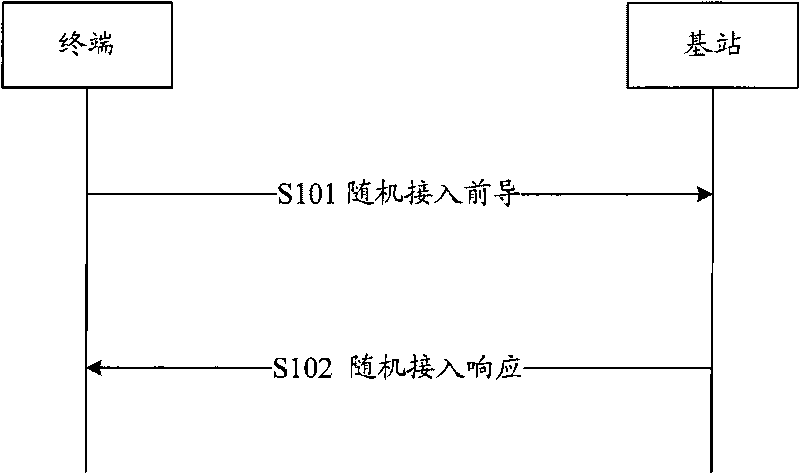
Random access method between terminal and base station in LTE system
A random access and physical random access technology, applied in access restriction, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve problems such as waste of RNTI resources, complexity of interoperability between the MAC layer and the physical layer of the wireless protocol, and reduce complexity flexibility, simplified process, resource reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0333] Embodiment 1 Collision-based random access procedure, FDD mode
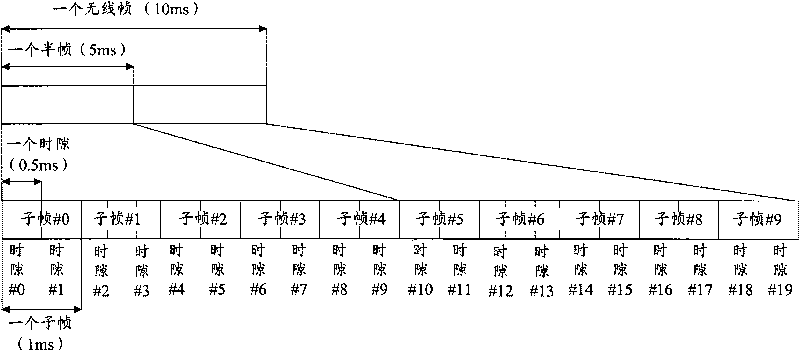
[0334] Assume that in a certain LTE cell, the PRACH configuration index is 12, and the receiving window size is 6ms. The subframe numbers of the PRACH start subframes corresponding to such configuration indexes are 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8, respectively. Their corresponding PRIs are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 respectively. Assuming that the terminal initiates a random access process in order to establish an RRC connection, and selects the PRACH channel with the starting subframe number 2 to send random access, then the random access process is as follows:
[0335] In step 11, the terminal selects a MAC layer protocol to send a random access preamble with an index of 37 on the PRACH channel whose subframe number is 2, that is, the PRI is 1, and sets the corresponding RA-RNTI to 1. Then notify the physical layer of the selected random access preamble, the corresponding RA-RNTI and transmission power parameters, and require th...
Embodiment 2
[0338] Embodiment 2 Collision-based random access process, TDD mode
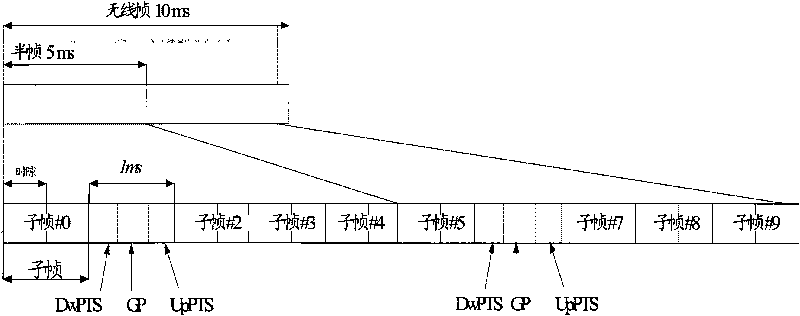
[0339] Assume that in an LTE cell, the PRACH configuration index is 18, the receiving window size is 10ms, and the uplink / downlink configuration is 1. The four-tuples of the PRACH starting subframe corresponding to this configuration index are (0, 0, 0, 0), (0, 0, 0, 1), (0, 0, 1, 0), (0, 0, 1, 1), (1, 0, 0, 1), (1, 0, 1, 1). Their corresponding PRIs are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 respectively. Assuming that the terminal initiates a random access process in order to establish an RRC connection, and selects a PRACH channel with a PRI of 5 to send random access, then the random access process is as follows:
[0340] Step 21, the terminal sends a random access preamble with an index of 37 on the PRACH channel with a PRI of 5 selected by the MAC layer protocol, and sets the corresponding RA-RNTI to 5. Then notify the physical layer of the selected random access preamble, the corresponding RA-RNTI and transmission power...
Embodiment 3
[0343] Embodiment 3 Non-collision-based random access process, FDD mode
[0344] Assume that in a certain LTE cell, the PRACH configuration index is 12, and the receiving window size is 6ms. The subframe numbers of the PRACH start subframes corresponding to such configuration indexes are 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8, respectively. Their corresponding PRIs are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 respectively. Assume that the terminal is in the RRC connection state, but has lost uplink synchronization. When the network has data arriving in the buffer in the downlink, it notifies the terminal to initiate a random access process through the PDCCH channel, then the random access process is as follows:
[0345] Step 30, the base station notifies the terminal through the PDCCH channel to send a random access preamble with an index of 37 on the PRACH channel with a PRI of 3;
[0346] Step 31, after the terminal receives the PDCCH signaling, the MAC layer sets the corresponding RA-RNTI to 3, and then notifies the p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com