Optical space transmission device using image sensor
An image sensor, space transmission technology, applied in free space transmission, transmission system, line of sight transmission and other directions, can solve the problems of enlarged pixel area, reduced signal readout speed, difficult adjustment of optical axis, etc., to improve high-speed communication, improve Effect of signal readout speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
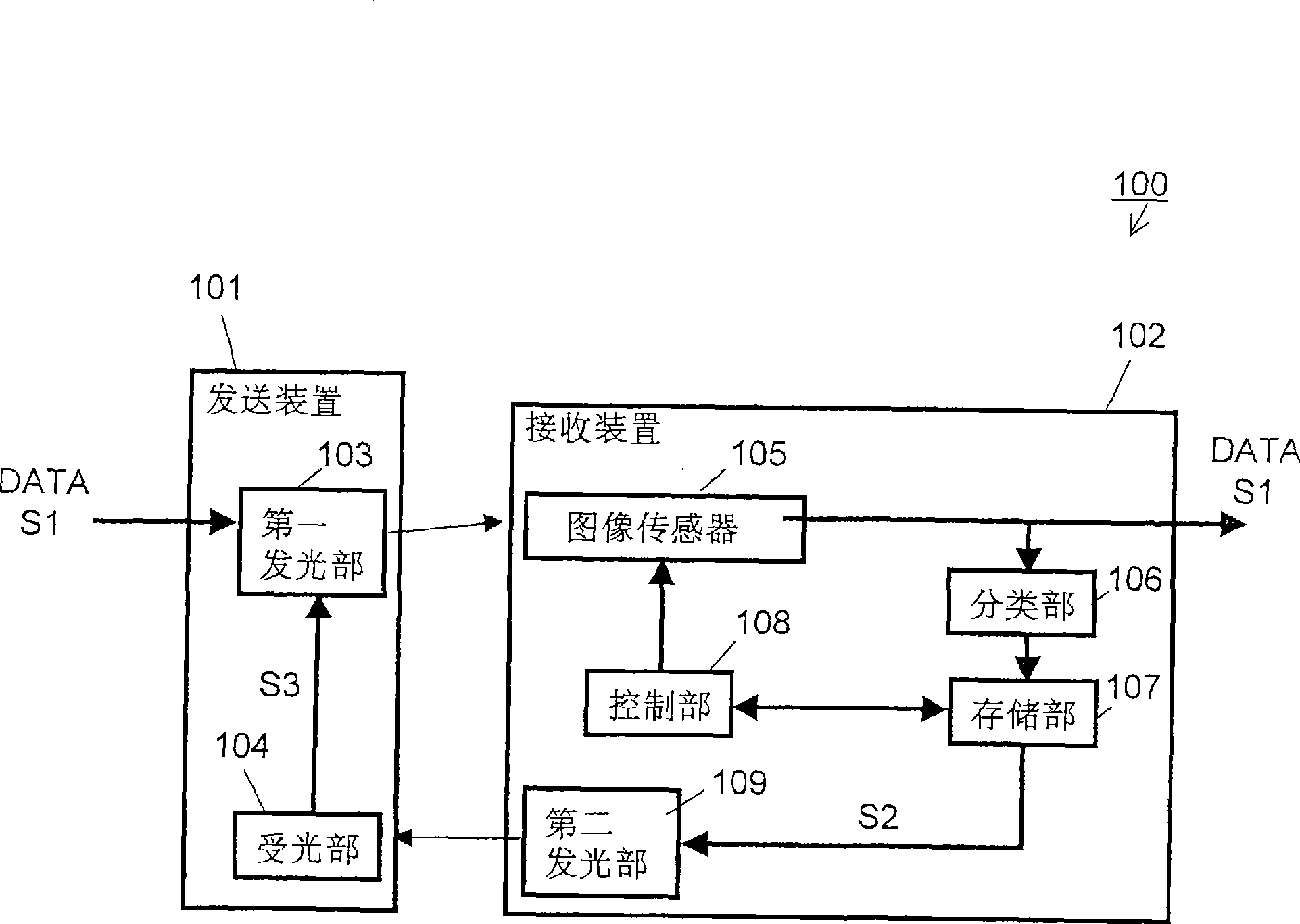
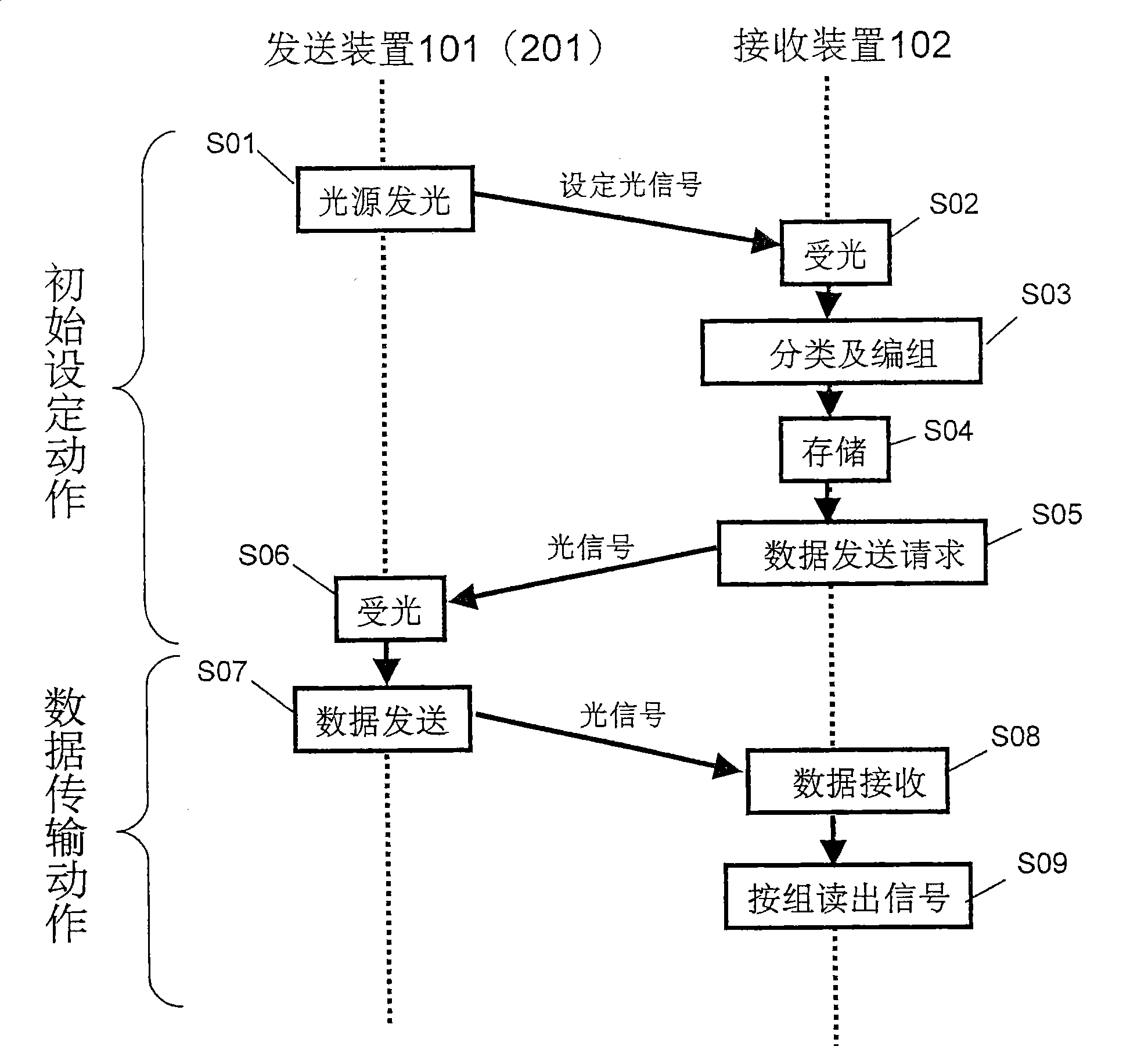
[0071] figure 1 It is a diagram showing a configuration example of the optical space transmission device 100 according to the first embodiment. Such as figure 1 As shown, the optical space transmission device 100 includes a transmitting device 101 and a receiving device 102 . The transmitting device 101 includes a first light emitting unit 103 and a light receiving unit 104 . The receiving device 102 includes an XY address system image sensor (hereinafter simply referred to as an image sensor) 105 , a classification unit 106 , a storage unit 107 , a control unit 108 and a second light emitting unit 109 .
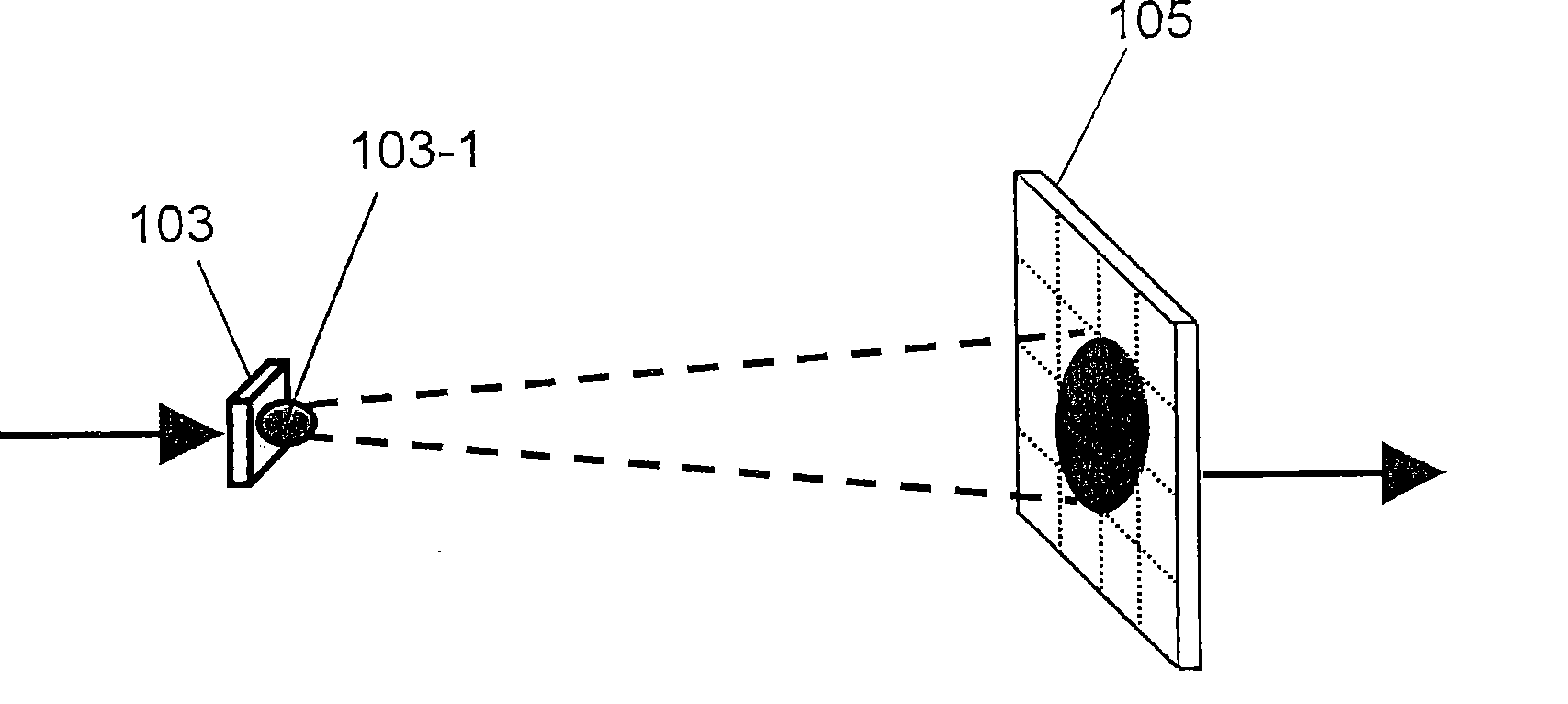
[0072] figure 2 is a diagram specifically showing the first light emitting unit 103 and the image sensor 105 . Such as figure 2 As shown, the first light emitting unit 103 is composed of one light source 103-1. The image sensor 105 has a pixel area composed of a plurality of pixels. The following description will be made assuming that the image sensor 105 has 16 p...
no. 2 approach
[0105] In the first embodiment, a case where an optical signal is transmitted along one optical axis is described, while a case where an optical signal is transmitted along a plurality of optical axes will be described in the second embodiment. Here, in the operation period of each pixel of the image sensor, there are a signal accumulation period for accumulating a signal and a signal readout period for reading out the accumulated signal. That is, each pixel cannot accumulate a signal during the signal readout period. Thus, by transmitting optical signals along a plurality of optical axes, it is possible to accumulate signals for pixels of another group during a period in which signals of a certain group of pixels are collectively read out (signal readout period). That is, according to the second embodiment, when performing data communication, by transmitting optical signals along a plurality of optical axes, it is possible to avoid a decrease in transmission speed due to a si...
no. 3 approach
[0126] In the first and second embodiments, description has been made on the premise that the positional relationship between the transmitting device and the receiving device does not change. On the other hand, in the third embodiment, in the optical space transmission device of the first and second embodiments, even if the positional relationship between the transmitting device and the receiving device changes and the optical axis deviates, data communication can be performed correctly. The composition is explained. Hereinafter, the optical space transmission device 200 according to the second embodiment will be described as an example.
[0127] In the third embodiment, the transmitting device 201 further includes a guide light source as a light source for optical axis correction. In addition, the first light emitting part 203 may also be equipped with a guide light source. The guide light source irradiates the pixel region of the image sensor 105 with a guide light signal,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com