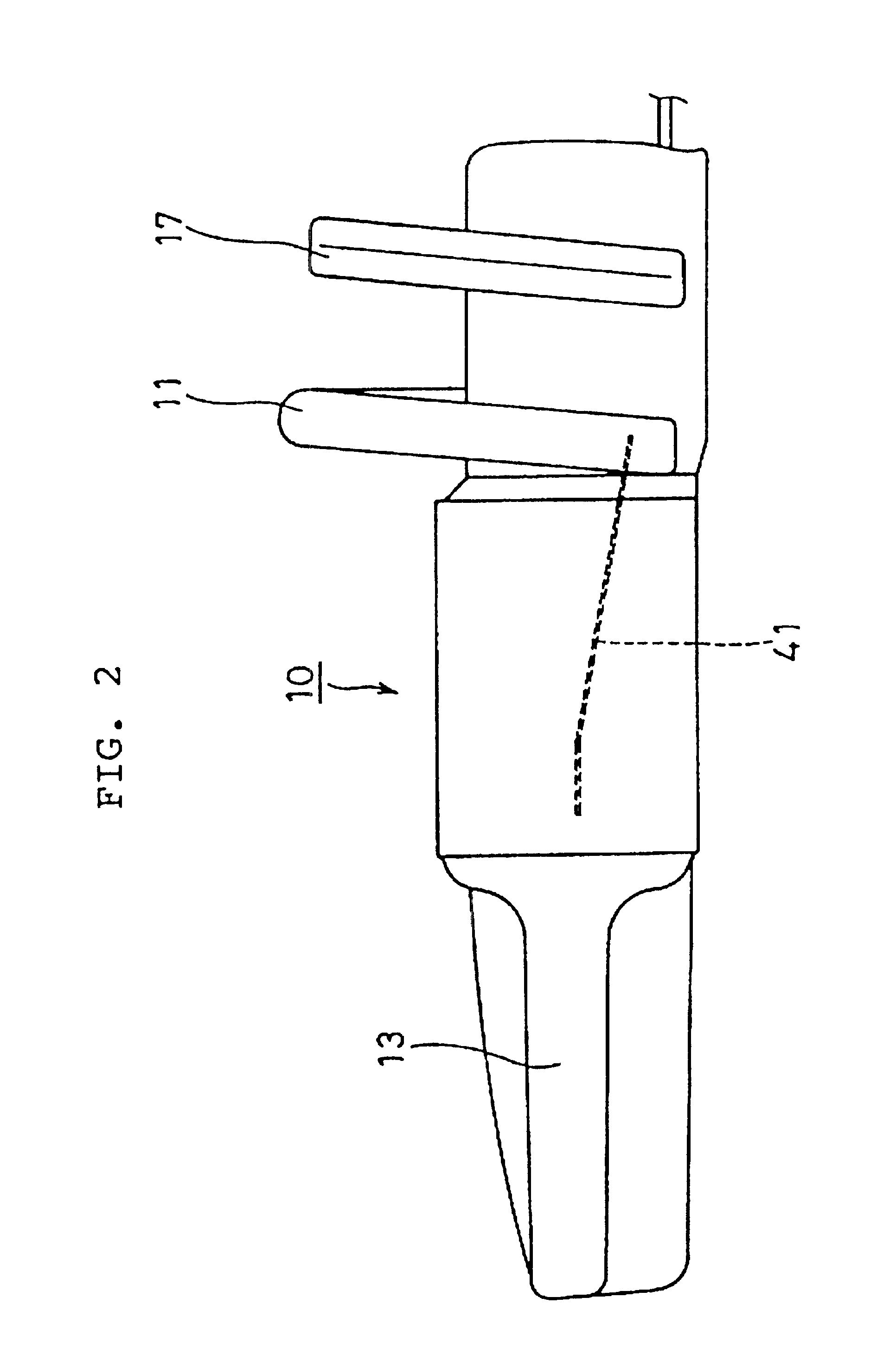
As shown in FIG. 1, in an electromotive chain saw 10 of the first embodiment, a chain CH is wound around a guide bar GB extending from a housing and is driven with an electric motor M (as shown in FIG. 8) and a not-shown centrifugal clutch built into the housing. The electromotive chain saw 10 is manually held with a forward handle 11 and a rearward handle 13. The grip of the rearward handle 13 is provided with a movable trigger lever 15. A hand guard 17 is disposed in front of the forward handle 11, with a hand guard brake device 20 built therein, which is operated by turning the hand guard 17 in the direction shown by arrow 16 in FIG. 3. The trigger lever 15 is normally urged, by a spring having a switch built therein, in the direction shown by an arrow 14 in FIG. 1, and is brought in contact with a push button 19a of a power switch 19 of the electric motor when depressed.
As shown in FIG. 3, the hand guard the brake device 20 applied in cooperation with the hand guard 17 is formed...
second embodiment
A second embodiment is now explained. The second embodiment is the same as the first embodiment in that the brake circuit 62 for dynamic braking as shown in FIG. 4, the hand guard brake device 20 operatively connected to the hand guard 17, and the centrifugal clutch are provided. The components having the same reference numerals as those of the components of the first embodiment are not explained hereinafter. only the aspect of the second embodiment different from the first embodiment, the structure of the mechanical brake device operated when the trigger lever is let off, is explained.
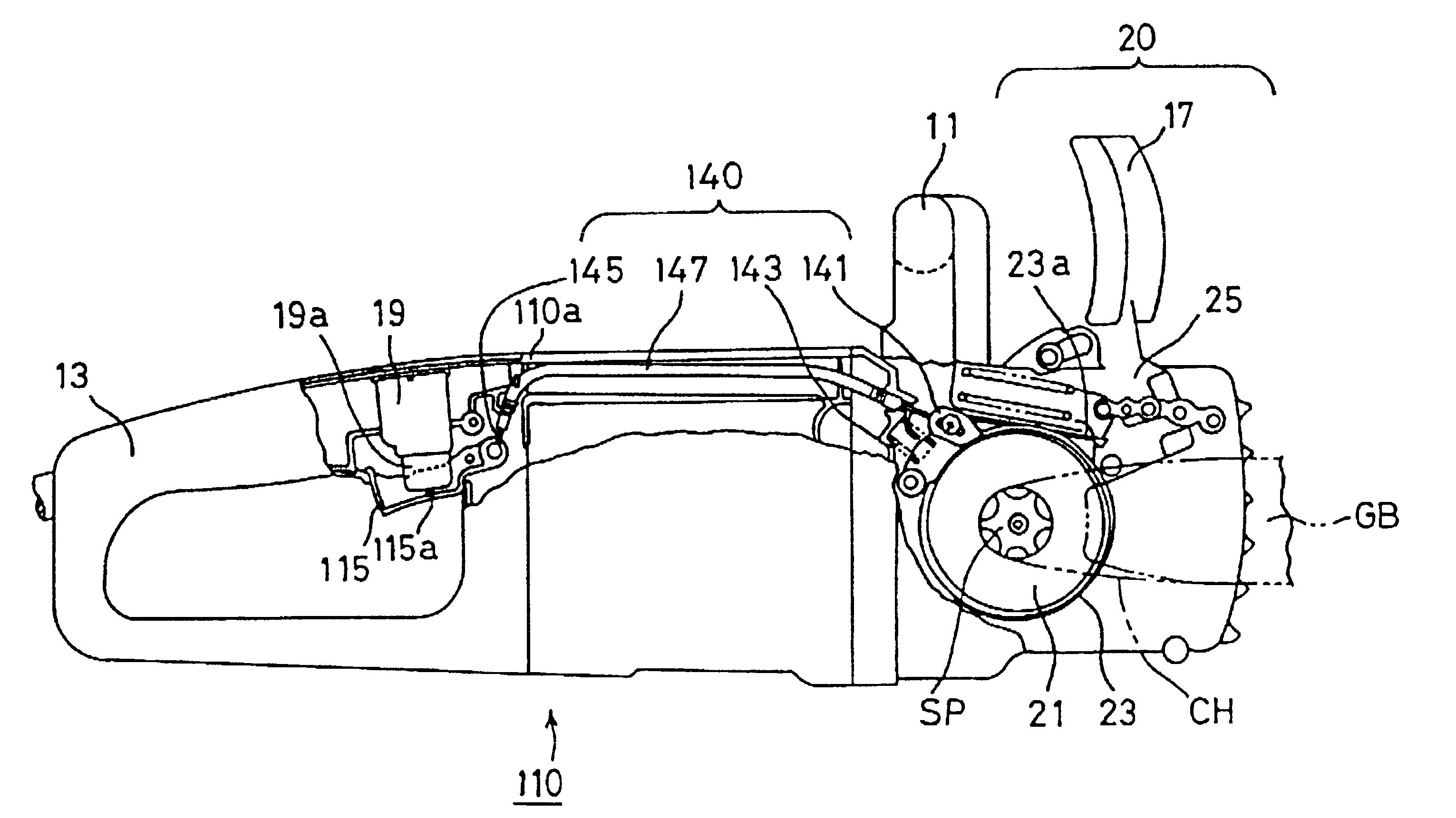
In a chain saw 110 according to the second embodiment, as shown in FIGS. 5 and 6, a mechanical brake device 140 is composed of a brake shoe 141 which can be swung on a support 142a and can be engaged with the periphery of brake drum 21. The mechanical brake device 140 is also composed of a coil spring 143 for urging the brake shoe 141 to engage with the brake drum 21, and a wire 145 connected at one e...
third embodiment
A third embodiment is now explained referring to FIGS. 8-12. The third embodiment is the same as the first embodiment in that the electric drive and brake device 60 for dynamic braking as shown in FIG. 4, and the hand guard brake device 20 operatively connected to the hand guard 17 are provided. The components having the same reference numerals as those of the components of the first embodiment are not explained hereinafter. The aspects of the third embodiment different from the first embodiment, the clutch mechanism, the mechanical brake device operated when the trigger lever is released and the circuit structure of the electric drive and brake device, are explained.
In an electromotive chain saw 560 according to the third embodiment shown in FIG. 8, a trigger-linked mechanical brake 570 is driven with a linkage when a trigger member 585 is released, thereby disconnecting a clutch 590 and stopping the brake drum 521. The hand gaurd brake device, operated by turning the hand guard 17...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Speed | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com