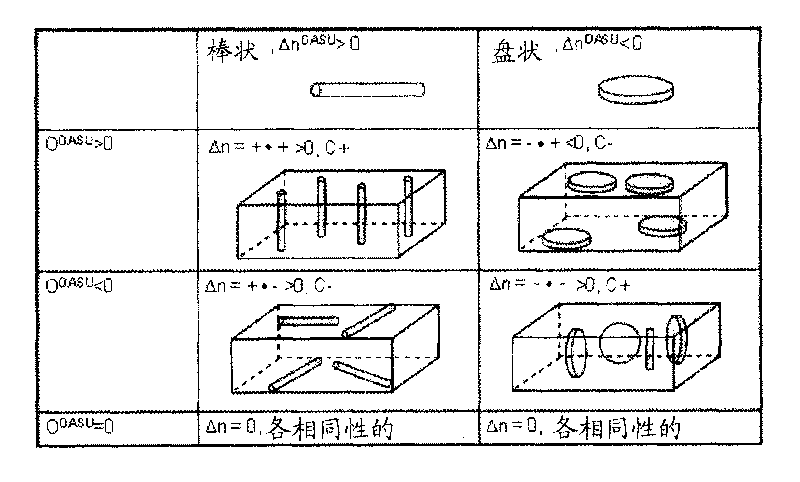
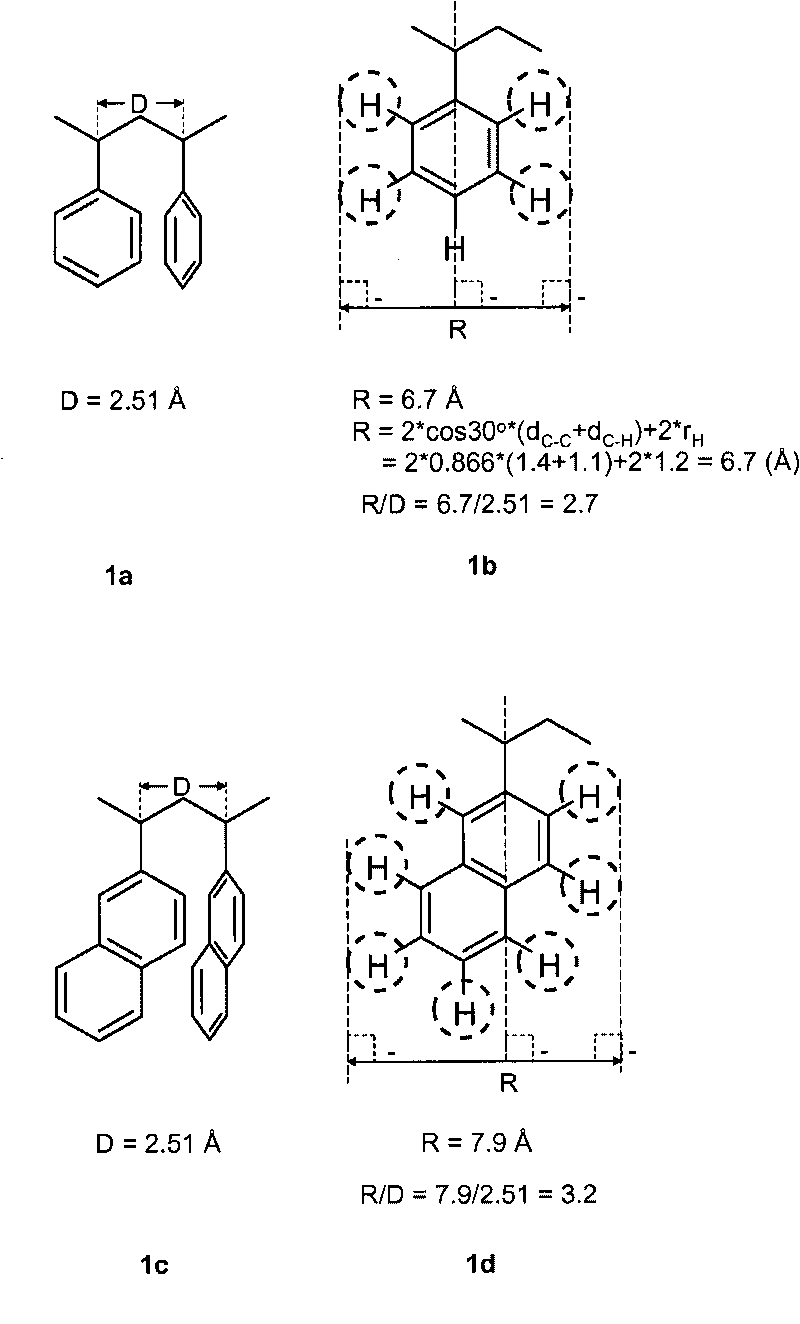
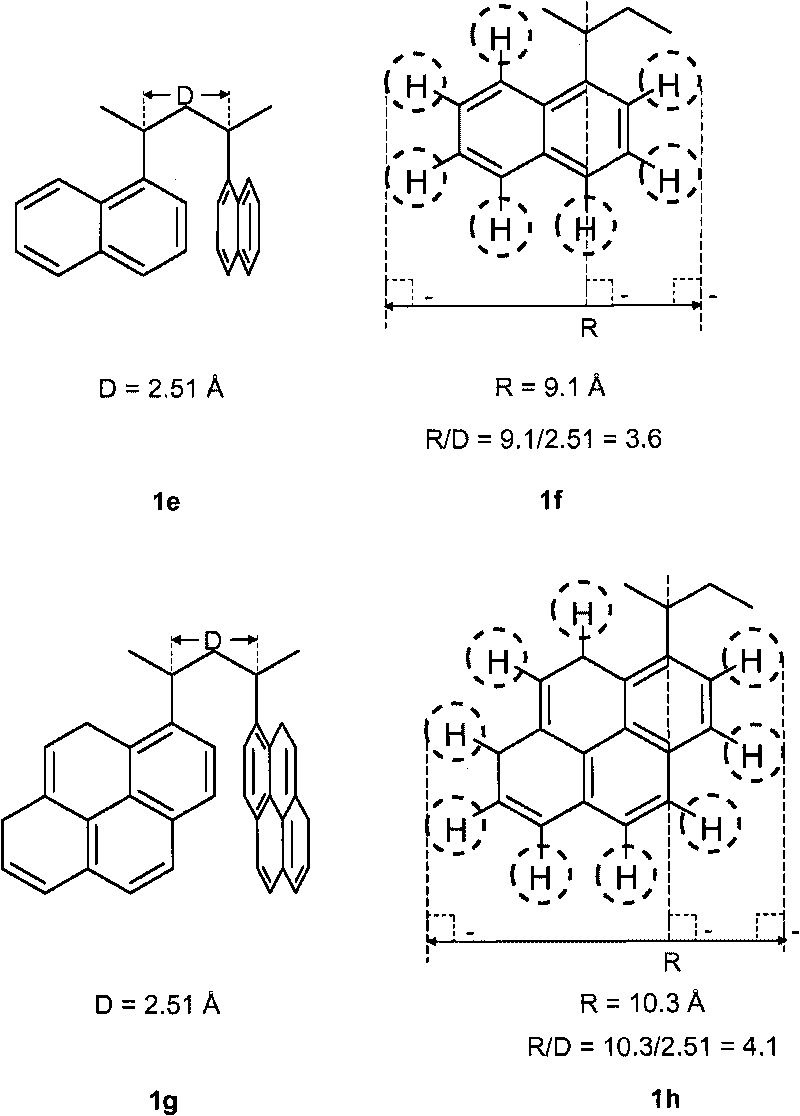
Optical compensation films having positive birefringence for liquid crystal display
一种液晶显示器、正双折射的技术,应用在光学、光学元件、液晶材料等方向,能够解决昂贵等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Embodiment 1
[0160] v f The value can be determined by many factors including, but not limited to, the evaporation rate of the solvent, ambient temperature, the solubility of the polymer in the solvent, and the polymer chemical structure, which affects relaxation. The rate of evaporation is preferably slow enough to ensure spherical collapse, but fast enough to ensure that the rate of relaxation is slower at more dilute concentrations. The rate of evaporation can be adjusted by adjusting the ambient temperature and pressure as known in the art. The rate of relaxation depends on the chemical structure of the polymer and the film casting temperature. Polymers with rigid segments can freeze readily at ambient temperature. Example Example 1: Birefringence measurement
[0161] A polymer sample is first dissolved in a suitable solvent, and the solution is cast onto a piece of clean glass measuring 1 by 1.5 inches. The thickness of the polymer film is controlled within the range of 15-20 μm...
Embodiment 2
[0162] 2-Vinylnaphthalene (2.00 g) was charged to a Schlenk tube. The tube was stoppered, evacuated by evacuation, and filled with argon. The tube was evacuated and then refilled with argon four more times. While under a positive pressure of argon, the tube was immersed in an oil bath maintained at 70°C for 24 hours. After cooling to room temperature, the solid plug material was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (THF). This solution was added dropwise to 500 mL of rapidly stirring methanol to precipitate the polymer. Precipitated polymer was collected by filtration and dried by forcing air through the material over a filter plate. The polymer was then dissolved in fresh THF and reprecipitated by dropwise addition to rapidly stirring methanol. After collection by filtration and drying, the polymer formed was found to have a MW of 127000 g / mol and a Tg of 139°C. Films cast from cyclopentanone (Cp) showed a positive birefringence of 0.0040 at 633 nm. Example 3: Preparation of p...
Embodiment 3
[0163] 2-Vinylnaphthalene (2.01 g), azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN, 1.5 mg) and benzene (0.98 g) were charged into a 50 mL round bottom flask containing a Teflon-coated magnetic stir bar. The stirred reaction mixture was degassed by bubbling dry argon through the stirred reaction mixture for 15 minutes. The vessel contents were then kept under a positive pressure of argon and immersed in an oil bath maintained at 60°C for 19 hours. After cooling the reaction mixture to room temperature, the vessel contents were diluted with 25 mL of benzene. The resulting solution was slowly poured into 500 mL of rapidly stirring methanol to precipitate the formed polymer. The precipitated polymer was collected by filtration and dried by forcing air through the material over a filter plate. The polymer was then dissolved in THF and added dropwise to rapidly stirring methanol for reprecipitation. After collection by filtration and drying, the polymer formed was found to have a MW of 251000 g / m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| bond length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| bond angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap