Process of preparing carbon steel with superfine heterogeneous structure
A carbon steel and ultra-refining technology, which is applied in the field of preparing ultra-refined multi-phase structure materials, can solve the problems of high strain rate, low carbon content, and inconspicuous characteristics of large-angle grain boundaries, and achieves the effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
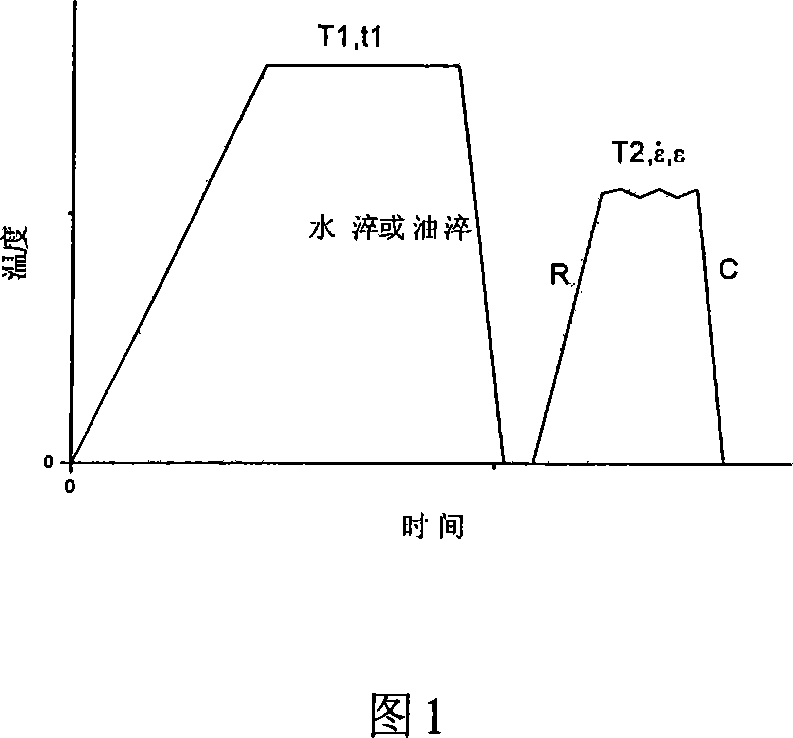
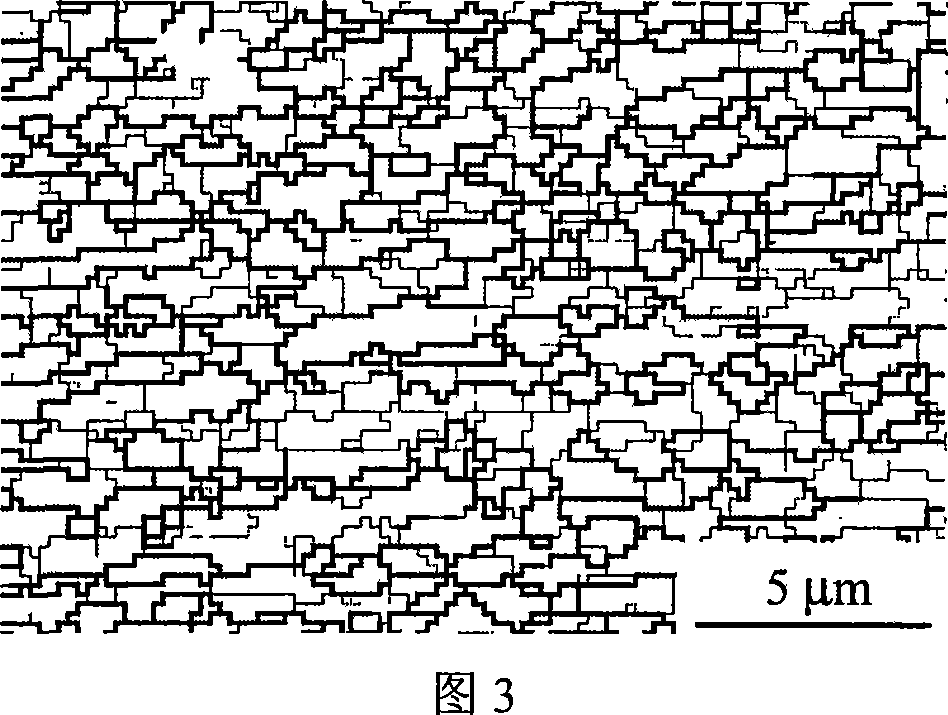
[0017] The material used is ordinary eutectoid steel with a carbon content of 0.80%, and the content of other alloy elements is within the usual range of ordinary carbon steel. Its A 1 The temperature was 724°C. The deformation process is shown in Figure 1: the sample is heated to A 1 850°C (T1) within the range of 50°C to 300°C above, heat for 10 minutes (t1) and then water quench to obtain martensite, and heat the obtained martensite at a heating rate (R) of 30°C / s with an induction heating device 0.1s immediately after reaching 650°C (T2) in the range of 600-650°C -1The strain rate is deformed, and the deformation adopts unidirectional compression deformation. After deformation, it is cooled to room temperature at a cooling rate (C) of 100°C / s in the range of 2-200°C / s. The deformed structure when the strain amount reaches 0.69 is shown in Figure 2. The deformed structure basically has the characteristics of the aforementioned ultra-fine multi-phase structure: the averag...
Embodiment 2
[0019] The material used is the same as in Example 1, and the strain rate in Example 1 is increased to 1s -1 , when the strain amount is 1.60, the deformation structure is shown in Fig. 5. The deformed structure has the characteristics of the above-mentioned ultrafine multi-phase structure with a bimodal distribution of cementite particle size: the average grain size of ferrite surrounded by high-angle grain boundaries is 0.58±0.13μm, distributed in the ferrite grain boundaries The average size of the submicron cementite particles on the surface is 162±71nm, and the average size of the nanoscale cementite particles inside the ferrite grains is 43±19nm.
Embodiment 3
[0021] The material used is ordinary medium-carbon steel with a carbon content of 0.48%, and the content of other alloy elements is within the usual range of ordinary carbon steel. Its A 3 The temperature is 760°C. The deformation process is shown in Figure 1: the sample is heated to A 3 950°C (T1) in the range of 50-300°C above, keep warm for 5 minutes (t1) and then water quench to obtain martensite, and use an induction heating device to heat the obtained martensite at a heating rate (R) of 20°C / s 0.01s immediately after reaching 600°C (T2) in the range of 600-650°C -1 The strain rate is deformed, the deformation adopts unidirectional compression, and after deformation, it is cooled to room temperature at a cooling rate (C) of 50°C / s in the range of 2-200°C / s. The deformed structure when the strain value is 1.60 is shown in Figure 6. The deformed structure has the characteristics of the aforementioned ultra-fine complex phase structure: the average grain size of ferrite s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com