Motor control device and control method thereof
A motor control and motor technology, applied in the direction of controlling electromechanical transmissions, controlling electromechanical brakes, control systems, etc., can solve the problems of not increasing speed, poor efficiency, and inability to generate torque.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
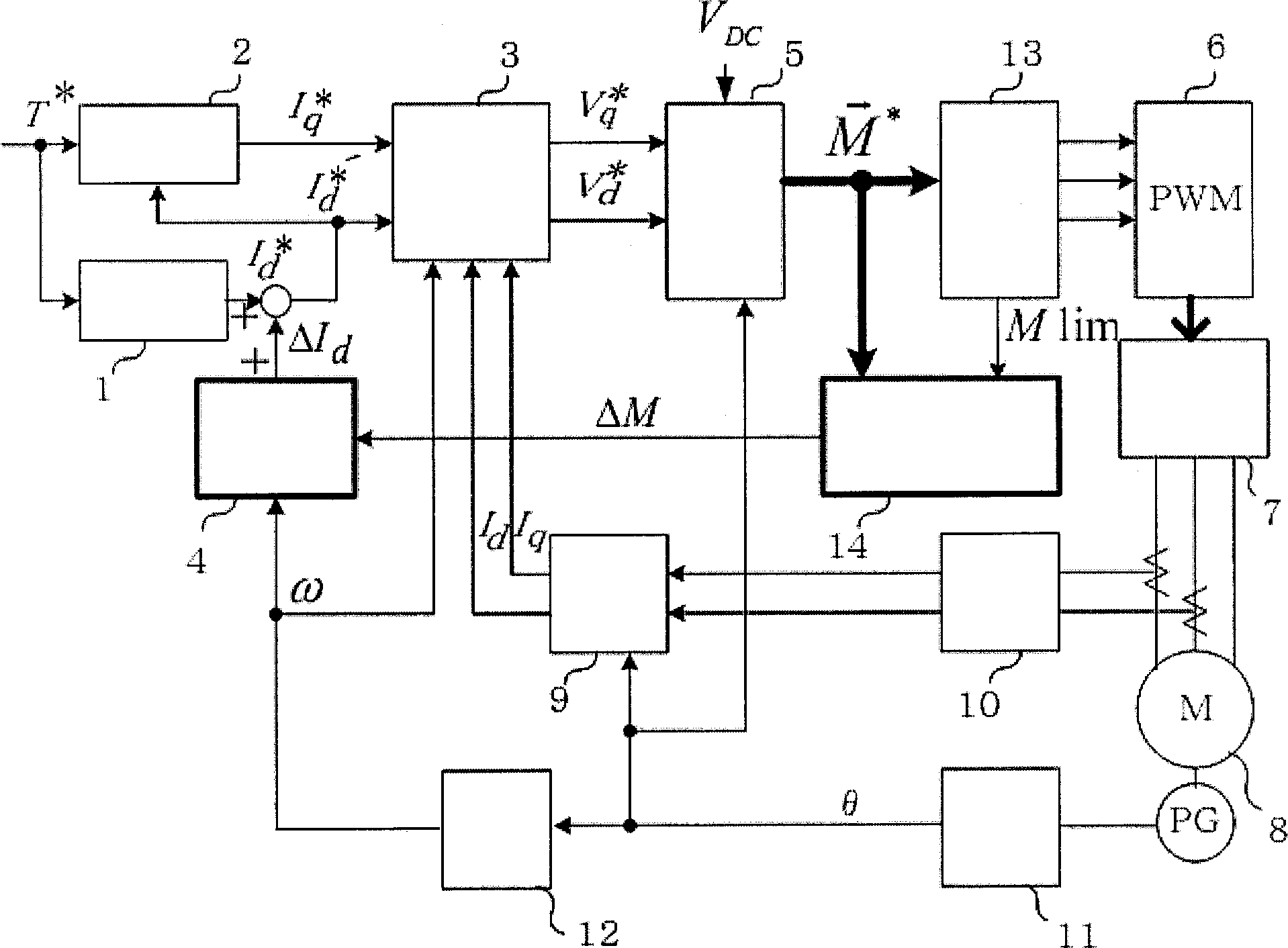
[0093] figure 1 It is a control block diagram showing an example in which the motor control device of the present invention is applied to a three-phase interior permanent magnet synchronous motor (IP MSM).
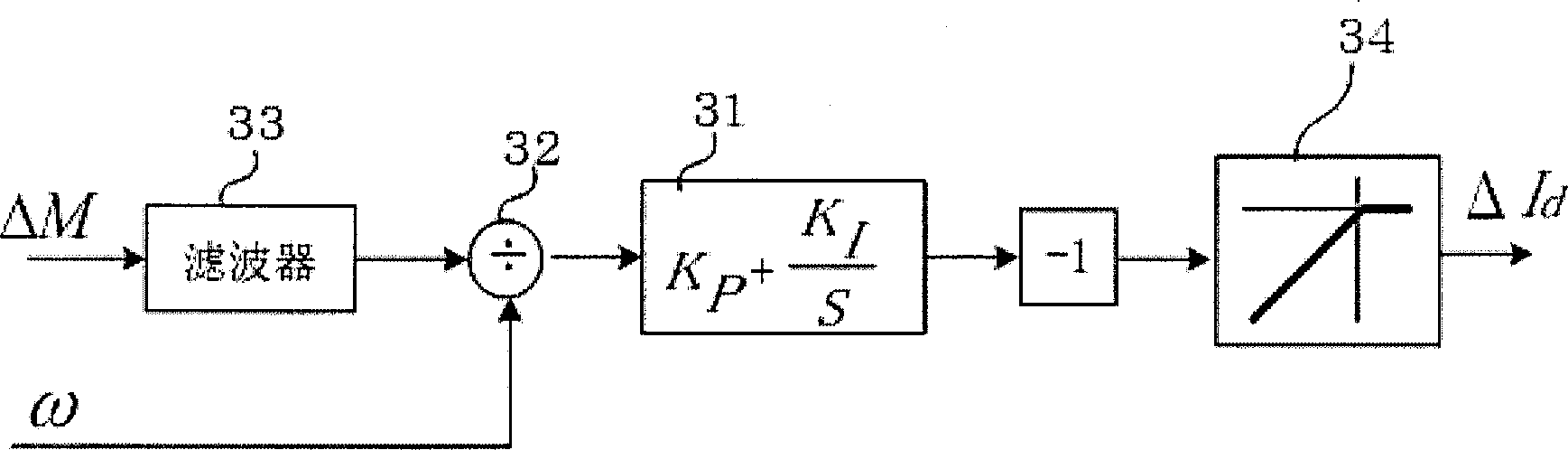
[0094] The d-axis current command calculation unit 1 inputs the torque command T*, and calculates the most suitable d-axis current command I according to the characteristics of the motor d *. The q-axis current command computing unit 2 inputs the torque command T* and the d-axis current command I d *, and calculate the q-axis current command I q *. The current command computing unit is constituted by the d-axis current command computing unit and the q-axis current command computing unit. The current control unit 3 inputs a dq-axis current command and a dq-axis current detection value, and obtains a voltage command by matching the dq-axis current detection value with the dq-axis current command. Current control generally consists of separate PI control and voltage FF c...
Embodiment 2
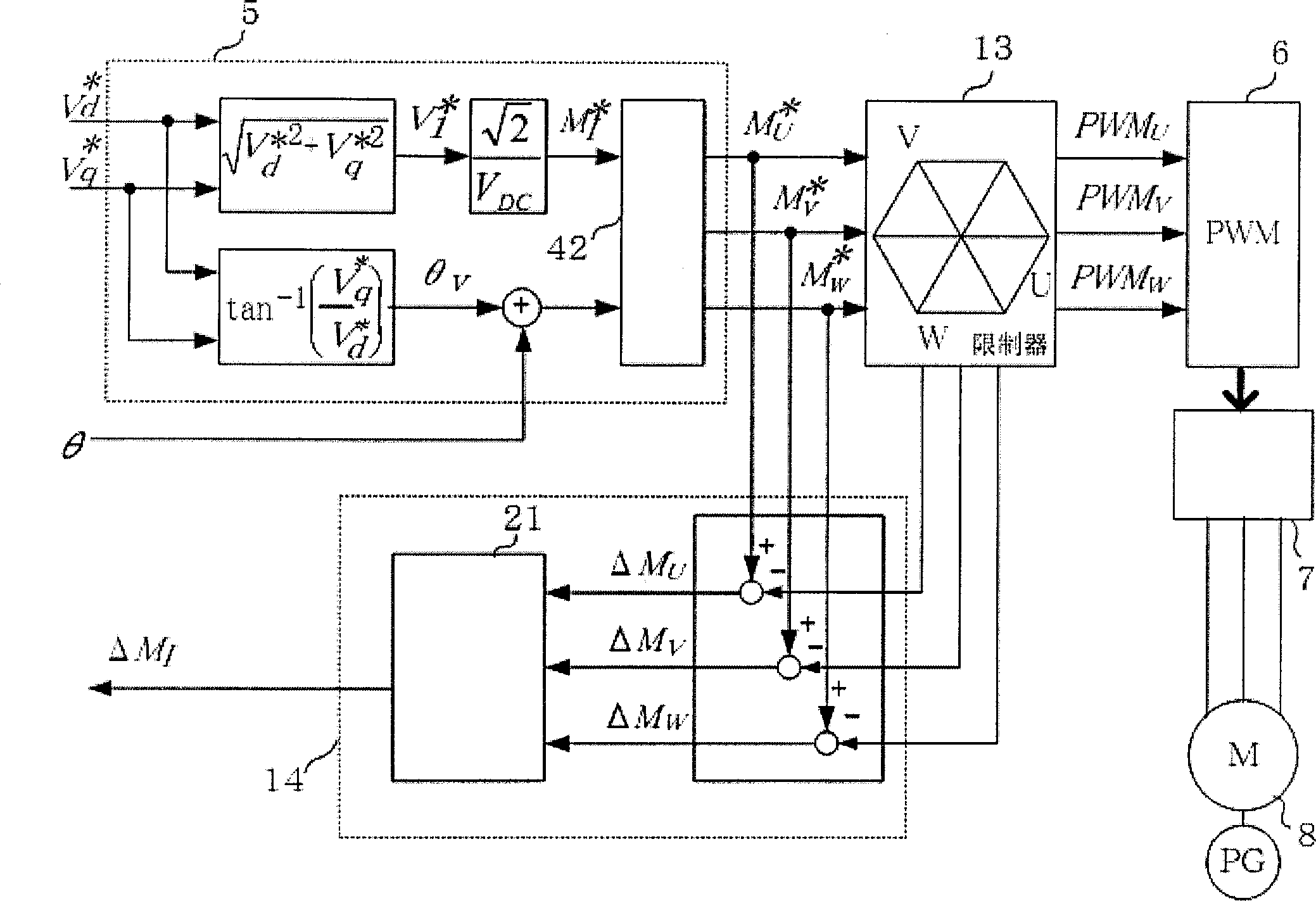
[0132] Figure 4 It is a block diagram showing the modulation wave command calculation unit 5, the modulation wave command restriction unit 13, and the modulation factor saturation calculation unit of the second embodiment. The modulated wave command calculation unit 5 obtains the modulation factor M from the dq axis voltage command I and output phase θ 0 On this point, it is the same as that described in Example 1 figure 2 same. The difference is that the modulation rate instruction M I and output phase θ 0 As the first modulated wave command, in the modulated wave command limiting unit 13, the modulation rate limiting unit 41 sets the modulation rate limit value M 1imit Limit modulation rate command M I And the second modulation rate command M' is obtained I , using the second modulation rate command M’ I and output phase θ 0 In the three-phase conversion unit 42 , the second modulated wave command for the three phases is obtained as follows, for example, as in Equ...
Embodiment 3
[0139] Figure 5 It is a block diagram showing the modulation wave command calculation unit 5, the modulation wave command restriction unit 13, and the modulation factor saturation calculation unit of the third embodiment. The modulated wave command calculation unit 5 obtains the modulation factor M from the dq axis voltage command I , the dq-axis voltage command and the modulation rate M I As the first modulation wave command. In the modulated wave command limiting unit 13, the modulation rate limits the value M 1imit Limit modulation rate M I And find M' I , in the dq modulated wave instruction computing unit 51, by M' I The modulated wave command M of the dq axis is obtained as follows with the dq axis voltage command d , M q .
[0140] V 1 = V d * 2 + V q ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com