Nanoemulsion vaccines
A nanoemulsion and adjuvant technology, applied in antiviral agents, allergic diseases, antibody medical components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0312] Compositions comprising nanoemulsion inactivated respiratory syncytial virus and methods of utilizing the same
[0313] Materials and Methods
[0314] mice. Balb / c mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratories. All animal work was performed in accordance with University of Michigan Committee on Use and Care of Animals policy.
[0315] Viral plaque assay. Right lung lobes from infected mice were harvested and sanded using a mortar and pestle. Samples from lungs were spun 2x, or obtained after incubation with nanoemulsions, and supernatants were serially diluted onto ~90% confluent monolayers of Vero cells. Samples were incubated for 2 hours at 37°C with gentle rotation, then the infected supernatant was removed and replaced with 0.9% methylcellulose. After 5 days of incubation at 37°C, methylcellulose was removed, replaced with methanol, and incubated at -80°C for 1 hour. After methanol removal, samples were stored at -80°C until plaque development. Plaques were d...
Embodiment 2
[0320] Nanoemulsion effectively inactivates RSV
[0321] To test the ability of the emulsion to inactivate RSV, RSV (10 6 Particle forming units (PFU) were incubated with the nanoemulsion at various concentrations (0% - 20%) and for various times (1 hour - 3 hours) (see figure 1 ). The number of infectious virus was determined via plaque assay using Vero cells. Nanoemulsion-incubated virus was used to infect subconfluent Vero cells. RSV plaques were visualized using immunohistochemical techniques. When as little as 1% nanoemulsion was incubated for 3 hours, there was no detection of active virus as assessed by standard plaque assays (see figure 1 ). Thus, the present invention provides nanoemulsions that are effective in completely killing RSV at concentrations of 2% in as little as 1 hour, or as little as 1% in 3 hours. Accordingly, in some embodiments, the present invention provides nanoemulsions that are effective in reducing and / or completely inactivating RSV infec...
Embodiment 3
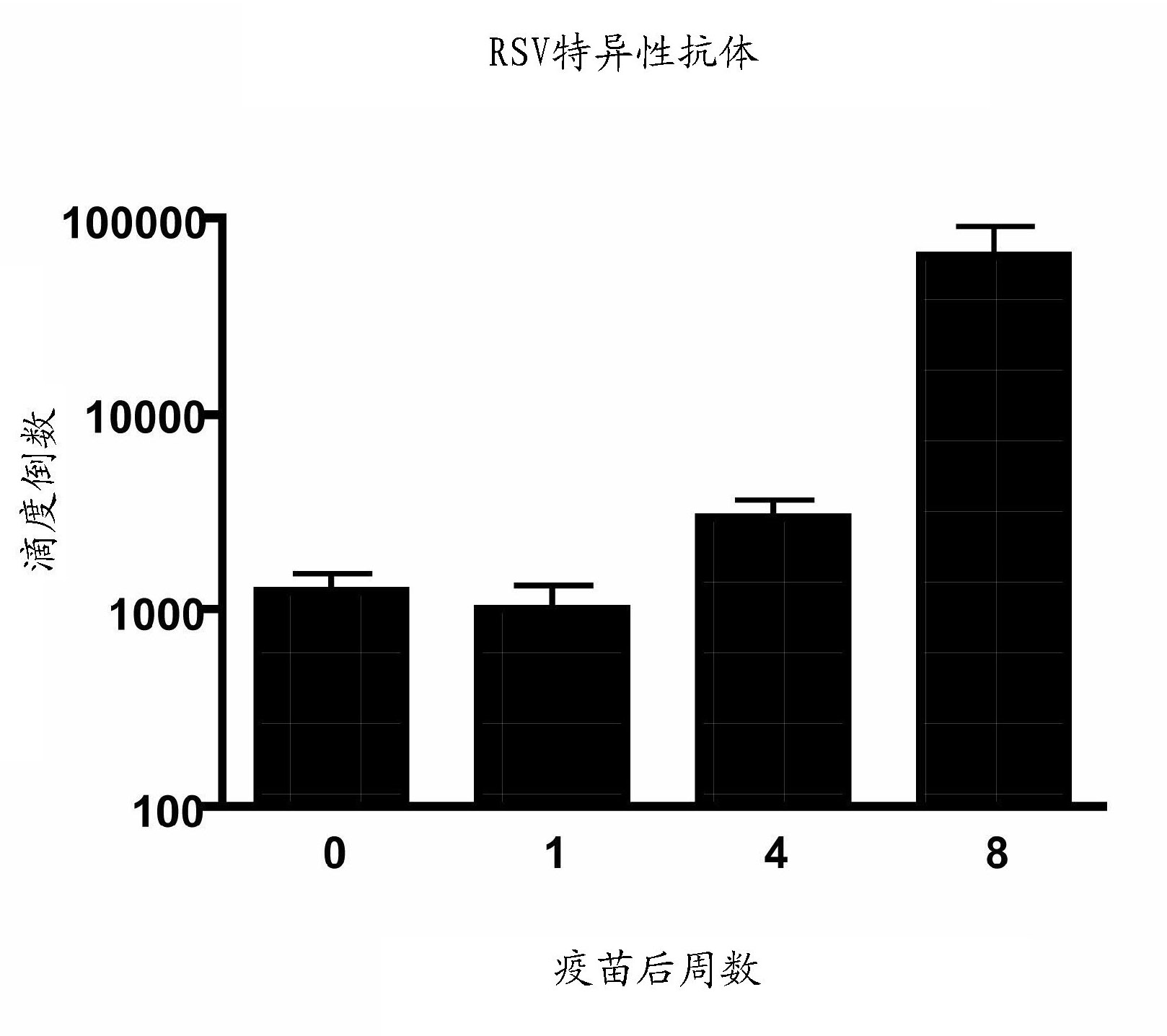
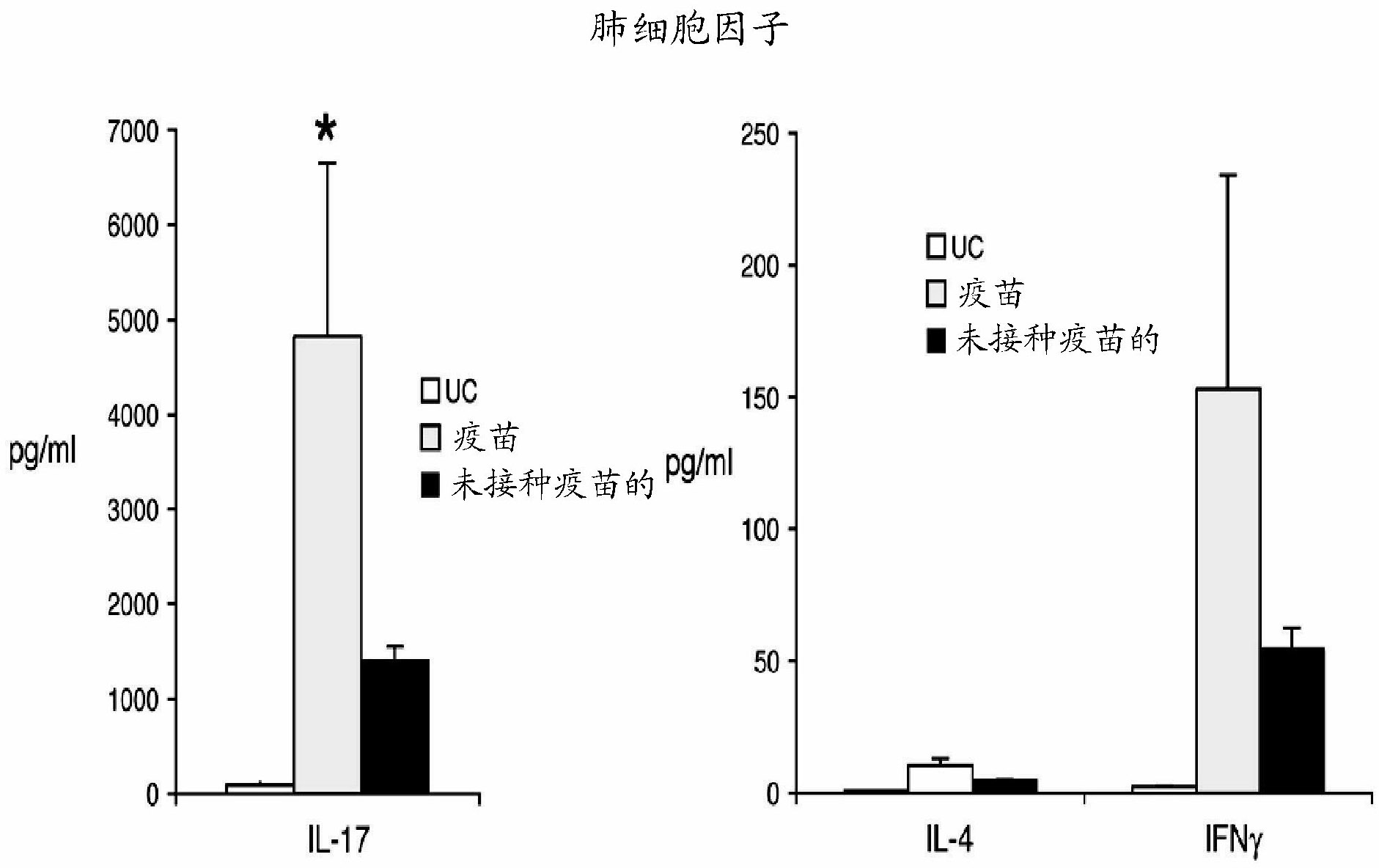
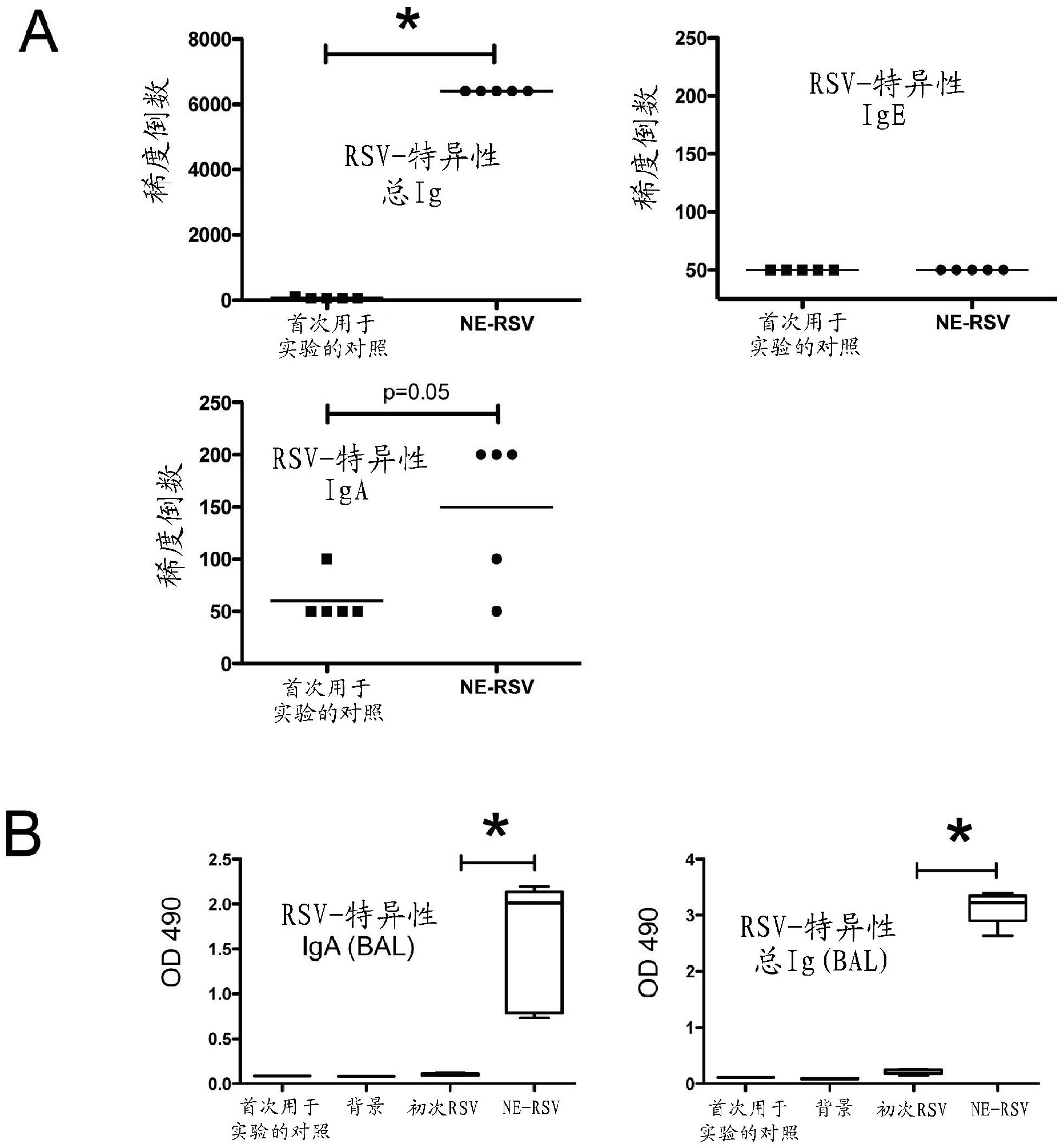
[0323] Nanoemulsion immunization enhances immunity upon RSV challenge
[0324] It was next determined whether nanoemulsions could be used as immune enhancing agents to induce immune responses important for protection against viral infection. To examine this aspect, an immunization protocol comprising intranasal priming (nanoemulsion (15%)-RSV mixture (total 10 μl, 5 μl / nostril)) or nanoemulsion alone without RSV as a control group. Animals were subsequently challenged with live, infectious RSV at day 56 (8 weeks) and assessed for evidence of protective immunity. One objective is to monitor RSV-specific antibody production during the immunization protocol. Reciprocal titers of RSV-specific antibodies in serum were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) against RSV protein extracts. Blood was harvested and sera were collected at specific time points post-immunization, including day 0, 1 week, 4 weeks, and 8 weeks (at RSV challenge), and total serum IgG specif...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com