Broadband impedance matching circuit using high pass and low pass filter sections
A technology of impedance matching circuit and low-pass filter, which is applied in the direction of impedance matching network, amplifier input/output impedance improvement, impedance network, etc., which can solve the problems of complex design of impedance matching circuit and increased return loss reflection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] Like reference characters designate like parts throughout the several views of the drawings.
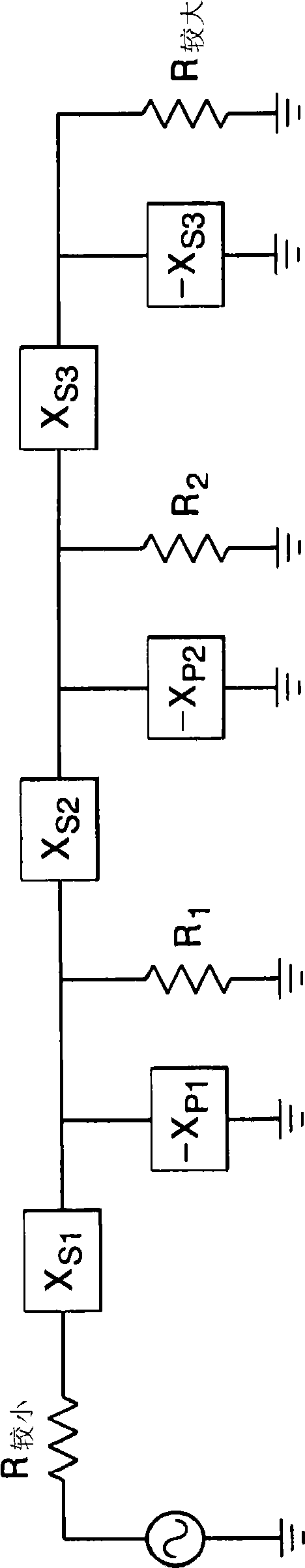
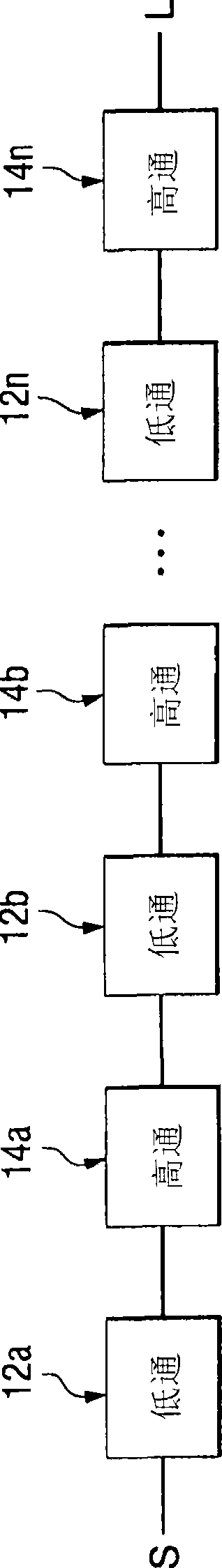
[0019] Referring to FIG. 2, a preferred embodiment of a broadband impedance matching circuit 10 includes a plurality of low-pass filters 12 and a plurality of high-pass filters 14, which are cascaded together alternately between a power source S whose impedance will be equal to The impedance of the load L is matched. Alternating cascaded sequences can start or end with a low-pass filter or a high-pass filter ( Figure 2A shows a sequence starting with a low-pass segment followed by a high-pass segment, while Figure 2B A sequence starting with a high-pass segment followed by a low-pass segment is shown).
[0020] More specifically, in Figure 2A In , the output of the first low-pass filter 12a is connected to the input of the first high-pass filter 12b. Next, the output of the first high-pass filter 12a is connected to the input of the second low-pass filter 12b, and the o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com