Solid-state image pickup device and mask manufacturing method
A technology of a solid-state imaging device and a manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of electric solid-state devices, optics, optical elements, etc., can solve the problems of reduced light concentration and small spacing, and achieve the effect of improving the light concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
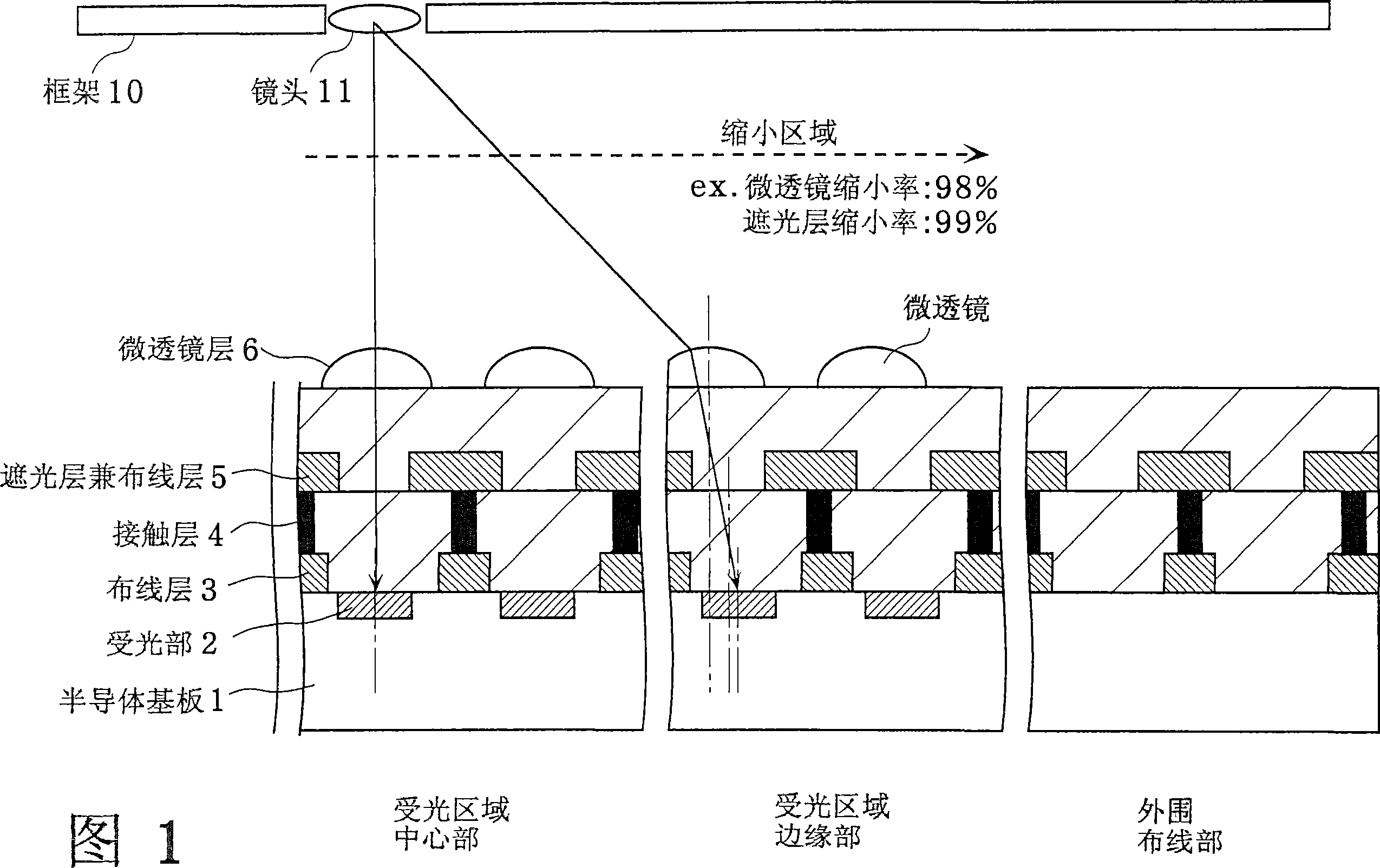
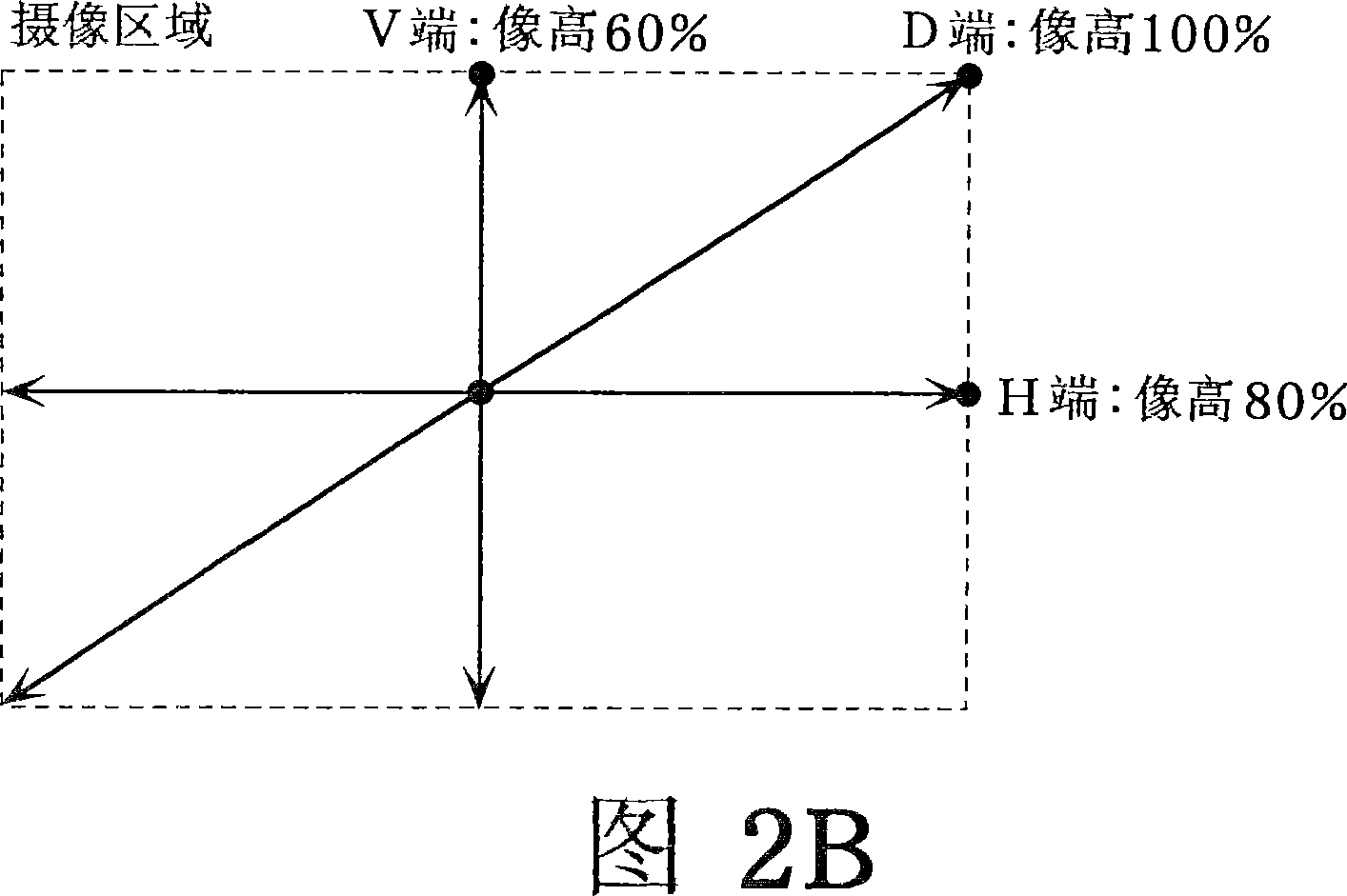
[0052]3A is a schematic diagram showing a plan view of the solid-state imaging device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 3A , the surface of the solid-state imaging device roughly includes a light receiving area and a peripheral circuit area. The light-receiving area is composed of imaging areas 1 , 2 , and 3 , which are a plurality of areas. Each imaging area is divided by a quadrangular boundary whose center is the center of the optical axis (or optical center). In addition, the imaging areas 1, 2, and 3 may be divided by polygonal boundaries instead of quadrangular boundaries, or may be divided by circular boundaries centered on the center of the optical axis as shown in FIG. 3B.
[0053] FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view showing the solid-state imaging device. This figure corresponds to the state in which four pixels near the boundary between imaging area 1 and imaging area 2 are arranged as shown in FIG. 3B or FIG. 3A , and the left side...
Embodiment approach 2
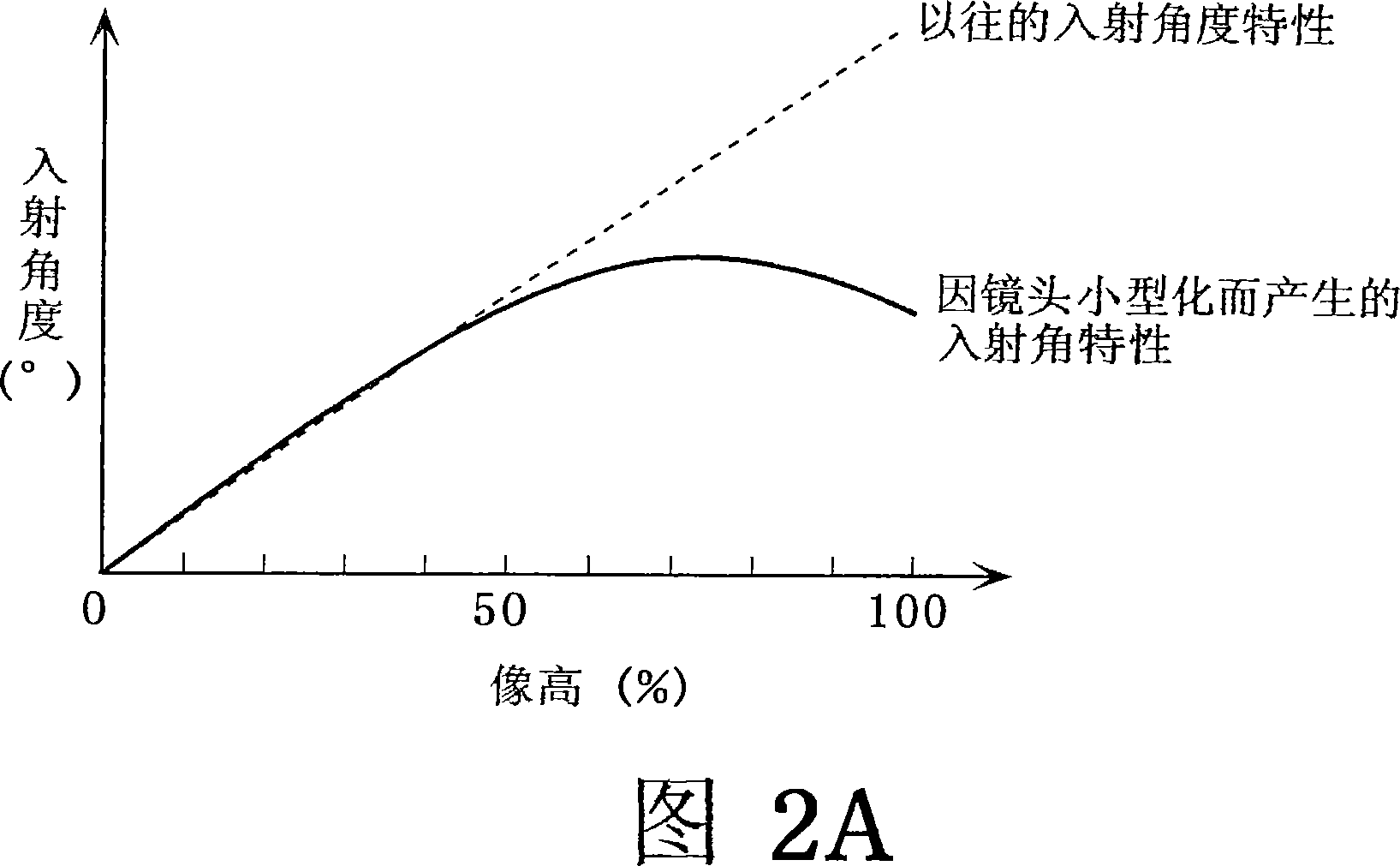
[0062] 7 is a cross-sectional view showing a solid-state imaging device according to Embodiment 2. FIG. In the same figure, the difference from the cross-section of the solid-state imaging device shown in FIG. The distance between them is L2, and the size of the opening is S2. The incident angle characteristics shown in FIG. 6A and FIG. 6B are the same. The description of the similarities will be omitted, and the description will focus on the differences. L1 and L2 are set to optimal values according to the incident angle characteristics of the imaging areas 1 and 2 . In this example, it is assumed that L2>L1, L12>L1, and L12>=L2. That is, the pitch of the openings in the imaging area 1 is smaller than the pitch in the imaging area 2 . The size of the openings and the distance between the openings are also different. This means that the reduction ratio is different for each imaging area. Since the reduction ratio is different for each imaging area, the pitch of the ope...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com