Sequence image splicing method and system of low-altitude unmanned vehicle
A technology of unmanned aerial vehicles and sequence images, which is applied in image communication, TV system components, TV, etc., and can solve the problems of sequence image error accumulation and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] In this embodiment, the SURF feature points and the HARRIS-AFFINE feature points, as well as the RANSAC fault-tolerant algorithm and epipolar geometric constraints are used to solve the homography matrix and improve the splicing quality.
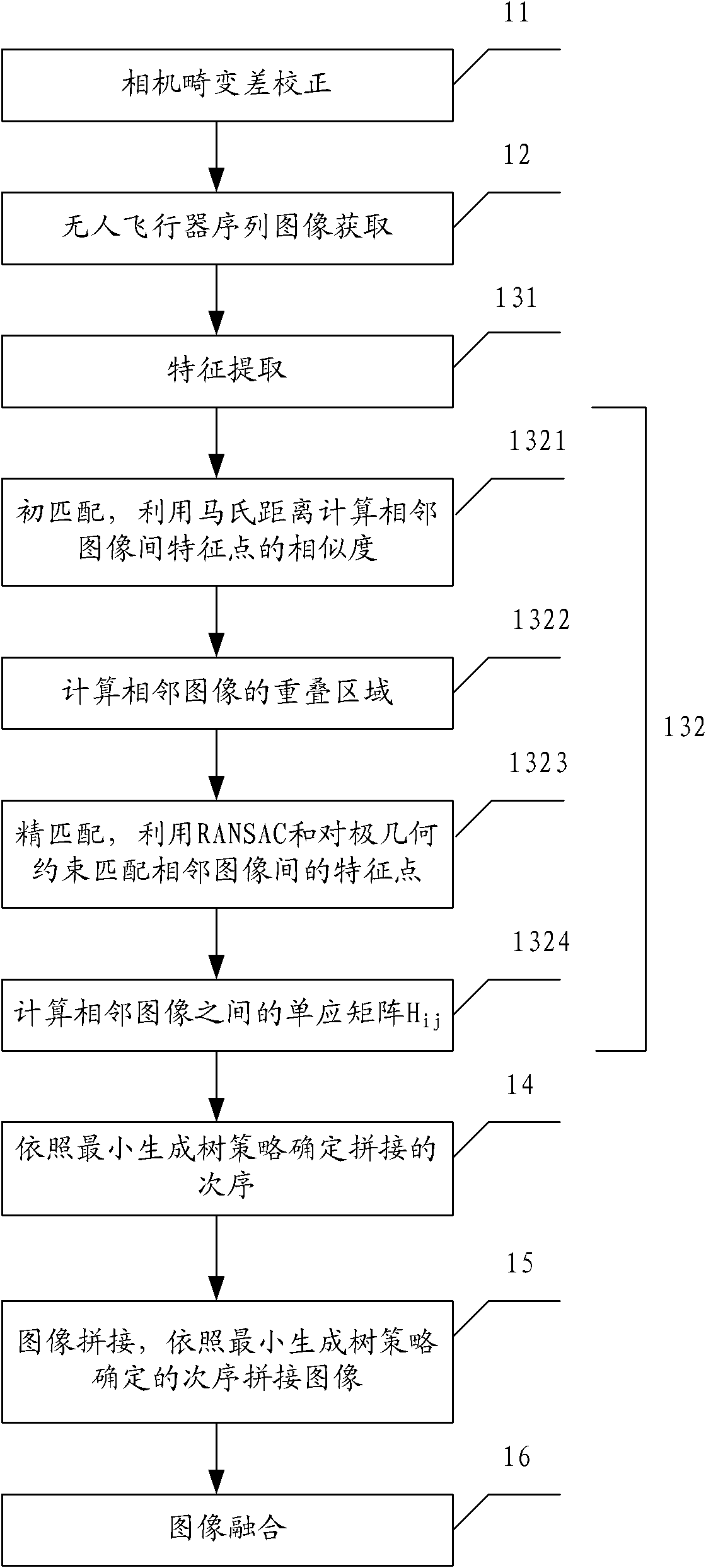
[0044] figure 1 Shown is the flowchart of the low-altitude unmanned aerial vehicle sequence image mosaic method of embodiment one of the present invention, including:
[0045] Step 11, camera distortion correction.
[0046] Step 12, UAV sequence image acquisition.
[0047] Step 13, image correction, determining the homography matrix between adjacent images, including the following sub-steps:
[0048] Step 131, feature extraction, extracting SURF feature points and HARRIS-AFFINE feature points from sequence images;
[0049] Step 132, image matching, includes the following sub-steps:
[0050] Step 1321, using Mahalanobis distance to calculate the similarity of feature points between adjacent images for initial matching;
[0051] St...
Embodiment 2
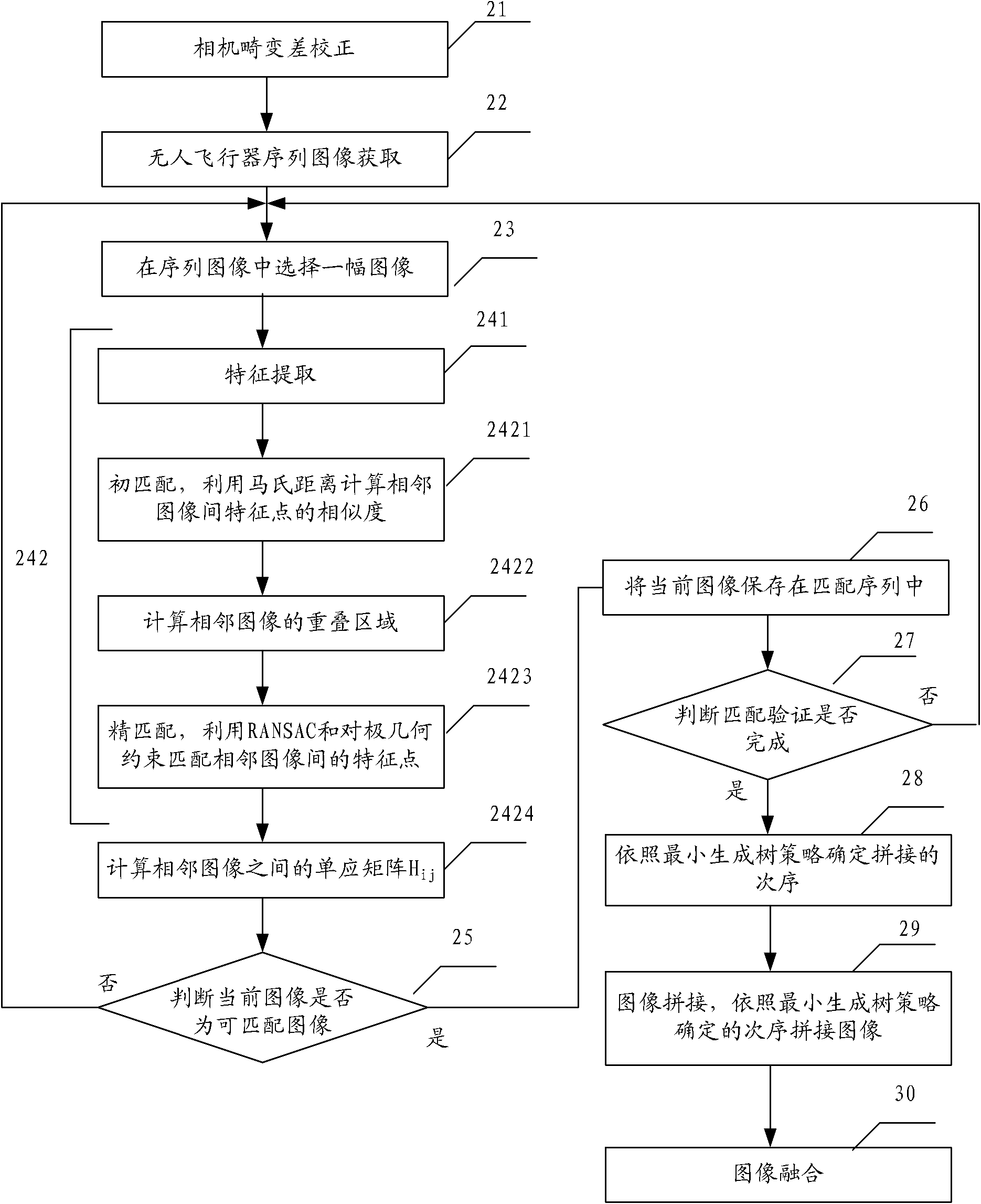
[0137] Different from the first embodiment, the second embodiment adds a matching verification step. Although the homography matrix is calculated and the images are matched in the first embodiment, further verification is required whether the matching result is correct. Especially for the image sequence acquired by the aircraft, there are bad images such as complete yaw inside, which need to be automatically removed during stitching.
[0138] figure 2 Shown is the flowchart of the low-altitude unmanned aerial vehicle sequence image mosaic method of the second embodiment of the present invention, including:
[0139] Step 21, camera distortion correction.
[0140] Step 22, UAV sequence image acquisition.
[0141] Step 23, select an image in the sequence of images.
[0142] Step 24, image correction, determining the homography matrix between adjacent images, including the following sub-steps:
[0143] Step 241, feature extraction, extracting SURF features and HARRIS-AFFINE...
Embodiment 3
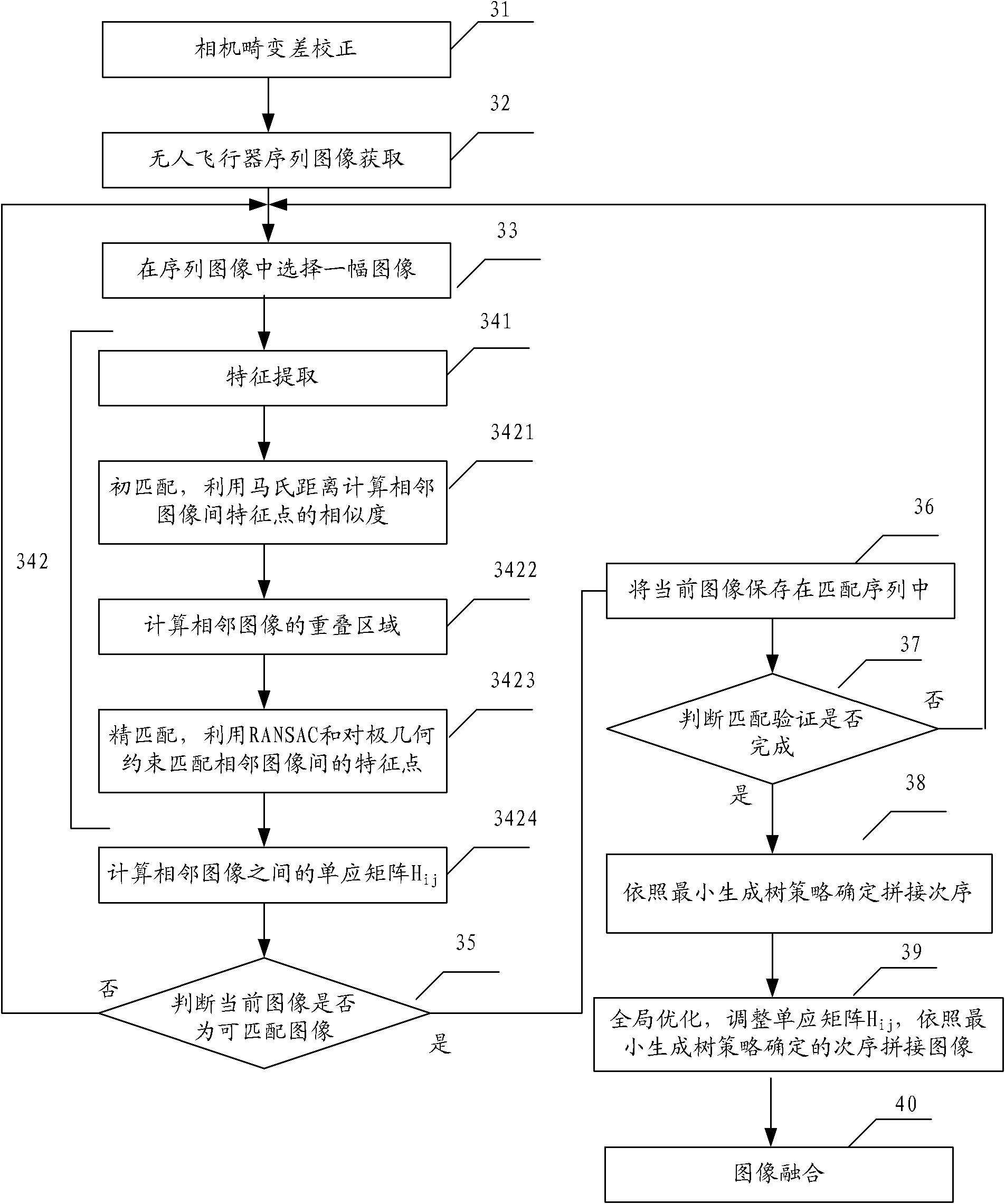
[0167] Different from the second embodiment, the step of global optimization and adjustment of the homography matrix is further added in the third embodiment.
[0168] image 3 Shown is the flowchart of the low-altitude unmanned aerial vehicle sequence image mosaic method of the third embodiment of the present invention, including:
[0169] Step 31, camera distortion correction.
[0170] Step 32, sequence image acquisition of UAV.
[0171] Step 33, select an image in the sequence of images.
[0172] Step 34, image correction, determining the homography matrix between adjacent images, including the following sub-steps:
[0173] Step 341, feature extraction, extracting SURF features and HARRIS-AFFINE features from sequence images;
[0174] Step 342, image matching, includes the following sub-steps:
[0175] Step 3421, using Mahalanobis distance to calculate the similarity of feature points between adjacent images for initial matching;
[0176] Step 3422, calculating the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com