Speed change control device of automatic transmission
一种自动变速器、控制装置的技术,应用在传动装置控制、带有齿的元件、皮带/链条/齿轮等方向,能够解决变速冲击、联接压超出等问题,达到避免变速冲击的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
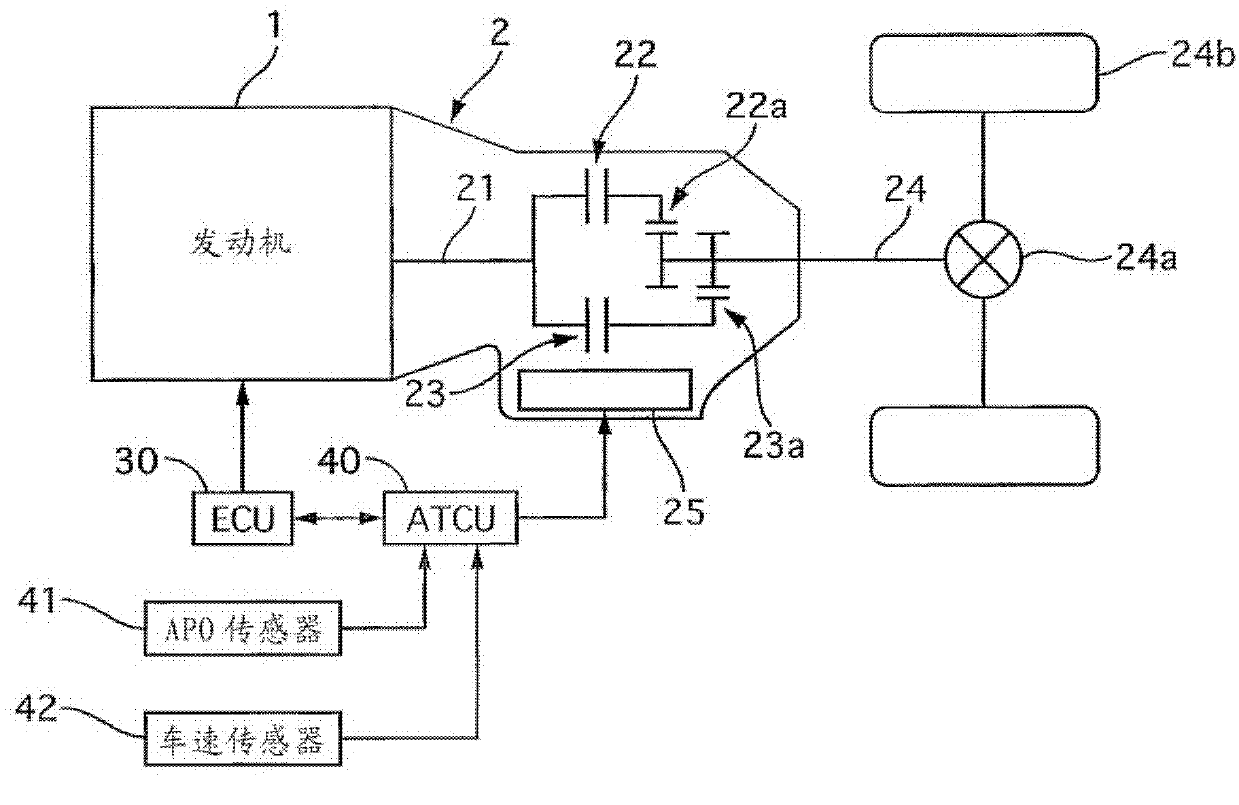
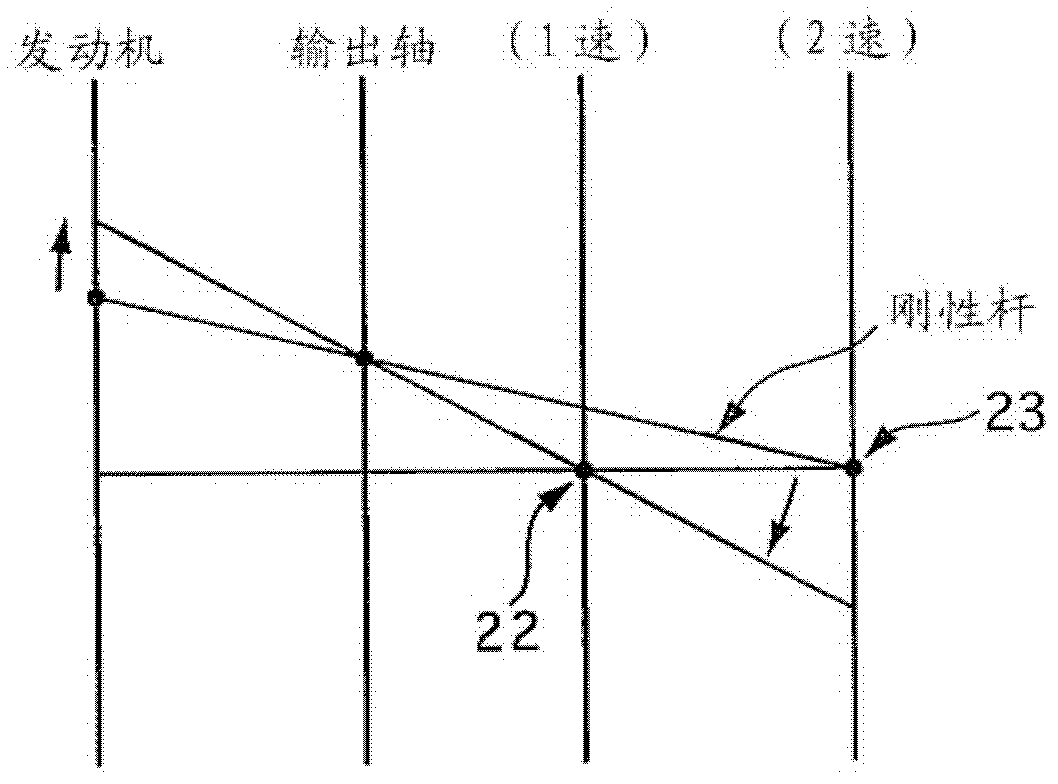
[0029] figure 1 It is a system diagram of a vehicle equipped with the shift control device of the automatic transmission according to the first embodiment. Such as figure 1 As shown, the engine 1 and the automatic transmission 2 are controlled by an electronic engine control unit (hereinafter referred to as ECU) 30 and an electronic control unit for transmission (hereinafter referred to as ATCU) 40 . The ECU 30 controls the engine 1 based on a throttle opening set by an APO sensor 41 that detects an accelerator opening and a vehicle speed input from a vehicle speed sensor 42 . Specifically, fuel injectors and ignition devices (not shown) are controlled in accordance with the running state.
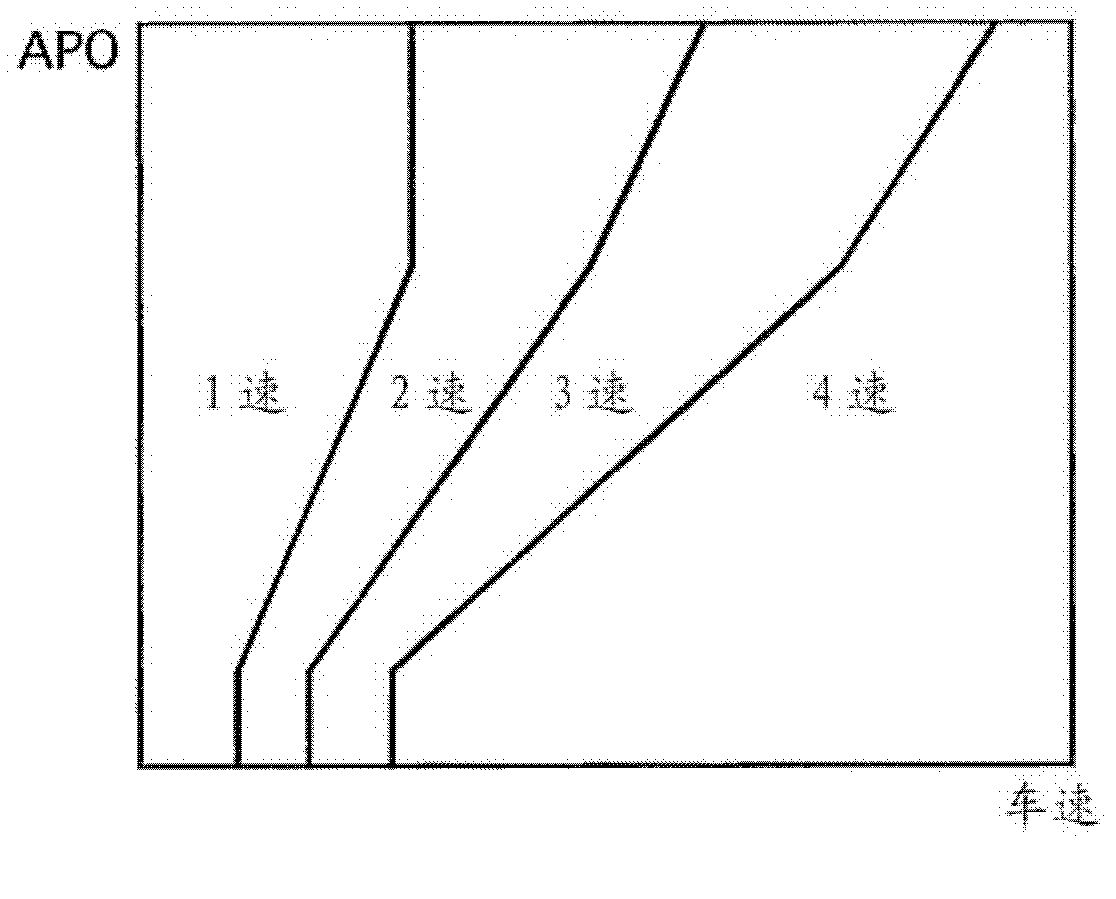
[0030] The ATCU 40 inputs the throttle opening degree input from the APO sensor 41 , the vehicle speed input from the vehicle speed sensor 42 , and the position of the shift lever detected by a disconnect switch not shown in the figure. Furthermore, based on the preset shift map (refer ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Next, Example 2 will be described. Since the basic configuration is the same as that of Embodiment 1, only the points of difference will be described. Figure 7 It is a flowchart showing the downshift control process of the second embodiment. In Embodiment 1, when the release-side engagement pressure is less than a predetermined value, the second release-side engagement pressure correction process that prohibits the increase correction is performed. In contrast, Embodiment 2 is different in that when the release-side engagement pressure is less than a predetermined value, the release-side engagement pressure correction process is prohibited, and the release-side engagement pressure is reduced in this state. In other words, cancel Figure 5 The processing of step S51.
[0062] Figure 8 It is a time chart showing the downshift control process of the second embodiment. basically with Image 6 The time chart is the same as that of , except that at time t5, the decrea...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Next, Example 3 will be described. Since the basic configuration is the same as that of Embodiment 1, only the points of difference will be described. Figure 9 It is a flowchart showing the downshift control process of the third embodiment. Although this control process is described as a process executed at the time of downshifting, it is also applicable to the time of upshifting, and is not particularly limited. In this control process, only the release-side coupling element 23 will be described, and the description about the engagement-side coupling element 22 is basically the same as that in Embodiment 1 except that it is performed in parallel with the control of the release-side coupling element 23 after a downshift request. , so the description is omitted.
[0065] In step S1, it is determined whether there is a downshift request. If there is a downshift request, the process proceeds to step S102. Otherwise, this control flow ends.
[0066] In step S102, switch...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com