Distributed collaborative signal identification method based on blind estimation of higher order statistics and signal to noise ratio
A technology of high-order statistics and signal recognition, which is applied to baseband system components, transmission systems, transmission monitoring, etc., can solve the problems of low signal recognition rate and poor fault tolerance performance, and achieve high recognition probability, multiple types, and maintain recognition The effect of accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
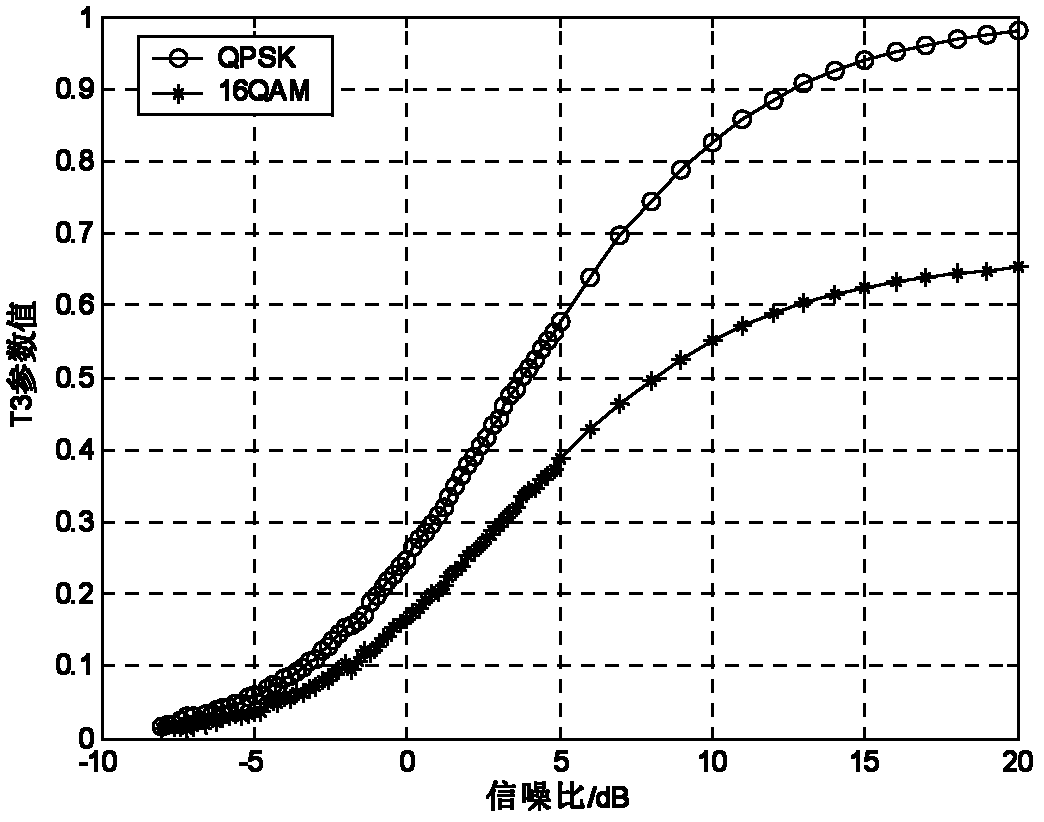
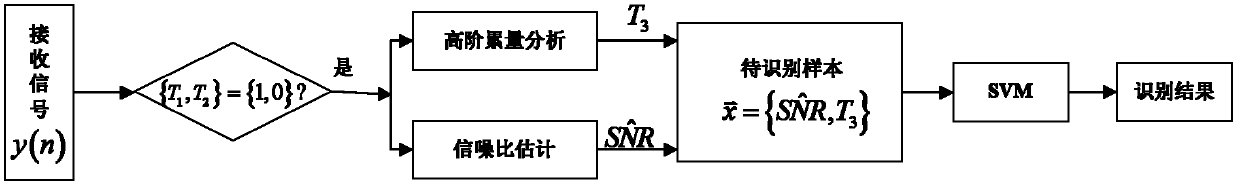
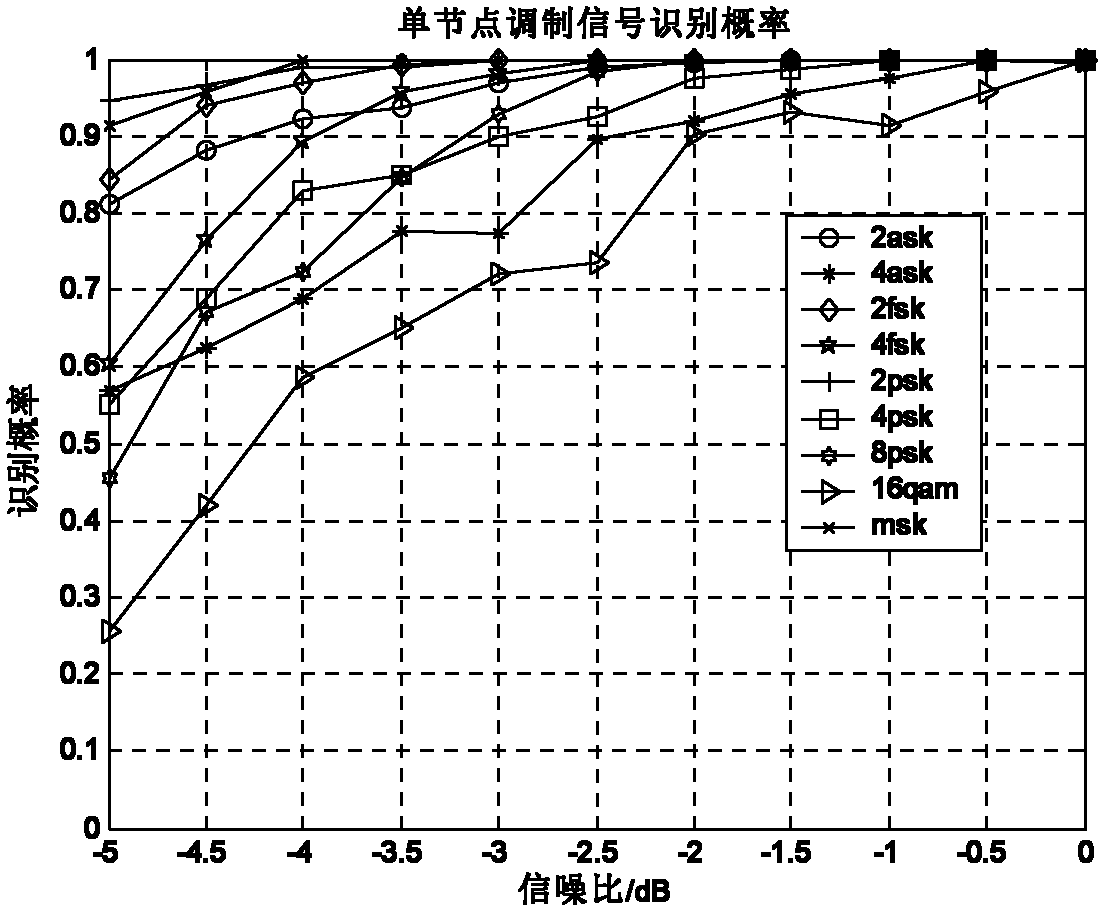
[0033] A distributed cooperative signal identification method based on high-order statistics and blind estimation of signal-to-noise ratio, which includes the following steps: the first step, when performing spectrum monitoring on electromagnetic signals, each sensor node restores the received signal to obtain a complex baseband signal r ( t ) = E Σ k = - ∞ ∞ a k p ( t - nT s ) exp [ j ( ω c t + ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com