Cross-talk reduction for active matrix displays
An active matrix and display technology, applied in the field of crosstalk, can solve problems such as optical crosstalk and particle distribution differences
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
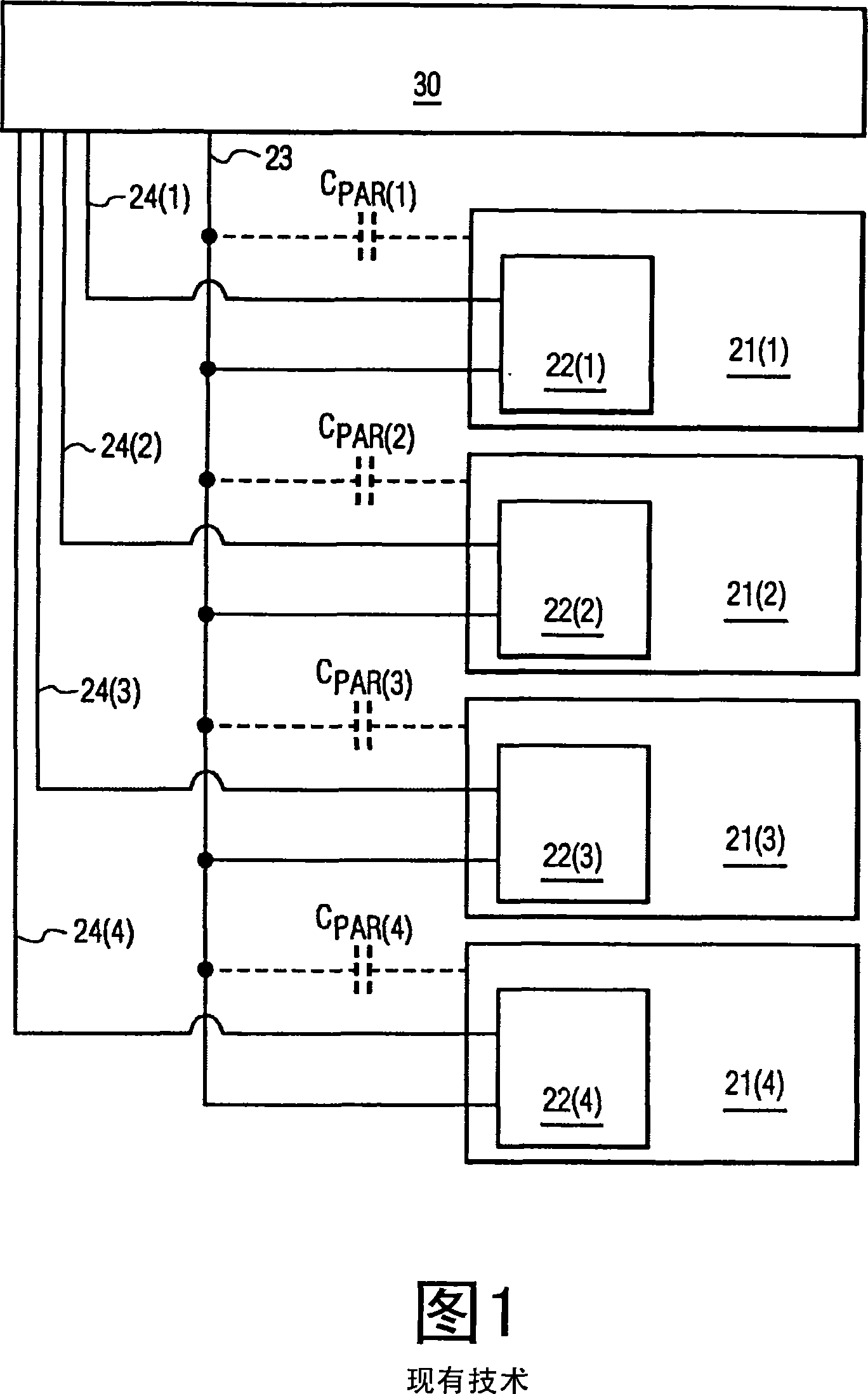
[0030] The schematic representation of pixel 21 (FIG. 1) as shown in FIG. 6 shows that pixel 21 uses a front plate capacitor C connected to pixel node PN and common reference CREF FP , and the storage capacitor C connected to the pixel node PN and the selection line 24 of the preceding pixel 21 STORE . An addressing element in the form of a thin film transistor OTFT is connected to the data line 23, the corresponding selection line 24 and the pixel node PN, whereby during selection of the pixel 21 via the corresponding selection line 24, the data line 23 is directly coupled to the pixel node PN, thus , the image driving data applied to the data line 23 at this time is received and stored in the pixel 21 . When image driving data is applied to the data line 23 and the pixel 21 is not selected via the selection line 24 (Y), a parasitic capacitance C is formed between the data line 23 and the pixel node PN. PAR .
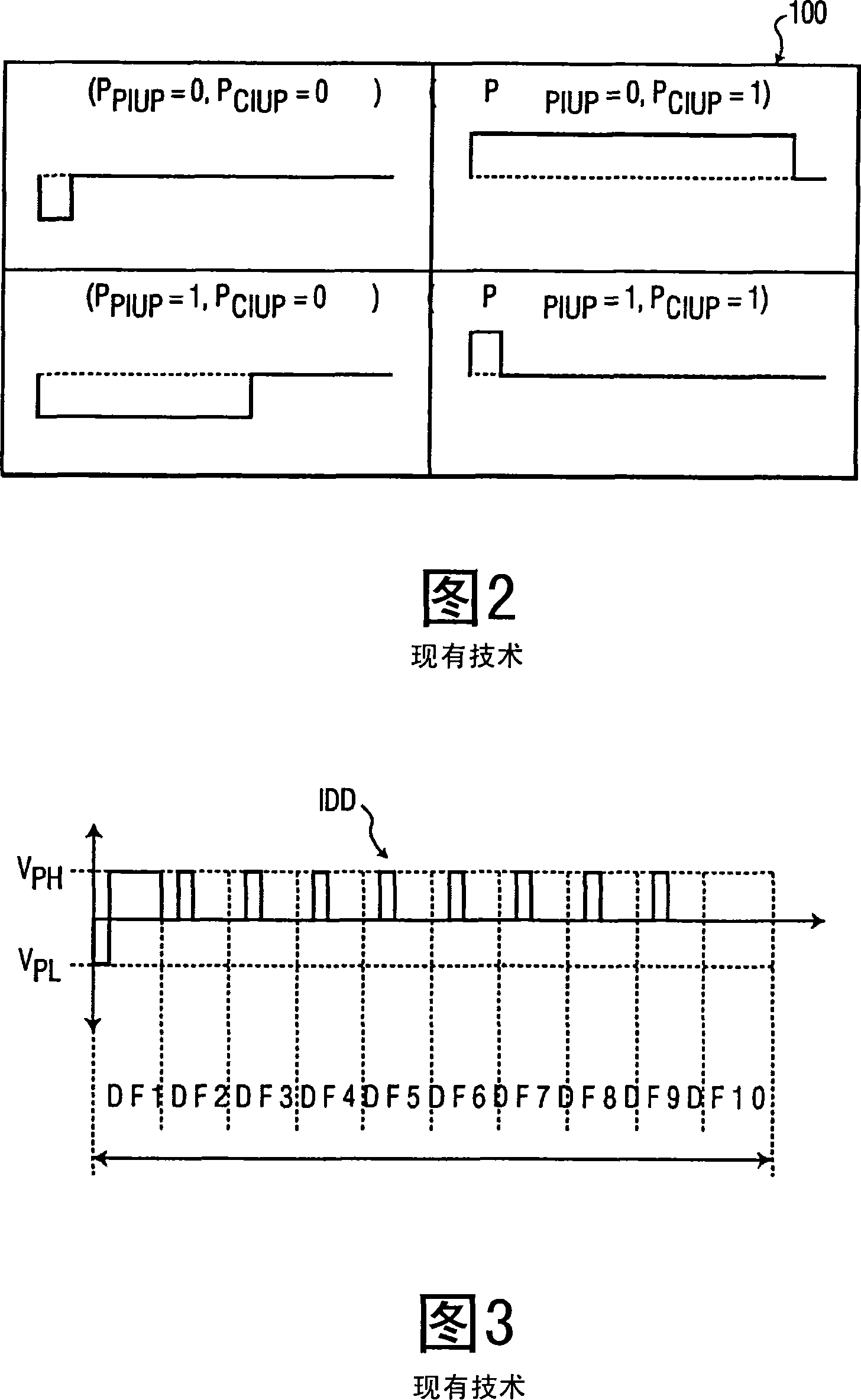
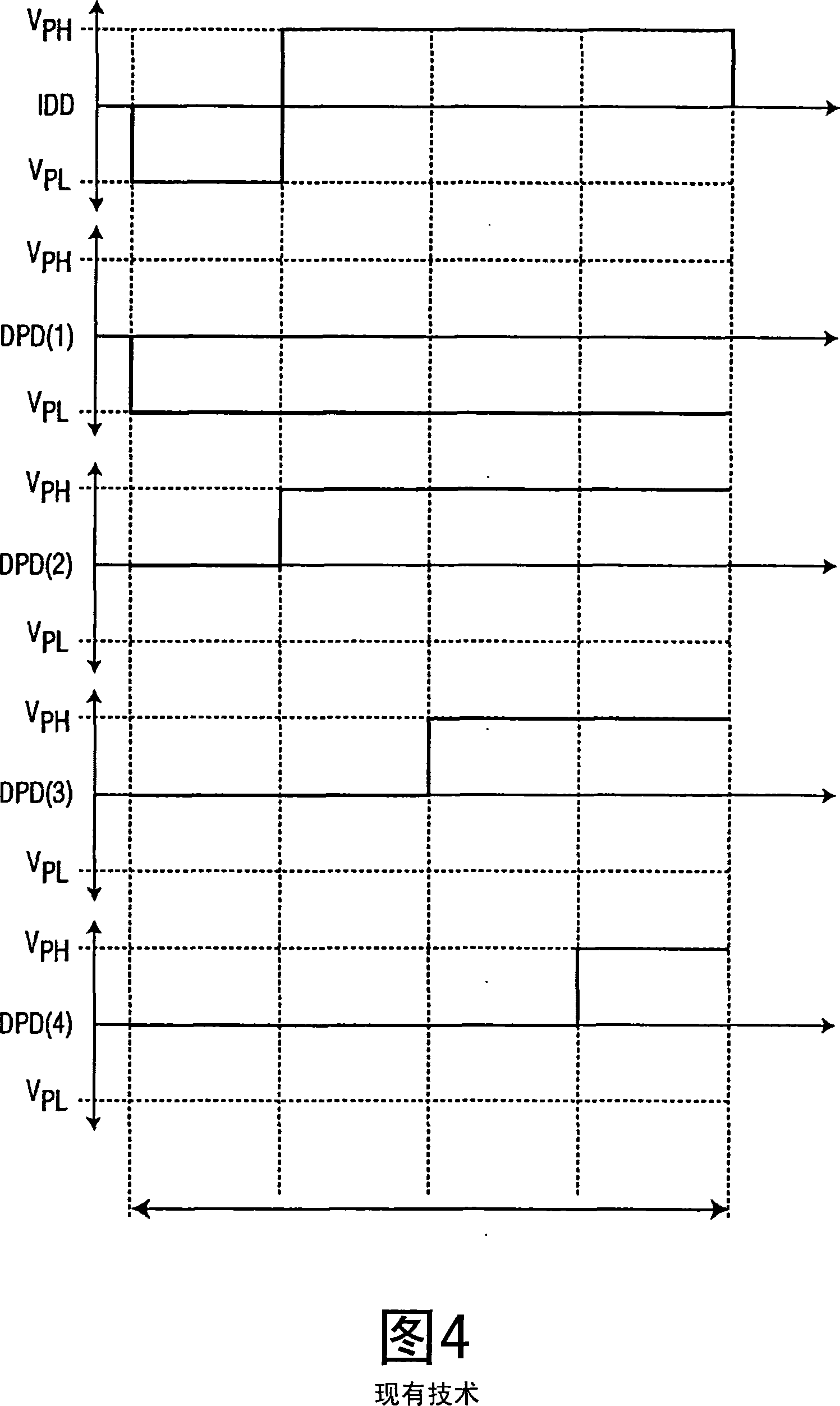
[0031]The image drive data system 40 of the present invention ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com