Digital signal processing methods and apparatus
A data and factorization technology, applied in the field of multi-line addressing technology, can solve the problems of lack of physical entities and multi-line addressing schemes not provided
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
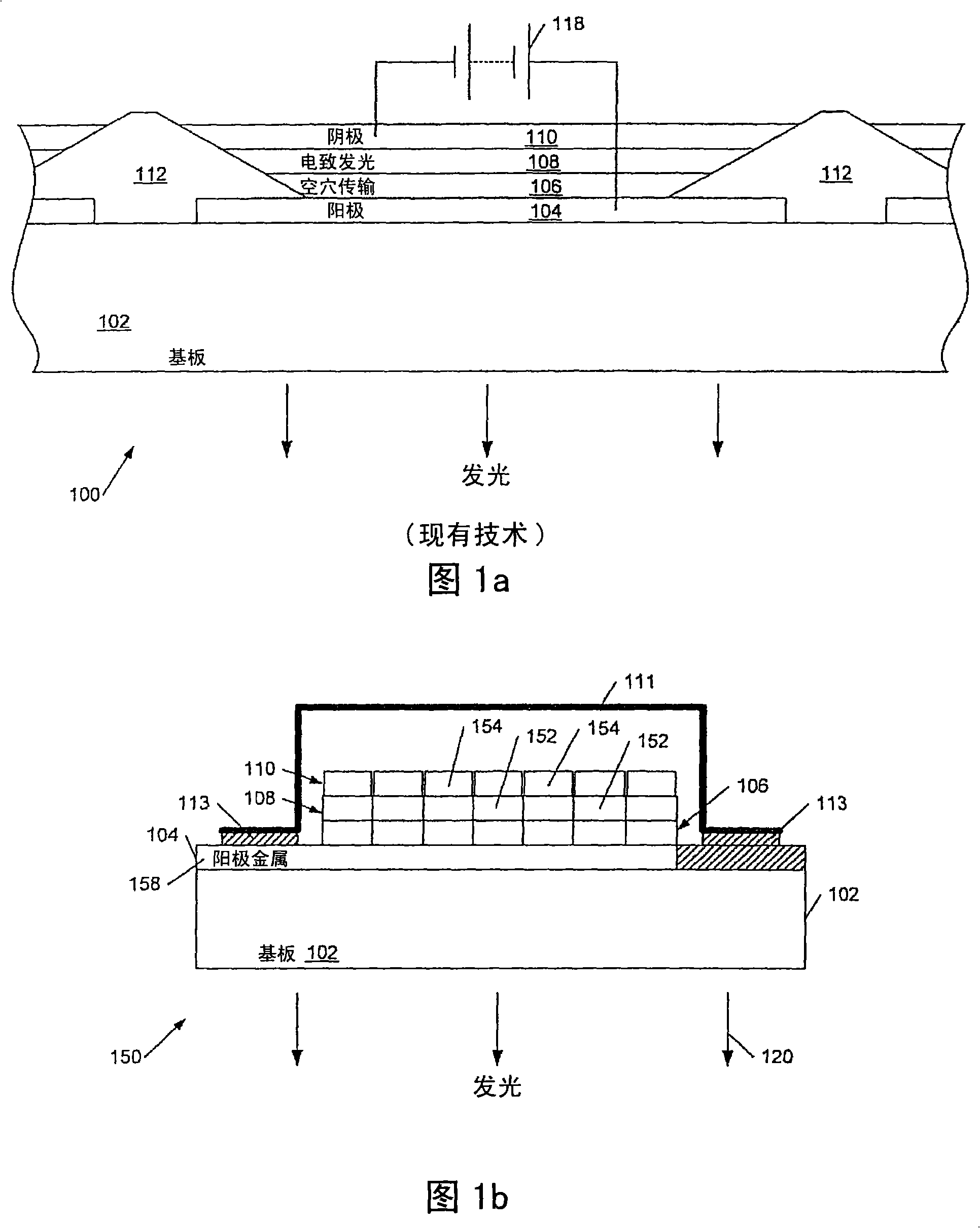
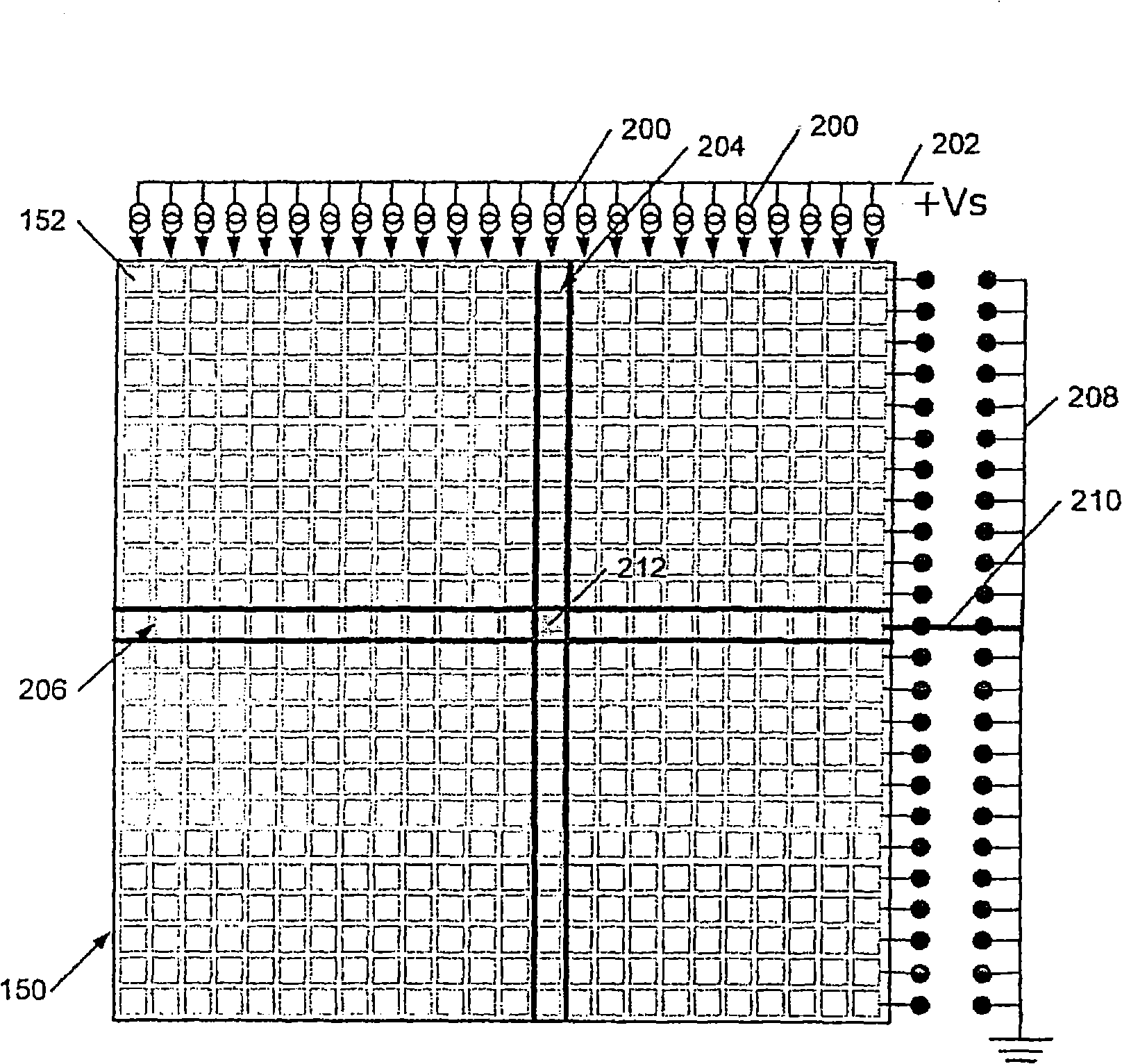
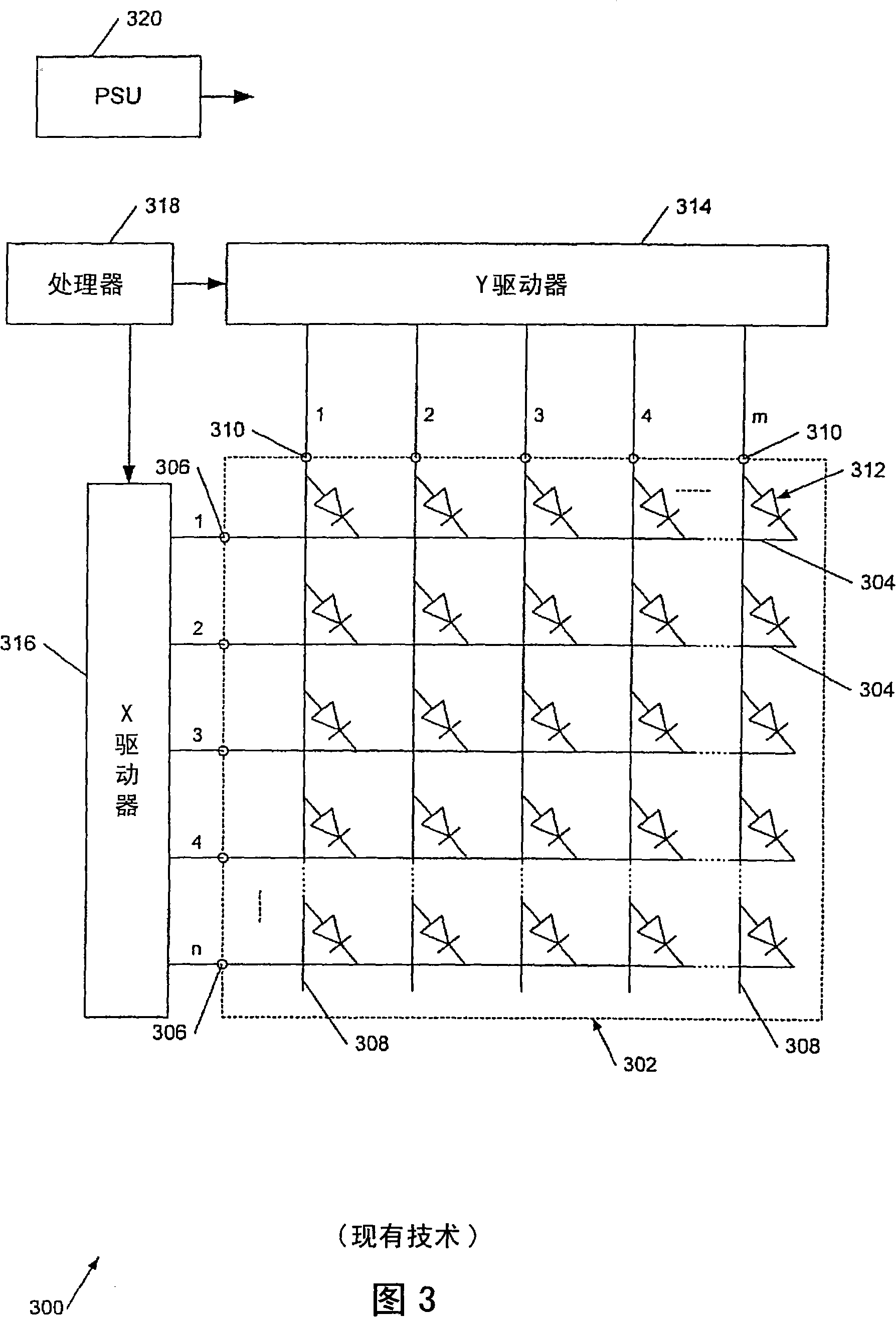
[0057] Embodiments of the invention will be described with particular reference to driving organic light emitting diode (OLED) displays using multi-line addressing (MLA) techniques, although it has been pointed out that the application of the invention is not limited thereto.
[0058] Organic Light Emitting Diode Display
[0059] Organic light emitting diodes including organometallic LEDs can be fabricated using materials including polymers, small molecules and dendrimers in a range of colors depending on the materials employed. Examples of polymer-based organic LEDs are described in WO 90 / 13148, WO 95 / 06400 and WO 99 / 48160; examples of dendrimer-based materials are described in WO 99 / 21935 and WO 02 / 067343; And examples of so called small molecule based devices are described in US 4,539,507. A typical OLED device includes two layers of organic materials, one layer with light-emitting materials such as light-emitting polymers (LEPs), oligomers, or light-emitting low-molecul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com