Module for stacking thin panels and method of stacking thin panels
A panel and thin plate technology, which is applied in the direction of special packaging objects, rigid containers, and packaging of vulnerable items, can solve problems such as instability, damage to the stability of columnar components, and difficult load transfer areas, so as to prevent falling off and ensure load transfer areas. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
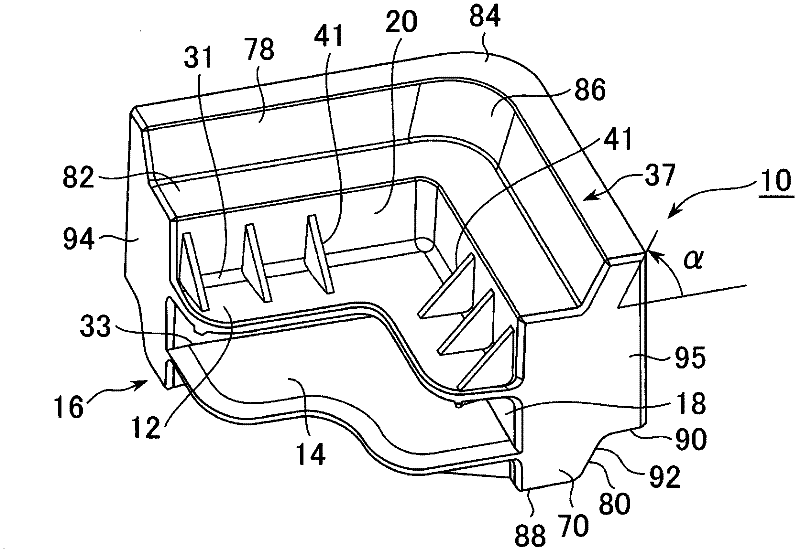
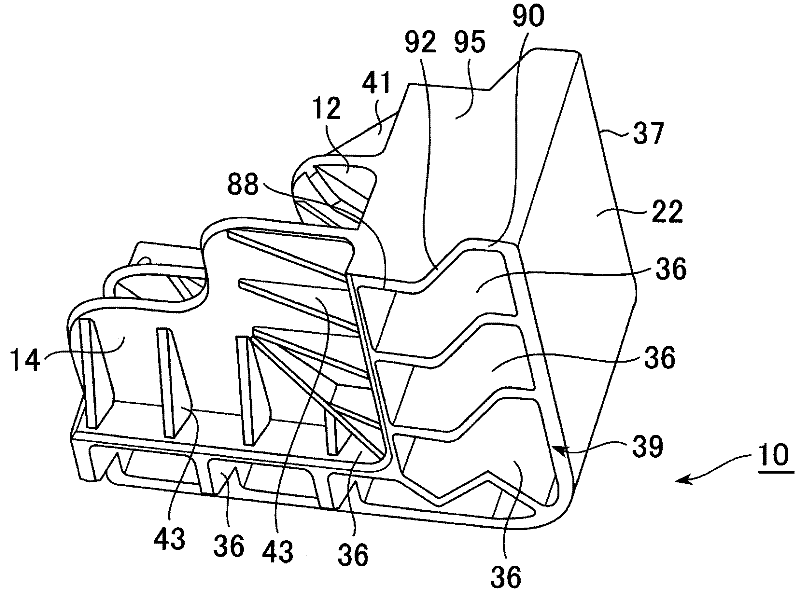
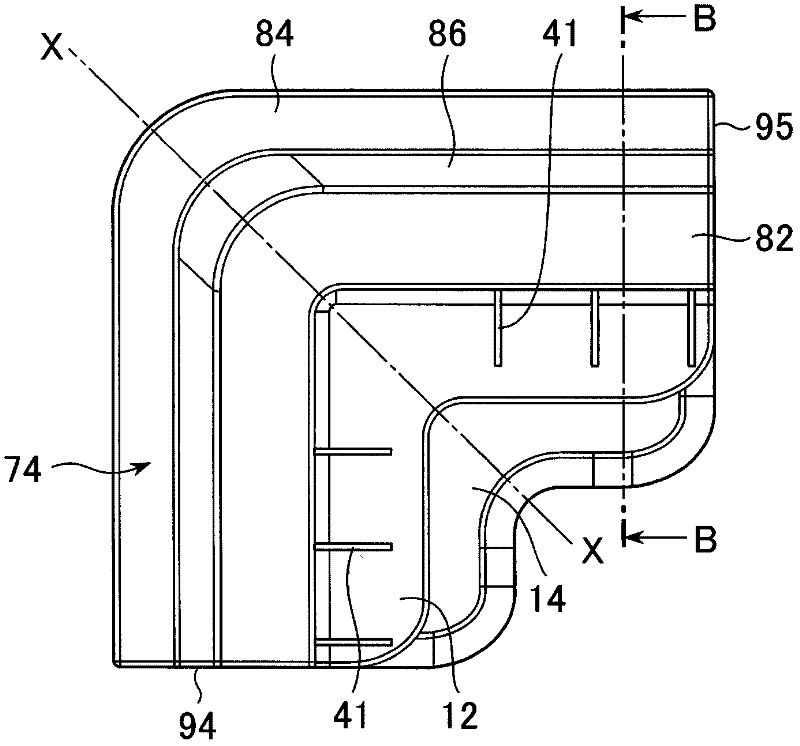
[0100] In the first embodiment of the module 10 of the present invention, a rectangular solar panel P is taken as an example of a laminated thin plate panel and will be described in detail below with reference to the drawings.
[0101] The solar panel P is in the form of a thin plate in which cells are connected in series and protected by resin, tempered glass, or a metal frame. The layered structure of silicon monomers has a thickness of several mm, an area of several m2, and a weight of 10 to 30 kg, so it is a precise and fragile structure.
[0102] In this embodiment, the case where the four corners of the solar panel P are directly supported by the modules 10 for lamination of thin-plate panels will be described.
[0103] The module 10 has: a clamping support part for clamping and supporting the solar panel P; a load transmission part connected to the clamping support part and transmitting the weight of the solar panel P in the vertical direction; mechanism.
[0104] Suc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com