Method for selectively breeding wheat-rye 1BL/1RS translocation lines
A technology of translocation lines and rye, which is applied in the direction of botany equipment and methods, applications, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve the problems of low frequency of selection of translocation lines, etc., to solve the problem of lack of germplasm resources, compact plant type, root system developed effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
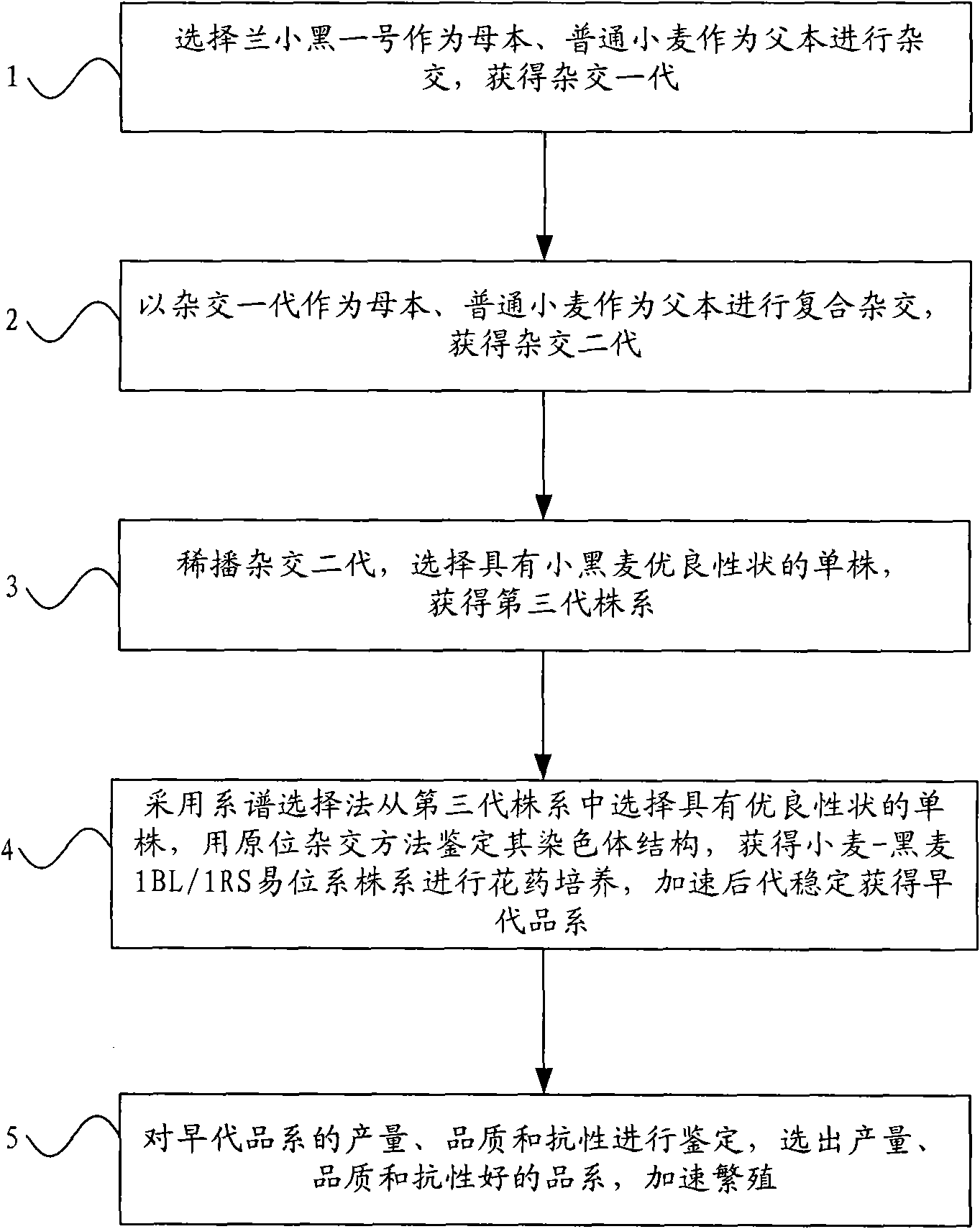
[0024] Step 101. In the first year of breeding, select 20 spikes of Lan Xiaohei No. 1 as the female parent and 20 spikes of common wheat as the male parent, and perform hybridization to obtain the first generation of hybridization;
[0025] Step 102, in the second year of breeding, select 40 ears of hybrid first generation as the female parent, 40 ears of common wheat as the male parent, and carry out compound hybridization to obtain the second generation of hybridization;
[0026] Step 103. In the third year of breeding, 2000 grains of the second-generation hybrids were sparsely sown for a field test, wherein the row spacing of the sparse sowing was 30 cm, and the plant-to-plant spacing was 15 cm. Then select plants with excellent traits such as compact plant type, upright leaves, large spikes and many grains, strong disease resistance, and well-developed root system of triticale to obtain the third-generation lines;
[0027] Step 104. In the fourth year of breeding, use the ...
no. 2 example
[0032] Step 201. In the first year of breeding, select 20 spikes of Lan Xiaohei No. 1 as the female parent and 20 spikes of common wheat as the male parent, and perform hybridization to obtain the first generation of hybridization;
[0033] Step 202, in the second year of breeding, select 50 ears of hybrid first generation as the female parent, 50 ears of common wheat as the male parent, and perform compound hybridization to obtain the second generation of hybridization;
[0034] Step 203. In the third year of breeding, 2500 grains of the second-generation hybrids were sparsely sown for a field test, wherein the row spacing of sparse sowing was 30 cm, and the plant-to-plant spacing was 18 cm. Then isolate and select plants with excellent traits such as compact plant type, upright leaves, large ears and many grains, strong disease resistance, and well-developed root system of triticale, and obtain the third-generation lines;
[0035]Step 204, in the fourth year of breeding, use...
no. 3 example
[0040] Step 301, in the first year of breeding, select 20 spikes of Lan Xiaohei No. 1 as the female parent and 20 spikes of common wheat as the male parent, and perform hybridization to obtain the first generation of hybridization;
[0041] Step 302, in the second year of breeding, select 60 ears of hybrid first generation as the female parent and 60 ears of common wheat as the male parent, and perform compound crossing to obtain the second generation of hybridization;
[0042] Step 303. In the third year of breeding, 3000 grains of the second-generation hybrids were sparsely sown for field experiments, wherein the sparse row spacing was 30 cm, and the plant spacing was 20 cm. Then isolate and select plants with excellent traits such as compact plant type, upright leaves, large ears and many grains, strong disease resistance, and well-developed root system of triticale, and obtain the third-generation lines;
[0043] Step 304. In the fourth year of breeding, use the pedigree s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com