Method for measuring nutrient concentration of leaves
A nutrient and concentration technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, analysis materials, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inaccurate calculation results, reduced weight of a single leaf, inappropriateness, etc., and achieve simple and accurate calculation methods. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
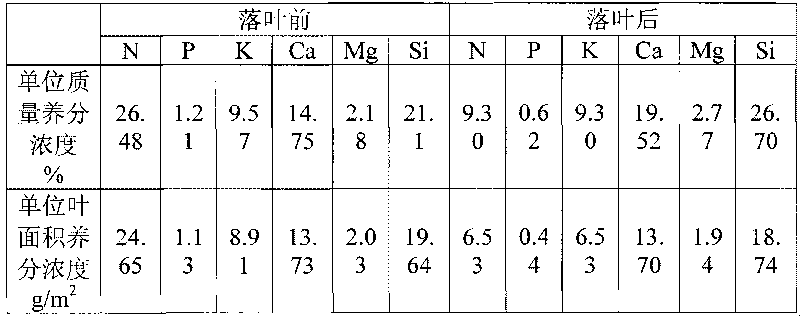
[0016] Take poplar as an example:
[0017] 1) A. Collect mature leaves and fallen leaves from a tree to be tested as leaf samples, randomly select 100 mature leaves as the group before falling leaves, and 100 leaves as the group after falling leaves; Make 400 holes respectively on the blade of group after falling leaves (on each blade, the leaf disc area=63-70% leaf area that gets off), obtain 800 leaf discs, the area of puncher is 2.77cm 2 , the two parts of leaves were dried at 80°C to constant weight and then weighed, and the calculated specific leaf weight LMA of leaves and fallen leaves were 93.1 and 70.2g / m 2 , LMA = total dry weight of all leaf discs / total area of all leaf discs.
[0018] B. Dry the leaf samples of the pre-defoliation group and the post-defoliation group of the trees to be tested at 80°C to constant weight, grind them, pass through a 2mm sieve, and take 0.5-5g of the leaves after grinding to measure the nutrient concentration. Determination, repea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com