Composite shoe sole, footwear constituted thereof and method for producing the same
A technology for compounding soles and fiber composite materials, which can be applied in the directions of soles, footwear, clothing, etc., can solve problems such as hindering water and gas transmission, and achieve the effects of good water and gas permeability and good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0164] A barrier material in which both fiber components consist of polyester, 50% by weight each of the total fiber composite, and the second fiber component is side-by-side polyester Bico.
[0165] The barrier material of Example 2 was made in the same way as the sheath-core Bico-fiber of Example 1 and had the same properties, except for the characteristic Bico-structure.
Embodiment 3
[0167] A barrier material comprising 50% by weight each of two fiber components, the first fiber component consisting of polyester and the second fiber component consisting of polypropylene.
[0168] In this example, instead of Bico, monocomponent fibers are used as the second fiber component. For the production of fiber composites, only two fiber components with different melting points are selected. In this case, 50% by weight polyester fiber (melting point about 230°C) is the carrier component, while the same 50% by weight polypropylene fiber has a lower melting point of about 130°C and is used as an adhesive Connected reinforcement components. In addition, the production process was carried out as in Example 1. Compared to Example 2, the nonwoven of Example 3 has a lower thermal stability, but it can also be produced at lower temperatures for this.
Embodiment 4
[0170] 80% polyester was used as the first fiber component and polyester sheath-core Bico as the barrier material for the second fiber component.
[0171] In this example, production takes place again as in example 1, with the difference, however, that the proportion of the second fiber component forming the reinforcing component is changed. Compared to 80% by weight of the first fiber component with a higher melting point, only 20% by weight of the second fiber component remains. By scaling down the strengthening component, the stabilization effect of the resulting barrier material is also reduced. This can be beneficial if a nonwoven material with high mechanical stability and high flexibility at the same time is required. The temperature resistance of this nonwoven corresponds to that of the first embodiment.
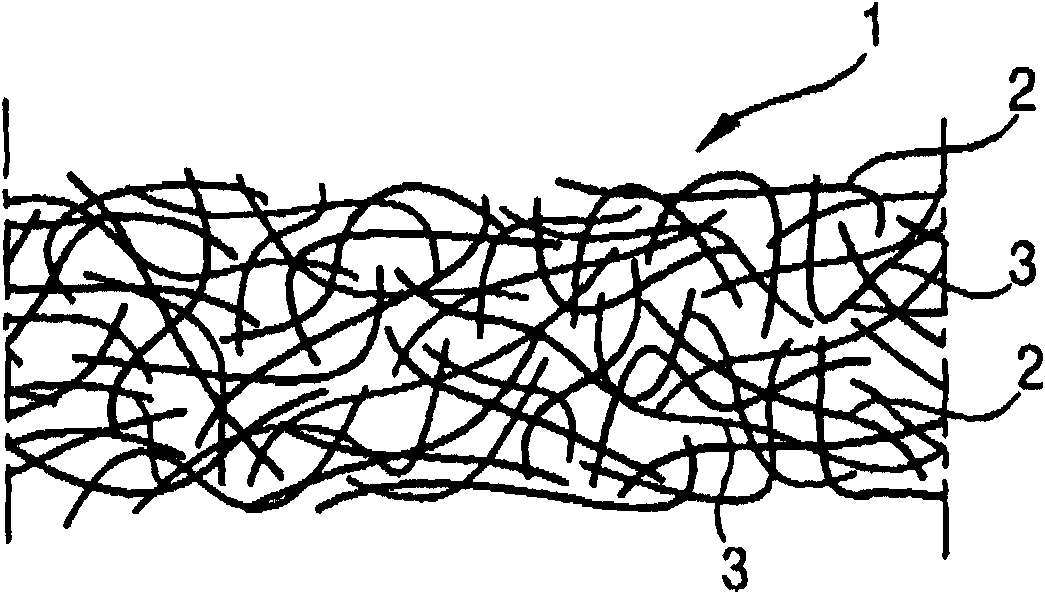
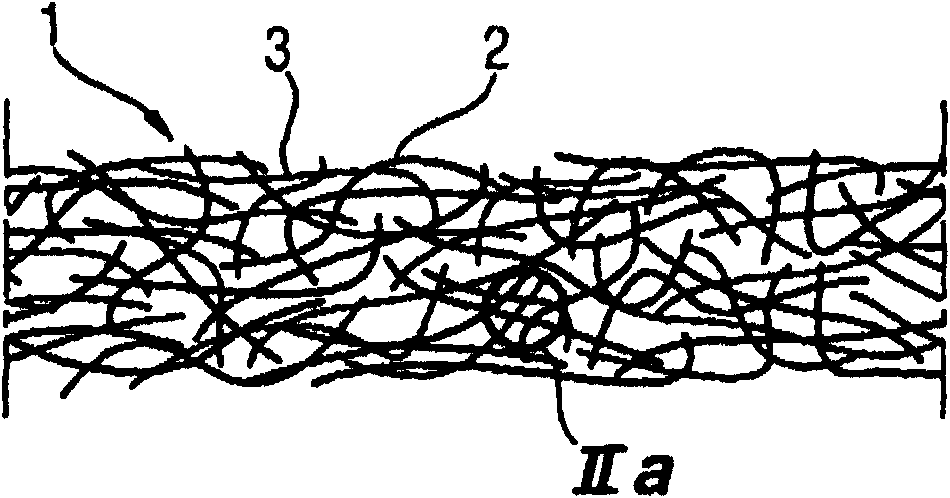
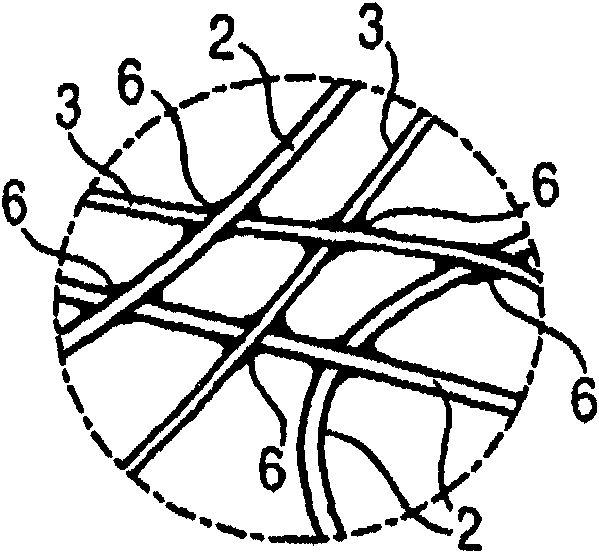
[0172] use Figures 4 to 11 Several examples for composite soles or blocking units or details therein are investigated.
[0173] Figure 4 A partial cross-secti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com