Methods for identifying inducers and inhibitors of propteolytic antibodies, compositions and their uses
A technology of antibodies and compounds, applied in the fields of immunology, molecular biology and medicine, can solve problems such as increased catalytic turnover
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment IA
[0085] Catalytic Antibodies for Tumor Immunotherapy
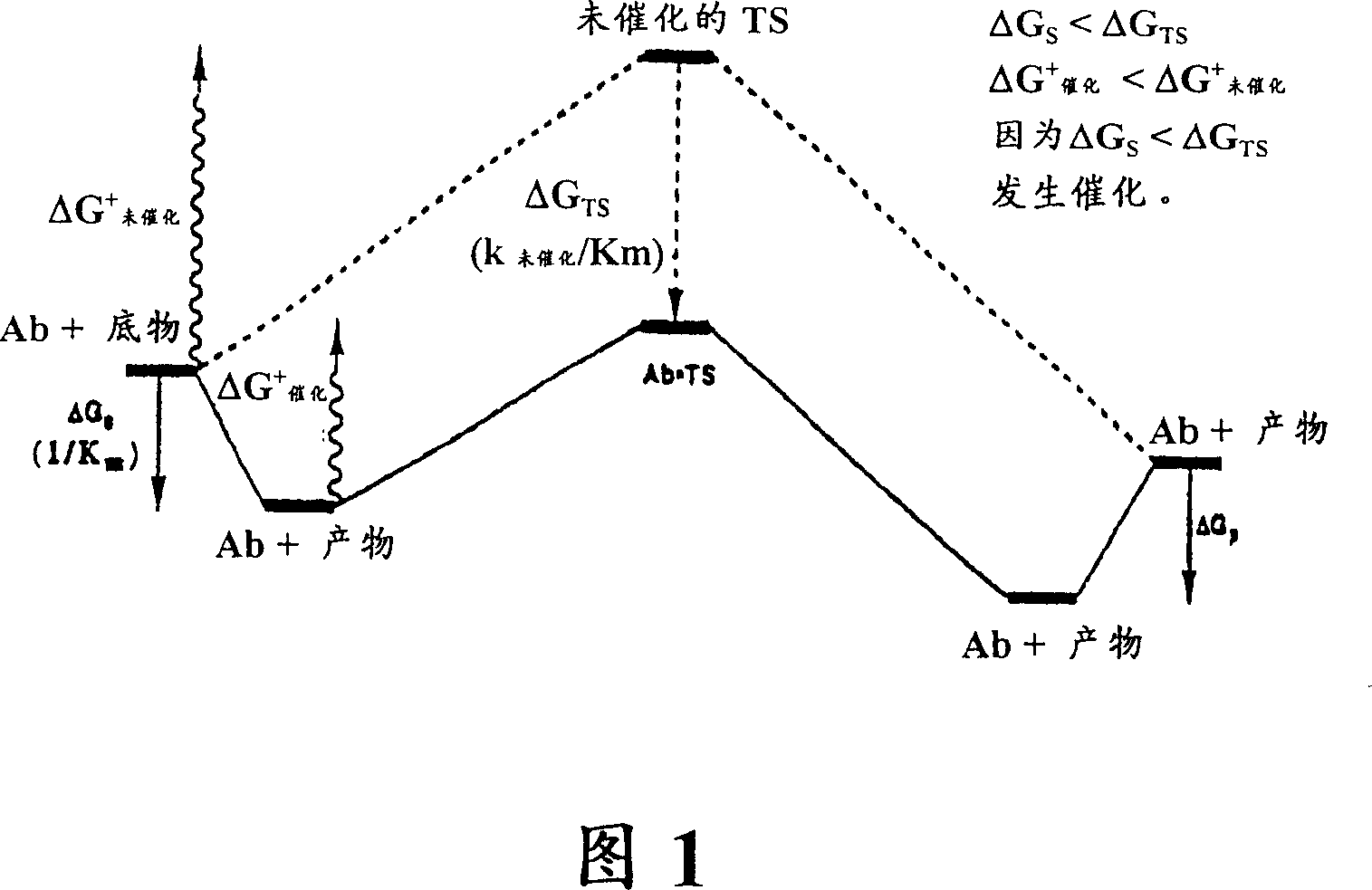
[0086] In this example a method for producing catalytic antibodies (Abs) suitable for the treatment of cancer is described. Such antibodies rely on catalytic functions to provide a superior immunotherapy option for cancer treatment, since cleavage of the target antigen should result in its permanent inactivation. Furthermore, a single antibody molecule can be reused to inactivate multiple antigen molecules. In contrast, non-catalytic antibodies bind antigen stoichiometrically and the binding is reversible. Upon dissociation from the complex, the antigen can resume its biological function.
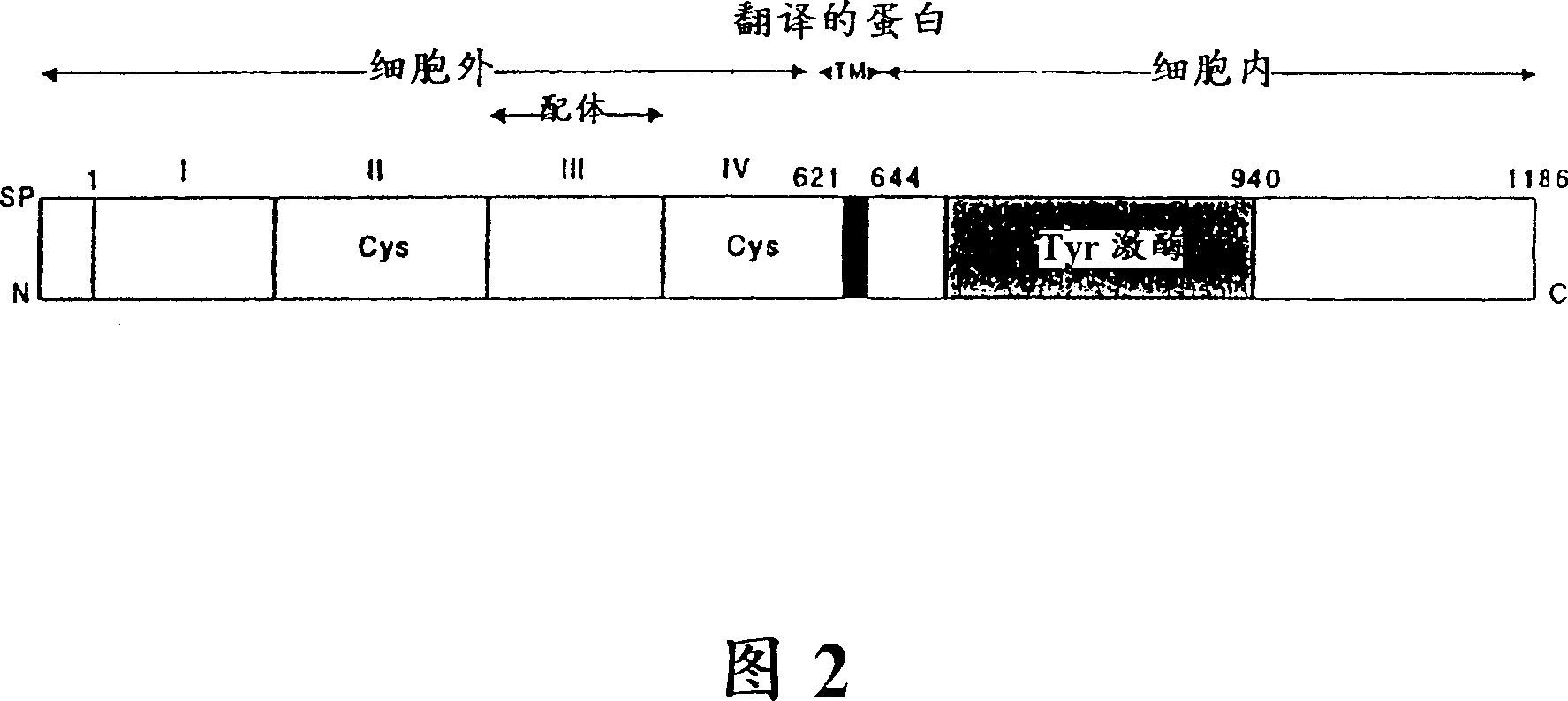
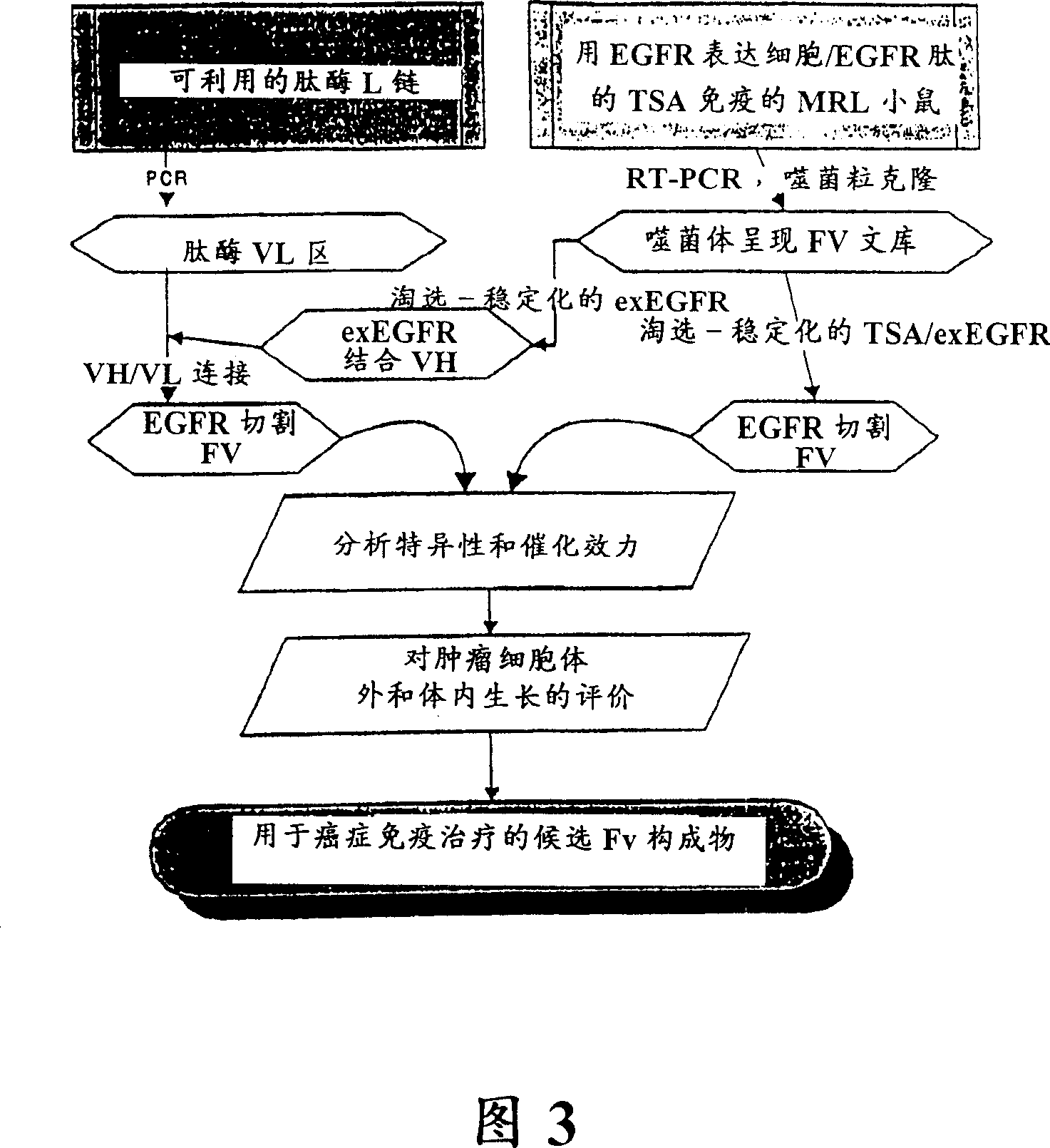
[0087] A tumor-associated antigen, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), will be used to synthesize an exemplary antigen suitable for stimulating the production of antibodies with enzymatic activity. Previous studies on peptidase antibodies have revealed that 1) certain antibodies are able to combine the ability to bind individual ...
Embodiment IB
[0136] Administration of Catalytic Antibody and Antisense p53 in a Combination Chemotherapy Regimen
[0137] When a cell suffers damage to its genome, there are mechanisms in place in the cell that will determine whether the cell will attempt to repair itself, or whether it will undergo programmed cell death. In order for proliferating cells to efficiently undertake genome repair, they must be taken out of cycle. This can be achieved using so-called "cell cycle checkpoints", which give proliferating cells time to repair genomic damage rather than pass it on to daughter cells.
[0138] Figure 18 illustrates the central role of normal (wild-type) p53 in inducing one or the other of these two possible cellular responses to genomic damage. Damage to the genome results in increased expression of p53, which in turn initiates a variety of other events that produce specific cellular responses to the damage.
[0139] Based on these relationships, it is reasonable to expect that certa...
Embodiment II
[0209] Catalytic antibodies in vaccination against HIV
[0210] Described herein is a vaccine construct useful in the treatment of AIDS comprising model B cell epitopes and T helper cell epitopes derived from gp120. The CRAA of the B cell epitope was used to elicit catalytic antibodies. Canonical B cell epitopes are derived from the CD4 binding site that is generally conserved among different HIV-1 strains. Furthermore, the CD4 binding site of gp120 is a suitable target because, unlike many other epitopes, the CD4 binding site is easily accessible by antibodies on the surface of native viruses [31]. The CD4 binding site is known to be a conformational determinant.
[0211] In the present invention, the preparation of catalytic antibodies recognizing a specific part of the CD4 binding site (as opposed to the complete CD4 binding site) is described. Additional peptide epitopes in gp120 (or other HIV proteins) that may be suitable targets for catalytic antibodies will also be ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com