Autonomous optical navigation method for soft landing for deep space probe
An independent technology for deep space probes and soft landings, applied in the aerospace field, can solve problems such as high system complexity and inability to support high-precision soft landing tasks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
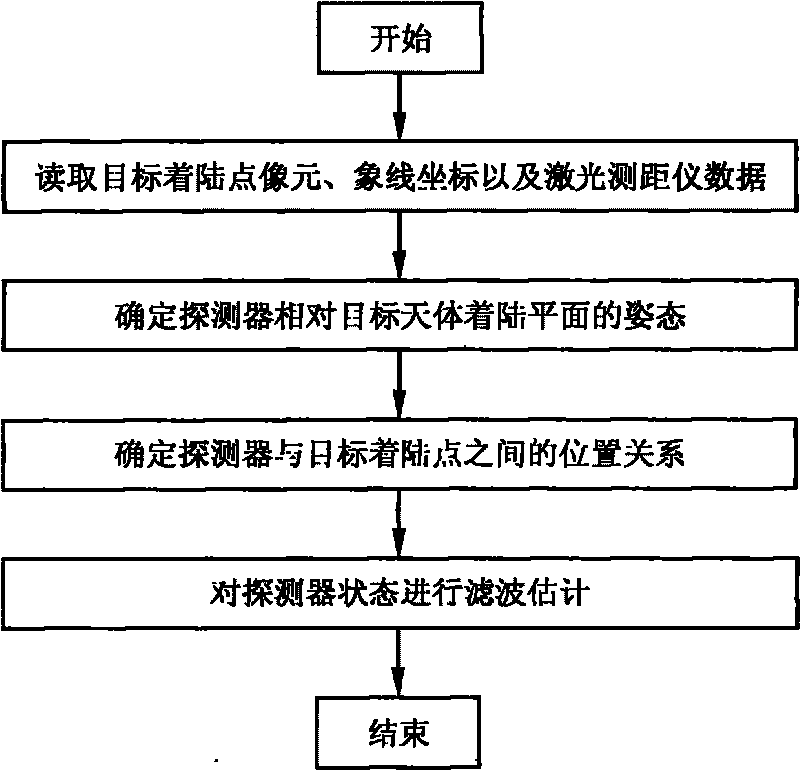
[0039] In order to better illustrate the purpose and advantages of the present invention, the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0040] The concrete steps of this embodiment are as follows:
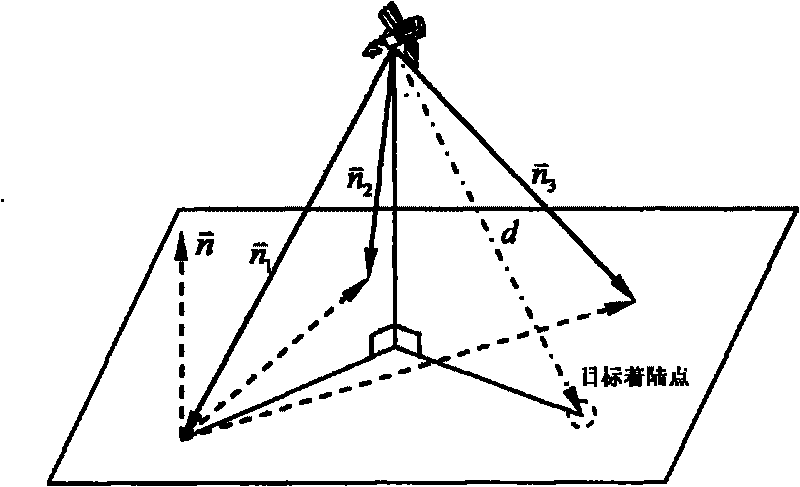
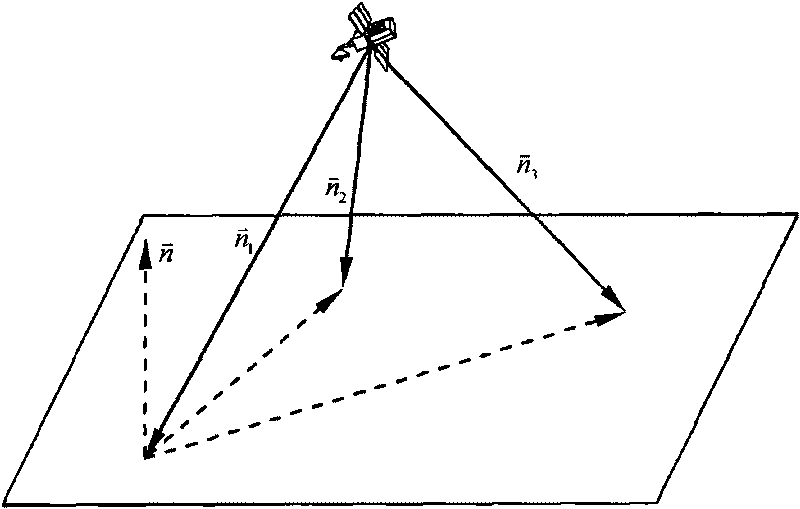
[0041] Step 1, read the corresponding pixel p and image line l coordinates of the target landing point on the image plane captured by the optical navigation camera, and the distance between the detector and the landing plane in the three laser rangefinder installation directions d i .
[0042] Use the optical navigation camera to track the pre-selected target landing point, and obtain the pixel p and image line l coordinates corresponding to the target landing point on the image plane captured by the optical navigation camera, and the pixel p and image line l coordinates are consistent with the target landing point The relationship between relative detector positions can be expressed by the followin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com