Force and torque sensing for surgical instruments
A technique of surgical instruments and instruments, applied in the field of surgical robot systems, can solve problems such as the placement of unfavorable force sensors, and achieve the effect of improving detection and feedback
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
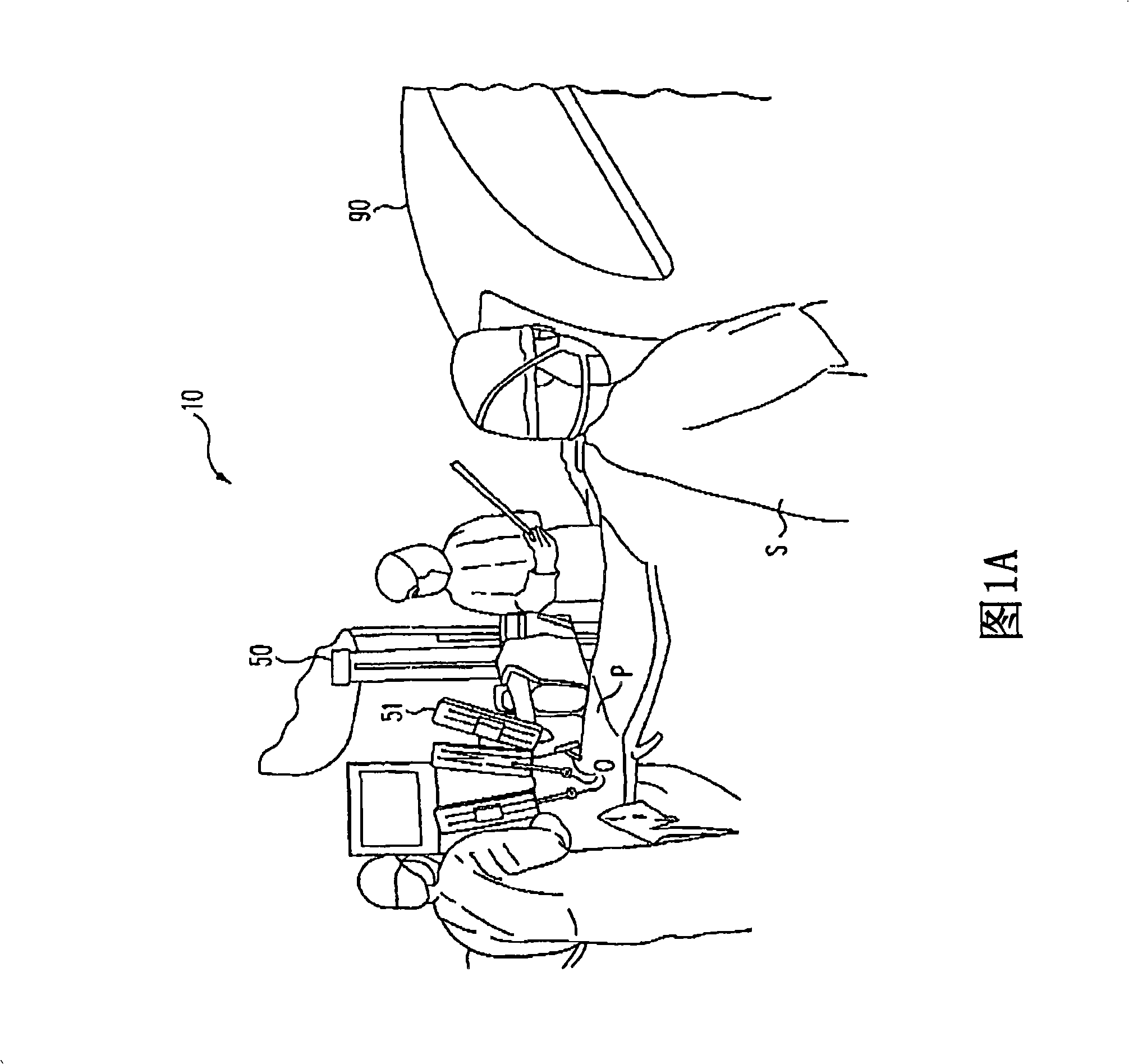
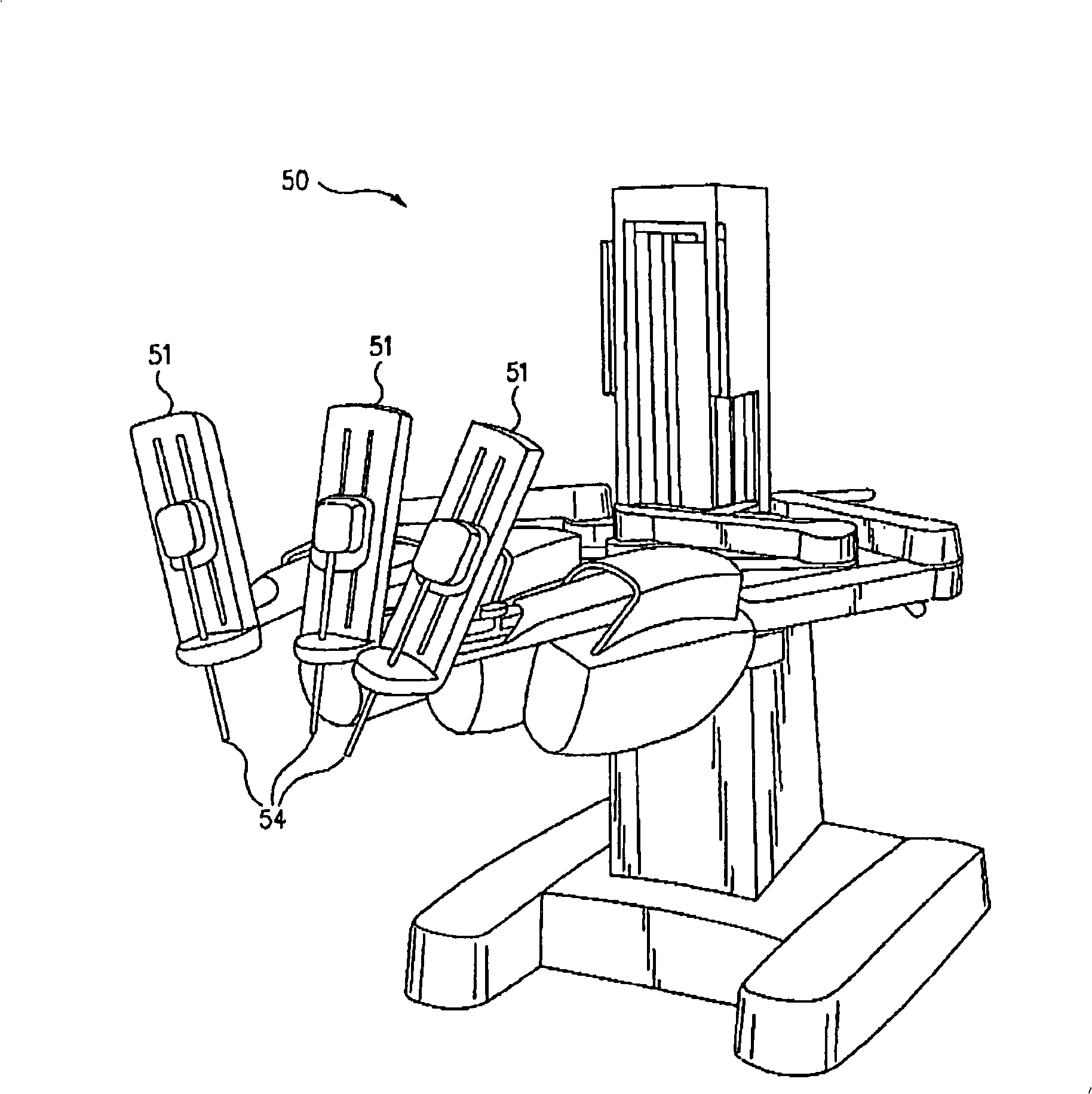
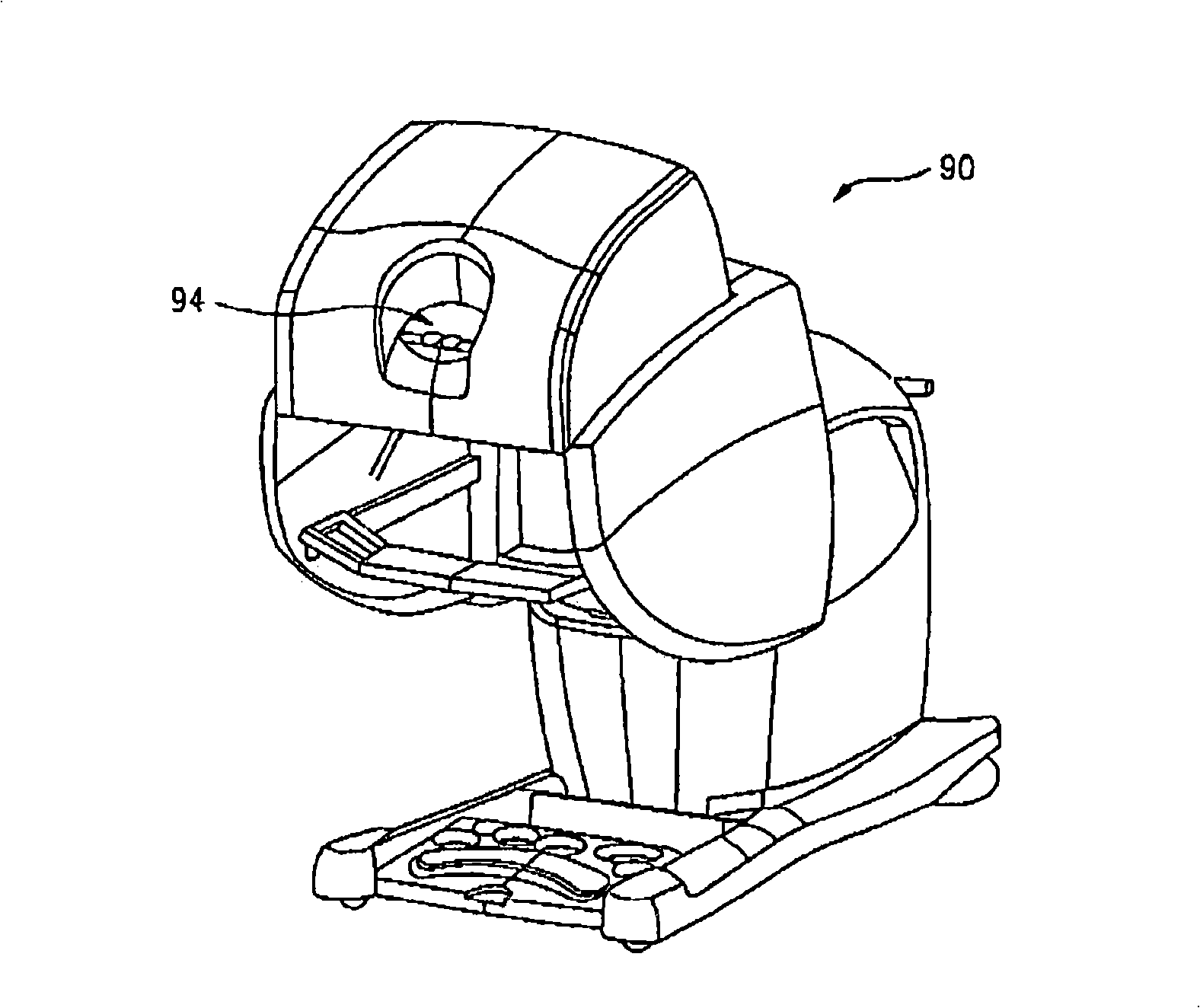
[0021] [0021] The present invention provides multi-component systems, devices, and methods for detecting forces applied to tissue when performing robotic-assisted surgical procedures on a patient, particularly including open surgical procedures, neurological procedures such as stereotaxic techniques. Surgical procedures and endoscopic procedures such as laparoscopy, arthroscopy, thoracoscopy and similar procedures. The systems and methods of the present invention are particularly useful as part of a telerobotic surgical system that allows a surgeon to manipulate surgical instruments via servo mechanisms from a location remote from the patient. Therefore, the manipulator device or slave of the present invention will typically be driven by a kinematically equivalent master with six or more degrees of freedom (e.g., 3 degrees of freedom controlling position and 3 degrees of freedom controlling orientation) Thus a telepresence system with force feedback is formed. A description o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com