Packet routing method and system of local mobility management network
A technology for mobility management and network management, applied in the field of local mobility management network, can solve the problems of reducing system efficiency, increasing propagation delay, routing detours, etc., to reduce transmission delay, flexible routing decision, and improve packet The effect of forwarding efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
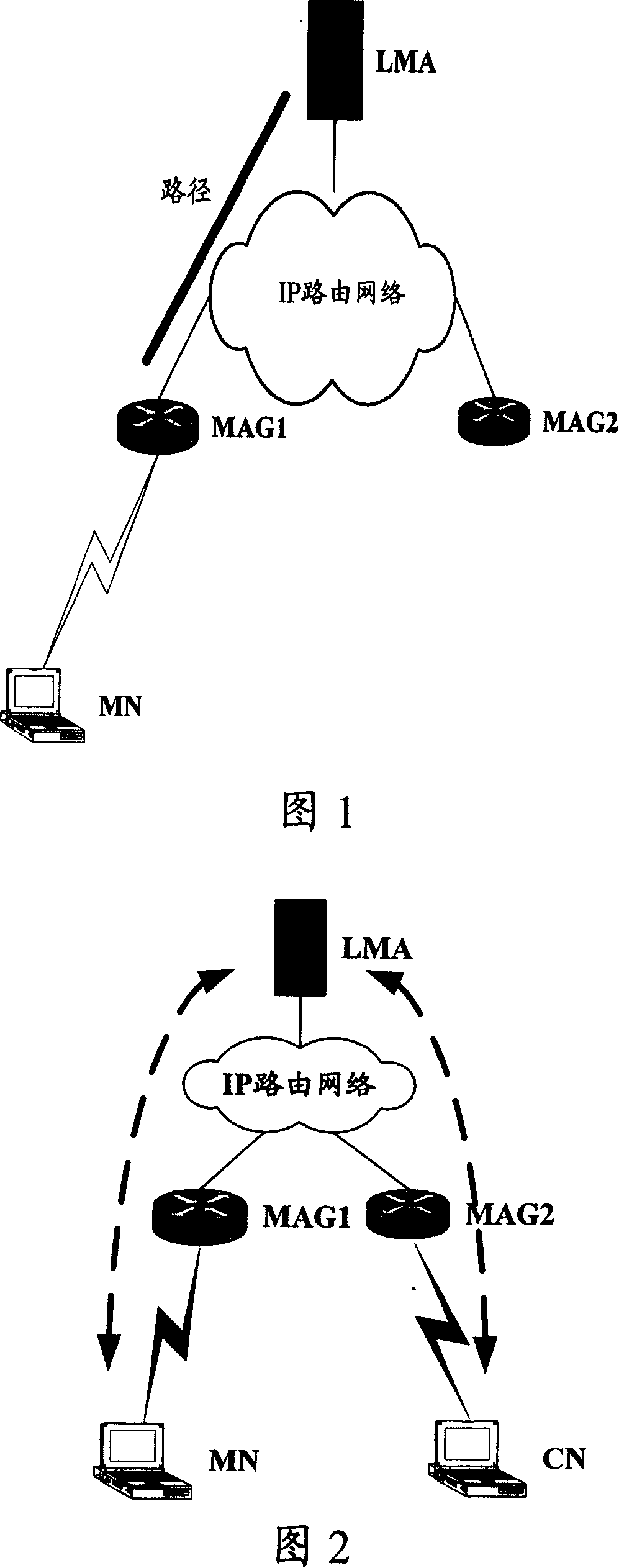
[0078] In this embodiment, it is assumed that the originating node MN and the receiving node CN of both communication parties belong to the same LMM domain, and they enter the local mobility management network through MAG1 and MAG2 respectively, and the access process, address configuration process and location update process of both parties will be Fully comply with the prior art, no more details here.
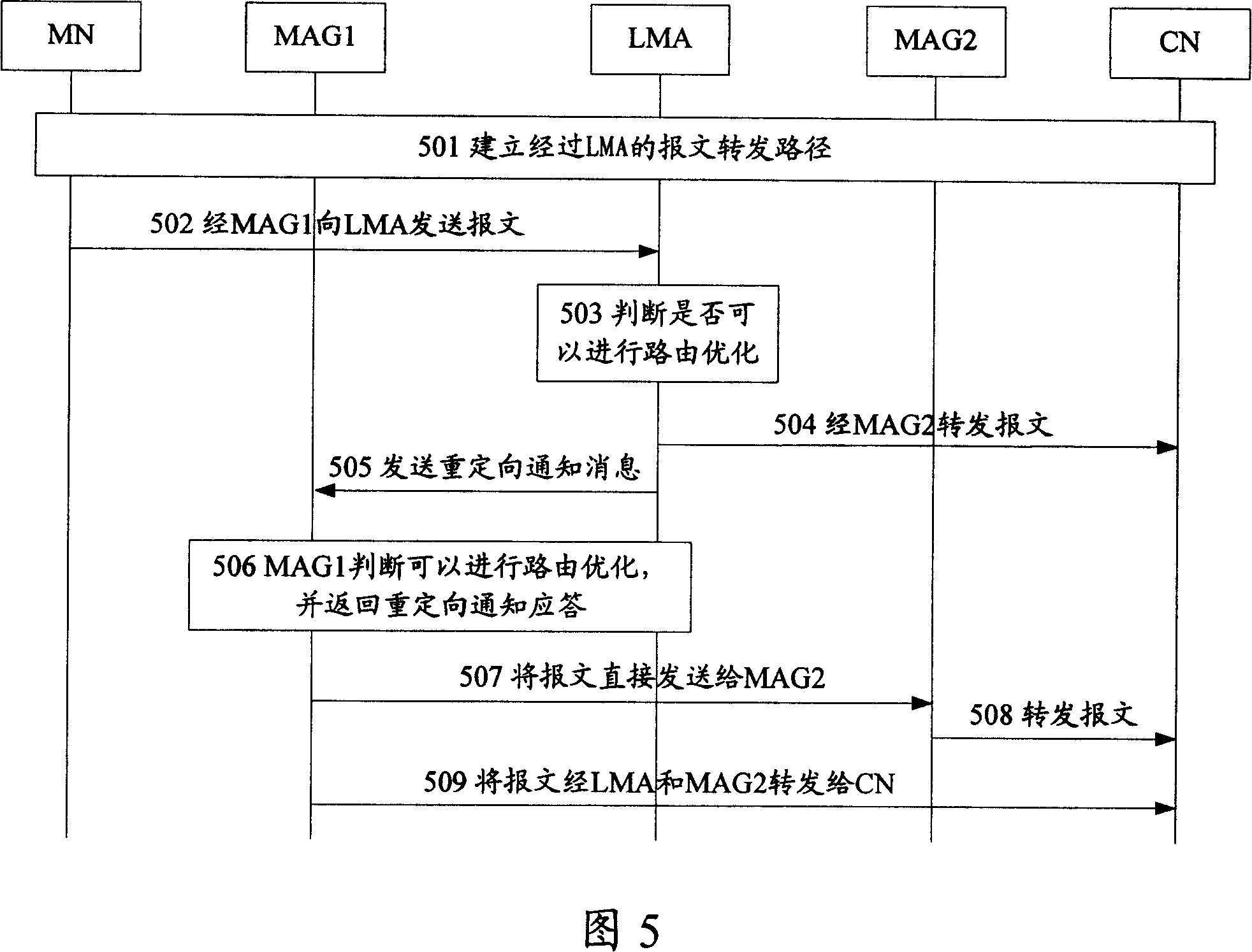
[0079] FIG. 5 is a specific flowchart of a packet routing method of a local mobility management network in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. As shown in Figure 5, the method includes:
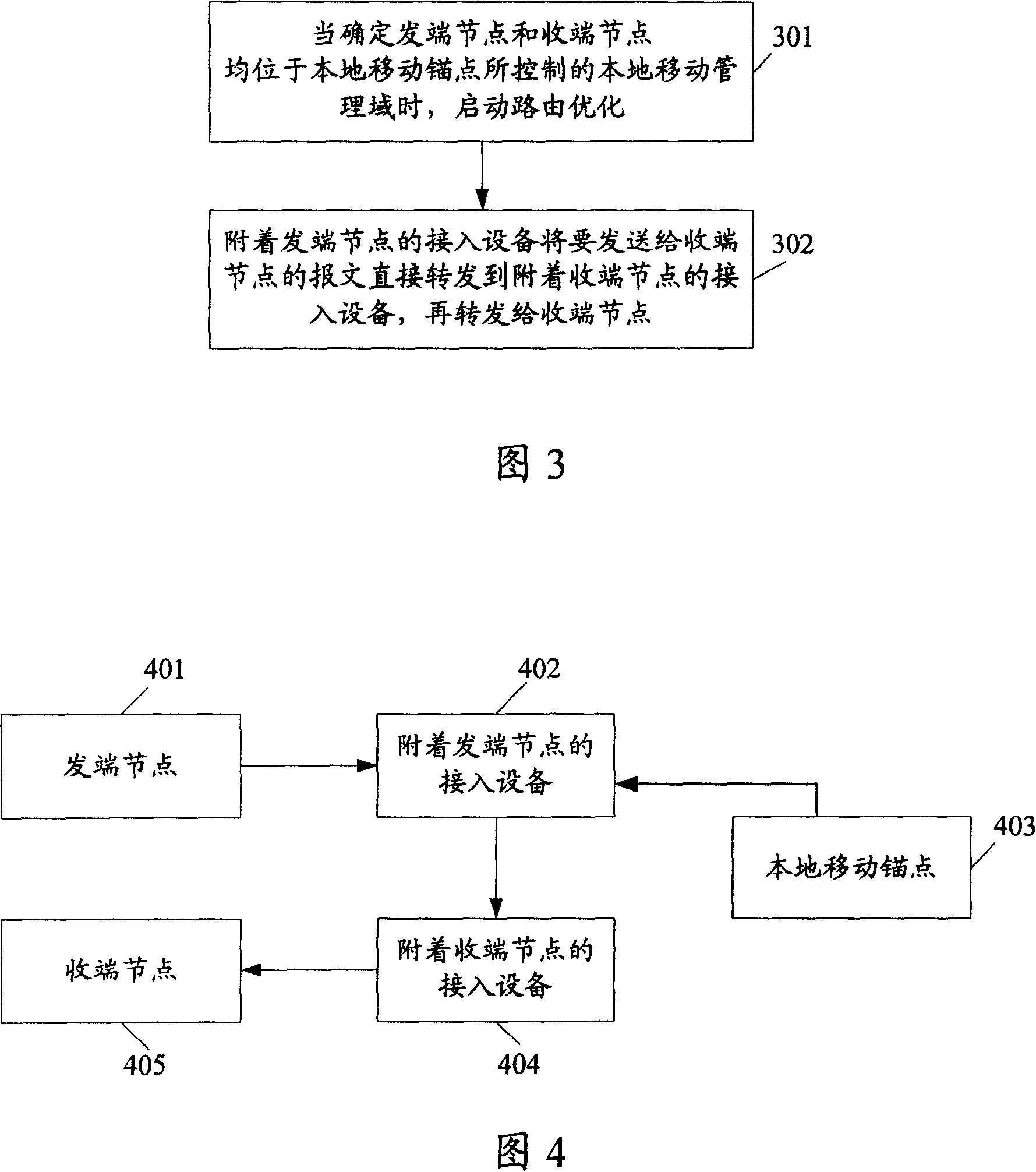
[0080] Step 501, establishing a message forwarding path;
[0081] In this step, MN and CN firstly forward data through traditional paths: LMA, MAG1 and MAG2 respectively store the access location information and message forwarding mode information of MN and CN, and establish tunnels between LMA and MAG1, and LMA and MAG2 . The tunnel between LMA and MAG1, and between LMA and MAG2 is IP...
Embodiment 2
[0115] In this embodiment, the same message forwarding path as the process shown in Figure 5 is adopted. In addition, it is also assumed that the redirection notification message sent by LMA to MAG1 has a certain validity period, and MAG1 will redirect the notification message within the validity period of the redirection notification message. The message is directly forwarded to CN through MAG2.
[0116] The scenario in this embodiment is: during the process of message forwarding, the receiving node CN moves in the local mobility management domain, so that the MAG attached to the CN changes from the original MAG2 to MAG3. After moving within the local mobility management domain, the access device MAG3 attached to the CN is still located in the local mobility management domain controlled by the original LMA.
[0117] After CN moves and CN's MAG changes, LMA will get the location registration message of CN's new location (namely MAG3). At this time, LMA will query the redirecti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com