Method for preparing nickel-based alloy by stepwise adding carbon in melting process
A nickel-based alloy, step-by-step technology, applied in the field of nickel-based alloys, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of composition control and reducing the deoxidation capacity of C in the alloy, and achieve the effects of reducing porosity, achieving precise control and improving the pass rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
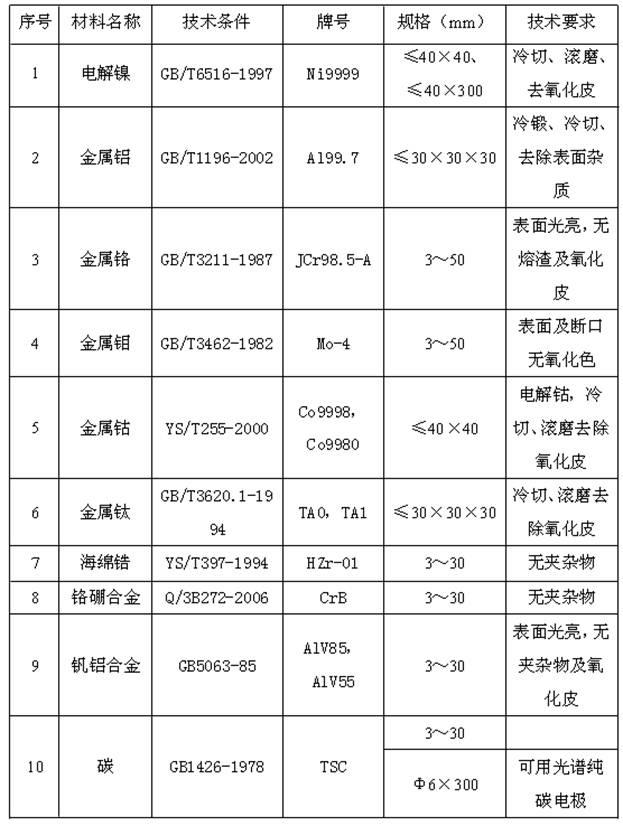
[0031] The process of adding carbon step by step during the smelting process to prepare the nickel-based alloy is as follows.
[0032] (1) Furnace loading
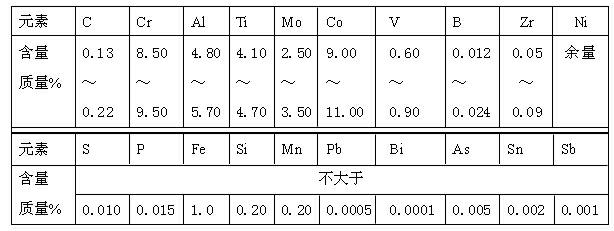
[0033] In the crucible from bottom to top, 68% of the total amount of Ni, 18% of the total amount of C, all of Co, all of Mo, all of Cr and the remaining Ni were loaded in sequence.
[0034] 18% of the total amount of C, the remaining C, V-Al, Al, Ti, CrB and Zr were separately charged in the feeding tank.
[0035] (2) Melting of the alloy
[0036] A vacuum induction melting furnace is used for smelting. When the vacuum degree of the vacuum induction melting furnace is ≤0.67Pa, the temperature starts to rise, and the temperature rise rate is controlled to be 7°C / min until the charge is melted.
[0037] (3) Alloy refining
[0038] When the vacuum degree of the vacuum induction melting furnace after alloying is ≤1.33Pa, the temperature is raised to a refining temperature of 1530°C at a heating rate of 15°C / min, and the re...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The process of adding carbon step by step during the smelting process to prepare the nickel-based alloy is as follows.
[0052] (1) Furnace loading
[0053] In the crucible from bottom to top, 70% of the total amount of Ni, 20% of the total amount of C, all of Co, all of Mo and all of Cr are sequentially loaded, and the remaining Ni is loaded into the feeding tank.
[0054] Separately charge 20% of the total amount of C, the remaining C, V-Al, Al, Ti, CrB and Zr in the feeding tank.
[0055] (2) Melting of the alloy
[0056] A vacuum induction melting furnace is used for smelting. When the vacuum degree of the vacuum induction melting furnace is ≤0.67Pa, the temperature starts to rise, and the temperature rise rate is controlled to be 10°C / min until the charge is melted. After the charge is melted, add the Ni in the feeding tank into the crucible.
[0057] (3) Alloy refining
[0058] When the vacuum degree of the vacuum induction melting furnace after alloying is ≤1...
Embodiment 3
[0071] The process of adding carbon step by step during the smelting process to prepare the nickel-based alloy is as follows.
[0072] (1) Furnace loading
[0073] In the crucible from bottom to top, 66% of the total amount of Ni, 16% of the total amount of C, all of Co, all of Mo, all of Cr and the remaining Ni were loaded in sequence.
[0074] 16% of the total amount of C, the remaining C, V-Al, Al, Ti, CrB and Zr were separately charged in the feeding tank.
[0075] (2) Melting of the alloy
[0076] A vacuum induction melting furnace is used for smelting. When the vacuum degree of the vacuum induction melting furnace is ≤0.67Pa, the temperature starts to rise, and the temperature rise rate is controlled at 5°C / min until the charge is melted.
[0077] (3) Alloy refining
[0078] When the vacuum degree of the vacuum induction melting furnace after alloying is ≤1.33Pa, the temperature is raised to the refining temperature of 1520°C at a heating rate of 10°C / min, and the ref...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com