Method for data exchange between network elements in networks with differing address ranges
A network unit, data exchange technology, applied in the field of data exchange, can solve problems such as disadvantages
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
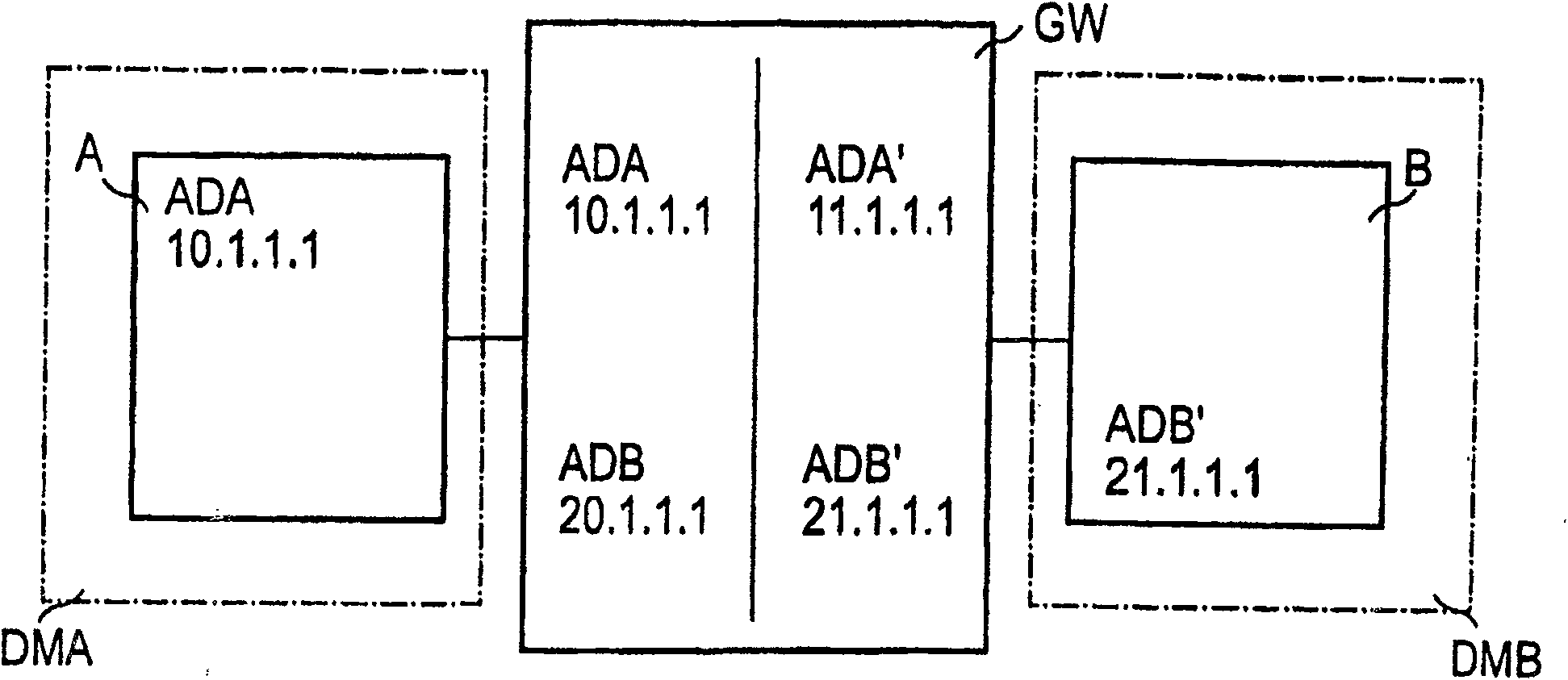
[0027] figure 1 shows the first network area DMA and the second network area DMB and the network node device GW connecting the two network areas DMA, DMB. In the figures, the network areas DMA, DMB are each symbolized by dotted lines.
[0028] The first network element A is arranged in the first network area DMA and the second network element B is arranged in the second network area DMB. In addition to the described network elements A, B, further (not shown) network elements can be arranged in the respective network areas DMA, DMB if necessary. Furthermore, in addition to the network node device GW, further (not shown) network node devices can also be used for the connection of the network areas A, B, if required.
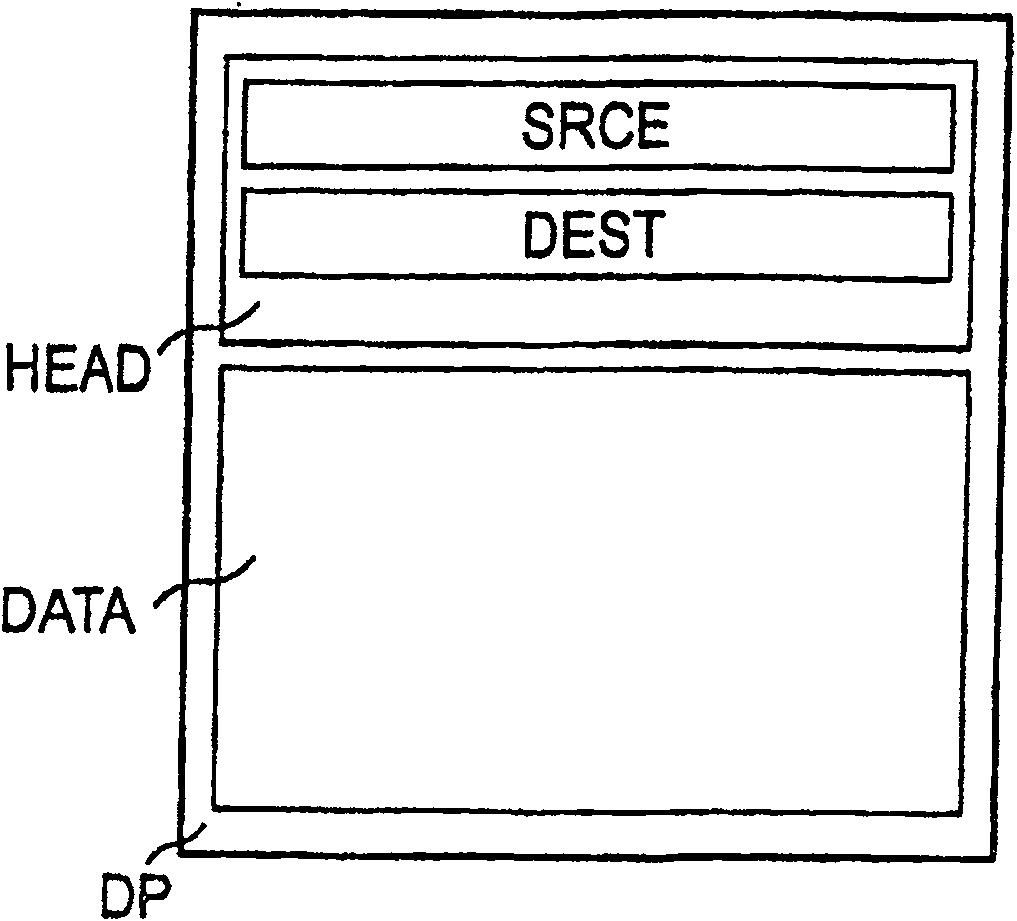
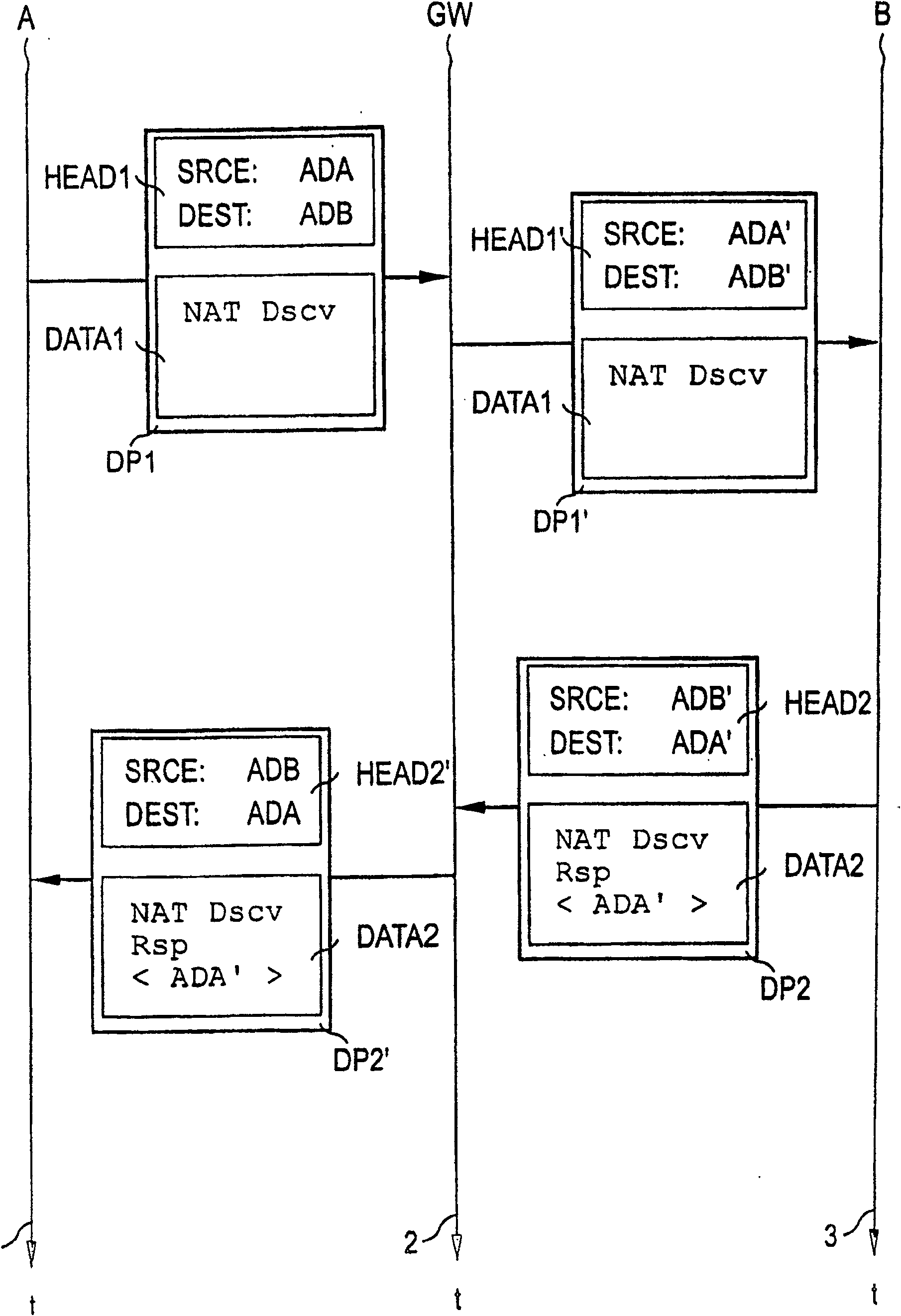
[0029] The address ADA valid in the first network area DMA is assigned to the first network unit A. The address ADA assigned to the first network unit A is preferably present as an IP address ('Internet Protocol'), but the invention is not restricted to the use ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com