Human face recognition method based on supervision isometric projection
A face recognition and isometric technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of high computational complexity of test data points, affecting the recognition rate of algorithms, and the inability of manifold learning algorithms to effectively eliminate redundant information, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] The present invention is described in more detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing example:
[0045] Its implementation steps are as follows:
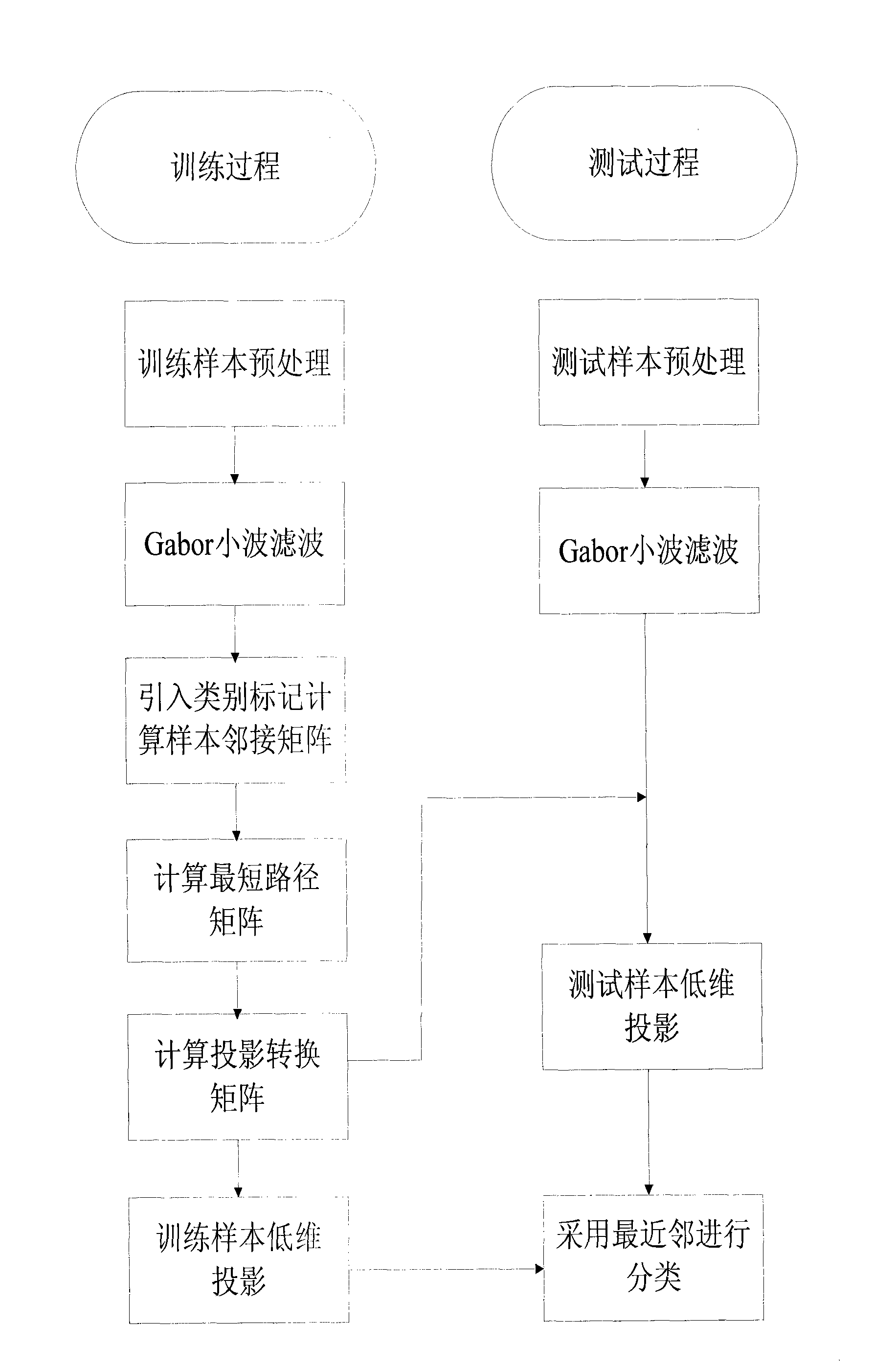
[0046] (1) Face sample training process
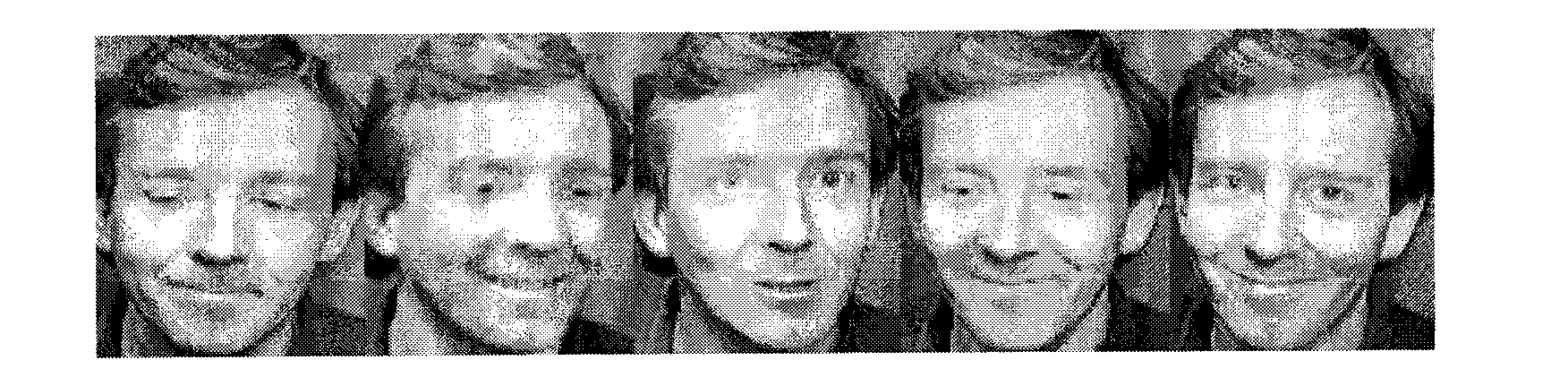
[0047] ① First, preprocess the face training image to obtain the original training sample matrix X in the high-dimensional space; the processing here is to crop each training image, set its resolution to 64×64, and then perform downsampling. to achieve a resolution of 32×32. Finally, each image is normalized with a mean of 0 and a variance of 1.
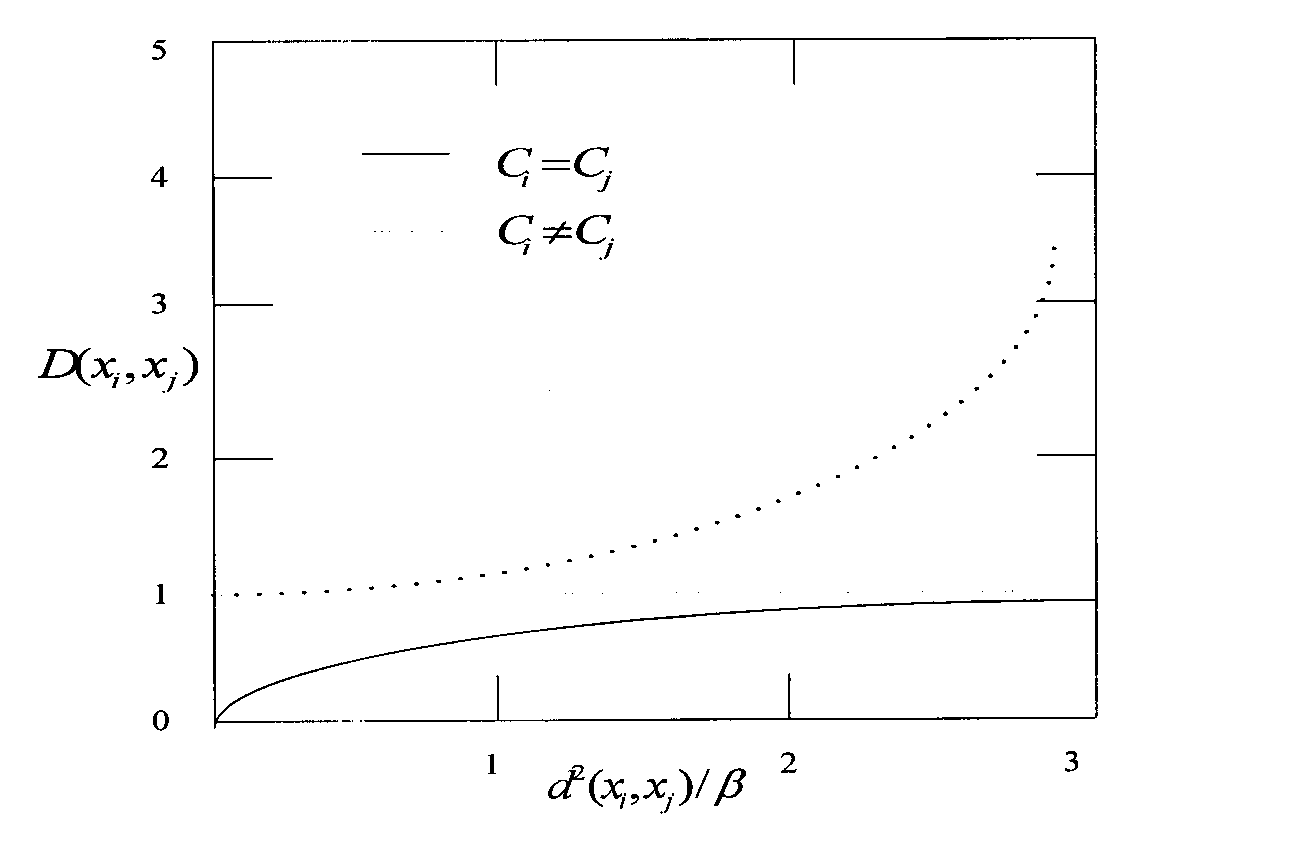
[0048] ②Gabor wavelet filters the image, if I(x, y) represents the original image, the new image features x i ′ = I ( x , y ) ⊗ Φ u , v ( x ,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com