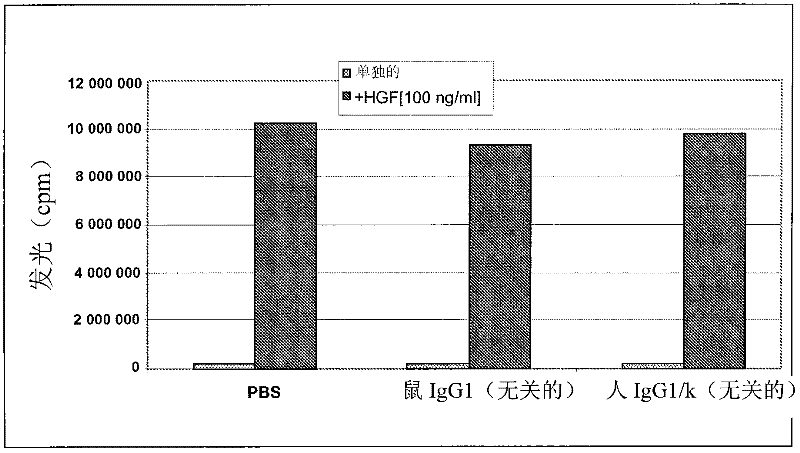
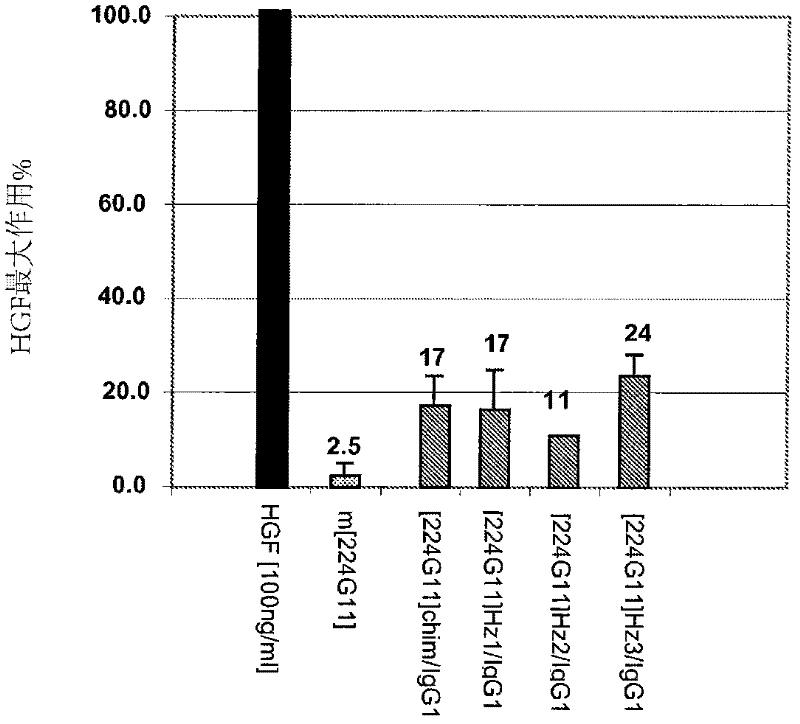
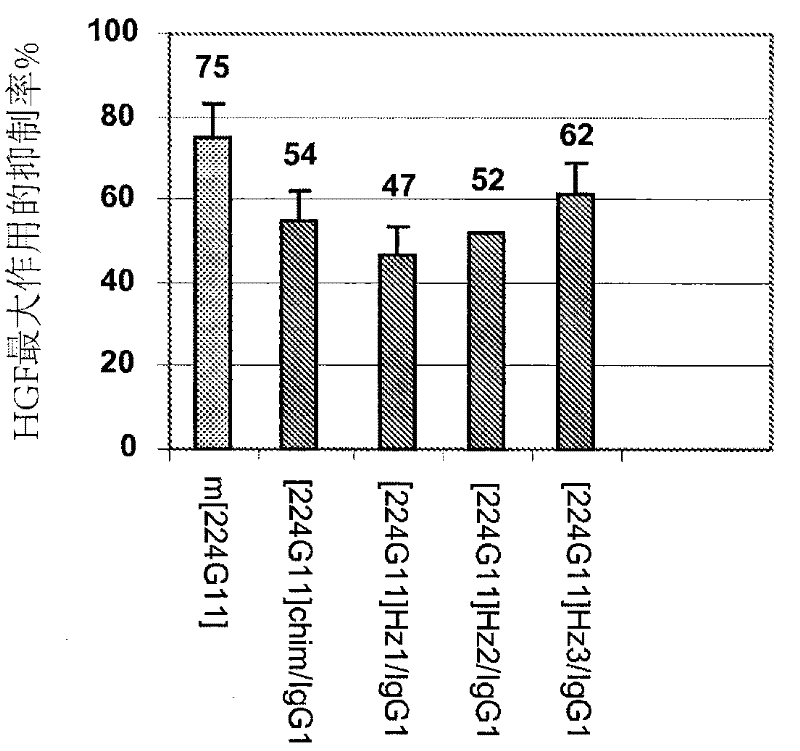
Anti-cmet antibody
A technology of antibody and monoclonal antibody, applied in the field of amino acid and nucleic acid sequence, can solve the problem of not describing the data showing any effect of Pfizer antibody
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0316] Example 1: Production of anti-c-Met antibodies
[0317] To generate anti-c-Met antibody, a cell line expressing c-Met on its plasma membrane transfected with CHO (20×10 6 cells / dose / mouse) subcutaneously immunize 8-week-old BALB / c mice 3 to 5 times, or with c-Met ectodomain fusion protein (R&D Systems, catalog #358MT) (10-15 μg / dose / mouse) Or immunize 8-week-old BALB / c mice with fragments of the recombinant protein for 2 to 3 times. For the first immunization, the fragments of the recombinant protein are mixed with complete Freund's adjuvant, and for subsequent immunizations, with incomplete Freund's adjuvant mix. A mixed protocol in which mice received both CHO-cMet cells and recombinant protein was also performed. Three days prior to cell fusion, mice were boosted i.p. or i.v. with the recombinant protein or fragment. Spleens from mice were then harvested and fused with SP2 / 0-Ag14 myeloma cells (ATCC) and subjected to HAT selection. Four fusions were performed. I...
Embodiment 2
[0323] Example 2: Humanization method of murine 224G11 by CDR-grafting
[0324] 1°) Humanization of the light chain variable domain (VL)
[0325] As a preliminary step, the nucleotide sequence of 224G11VL was compared to the murine germline gene sequence included in the IMGT database (http: / / imgt.cines.fr). Murine IGKV3-5*01 and IGKJ4*01 germline genes have been identified showing 99.31% sequence identity for the V region and 94.28% sequence identity for the J region, respectively. Due to these high homology, the 224G11VL nucleotide sequence was directly used to search for human homology, instead of the corresponding murine germline.
[0326] In a second step, the human germline genes exhibiting the best identity to 224G11VL have been searched to identify the best human candidates for CDR grafting. For selection optimization, alignments between amino acid sequences were performed. The human IGKV4-1*01 germline genes provided 67.30% sequence identity but showed different l...
Embodiment 3
[0333] Example 3: Engineering of Improved Hinge Mutants
[0334] It is well known to those skilled in the art that the hinge region is actively involved in the flexibility of immunoglobulin variable domains (see Brekke et al., 1995; Roux et al., 1997). During the chimerization of 224G11 Mab, the murine constant domain IGHG1 was partially replaced by the equivalent IGHG1 of human origin. Since the amino acid sequences of the hinge regions are highly diverse, "murinization" of the hinge region was performed to preserve its length and rigidity. Since the human IGHG2 hinge region corresponds to the closest homologue of the murine IGHG1 hinge, this sequence was also considered. A series of 7 different hinge sequences (SEQ ID No. 22 to 28) were constructed by incorporating parts of the mouse IGHG1 and human IGHG2 hinges into the human IGHG1 hinge part.
[0335] Another series of hinge mutants (SEQ ID No.58 to 72) was designed and constructed to evaluate the additional cysteine a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com