Method, apparatus and computer program to dynamically adjust segmentation at a protocol layer, such as at the medium access control (MAC) layer
A computer program and protocol layer technology, applied in the field of wireless digital communication systems, can solve problems such as reducing the flexibility of scheduling link adaptation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
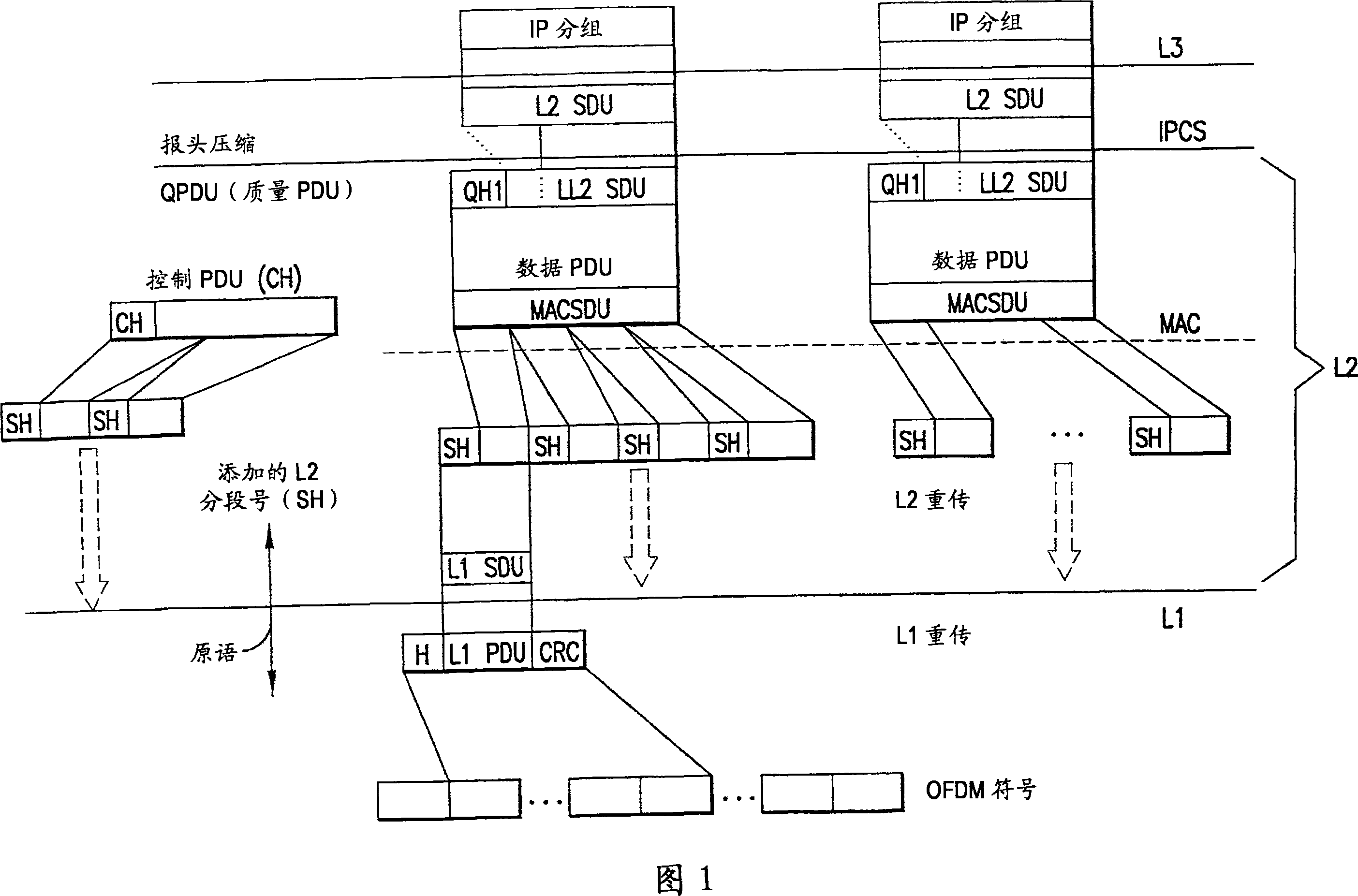
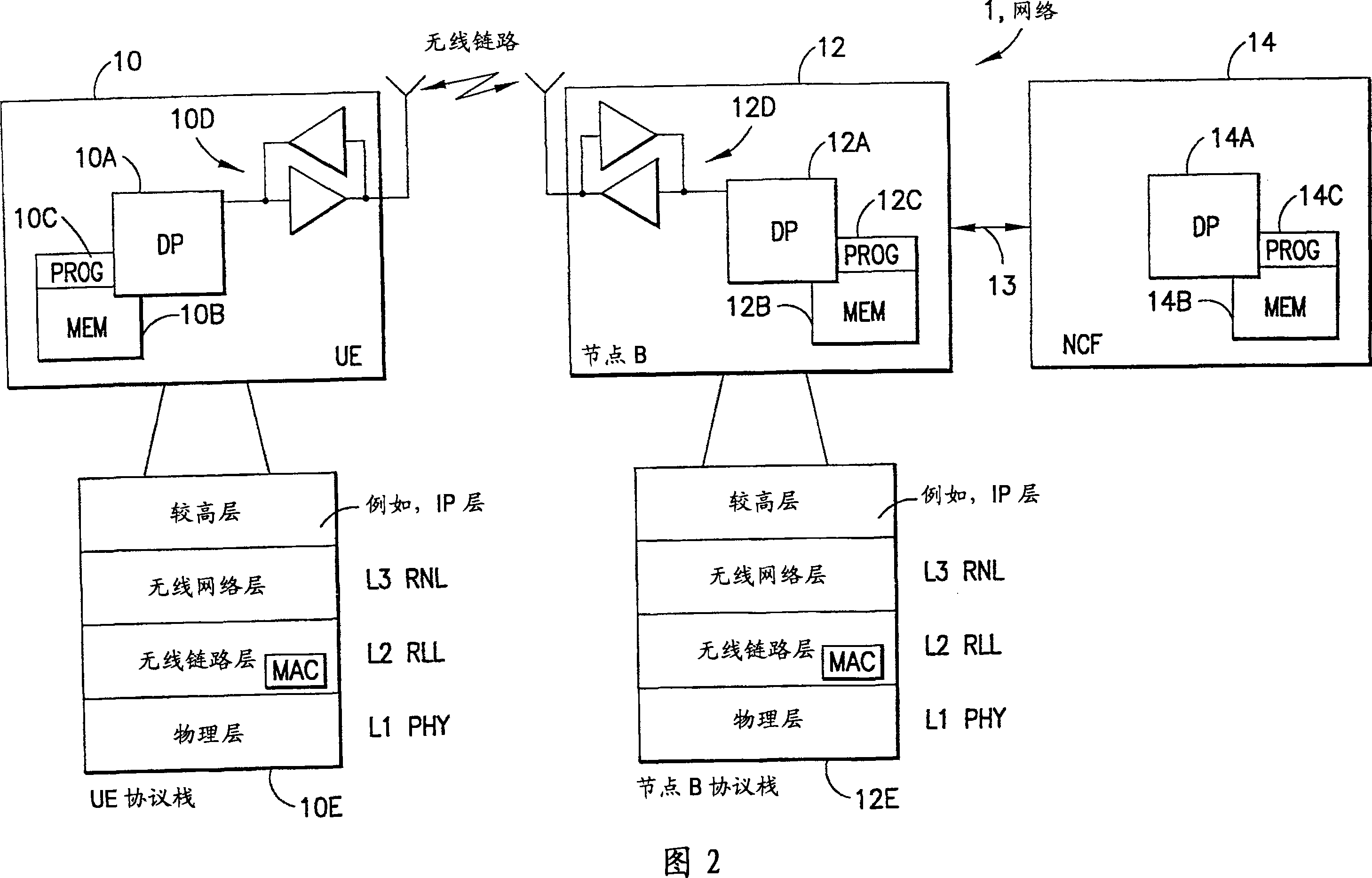
[0014] Exemplary embodiments of the present invention relate to the segmentation of packet data between two protocol layers capable of supporting data packets of different sizes. A non-limiting example is L1 and L2 as in a Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network - Long Term Evolution (UTRAN-LTE) cellular communication system (also sometimes referred to as a "3.9G" system).
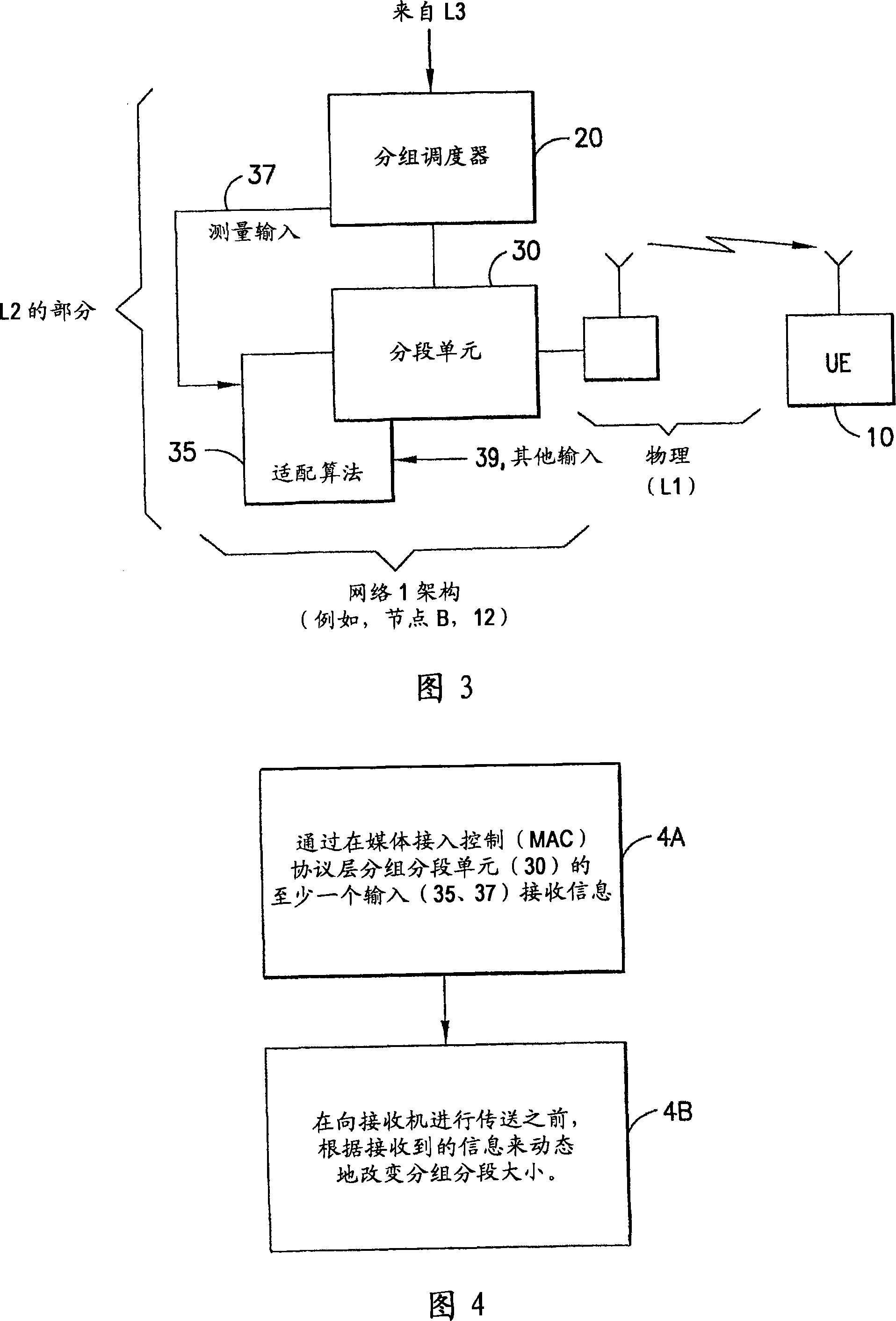
[0015] Note that although the following description is mainly made using the example of the packet segmentation unit arranged in the medium access control (MAC) protocol layer, in other implementations, the packet segmentation unit may be arranged in different protocol layers , for example in the Radio Link Control (RLC) or the Radio Network Layer (RNL), or may even be arranged at the PHY layer. However, in all these possible implementations, an exemplary embodiment of the present invention is characterized in that the size of the segments can be varied according to dynamic changes, such as but not limi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com