Straight-through current transformer capable of conveniently taking voltage
A current transformer and feedthrough technology, applied in the field of transformers, can solve the problems of not easy to prevent electricity theft, complex structure and high cost, and achieve the effects of saving labor time, safe operation and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
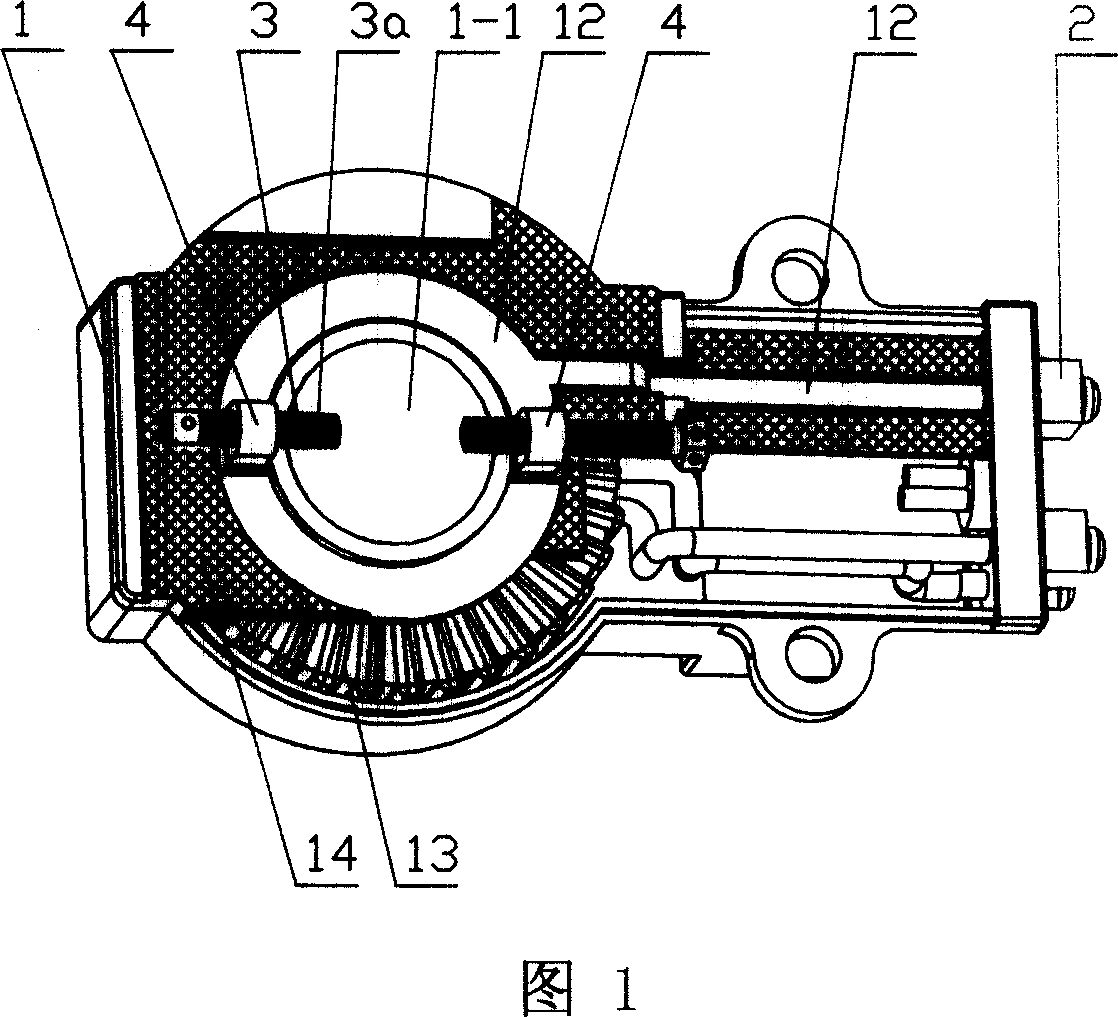
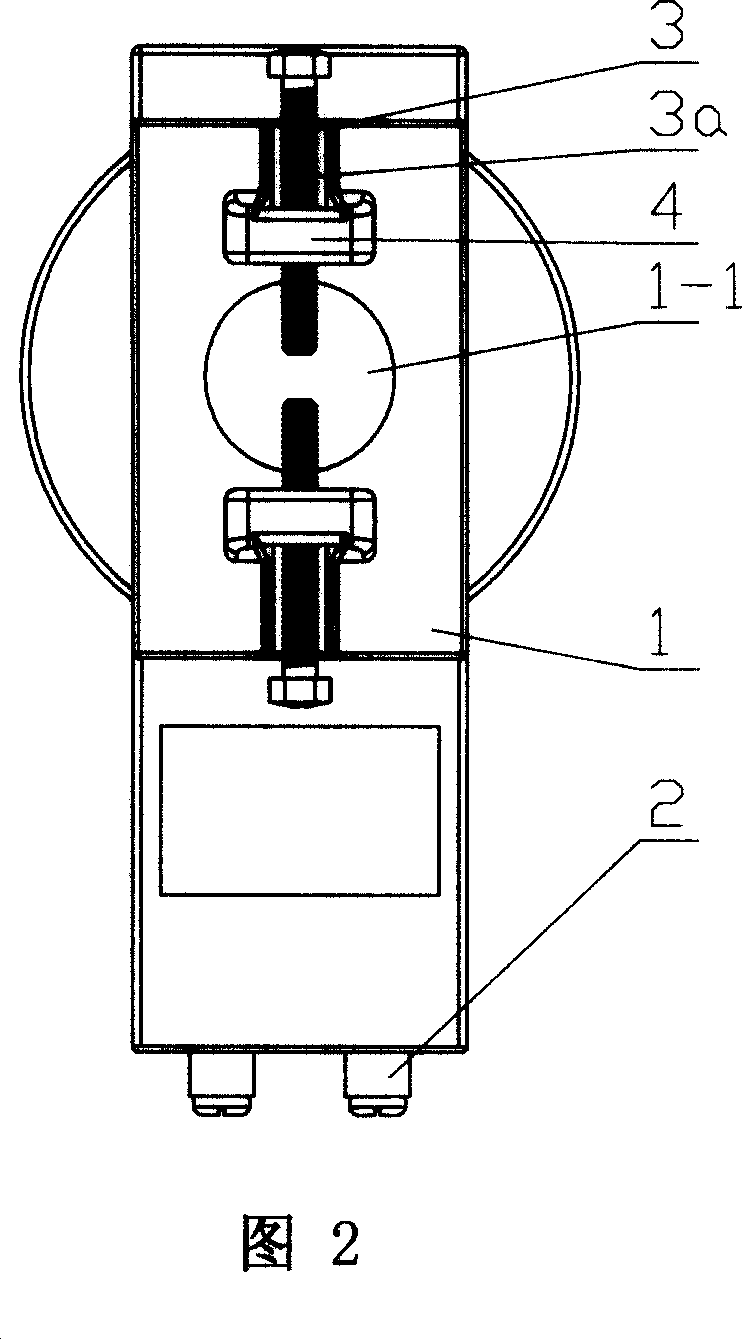
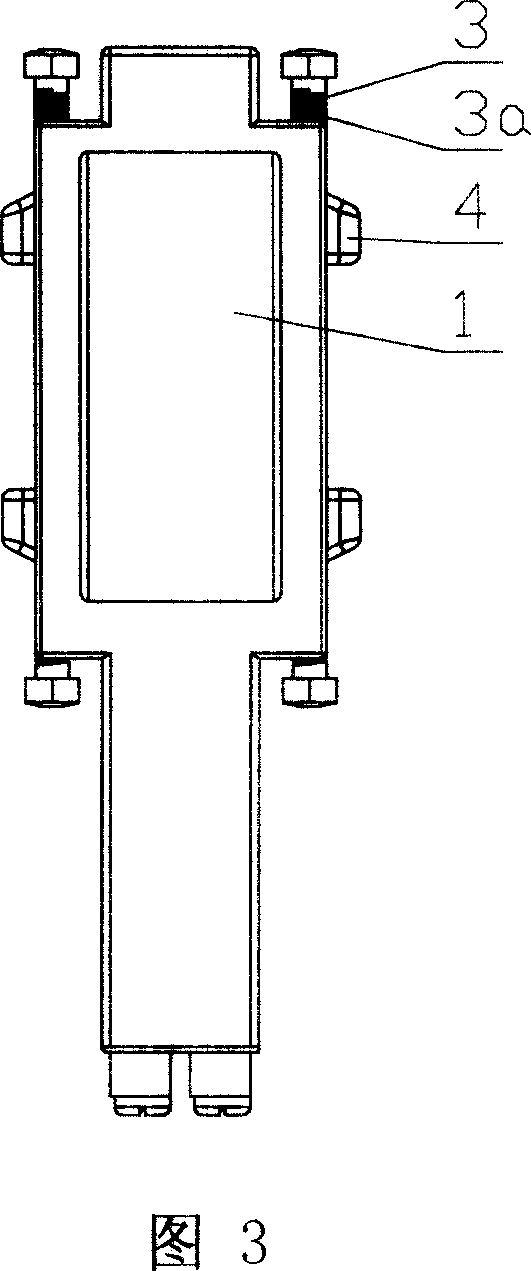
[0053] The current transformer described in this embodiment is mainly used in the case of taking voltage from a bare metal bar. It includes a transformer body 1 with a through hole 1-1. The transformer body 1 is provided with a voltage line outlet terminal 2 that is electrically connected to each other and a voltage-taking component 3. The voltage-taking component 3 is arranged on the through-center One side of the hole 1-1, and the voltage-taking component 3 can move radially along the through hole 1-1.
[0054] Setting the voltage-taking part 3 on one side of the through-hole can prevent the voltage-taking part from occupying the position of the through-hole and affecting the use of the transformer. At the same time, the radial movement of the voltage-taking part along the through-hole can make the mutual inductance of this structure The transformer adapts to the needs of buses with different inner diameters and cross-sectional shapes, thus increasing the adaptability of the...
Embodiment 2
[0062] The current transformer described in this embodiment is mainly used in the case of taking voltage from a transformer guide rod. Unless otherwise specified, the structure described in this embodiment is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
[0063] The difference in structure between the current transformer described in this embodiment and the transformer described in Embodiment 1 is that, referring to Fig. 6A, Fig. 6B, Fig. 7 and Fig. 8, it also includes a nut 5, and the nut 5 The side is provided with hole 5-1, and the hole is provided with the internal screw thread that cooperates with metal stud 3a front end.
[0064] When in use, first penetrate the central hole of the transformer into the guide rod 15 of the transformer, then screw the nut 5 on the guide rod 15 of the transformer, and then screw the metal stud 3 threaded with the metal insert 4
[0065] The front end of a is screwed in the threaded hole 5-1 of nut 5 sides. In this way, it can ensure that the transfo...
Embodiment 3
[0070] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 is that the structure of the transformer also includes a No. 1 anti-theft electricity mask 6, and the difference with the existing structure is that the No. 6 is connected with the surface of the transformer body 1 in a non-detachable manner. It can be seen that the anti-theft mask of this embodiment is fixed on the transformer body, so that the transformer can be used in any position without limitation in the box. The mask is connected to the transformer body in a non-detachable way, that is to say, after the metering department fixes the anti-stealing mask to the transformer, the mask cannot be removed from the transformer without destroying it. Those who can't hide the eyes and ears to steal electricity can greatly increase the degree of protection against electricity theft.
[0071] Figure 2 and Figure 4 clearly show the structure of the outer surface of the transformer body 1, on the basis of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com