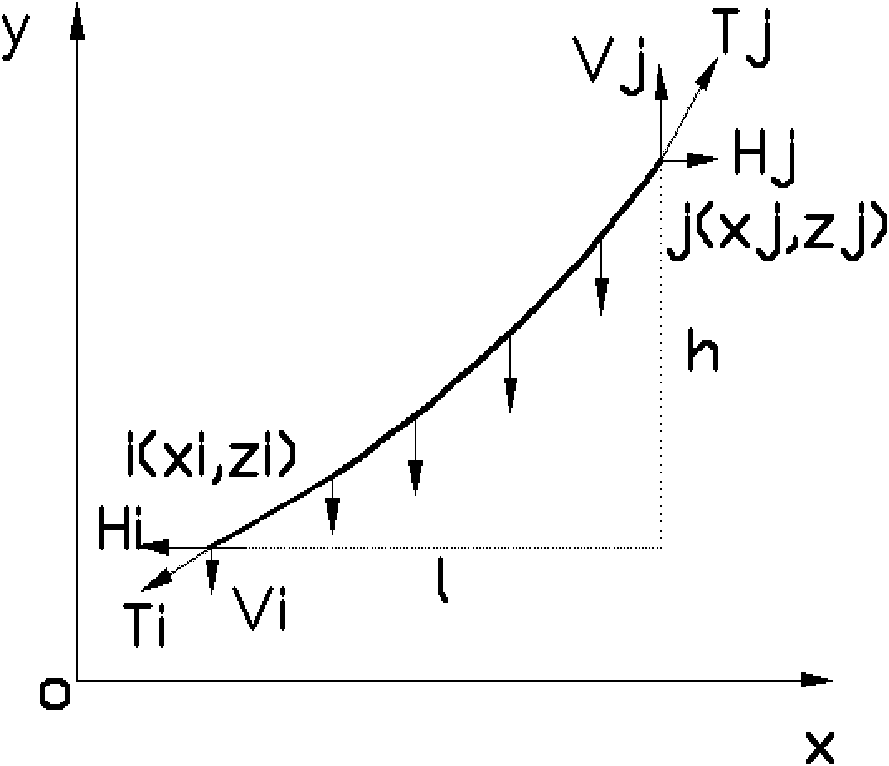Method for precisely solving length of unstressed cable of cable-stayed bridge
A stress-free, cable-stayed technology, applied in the field of bridge and culvert engineering in the transportation industry, can solve problems such as calculation errors, difficulty in iteration convergence, divergence, etc., and achieve the effects of small calculation errors, large practical engineering application value, and fast convergence speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
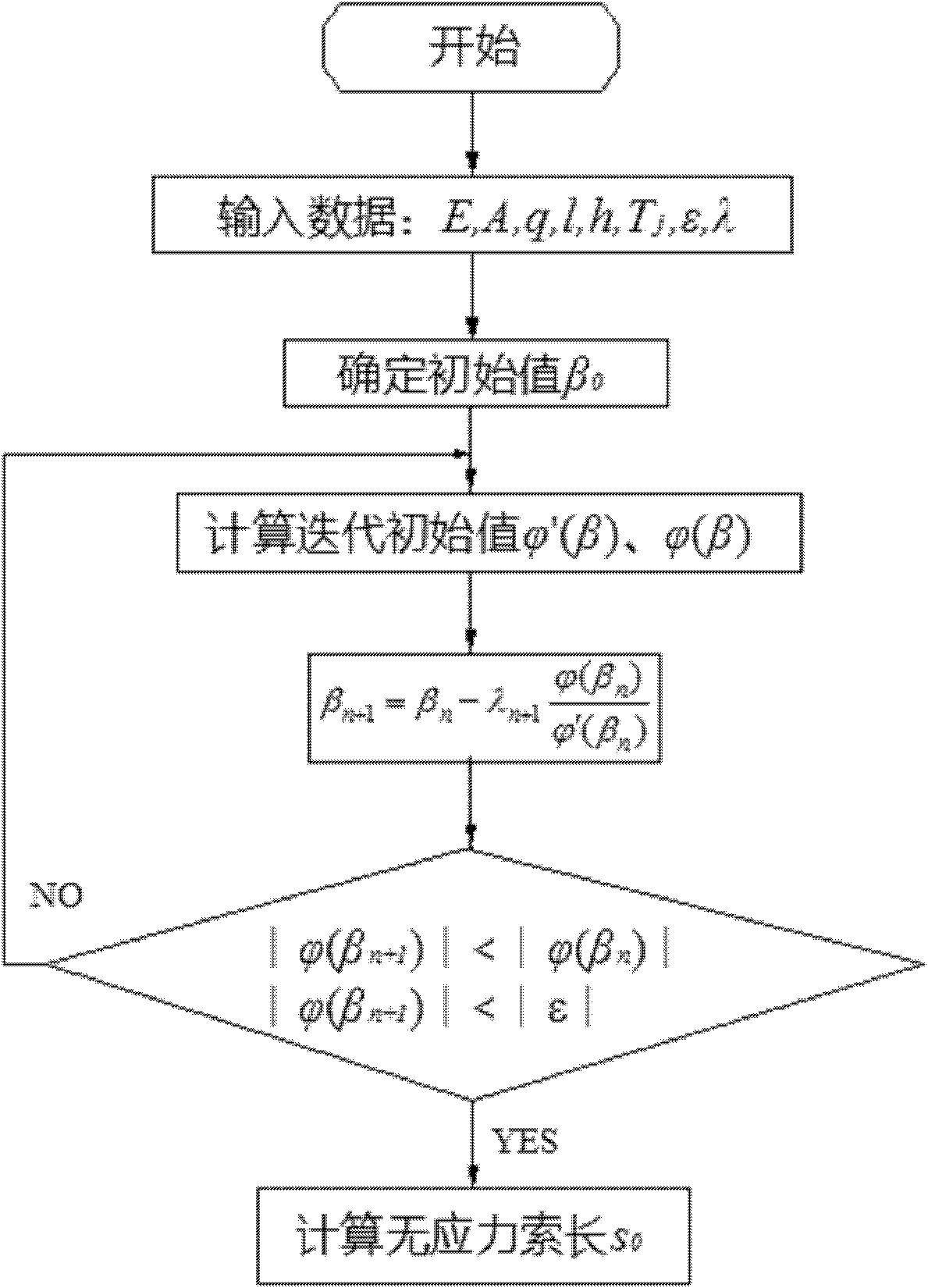
[0032] Embodiment 1, the accurate solution method of unstressed cable length of cable-stayed bridge:
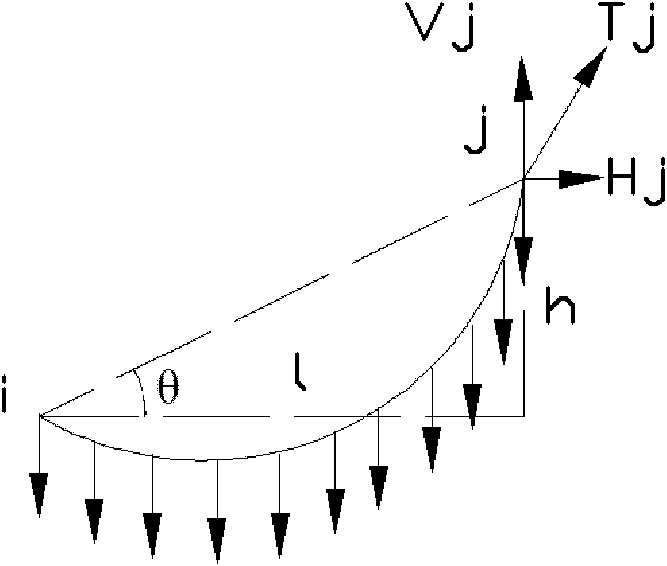
[0033] Such as figure 1 In the analysis and calculation of the catenary element of the shown cable, the following assumptions are adopted: (1) the cable is ideally flexible and can only bear tension but not compression and bending; (2) the cable is a linear elastic material, and its The stress-strain relationship conforms to Hooke's law; (3) Except for the support at both ends, the cable is only subjected to a vertically downward load uniformly distributed along the length of the cable; (4) Regardless of the change of the cable cross-section before and after deformation, its self-weight is constant The load concentration is constant along the length of the cable. According to the above assumptions, the cable type under the action of its own weight is a catenary.
[0034] exist figure 1 In the rectangular coordinate system xoy shown, the catenary element is ij, and the coor...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Embodiment 2, the application of the accurate solution method of unstressed cable length of cable-stayed bridge:
[0077] In order to verify the accuracy and effectiveness of the proposed calculation method for unstressed cable length, a calculation program was compiled using the mathematical software MATLAB7.1, and compared with the calculation results of Ridders' improved chord cut method. The material properties of the cable in the calculation example are: elastic modulus E=1.31×10 11 N / m 2 ; The cross-sectional area of the cable is A=5.48×10 -4 m 2 ; Uniformly distributed load along the length of the cable q = 46.11N / m. Calculation of two working conditions will be carried out (1) l=100m, h=10m, cable end pretension T j =12kN; (2) l=10m, h=300m, cable end pretension T j =30kN; the calculation results are shown in Table 1. From the comparison of the results in Table 1, it can be seen that compared with the iterative method using Ridders' improved chord cut me...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com