Multi-hop positioning method for lightweight wireless sensor networks
A wireless sensor and positioning method technology, applied in wireless communication, network topology, electrical components, etc., can solve problems that affect the development of wireless sensor networks, low positioning accuracy, unbalanced calculation complexity and positioning accuracy, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
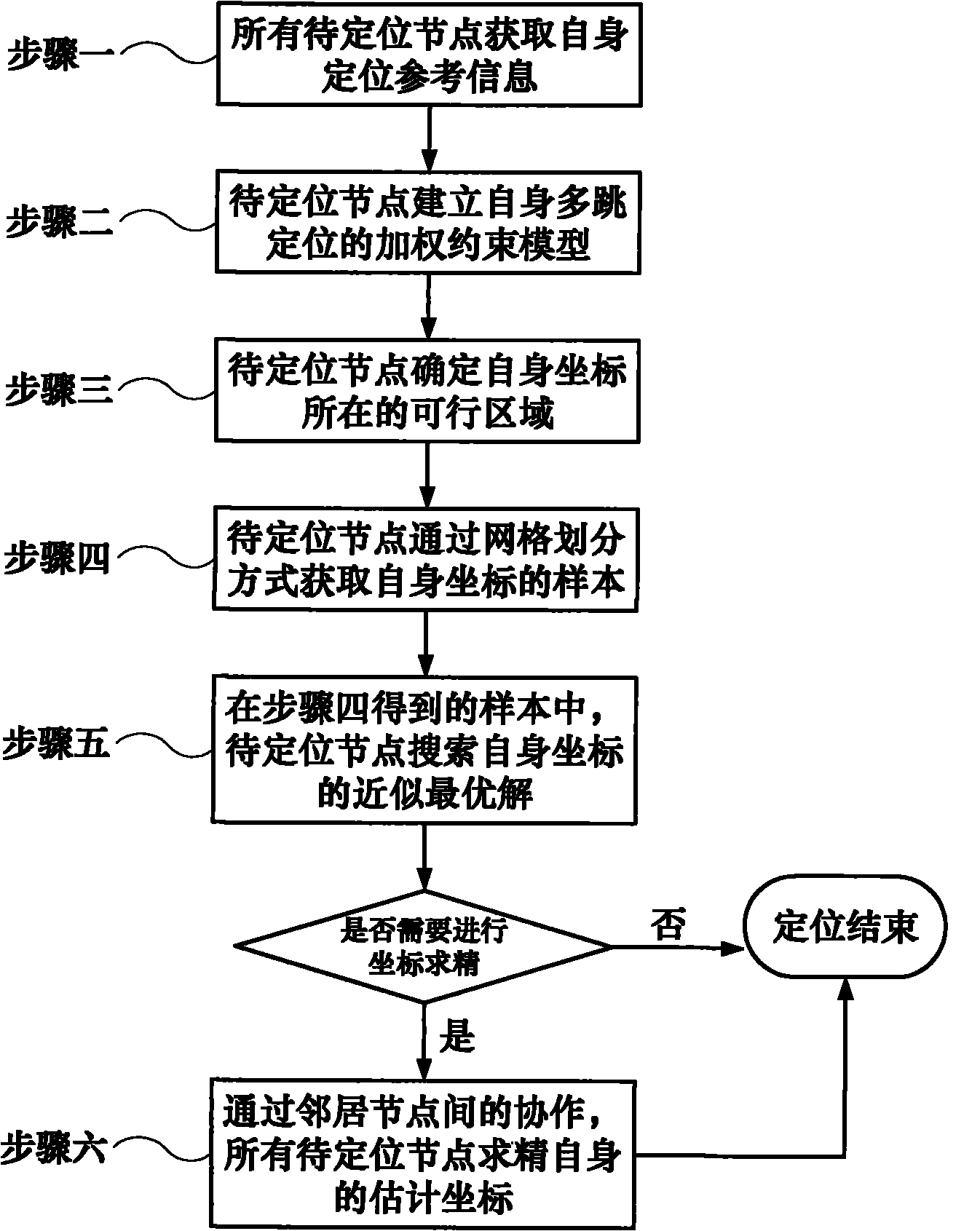
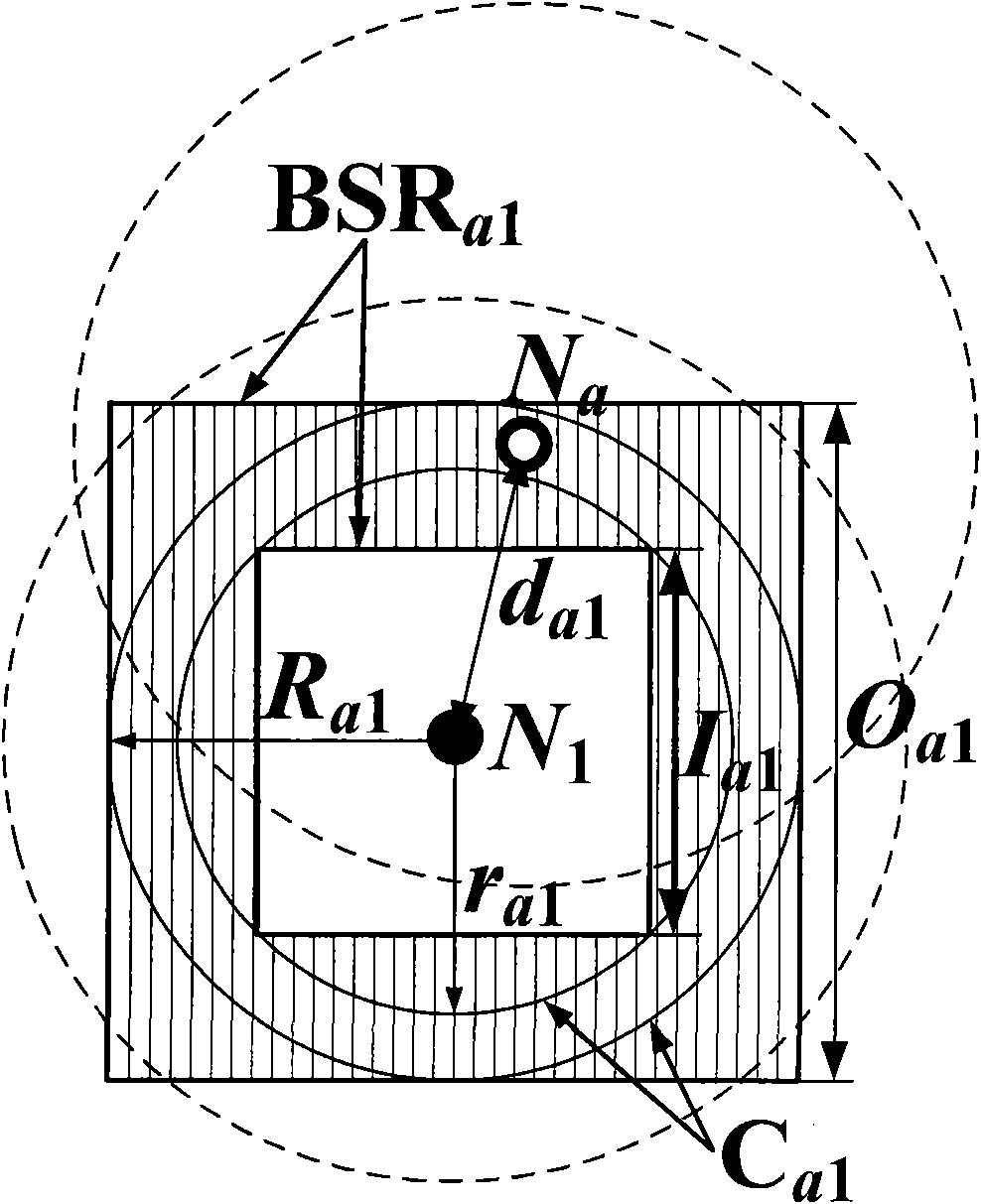
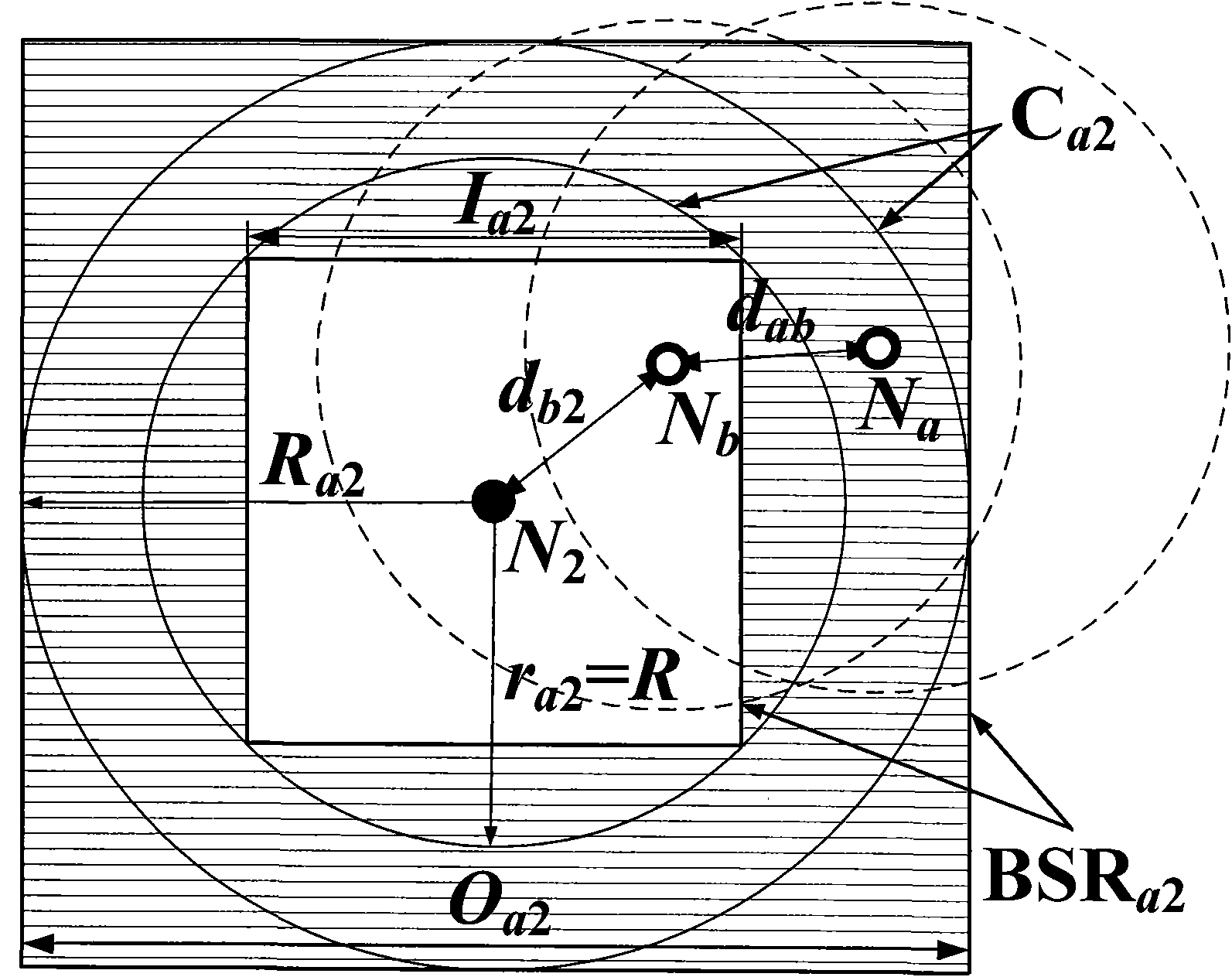
Embodiment
[0148] Such as Figure 5 As shown, 200 sensor nodes are deployed in a 200m×200m plane area to form an H-shaped anisotropic wireless sensor network. The communication radius of all nodes is 25.6m, and the connectivity of the network is 9 at this time. Figure 5In the figure, the solid circle represents the beacon node, the ratio is 10%, and the ID is 1-20; the hollow circle represents the node to be located, the ratio is 90%, and the ID is 21-200; the solid line between the nodes represents that two nodes can For direct communication, the length of the solid line represents the Euclidean distance between two nodes; all nodes have the ranging function, the ranging error proportional coefficient is 0.1, and the life cycle TTL of the information frame is 5.
[0149] exist Figure 5 In the shown network environment, a lightweight wireless sensor network multi-hop positioning method of the present invention is used to perform node multi-hop self-positioning; without node cooperatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com