Magnetron
A technology of magnetron and anode tube, which is applied in the field of magnetron, can solve the problems of excess electrons, failure to pay attention to the relationship of peak anode current value, and no noise reduction effect, etc., to achieve the effect of suppressing attenuation and reducing noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
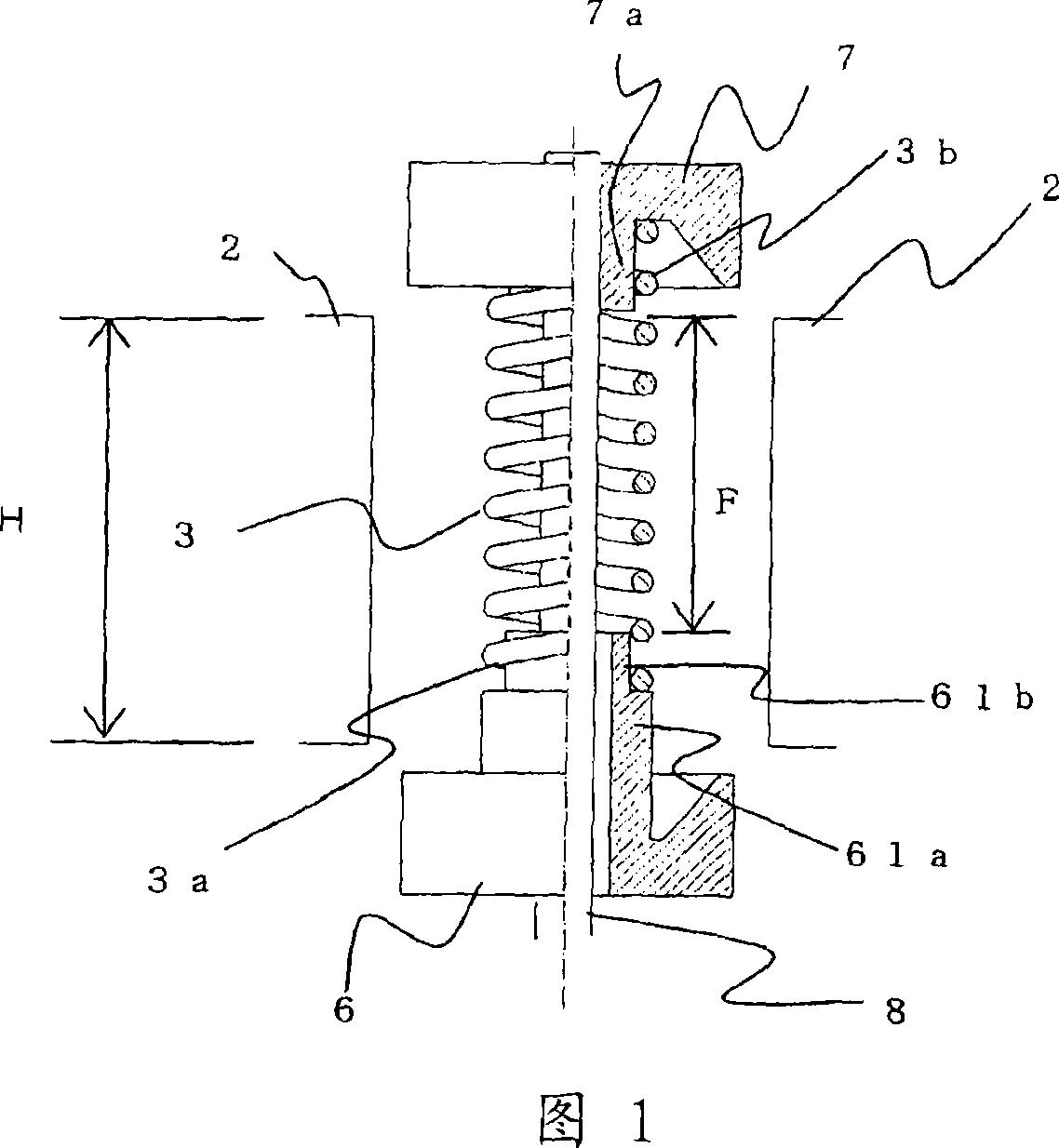
[0099] 1 is a partial longitudinal sectional view of a cathode portion of a magnetron according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In addition, since components other than the cathode shown in this figure are the same as those of the conventional magnetron shown in FIG. 32 described above, their descriptions are omitted.
[0100] Referring to FIG. 1 , the magnetron of this embodiment is configured so that the spiral filament 3 is disposed between the input side end cap 61 and the output side end cap 7 supported by the cathode support rod 8 . In particular, in the present embodiment, the input side end cap 61 is configured so that the sleeve 61a having a larger diameter extends toward the inside of the interaction space compared with the shape in FIG. 32 , and the sleeve 61b having a smaller diameter and the end 3a of the filament 3 are fixed to each other. The output-side end cap 7 has the same shape as a conventional end cap, and the sleeve 7 a and the end 3 b of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0109] Fig. 6 is a partial longitudinal sectional view of a cathode portion of a magnetron according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. In addition, since components other than the cathode shown in this figure are the same as those of the conventional magnetron shown in FIG. 32 described above, their descriptions are omitted.
[0110] In FIG. 6, the magnetron of this embodiment is configured so that the cathode of the above-mentioned Embodiment 1 shown in FIG. 1 is reversed, and the electron-emitting portion is shifted toward the input side.
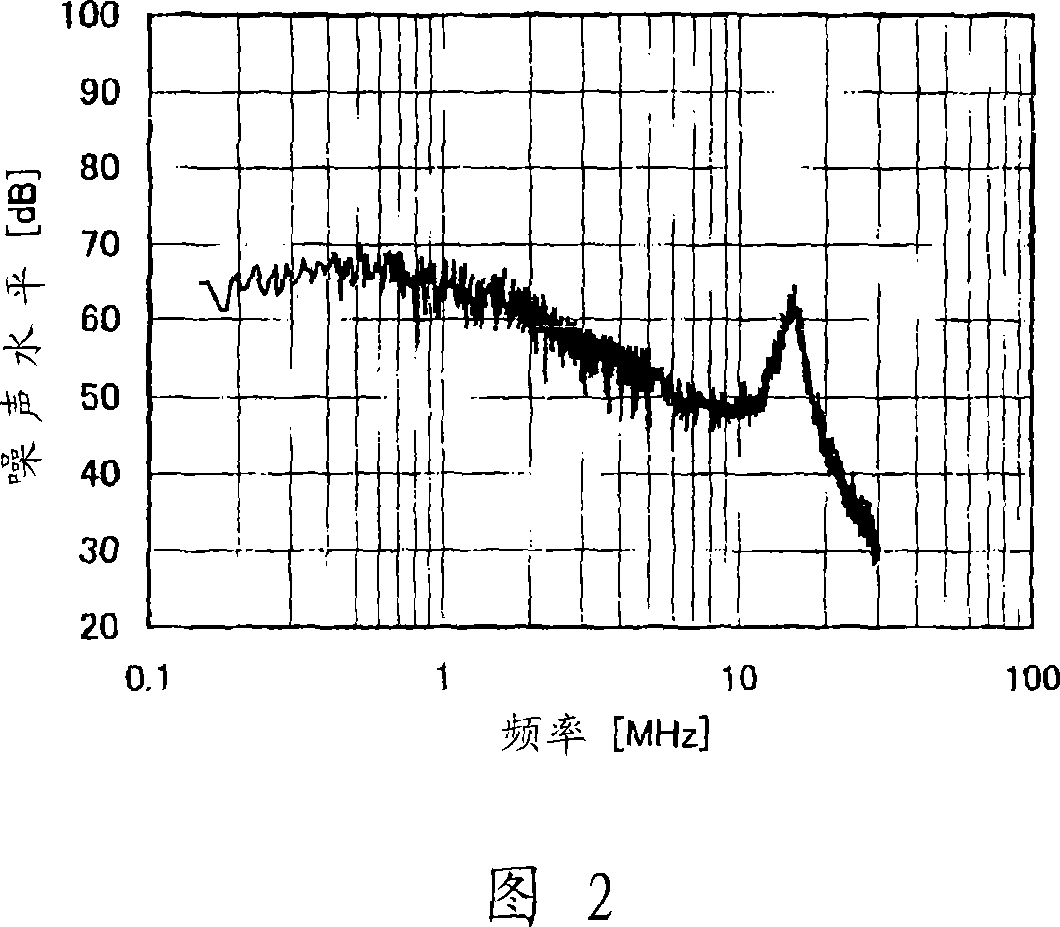
[0111] 7 is a waveform diagram showing a noise level of 30 MHz or less when the size of the electron emission portion of the present embodiment is set to about 75% of the axial dimension of the plate blade and the electron emission portion is shifted to the input side.
[0112] Even if the electron emission portion is shifted toward the input side like this embodiment, the noise level of 30 MHz or below is suppressed as compared w...
Embodiment 3
[0115] Fig. 8 is a partial longitudinal sectional view of a cathode portion of a magnetron according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. In addition, since components other than the cathode shown in this figure are the same as those of the conventional magnetron shown in FIG. 32 described above, their descriptions are omitted.
[0116] In FIG. 8 , the magnetron of the present embodiment is configured such that the electron emission portion is configured to extend into the recess 72 a of the output-side end cap 72 . This embodiment is described with reference to the drawings, and the input side end cap 61 has the same structure as that of Embodiment 1 shown in FIG. 1 . The output side end cap shown in FIG. 1 is configured such that the shaft sleeve 7a of the output side end cap 7 and the inner diameter portion of the end portion 3b of the filament 3 are fixed to each other, while the output side end cap 72 shown in FIG. 8 is formed as an output side end cap 72. The inner...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wire diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pitch | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com