Necking detecting and controlling method for melted-electrode arc welding
An arc welding and consumable electrode technology is applied in the field of necking detection and control of consumable electrode arc welding to achieve the effect of increasing the generation of sputtering and the smooth reproduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
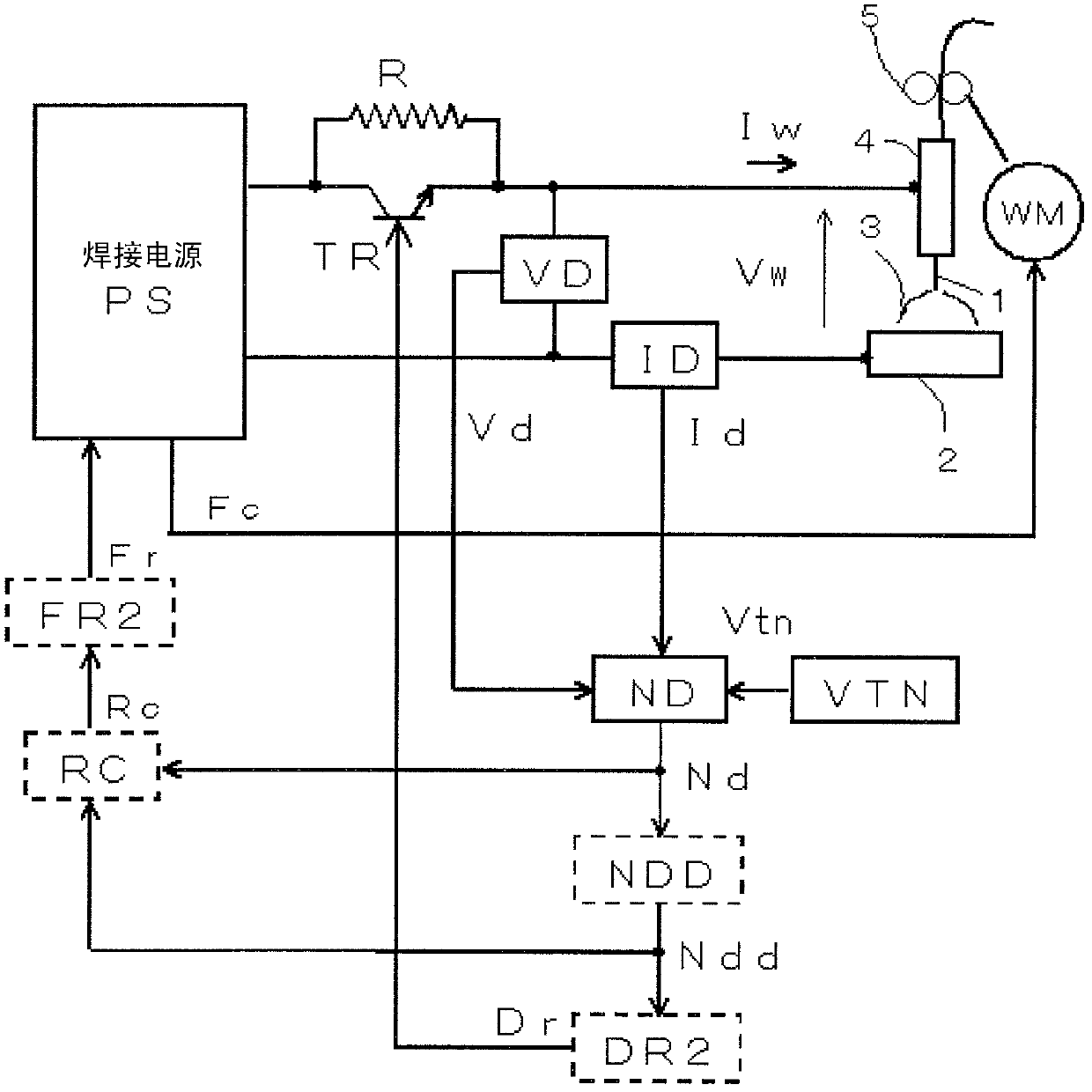
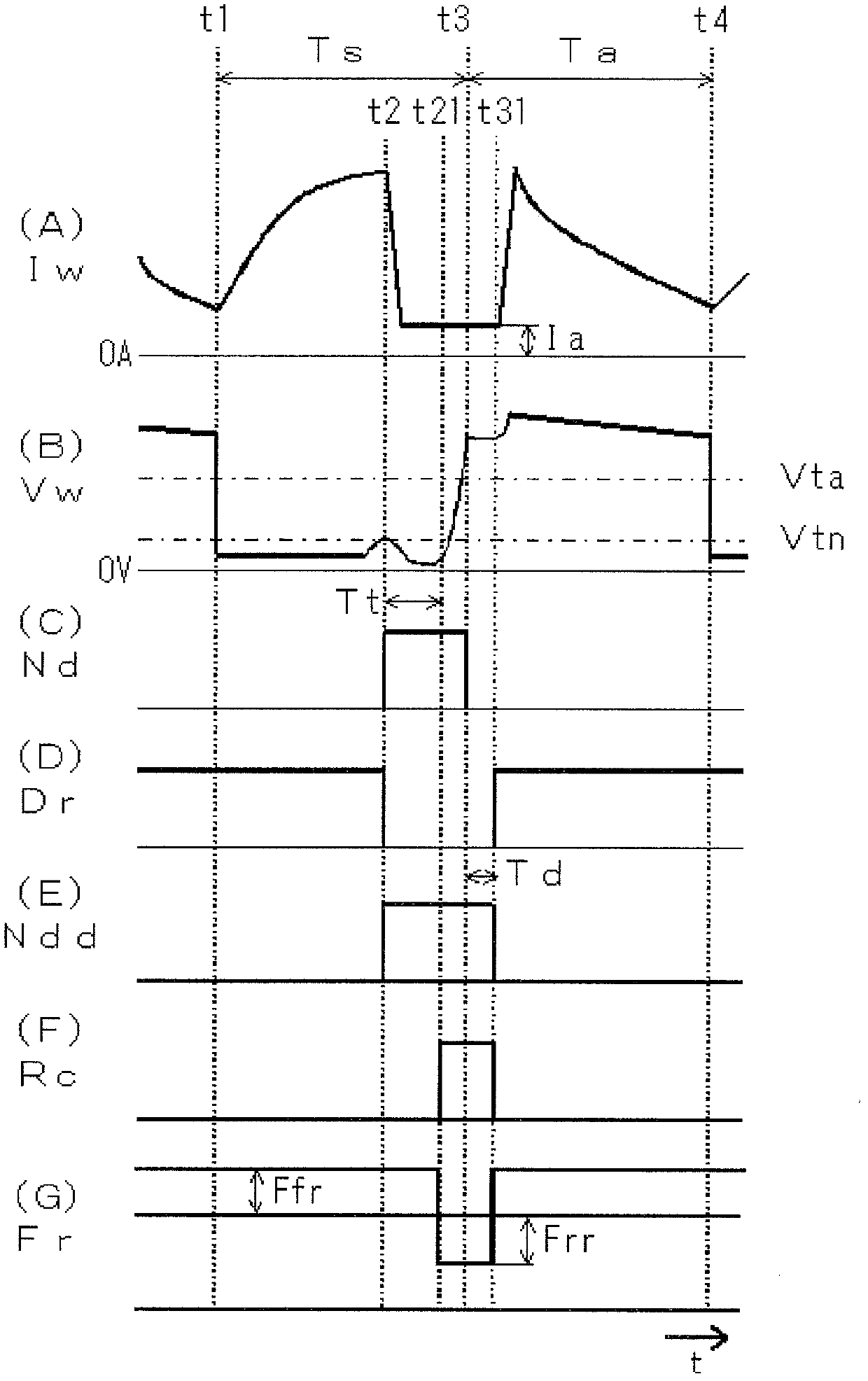
[0037] In the invention according to Embodiment 1, when the elapsed time t from the necking detection time reaches a predetermined reference time Tt before the arc is regenerated, the welding wire is moved backward to move away from the base material, thereby maintaining a state of a small current value. The arc is generated again, and if the arc is generated again, the aforementioned backward movement is stopped. In Embodiment 1, the above-mentioned retreating movement of the welding wire is performed by retreating feed. Therefore, the above-mentioned stop of the backward movement means stopping the backward feeding and returning to the normal forward feeding. Hereinafter, Embodiment 1 will be described.
[0038] figure 1 It is a block diagram of a welding device for implementing the constriction detection and control method of consumable electrode arc welding according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. exist figure 1 in, on and above Image 6 The same symbols ar...
Embodiment approach 2
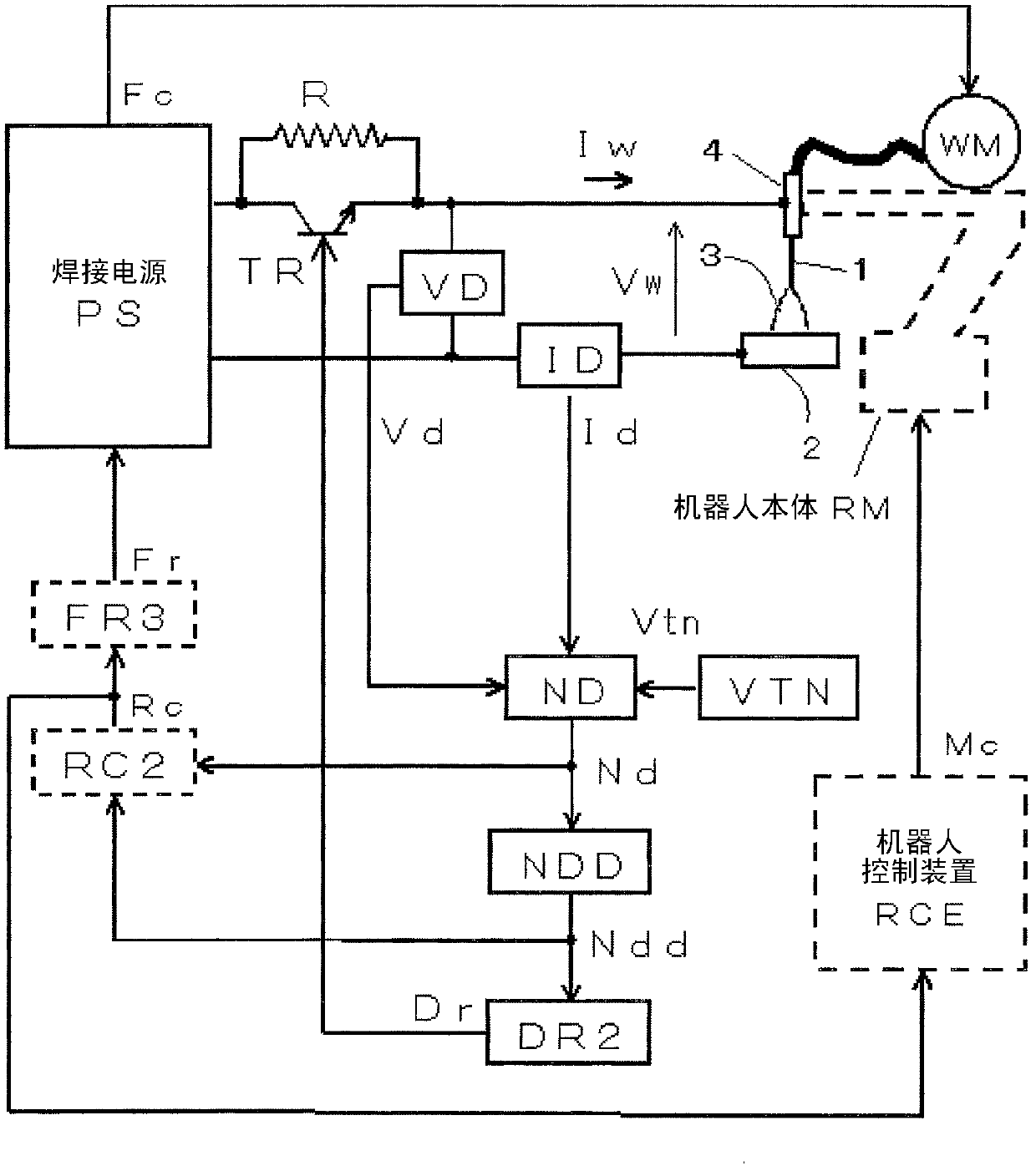
[0050] In the invention according to the second embodiment, as in the first embodiment, when the elapsed time t from the necking detection time reaches the predetermined reference time Tt before the arc is regenerated, the welding wire is moved backward to move away from the base metal, and the welding wire is kept. The arc is generated again in the state of a small current value, and if the arc is generated again, the aforementioned backward movement is stopped. In Embodiment 2, the welding torch is moved backward by the above-mentioned backward movement of the welding wire, and the height Lt of the welding torch is increased. Then, after the backward movement stops, the torch is moved forward to return the torch height Lt to the original height. During the backward movement, the forward feed of the wire continues. Hereinafter, Embodiment 2 will be described.
[0051] image 3 It is a block diagram of a welding device for implementing the constriction detection and control...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com