Multi-scale finite-volume method for use in subsurface flow simulation
A finite-volume, multi-scale technology, applied in the fields of fluid extraction, design optimization/simulation, application-specific simulation process, etc., can solve problems such as error prior estimation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] I. Mobility issues
[0033] A. Single-phase flow
[0034] Fluid flow in porous media can be described by an elliptic problem:
[0035] on Ω, ▿ · ( λ · ▿ p ) = f - - - ( 1 )
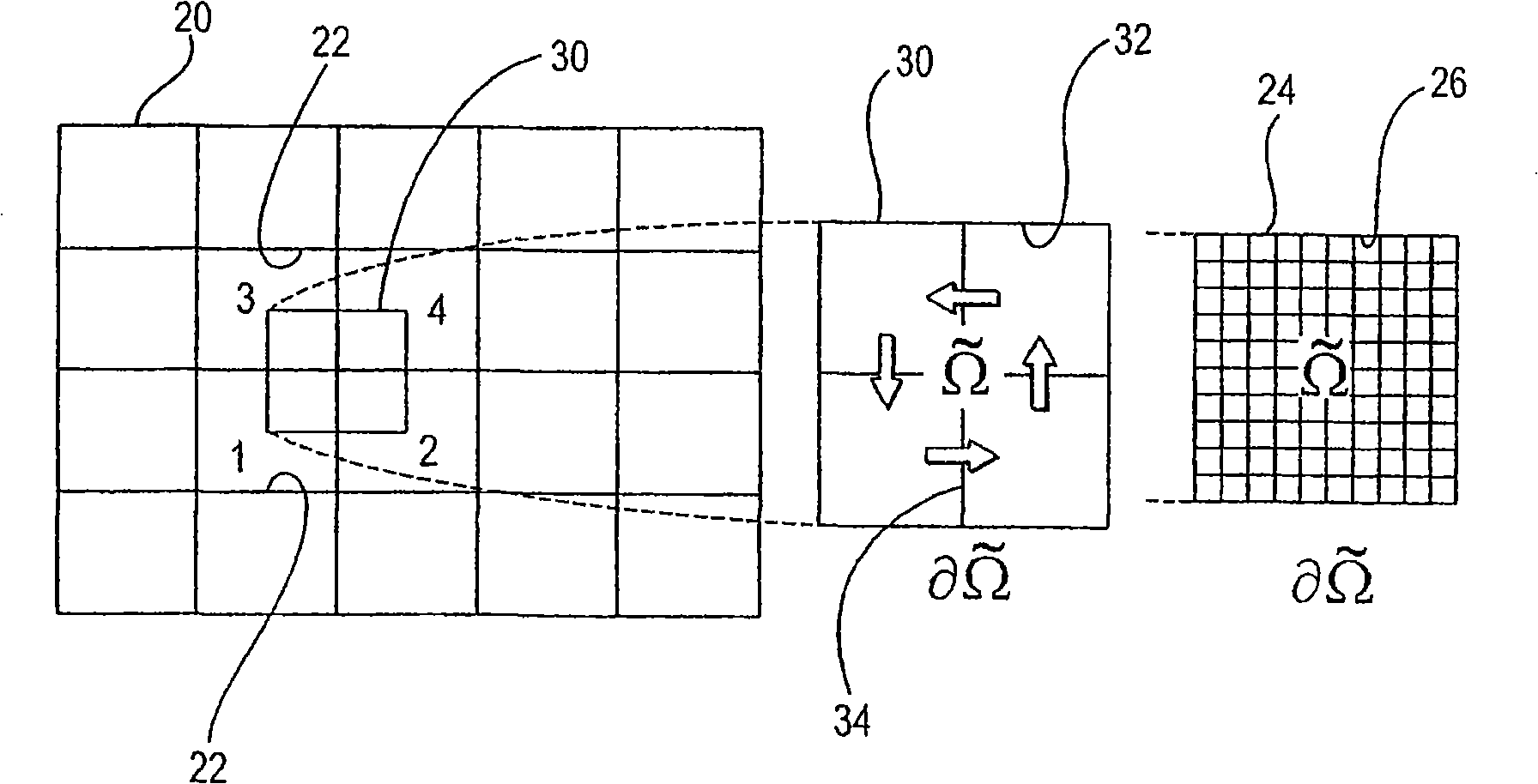
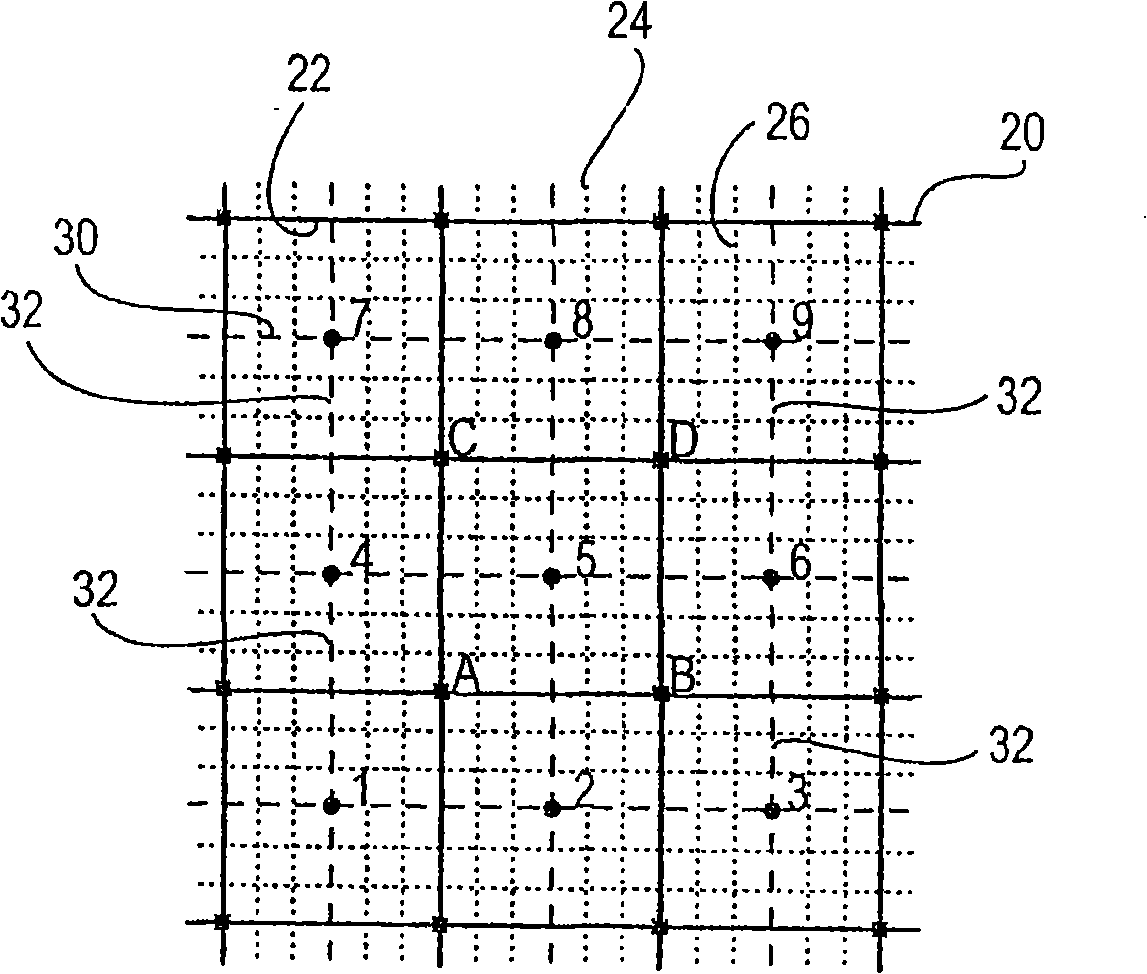
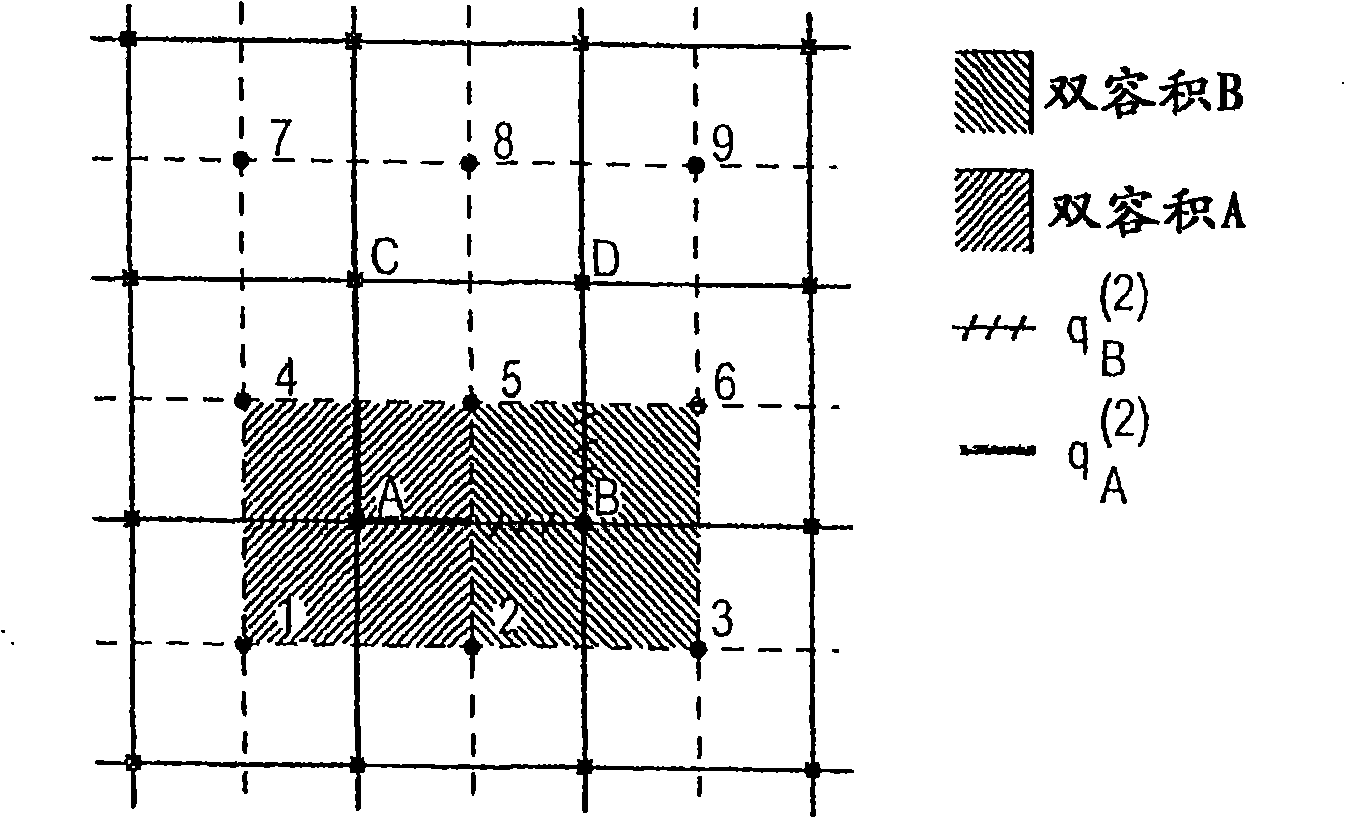
[0036] where p is the pressure, λ is the flow coefficient (permeability K divided by the fluid velocity μ) and Ω is the simulated subsurface volume or region. The source term f represents the well and, in the compressible case, the time derivative. Permeability heterogeneity is a major factor indicative of flow behavior in naturally porous bed rocks. The heterogeneity of permeability K is usually expressed as a complex multiscale function of space. Moreover, the permeability K tends to be a highly discontinuous full tensor. Solving for the space-dependent structure and capturing th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com